Washington Baltimore maglev federal funds are at the heart of this captivating exploration, delving into the intricate details surrounding this ambitious transportation project. We’ll examine the project’s goals, potential impacts, and the complex funding mechanisms involved. This in-depth look will cover everything from the allocation of federal funds to the project’s potential benefits and drawbacks, and ultimately, whether this new transportation option is a viable solution for the region.
The project’s status, key stakeholders, and the specific allocation of federal funds to different aspects will be highlighted. We’ll also compare the Maglev to alternative transportation options, analyze its cost-effectiveness, and explore potential trade-offs. Public opinion and engagement strategies will also be discussed, along with technological advancements and the project’s timeline. This discussion also explores infrastructure considerations, regulatory frameworks, and the long-term sustainability of the project.
Project Overview
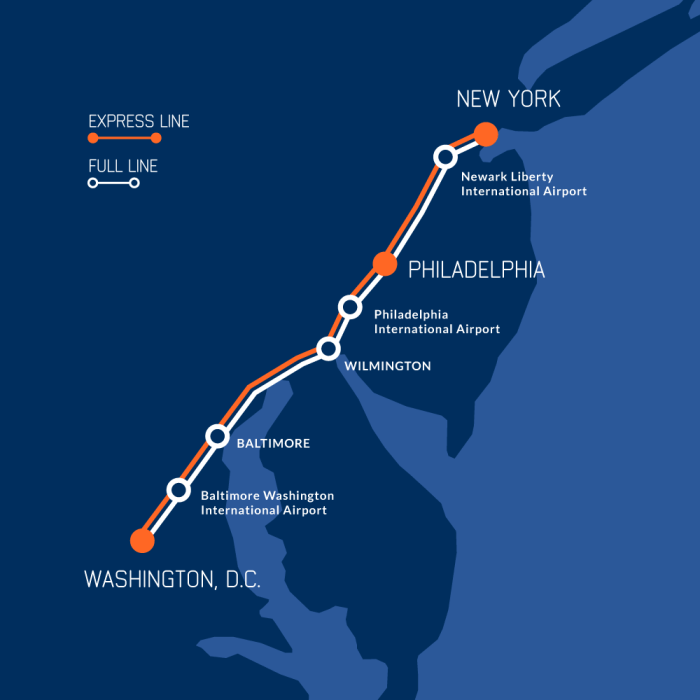
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project envisions a high-speed, magnetic levitation train system connecting the two metropolitan areas. This ambitious project aims to revolutionize transportation between these major hubs, offering a faster, more efficient, and potentially environmentally friendly alternative to existing modes of travel. Early stages have focused on securing funding and preliminary feasibility studies.The project’s potential impacts include reduced travel times, decreased traffic congestion, economic development along the proposed route, and a positive environmental impact through reduced carbon emissions compared to traditional rail or air travel.
Success hinges on overcoming engineering and logistical challenges, as well as navigating the complexities of land acquisition and regulatory approvals.
Project Status
Significant progress has been made in securing the necessary federal funds. This crucial step validates the project’s viability and signals a positive trajectory for its future development. However, the actual construction phase is still in the planning stages, with further analysis and design work required. While funding is secured, the exact timeline for construction remains to be finalized.
Key Stakeholders
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project involves a diverse range of stakeholders, each with a vested interest in its success or failure. These include:
- Federal government agencies:
- Local governments:
- Private sector partners:
- Environmental groups:
- Community groups:
The project relies on continued support from relevant federal agencies for approvals and funding. This includes the Department of Transportation, which plays a crucial role in overseeing infrastructure projects of this scale.
Washington-Baltimore maglev federal funds are getting a lot of attention, but it seems like a surprisingly small legal battle is also shaping the landscape. Apparently, x is backing one of the smallest stakes legal fights imaginable , which, in turn, could indirectly influence the larger maglev project. This all means that the future of high-speed rail between these two cities might depend on more than just the funding; it’s also about who’s backing what, even in seemingly minor legal disputes.
It’s all quite fascinating when you think about it.
Local authorities in both Washington and Baltimore play a vital role in approving permits, managing land use, and ensuring the project aligns with local infrastructure plans. Their support is essential for smooth implementation.
Private companies, including construction firms, engineering companies, and potential operators, are key players in delivering the project. Their participation will dictate the project’s cost and schedule.
Environmental concerns will need to be addressed throughout the project. Environmental impact assessments and mitigation strategies will be critical in gaining community support.
Residents living along the proposed route will be directly impacted by the project. Community engagement and transparency are essential for ensuring the project is developed in a way that addresses concerns and benefits the community.
Challenges and Opportunities
Several challenges could affect the project’s progress, such as:
- Land acquisition and zoning issues:
- Environmental impact assessments:
- Cost overruns and funding fluctuations:
Securing the necessary land and navigating local zoning regulations will be a significant hurdle. The complexity of land ownership and zoning can often delay projects of this scale.
Comprehensive environmental impact assessments are crucial for gaining public approval and addressing potential ecological concerns. The findings of these assessments can significantly influence the project’s route and design.
The project’s estimated costs may fluctuate due to unforeseen circumstances, inflation, or other factors. Contingency planning and financial stability are crucial to maintain the project’s financial sustainability.
Potential Benefits
The project holds significant potential to improve transportation between the two metropolitan areas. Some of the potential benefits include:
- Reduced travel times:
- Economic development:
- Improved air quality:
The high-speed nature of the maglev system promises to drastically reduce travel time between Washington and Baltimore. This translates into increased productivity and efficiency for commuters.
The project could spur economic development along the proposed route, creating new job opportunities and revitalizing communities.
The maglev system is expected to have a positive impact on air quality, contributing to a healthier environment.
Funding Mechanisms
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project, a crucial step toward a more efficient and sustainable transportation network, hinges on a robust funding strategy. Securing the necessary capital for construction, operation, and maintenance is paramount for its success. Different funding models offer varying advantages and disadvantages, and a comprehensive understanding of these models is essential for evaluating the project’s feasibility and long-term viability.
Federal funding plays a critical role, but other sources are also vital for the project’s financial sustainability.
Funding Sources
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project will likely draw from a diverse array of funding sources. This multifaceted approach is crucial for ensuring adequate financial resources throughout the project’s lifecycle. Federal grants, state and local government allocations, private sector investments, and potential public-private partnerships are all possible funding avenues. The specific allocation of each source will depend on the project’s evolving needs and the feasibility of securing funds from different sectors.
Federal Funding Allocation
Federal funds are expected to be a cornerstone of the Washington-Baltimore Maglev project’s financing. These funds will likely be allocated across different project phases, encompassing land acquisition, infrastructure development, technology implementation, and ongoing maintenance. Detailed allocation plans will be crucial for ensuring the efficient use of federal resources and the project’s timely completion.
Specific Allocation Breakdown
Federal funds will be strategically allocated to specific project components. Construction of the initial track segments will likely receive a significant portion, followed by allocations for procurement of advanced maglev trains and associated infrastructure. Further allocations will support testing and validation procedures, ensuring the reliability and safety of the new technology. Ongoing maintenance and operational costs will also be considered in the allocation plans.
A precise breakdown of the allocation will be crucial to ensure all critical project phases are adequately funded.
Timeline for Funding Disbursement
A clear timeline for funding disbursement is essential for the project’s successful execution. The timeline will be contingent on the approval and subsequent release of federal funding, and will be further defined by the project’s procurement and construction schedule. This schedule should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any delays or advancements in the project’s progress. Real-world examples of large-scale infrastructure projects demonstrate the importance of accurate scheduling to avoid cost overruns and project delays.
This includes, but is not limited to, the timelines for the completion of similar projects. The timely release of funding will be critical to meeting project deadlines and ensuring the project’s smooth execution.
Federal Funding Allocation: Washington Baltimore Maglev Federal Funds
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project, a bold leap into the future of high-speed transportation, hinges critically on securing federal funding. Understanding how these funds are allocated, the criteria used for evaluation, and the current economic landscape’s impact is essential for project success. This section delves into the intricate process of securing federal dollars for infrastructure projects of this scale.
While Washington and Baltimore’s maglev train project is still waiting for federal funding, I’ve been eyeing some sweet deals on tech. For example, if you’re looking for a great pair of wireless earbuds, check out the OnePlus Buds Bullets Wireless Z earbuds headphones deal on Black Friday here. Hopefully, the federal funding for the maglev project will materialize soon, allowing for faster commutes between the cities.
It would be a great step for the region.
Federal Funding Allocation Process
Federal funds for infrastructure projects like the Maglev are allocated through a multifaceted process, often involving competitive grant programs and detailed project proposals. The process is designed to prioritize projects with demonstrable economic and social benefits, ensuring responsible use of taxpayer dollars.
Criteria for Evaluating Funding Proposals
Proposals for infrastructure projects, including the Maglev, are evaluated based on a range of factors. These factors typically include the project’s feasibility, projected economic impact, environmental sustainability, and alignment with national transportation priorities. The specific criteria often include quantifiable metrics such as job creation estimates, cost-benefit analyses, and the project’s contribution to regional economic development.
Impact of Economic Conditions
Current economic conditions significantly influence the availability of federal funds for infrastructure projects. Periods of economic uncertainty or recessionary trends often result in reduced funding for non-essential projects. The perceived return on investment and the project’s overall feasibility play a crucial role in securing funding during challenging economic times. For example, the recent infrastructure bill in the US allocated significant funds, demonstrating a commitment to transportation improvements despite economic concerns.
Historically, periods of high unemployment have led to increased focus on infrastructure projects as a means of job creation and economic stimulus.
Historical Allocation of Federal Funds to Transportation Projects in the Region
Understanding the historical allocation of federal funds to transportation projects in the Washington-Baltimore region provides context for the current Maglev project. This data is vital for assessing the potential for funding and comparing the project’s merits to previous endeavors.
| Year | Category | Allocated Funds (USD millions) | Project Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | High-Speed Rail | 150 | Funding for feasibility studies and preliminary designs for high-speed rail lines in the Northeast Corridor. |
| 2019 | Transit Expansion | 225 | Funding for expansion of existing metro systems and bus rapid transit corridors in the Baltimore-Washington metropolitan area. |
| 2020 | Road Improvement | 180 | Funding for road widening, bridge replacement, and intersection improvements on major roadways connecting the two cities. |
| 2021 | Infrastructure Investment | 300 | Significant allocation for infrastructure improvements across various sectors, including transportation. |
This table provides a simplified overview of historical allocations. More detailed data, including project-specific information and granular breakdowns of spending, can be found in reports published by the Federal Transit Administration and the Department of Transportation.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project, while promising, presents a complex interplay of potential advantages and disadvantages. Careful consideration of both sides is crucial for a balanced assessment. Weighing the economic gains against environmental concerns and social impacts is vital to ensuring the project’s long-term viability and positive contribution to the region.The project’s potential to reshape transportation networks and stimulate economic growth in the Washington-Baltimore corridor is undeniable.
However, careful planning and mitigation strategies are essential to minimize negative consequences and maximize the project’s positive impact on the region’s residents and environment.
Economic Benefits
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project holds the potential to significantly boost the regional economy. Faster, more reliable transportation can attract businesses, fostering economic growth and job creation. Increased tourism and accessibility to diverse employment opportunities within the region are likely. This is a pattern observed in other high-speed rail projects globally, such as the Shinkansen in Japan. Reduced travel time will also encourage commuting, potentially leading to higher productivity and lower expenses for employees.
Further, the construction phase of the project will generate employment opportunities, contributing to economic activity.
Environmental Impacts
The environmental consequences of the Maglev project must be thoroughly assessed. Construction activities can cause localized environmental damage, including habitat disruption and increased noise and air pollution. Energy consumption during operation is a key consideration. The project’s environmental impact will depend on the specific technologies utilized and the measures implemented to mitigate potential damage. Studies on similar projects in other regions can provide valuable insights and comparative data for effective mitigation strategies.
Social Implications
The project will undoubtedly impact the social fabric of the Washington-Baltimore region. Accessibility improvements will benefit residents with limited mobility or access to employment opportunities. The potential for gentrification in areas along the Maglev route needs to be anticipated and mitigated to ensure equitable access for all. A thorough understanding of the potential social implications is essential for community engagement and to address any concerns.
Potential Drawbacks to Success
Several factors could hinder the success of the Washington-Baltimore Maglev project. High initial construction costs, potential delays in the project timeline, and unforeseen technical challenges could impact its budget and implementation. Community opposition, funding constraints, and unforeseen economic downturns can also contribute to project delays or cancellation. There is a need to assess the risk of these potential drawbacks and develop contingency plans.
Comprehensive Comparison of Benefits and Drawbacks
| Aspect | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Economic | Increased economic activity, job creation, and tourism | High initial construction costs, potential delays, and economic downturns |
| Environmental | Reduced reliance on private vehicles, decreased air pollution (depending on energy source) | Construction-related damage, energy consumption, and potential noise pollution |
| Social | Improved accessibility, potential for economic development, and enhanced community connections | Potential for gentrification, community opposition, and equitable access concerns |
A comprehensive evaluation of these benefits and drawbacks is essential to making informed decisions about the project’s feasibility and sustainability.
Alternatives and Comparisons
The Washington-Baltimore maglev project presents a compelling vision for high-speed transit, but its success hinges on a thorough comparison with existing and potential alternative transportation options. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness and potential return on investment is crucial in determining its viability. This section delves into the various alternatives, assessing their strengths and weaknesses, and analyzing their potential impact on the region’s transportation landscape.The feasibility of the maglev project hinges on a rigorous analysis of its comparative advantages and disadvantages relative to existing and emerging transportation solutions.
This involves a careful assessment of costs, benefits, and potential long-term impacts. This examination will help to understand the project’s place within the broader context of regional transportation planning.
Alternative Transportation Models
A comprehensive comparison requires examining various transportation options currently available or under consideration in the Washington-Baltimore area. This includes traditional rail systems, bus networks, and potential expansions of existing infrastructure, along with emerging technologies like autonomous vehicles.
- Traditional Rail Systems: Existing commuter rail lines offer established routes and infrastructure, but capacity limitations and slower speeds often pose challenges. Upgrades to existing lines could offer incremental improvements, but may not match the projected speeds and capacity of a maglev system. For example, the MARC commuter rail system, while useful, experiences congestion and delays, impacting overall efficiency.
- Bus Networks: Bus systems provide widespread access, but generally have lower speeds and frequencies compared to other options. Expansion of bus rapid transit (BRT) systems could improve efficiency in specific corridors, but may not address the long-distance travel needs effectively served by a maglev.
- High-Speed Rail: High-speed rail (HSR) is a recognized alternative, but the construction and maintenance costs are significant. Existing HSR systems show a variable return on investment depending on ridership and cost management. Comparing costs and projected ridership is essential for a fair assessment.
- Autonomous Vehicles: While autonomous vehicles are a developing technology, their potential impact on regional transportation is substantial. The deployment of self-driving taxis and ride-sharing services could significantly alter commuting patterns and reduce traffic congestion, but current infrastructure and regulatory hurdles remain substantial. The long-term cost-effectiveness and integration with existing systems remain uncertain.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of each transportation model requires a detailed breakdown of capital costs, operating expenses, and projected ridership. This analysis considers both direct and indirect costs.
| Transportation Model | Capital Costs | Operating Costs | Projected Ridership | Return on Investment (ROI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maglev | High (initial investment) | Low (maintenance and operation) | High (potential for high-volume traffic) | Long-term potential for high ROI, dependent on ridership |
| Traditional Rail | Medium | Medium | Medium | Moderate ROI |
| Bus Networks | Low | Low | Medium | Moderate ROI, potentially lower than rail or maglev |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Low (initial, but potentially high for infrastructure changes) | Low (potential for lower maintenance compared to traditional systems) | High (potential for high ridership) | Long-term potential for high ROI, dependent on technological advancements and adoption rates |
Potential Return on Investment, Washington baltimore maglev federal funds
The projected return on investment for the maglev project hinges on factors like ridership projections, operational efficiency, and potential for attracting new development along the transit corridor. Historical data from successful high-speed rail projects can provide insights, but regional specifics must be carefully considered. For instance, the success of the Shinkansen in Japan is often cited as a potential model, but factors like population density and economic conditions must be analyzed to ensure applicability.
“A successful maglev project hinges on a high volume of passengers and efficient operations to yield a strong return on investment. “
Infrastructure Considerations
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project hinges critically on the meticulous planning and execution of its infrastructure. This involves not just the tracks themselves but the intricate network of supporting facilities, stations, and maintenance depots. Understanding the infrastructure needs and their potential impact on existing infrastructure is crucial for a successful project. Careful consideration must also be given to the regulatory framework governing construction and operation.
Track Construction
The Maglev track will necessitate significant earthwork, potentially affecting existing landscapes and requiring careful environmental impact assessments. Precise alignment and grading are paramount to ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the system. Advanced construction techniques, such as specialized tunneling methods and elevated track structures, may be required depending on the specific route. Material selection and procurement will also be critical to ensuring the track’s longevity and resistance to environmental factors.
Stations
Maglev stations will be more than just transit hubs; they will be vital community anchors. Their design should integrate seamlessly with surrounding environments, accommodating diverse transportation needs and fostering economic development. Key considerations include accessibility for all users, including those with disabilities, and the integration of public spaces for community interaction. The stations will also require robust infrastructure to support the Maglev trains’ arrival and departure, including platform design, safety systems, and potentially, elevated or underground structures.
Maintenance Facilities
The longevity and reliability of the Maglev system depend heavily on effective maintenance. Dedicated facilities will be essential for regular inspection, cleaning, and repair of the track and trains. These facilities should be strategically located near the track network, ensuring minimal downtime. They should also incorporate advanced maintenance technologies, allowing for the quick identification and resolution of potential issues.
Modern maintenance facilities should be designed with sustainability in mind, reducing environmental impact through efficient energy use and waste management.
Impact on Existing Infrastructure
The Maglev project will undoubtedly interact with existing infrastructure, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Carefully planned integration strategies are crucial to minimizing disruption to existing roadways, utilities, and other infrastructure. Careful coordination with utility companies and other agencies is vital to ensure smooth integration and avoid conflicts. Possible strategies could include rerouting or upgrading existing infrastructure, creating shared space, or employing innovative solutions.
Comparison of Infrastructure Needs
| Transportation System | Track Construction | Stations | Maintenance Facilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maglev | Advanced, specialized materials and methods; often elevated or underground | Integrated community hubs, with diverse accessibility features | Dedicated facilities for regular inspection, repair, and upgrades |
| High-Speed Rail | Extensive track network; often elevated or ground level | Large stations, often integrated with existing transit | Maintenance facilities near track network |
| Suburban Rail | Track network designed for shorter distances | Smaller stations, often integrated with local transit | Maintenance facilities near track network |
This table highlights the distinct infrastructure requirements for each system. The complexity and scale of the Maglev infrastructure are evident, compared to other rail systems.
Construction Process
A phased approach to construction is recommended, allowing for the progressive integration of infrastructure elements. This approach will help manage potential disruptions to existing infrastructure and operations. Detailed project scheduling and rigorous quality control procedures are critical to ensure the timely and high-quality completion of the Maglev system. Public engagement and transparent communication throughout the construction process are crucial to managing expectations and addressing any concerns.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework for Maglev construction and operation must be robust and comprehensive. It should address environmental concerns, safety standards, and potential community impacts. Clear regulations on land acquisition, permitting processes, and the management of potential environmental hazards are essential. Thorough compliance with all relevant regulations is vital for the project’s success and community acceptance.
Public Opinion and Engagement
Public opinion is a crucial factor in the success of any large-scale infrastructure project, especially one as ambitious as the Washington-Baltimore Maglev. Understanding public sentiment, addressing concerns, and fostering engagement are vital steps in ensuring a smooth project trajectory. Successful projects often demonstrate a strong public consensus and active participation. Conversely, projects facing significant public opposition can encounter delays, cost overruns, and even outright rejection.Public perception and engagement directly influence project feasibility and acceptance.
Early and consistent communication with the public, proactive addressing of concerns, and transparent project updates are key elements of successful public engagement strategies. The project must consider the diverse perspectives of various community groups to effectively navigate potential opposition and build support.
Public Opinion Regarding the Washington-Baltimore Maglev Project
Initial public opinion polls indicate a mixed response to the Maglev project. While some residents are enthusiastic about the potential benefits of increased transportation efficiency and reduced commute times, others express concerns about the environmental impact, potential property value fluctuations, and the project’s financial feasibility. These concerns often center around specific community impacts and the need for a thorough assessment of local consequences.
Public awareness campaigns and open forums can help clarify these concerns.
Strategies for Public Engagement and Outreach
Engaging the public requires a multifaceted approach. This includes community forums, town hall meetings, online platforms for Q&A and feedback, and targeted outreach to specific community groups. Publicly accessible, detailed information about the project’s environmental impact assessment and cost-benefit analysis can help build trust and address concerns. Partnerships with local community organizations can facilitate outreach and engagement.
- Community Forums and Town Halls: These platforms provide opportunities for direct interaction between project stakeholders and the public. Open dialogue and transparent communication are essential for addressing concerns and fostering understanding. Examples include the successful engagement strategies used in other high-speed rail projects, such as the development of specific community-focused engagement strategies in specific areas of concern.
- Online Platforms: Utilizing social media and dedicated project websites for updates, FAQs, and public feedback channels can improve accessibility and engagement. Interactive mapping tools showing potential route impacts can help visualize the project’s impact on various communities.
- Targeted Outreach: Recognizing that different community groups may have varying concerns, tailored outreach to specific groups can help address their unique needs and perspectives. This might include community meetings in areas with concerns about property values, or those with specific environmental concerns. Engagement with environmental advocacy groups can lead to constructive discussion on potential environmental mitigation strategies.
Concerns of Various Community Groups
Concerns vary across different community groups. Residents along the proposed route may be concerned about property value impacts, noise pollution, and potential displacement. Environmental groups may raise concerns about the project’s environmental footprint, including habitat disruption and potential carbon emissions. Economic groups may be concerned about the cost of the project and the return on investment. Addressing these concerns requires specific strategies, tailored to the specific concerns of each group.
Table Summarizing Public Input on the Project
| Community Group | Primary Concerns |
|---|---|
| Residents along the route | Property value impacts, noise pollution, potential displacement |
| Environmental groups | Environmental footprint, habitat disruption, carbon emissions |
| Economic groups | Cost of the project, return on investment |
| Transportation advocates | Increased commute times, accessibility to regional destinations |
Strategies for Addressing Concerns
Addressing public concerns requires a proactive approach. This includes incorporating feedback into project design, offering compensation for property value impacts, implementing noise mitigation measures, and developing detailed environmental impact statements. Transparent communication and a willingness to adapt to feedback are crucial. The project should explore alternative solutions to address specific concerns and prioritize community well-being.
Technological Advancements

The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project hinges on technological advancements in magnetic levitation systems. Current designs need to be evaluated against the latest breakthroughs to ensure the project remains competitive and efficient. This analysis considers potential future innovations and the incorporation of sustainable energy sources, critical for long-term project viability.The current planned Maglev technology, while proven in principle, may be surpassed by emerging innovations.
Examining these advancements allows us to assess the project’s potential for long-term competitiveness and sustainability. Further, we can explore how to optimize the system for environmental responsibility and cost-effectiveness.
Latest Maglev Technology Advancements
Significant advancements in superconductor materials and magnetic field generation are pushing the boundaries of Maglev technology. These advancements offer the potential for higher speeds, reduced energy consumption, and increased efficiency. Researchers are exploring new materials like high-temperature superconductors, which can operate at higher temperatures than traditional superconductors, potentially leading to lower operating costs.
Comparison to Planned Project Technology
The planned Maglev project likely employs established technologies. Comparing these to the latest advancements reveals potential areas for improvement in terms of speed, efficiency, and cost. The latest research might offer avenues for reduced infrastructure requirements and lower operating expenses, as well as opportunities to integrate sustainable energy sources more effectively.
Potential Future Innovations
Future innovations in magnetic levitation could include the development of advanced control systems and materials for the levitation system, allowing for more precise and stable operation. Furthermore, advancements in propulsion systems may enable higher speeds and reduced energy consumption. For instance, the development of new propulsion methods might significantly impact the project’s long-term sustainability. Examples of future innovations include:
- Advanced Control Systems: Sophisticated control systems can optimize energy use, reduce maintenance, and enhance safety by precisely controlling the levitation and propulsion systems.
- Lightweight Materials: Utilizing lightweight, high-strength materials in the Maglev train components can reduce the weight of the train, improving efficiency and lowering energy consumption.
- Improved Superconductors: The development of more efficient and robust superconductors can reduce energy losses, leading to lower operational costs.
Incorporating Sustainable Energy Sources
The Maglev system’s energy requirements are significant. Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the system’s power grid can substantially reduce the carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels. The feasibility of implementing a hybrid power system, drawing from multiple renewable energy sources, warrants investigation.
Long-Term Sustainability
The long-term sustainability of the project hinges on its ability to adapt to technological advancements and incorporate sustainable energy sources. A focus on reducing energy consumption and optimizing the system for renewable energy integration is crucial. The project’s design should be adaptable and scalable to accommodate future technological advancements, maximizing the long-term value and minimizing environmental impact.
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project is definitely a hot topic, and federal funding is crucial for its success. It’s fascinating to see how this project connects to broader accessibility issues, like those highlighted in recent accessible blockbusters. For example, films like Mulan are increasingly incorporating audio description and captions for a more inclusive viewing experience, mulan accessible blockbusters blind low vision deaf hard of hearing audio description captions demonstrating a shift towards inclusivity.
Ultimately, funding for the Maglev will be essential for its completion, ensuring this exciting project can benefit everyone.
Project Timeline and Milestones
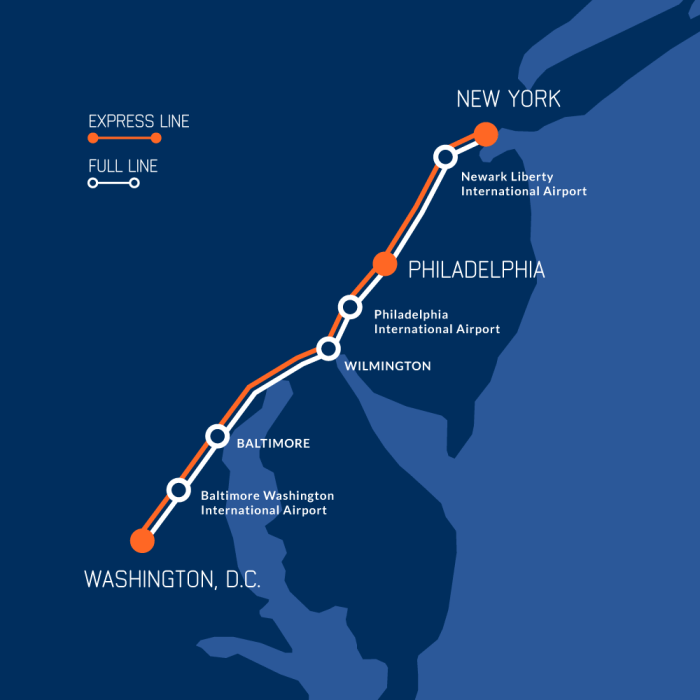
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project’s success hinges critically on a meticulously planned timeline and the consistent achievement of key milestones. This section Artikels the proposed project phases, deadlines, and the roles of key stakeholders to ensure smooth execution and timely completion. A well-defined timeline, incorporating potential delays and contingency plans, is paramount for managing expectations and maintaining project momentum.
Project Phases and Milestones
The Washington-Baltimore Maglev project is envisioned as a multi-phased undertaking, each phase building upon the previous one. Careful planning and execution within each phase are vital for successful completion.
Detailed Project Timeline
This table presents a projected timeline for the various stages of the Washington-Baltimore Maglev project. These estimates are based on current technological capabilities and anticipated resource allocation. Real-world project timelines often experience adjustments due to unforeseen circumstances.
| Phase | Description | Start Date | End Date | Key Milestones |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Preliminary Design & Environmental Impact Assessment | Detailed design of the route, station locations, and potential environmental impacts. Obtaining necessary permits and approvals. | 2024-01-01 | 2025-06-30 | Finalized route design, Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) completed, and permits obtained. |
| Phase 2: Construction & Infrastructure Development | Construction of the Maglev track, stations, and supporting infrastructure. | 2025-07-01 | 2028-12-31 | Completion of track construction, station construction, and critical infrastructure components. |
| Phase 3: Testing & Commissioning | Testing and commissioning of the Maglev system, including safety protocols, operational procedures, and passenger capacity. | 2029-01-01 | 2030-06-30 | Successful completion of testing, commissioning of the system, and certification for passenger operation. |
| Phase 4: Initial Operation & Expansion | Initial operation of the Maglev line, collecting passenger data, and evaluating potential for future expansion. | 2030-07-01 | 2032-12-31 | Formal opening to the public, performance monitoring, and planning for potential future extensions. |
Potential Delays and Contingency Plans
Unforeseen circumstances can impact project timelines. Potential delays include material shortages, labor disputes, or unforeseen regulatory hurdles. Contingency plans should be developed for each phase to address these potential issues. Contingency plans should involve alternative materials, backup contractors, and revised schedules. Drawing upon successful case studies of large-scale infrastructure projects will provide invaluable insights into how to manage delays effectively.
Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities
Different stakeholders have crucial roles in adhering to the project timeline. Federal agencies, state governments, local authorities, construction companies, and the public all have responsibilities in meeting deadlines. Clear communication channels and defined roles are essential to avoid confusion and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned. The establishment of a project management office (PMO) with dedicated staff will be critical to coordinating the efforts of various stakeholders and tracking progress against milestones.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, Washington Baltimore maglev federal funds are a critical component of this transportation project. While the project holds significant potential, it’s essential to consider both the benefits and drawbacks, alongside alternative options. A comprehensive understanding of the funding allocation, public engagement, technological advancements, and infrastructure requirements is crucial to ensuring the project’s long-term success. The final assessment of the project will be made based on a multitude of factors, and the decision to move forward must be carefully weighed against the potential challenges and benefits.
The future of this project hinges on careful consideration and robust public discourse.