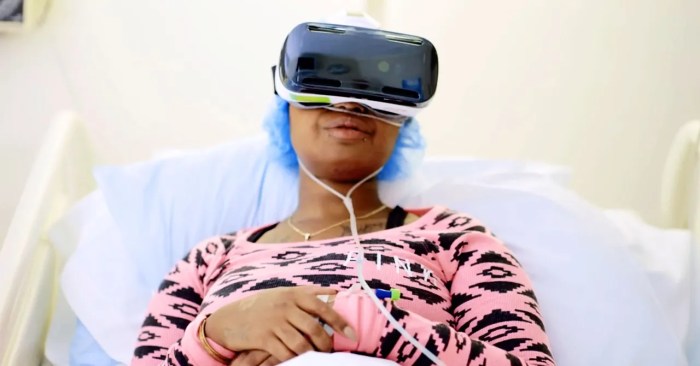
VR chronic pain FDA sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of how virtual reality is being used to treat chronic pain, and the role the FDA plays in regulating these innovative therapies. We’ll delve into the technology itself, examining different VR systems and their potential benefits, alongside a critical look at the FDA’s regulatory framework for these devices.
The discussion will also encompass clinical trials, safety concerns, and potential future applications.
This deep dive into the intersection of VR, chronic pain, and FDA regulations will offer a comprehensive overview of the current state of affairs and highlight both the promise and the challenges of this emerging field. The potential for personalized pain management strategies is particularly compelling, and we’ll explore how VR might integrate with existing treatments.
VR and Chronic Pain
Virtual reality (VR) is an immersive technology that creates simulated environments using computer graphics and sensory feedback. In healthcare, VR offers potential applications ranging from pain management and rehabilitation to surgical training and mental health support. The technology’s ability to transport users to different worlds and provide interactive experiences makes it a promising tool for treating various conditions.
Chronic pain, a persistent and debilitating condition, significantly impacts patients’ quality of life. Addressing this challenge requires innovative approaches, and VR therapy shows potential to help alleviate pain and improve well-being.
Virtual Reality Technology in Healthcare
Virtual reality technology is rapidly advancing, with significant potential in diverse healthcare settings. VR applications are increasingly being used to engage patients, reduce stress, and provide immersive therapies. The interactive nature of VR can make treatments more engaging and effective, leading to better patient outcomes. This technology provides a new avenue for healthcare professionals to interact with patients in a dynamic and engaging way, potentially leading to improved patient engagement and compliance with treatment plans.
Chronic Pain and its Impact
Chronic pain is defined as persistent or recurring pain lasting for three months or longer. This condition can significantly impact patients’ daily lives, affecting their ability to work, engage in social activities, and maintain their overall well-being. The emotional toll of chronic pain can be substantial, leading to anxiety, depression, and reduced quality of life. The experience of chronic pain is highly individualized, with symptoms varying in intensity, location, and duration.
VR Therapy for Pain Management
VR therapy is increasingly being used to manage various types of pain, including back pain, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. These therapies often involve exposing patients to virtual environments that distract from pain signals, promoting relaxation, and building coping mechanisms. The interactive nature of VR allows patients to actively participate in their pain management.
Types of VR Systems for Pain Management
Various VR systems are being developed and implemented for pain management. These systems utilize different sensory modalities, including visual displays, haptic feedback devices, and auditory stimuli. Each system is tailored to target specific pain types and patient needs. A common approach involves creating virtual environments that promote relaxation, distraction, and engagement, thereby diverting attention from pain signals.
The FDA’s stance on VR chronic pain treatment is definitely something to watch. While innovative VR applications show promise, there’s still much to learn about their long-term effects. This is a crucial area of research, especially given the growing popularity of immersive experiences like the upcoming Percy Jackson Disney Plus series, based on Rick Riordan’s popular books and streaming on Fox.
To delve deeper into the world of fantasy and streaming, check out the latest info on the Percy Jackson series here. Ultimately, the focus needs to remain on responsible VR development for chronic pain relief, ensuring safety and efficacy before widespread adoption.
Comparison of VR Approaches for Chronic Pain Management
| VR System Type | Key Features | Target Pain Types | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immersive Virtual Environments | Provide highly realistic virtual environments, often with interactive elements. | Chronic pain, musculoskeletal pain, neuropathic pain | Distraction, relaxation, improved coping mechanisms, reduced pain perception |
| VR-Based Biofeedback | Combine VR with physiological monitoring to provide real-time feedback on stress responses and relaxation techniques. | Chronic pain, anxiety, stress-related pain | Improved self-awareness of pain triggers, enhanced relaxation techniques, reduced pain intensity |
| VR-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Use VR to simulate real-life situations and practice coping strategies in a safe and controlled environment. | Chronic pain, anxiety, depression | Improved coping skills, reduced catastrophizing, improved emotional regulation |
FDA Regulations and VR Pain Management
Navigating the regulatory landscape for virtual reality (VR) pain management tools is crucial for ensuring patient safety and efficacy. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in this process, overseeing the development and approval of medical devices, including those designed to treat chronic pain. Understanding the specific requirements and potential challenges is vital for the responsible development and implementation of VR-based pain therapies.The FDA’s jurisdiction extends to medical devices intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure disease, or to affect structure or function of the body.
The FDA’s stance on VR and chronic pain is fascinating, but it’s also interesting to see how economic factors like Sony’s earnings, tariffs, and PS5 price adjustments in US manufacturing affect the broader tech landscape. For example, sony earnings tariffs ps5 price us manufacturing could potentially influence the development and accessibility of VR solutions for pain management.
Ultimately, the FDA’s regulations on VR chronic pain treatment will be crucial for the future of this technology.
This includes VR pain management tools, which aim to alter patient experience and potentially alleviate pain symptoms. Consequently, these tools fall under the FDA’s purview and must adhere to stringent regulations to ensure safety and effectiveness.
FDA’s Role in Regulating Medical Devices
The FDA regulates medical devices based on their intended use and risk classification. This tiered system categorizes devices into classes based on the level of risk they pose to patients. Class I devices pose the lowest risk and typically require the least regulatory oversight, while Class III devices carry the highest risk and necessitate premarket approval. The classification of a VR pain management device will dictate the specific regulatory pathway it must follow.
This classification process is based on the device’s intended use and the potential risks involved.
Specific Regulatory Requirements for VR Pain Management Technologies
VR pain management technologies, as medical devices, are subject to the same fundamental regulations as other medical devices. However, unique considerations arise from the technology’s interactive nature and its potential for personalized treatment approaches. Specific requirements may include demonstrating the safety and efficacy of the VR experience in reducing pain perception and influencing neural pathways. Clinical trials and rigorous data analysis are essential components of this process.
This includes demonstrating that the VR experience is safe for the target patient population.
Challenges in Applying FDA Regulations to VR Pain Management, Vr chronic pain fda
One key challenge lies in defining and measuring the therapeutic outcomes of VR-based pain management. Traditional metrics used for evaluating medical devices might not be directly applicable to the subjective experience of pain reduction through VR. This necessitates the development of novel methodologies to evaluate the effectiveness of these technologies. Another challenge is adapting existing regulatory frameworks to the evolving nature of VR technology.
Rapid advancements in VR technology require flexibility in the regulatory process to accommodate innovative approaches while maintaining patient safety. This includes ensuring that the VR experience is not harmful or distracting to the patient.
The FDA’s stance on VR for chronic pain treatment is fascinating, but it’s worth noting the ripple effects elsewhere. Companies like Amazon, with CEO Andy Jassy recently mandating a return to office policy for remote employees ( amazon ceo andy jassy remote employees return to office ), are navigating similar shifts in workplace culture. Ultimately, the future of VR pain relief hinges on robust clinical trials and clear regulatory pathways, mirroring the evolving landscape of work itself.
Comparison of FDA Approval Processes
The FDA approval process for VR pain management technologies differs from other medical devices depending on the classification of the technology. Class I devices typically require premarket notification (510(k)), whereas Class II and III devices require premarket approval. This distinction is vital for understanding the regulatory path that a specific VR pain management tool must follow.
Steps Involved in Obtaining FDA Clearance or Approval
| Step | Description | Timeframe (estimated) | Required Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Device Classification | Determine the device’s risk classification based on intended use and potential risks. | Variable (weeks to months) | Detailed device description, intended use, and potential risks |
| 2. Premarket Submission (510(k) or Premarket Approval) | Submit necessary documentation to the FDA, including clinical trial data and safety information. | Variable (months to years) | Clinical trial data, preclinical studies, risk assessments, manufacturing information, and other required documents. |
| 3. FDA Review and Response | The FDA reviews the submitted documentation to assess the safety and efficacy of the device. | Variable (months to years) | Follow-up communication with FDA and response to any requested information. |
| 4. Approval or Clearance | Obtain FDA clearance or approval to market the device. | Variable (months to years) | Compliance with FDA requirements and subsequent device monitoring. |
VR for Chronic Pain
Virtual reality (VR) is emerging as a promising therapeutic tool for managing chronic pain. Its immersive nature and ability to distract from pain signals offer a unique approach to pain relief, potentially reducing reliance on medication and improving overall well-being. Early research suggests VR interventions can be effective, but more robust clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings and understand the optimal use of VR in diverse patient populations.The effectiveness of VR in chronic pain management hinges on its ability to create an environment that shifts the focus away from the pain experience.
By immersing patients in engaging virtual worlds, VR can potentially alter their perception of pain, offering a distraction technique that complements existing pain management strategies. This approach is particularly attractive for conditions where conventional treatments may not fully address the underlying psychological and emotional factors contributing to pain.
Clinical Trials Investigating VR for Chronic Pain Management
Existing clinical trials exploring VR for chronic pain management have yielded promising preliminary results. Studies have investigated various types of chronic pain, including back pain, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. The methodologies employed in these studies vary, but common features include pre- and post-intervention assessments of pain intensity, functional capacity, and psychological well-being. These assessments help evaluate the impact of VR on pain reduction and quality of life.
Effectiveness of VR in Reducing Chronic Pain Symptoms
Data from some studies indicate that VR interventions can significantly reduce chronic pain symptoms. Participants in these trials often reported decreased pain intensity and improved functional capacity following VR exposure. However, the magnitude of these effects can vary across different studies, highlighting the need for further research to understand factors influencing treatment response. For example, one study might find VR to be particularly effective for patients with specific types of neuropathic pain, while another might find its impact less pronounced in individuals with fibromyalgia.
Methodologies Used in VR Pain Management Studies
The methodologies used in VR pain management studies encompass a range of approaches. Some studies utilize immersive VR environments with specific tasks or activities designed to distract patients. Others explore the use of VR in combination with other therapies, such as mindfulness or cognitive behavioral therapy. The length of VR exposure, the frequency of sessions, and the specific type of VR experience are also key variables considered in these studies.
For example, a study might employ VR exposure for 30 minutes, twice a week, over a period of six weeks, focusing on virtual environments designed to evoke relaxation or promote sensory stimulation. Table 1 below summarizes key elements from some existing studies.
Limitations of Existing Research
Despite the promising preliminary findings, existing research on VR for chronic pain management faces several limitations. Sample sizes in some trials are relatively small, potentially limiting the generalizability of the results. The long-term effects of VR interventions also require further investigation, as some studies focus on short-term outcomes. Furthermore, the diverse nature of chronic pain conditions, and the individual variability in patient responses, necessitate more extensive research with a wider range of participants to determine the optimal VR interventions for specific pain types.
Potential Future Research Directions
Future research directions in VR for chronic pain management should focus on addressing existing limitations and expanding the scope of investigations. A crucial area is developing personalized VR interventions tailored to individual patient characteristics and pain profiles. This includes examining how VR experiences can be adjusted based on individual pain intensity, location, and psychological factors.
- Developing VR applications that integrate existing therapies, such as mindfulness or cognitive behavioral therapy, to enhance the effectiveness of VR interventions.
- Investigating the potential of VR for pain prevention, exploring its role in managing pain before it becomes chronic.
- Examining the long-term effects of VR on chronic pain, including the maintenance of pain reduction and functional improvements.
- Exploring the use of VR in conjunction with other pain management modalities, like medication or physical therapy, to optimize treatment outcomes.
- Conducting studies with larger sample sizes, encompassing diverse patient populations, to establish the generalizability of VR interventions.
VR Pain Management: Vr Chronic Pain Fda
Virtual reality (VR) pain management shows promise as a novel therapeutic approach. However, its implementation necessitates careful consideration of safety and efficacy factors. This exploration delves into the potential risks, crucial safety protocols, and user experience aspects to ensure responsible and effective VR pain management.VR pain management, while emerging, is not a panacea. It’s a tool that, when integrated correctly with existing pain management strategies, can potentially offer substantial benefits.
Understanding the nuances of its application and its inherent limitations is vital for successful implementation.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
VR experiences, though generally considered safe, can trigger adverse reactions in susceptible individuals. Motion sickness, nausea, and discomfort are potential side effects, particularly with complex or immersive VR environments. Psychological distress, although rare, is possible in individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions or a history of trauma. Individual sensitivity to VR stimuli and the intensity of the experience play significant roles in determining the likelihood of these effects.
Safety Protocols and Measures
Robust safety protocols are paramount for VR pain management. Prior to any VR pain management session, thorough patient screening is crucial. This should include assessing for pre-existing medical conditions, psychological vulnerabilities, and any history of adverse reactions to similar stimuli. Close monitoring during the VR session is essential. Trained personnel should be present to address any immediate concerns, including discomfort or distress.
Clear communication channels between patients and healthcare providers are vital for a safe and effective experience. Emergency procedures should be readily available and well-practiced.
User Experience and Customization
User experience is paramount in VR pain management. A personalized and engaging VR environment can significantly enhance therapeutic outcomes. Tailoring the VR experience to individual patient preferences, pain types, and coping mechanisms is crucial. This includes adjusting the intensity, complexity, and sensory elements of the VR environment. Patient feedback and iterative design are vital for refining the VR experience and optimizing its efficacy.
Efficacy Comparison with Traditional Methods
Comparative studies on the efficacy of VR pain management versus traditional pain management methods are still emerging. However, preliminary findings suggest that VR can be a valuable adjunct therapy, offering complementary benefits. For example, VR can be used to distract from pain, reduce anxiety, and promote relaxation. This approach complements existing pharmacological and physical therapies.
Factors Affecting VR Efficacy
The effectiveness of VR pain management varies greatly among patients. Individual factors, such as pain type, severity, and psychological resilience, significantly influence the outcomes. The quality of the VR experience, the consistency of implementation, and the training of the personnel administering the treatment also play crucial roles. Additionally, the duration and frequency of VR sessions may impact individual response.
Potential Adverse Events and Countermeasures
| Adverse Event | Description | Frequency | Countermeasures ||—|—|—|—|| Motion Sickness | Dizziness, nausea, vomiting | Variable, potentially high in susceptible individuals | Adjust VR environment, use anti-motion sickness medications (as prescribed), shorten initial sessions, provide clear instructions, and offer alternative distraction techniques || Anxiety/Panic | Feelings of intense fear, apprehension, or dread | Low to moderate, potentially higher in individuals with pre-existing conditions | Provide pre-session reassurance, adjust VR intensity, offer coping mechanisms, and have trained personnel available to provide support.
|| Discomfort/Physical Distress | Pain, discomfort, or other physical sensations | Variable | Adjust VR environment, offer breaks, provide feedback mechanisms, and have trained personnel available to monitor and intervene. || Psychological Distress | Feelings of unease, emotional distress | Low, but potential exists in susceptible individuals | Thorough pre-session screening, provide support and coping mechanisms, and offer alternative coping strategies.
|| Technical Issues | Equipment malfunctions or software glitches | Possible | Regular maintenance of VR equipment, backup systems, and trained personnel to resolve issues promptly. |
Future Trends and Implications

Virtual reality (VR) is poised to revolutionize chronic pain management, offering a powerful new tool for pain relief and improved patient outcomes. The potential for personalized treatments, integrated therapies, and enhanced patient engagement is significant, but the future also brings ethical and practical considerations that must be addressed. The integration of VR into existing healthcare systems and the broader societal impact of this technology demand careful planning and consideration.The evolving nature of VR technology will likely lead to increasingly sophisticated and effective applications in pain management.
Improvements in hardware, such as more comfortable headsets and haptic suits, coupled with advancements in software and algorithms, will undoubtedly contribute to a more immersive and tailored VR experience. This will be critical in enhancing user engagement and ultimately improving pain relief outcomes.
Potential Future Developments in VR Technology
Advancements in VR technology are expected to enhance its applications in chronic pain management. Expect more realistic and engaging virtual environments, incorporating elements of personalization and adaptation. Haptic feedback systems will become more sophisticated, allowing for more precise and targeted stimulation of the body. This will enable a greater range of applications for managing various types of chronic pain.
For example, a VR environment simulating a relaxing beach could trigger the release of endorphins, offering a natural pain-relief mechanism.
Impact of VR on the Healthcare Industry
The integration of VR into healthcare practices will likely lead to a more patient-centered approach. Patients will have increased control over their treatment plans and can actively participate in their recovery. VR-based therapies can be administered remotely, expanding access to care in underserved communities and reducing the burden on healthcare facilities. This increased accessibility, combined with the potential for cost-effectiveness, could lead to a more efficient healthcare system.
Telehealth integration with VR will be crucial for broader access and scalability.
Societal Implications of Widespread VR Adoption
Widespread adoption of VR in pain management could have significant societal implications. It could lead to a reduction in the reliance on opioid medications, thereby improving public health. However, ensuring equitable access to VR technology and addressing potential concerns regarding privacy and data security are essential. Ethical considerations, particularly in regards to data security and privacy, are critical to responsible implementation.
Integration of VR with Other Treatment Modalities
VR pain management can be integrated seamlessly with existing treatment modalities. For instance, VR could be used to complement physical therapy exercises, providing a more engaging and motivating experience. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques can be integrated within VR environments to help patients develop coping mechanisms and manage their pain perceptions. The use of VR for pain management is expected to become an integral component of multidisciplinary approaches to chronic pain treatment.
VR could enhance adherence to treatment regimens, leading to better long-term outcomes.
Long-Term Impact of VR on Pain Management Practices
VR has the potential to transform chronic pain management practices in the long term. By providing personalized, accessible, and engaging treatments, VR could improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. VR’s role in promoting patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans will be crucial in optimizing long-term pain management strategies. The development of standardized protocols and evidence-based guidelines will be essential to ensure the safe and effective use of VR technology in this field.
Role of VR in Personalized Pain Management Strategies
VR can play a pivotal role in creating personalized pain management strategies. By tailoring virtual environments and therapeutic interventions to individual patient needs and pain profiles, VR can offer highly individualized treatments. This level of personalization is critical for optimizing the effectiveness of pain management strategies. VR’s adaptability to specific pain types and individual responses allows for highly personalized approaches.
Last Recap
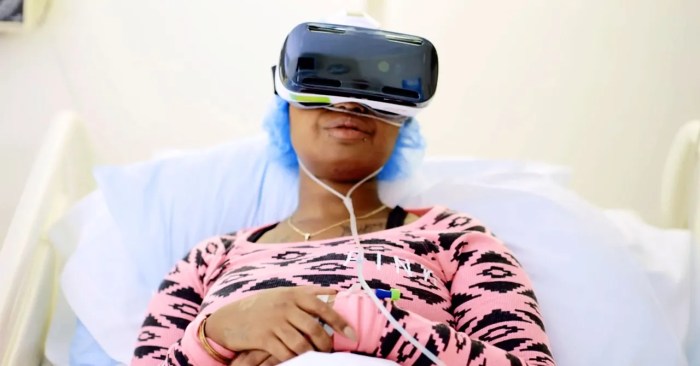
In conclusion, VR chronic pain FDA presents a complex and evolving landscape. While the potential for VR to revolutionize pain management is undeniable, rigorous clinical trials, robust FDA regulations, and careful consideration of safety and efficacy are crucial. The journey ahead involves ongoing research, refined technologies, and a careful balancing act between innovation and responsible implementation. The future of personalized pain management may well depend on navigating these intricacies.