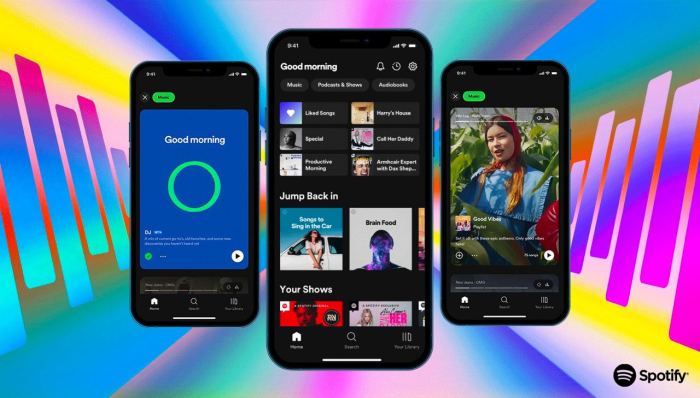
Spotify your library UI update dynamic filters sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of how user interfaces are evolving. This update introduces dynamic filtering options, promising a more personalized and efficient music discovery experience within Spotify’s library. We’ll delve into the key changes, the underlying technical aspects, and the potential impact on user experience.
The new dynamic filters will likely use listening history and preferences to suggest relevant music. This could involve genres, moods, artists, or even specific moments in a user’s life, providing tailored playlists and recommendations. The update aims to enhance the way users interact with their music library and find new discoveries.
Introduction to Spotify Library UI Updates
Spotify’s recent library UI updates signify a significant shift in how users interact with their music collections. These changes are part of a broader trend towards enhancing user experience and streamlining access to vast music libraries. The updates appear designed to improve navigation and organization, reflecting a likely response to user feedback and evolving music consumption patterns.The core objective of these modifications seems to be to make the user’s experience more intuitive and efficient.
This is crucial in a world where users expect seamless and personalized access to their digital assets. The enhanced interface likely aims to streamline the process of finding, organizing, and managing music across different genres, playlists, and artists.
Key Changes and Improvements
Spotify’s library overhaul incorporates several key changes designed to improve user experience. These improvements include enhanced filtering options, reorganized sections, and more visually appealing layouts. The goal is to provide users with more targeted and personalized recommendations.
Dynamic Filtering
The introduction of dynamic filters in the updated library allows users to refine their music selections with greater precision. This feature enables users to quickly isolate specific tracks, albums, or artists based on criteria such as mood, genre, or tempo. This dynamic feature, compared to previous static options, allows for more intricate search options and more targeted recommendations.
Reorganized Sections
The reorganization of sections within the library UI enhances navigation. Users can now find specific content faster, with a more intuitive and streamlined approach. This reorganization likely aims to cater to common user workflows and preferences, enhancing the user experience.
Visual Enhancements
The updated interface boasts a more visually appealing design. Color palettes, typography, and overall layout elements have been thoughtfully refined to create a more engaging and modern aesthetic. These visual updates improve the user’s interaction with the platform, making it more appealing and user-friendly.
Motivations Behind the Changes
Several factors likely contributed to these UI updates. Spotify’s primary motivation is likely to improve user satisfaction and engagement. Increased user engagement, in turn, can lead to higher subscription rates and overall platform profitability. Improved usability and aesthetic appeal are key to achieving these goals. Another motivation is to stay ahead of the competition in a highly competitive digital music market.
Specific Changes Observed
To illustrate the changes, here’s a table outlining examples of modifications observed in the user interface:
| Before Update | After Update | Description of Change |
|---|---|---|
| Cluttered “New Releases” section | Streamlined “New Releases” section with filtering options | The “New Releases” section now allows users to filter by genre, mood, or artist, making it easier to discover new music. |
| Limited search options for specific artists | Advanced search options including artist-specific playlists and albums | The update allows for more targeted searches for specific artists, enabling users to access their work more quickly and effectively. |
| Static “Liked Songs” section | Dynamic “Liked Songs” section with filtering options | Users can now filter their “Liked Songs” by mood, genre, or year, providing more refined browsing options. |
Dynamic Filters in Spotify Library
Spotify’s library is a treasure trove of music, but navigating it can feel overwhelming. Dynamic filters aim to solve this by tailoring the displayed content to the user’s specific listening habits and preferences in real-time. This dynamic adaptation ensures that the library remains a personalized and relevant experience, constantly evolving with the user’s musical journey.Dynamic filters are a powerful feature that transforms the Spotify library from a static collection into a personalized, ever-evolving experience.
They actively learn from the user’s listening history and preferences, adjusting the displayed content accordingly. This means users can discover new music that aligns with their tastes without having to manually sift through countless tracks.
Functionality of Dynamic Filters
Dynamic filters within Spotify’s library function by continuously analyzing a user’s listening history, including the artists, genres, moods, and tempos of the music they enjoy. This analysis is performed in the background, allowing the filters to adapt and refine their recommendations as the user’s preferences evolve. The algorithms behind these filters use complex statistical models to predict what the user might enjoy next, based on past listening patterns.
I’m really digging the new dynamic filters in Spotify’s library UI update. It’s so much easier to find those hidden gems in my music collection now. Speaking of finding hidden gems, this Black Friday deal will keep your yard looking great this spring, check it out. Seriously, top-notch deals on landscaping supplies are a must-have, and it’ll make your garden shine this spring.
It’s like a total game-changer for organization, just like the dynamic filters in Spotify!
Interaction with User Preferences
Dynamic filters meticulously observe a user’s listening patterns. This observation encompasses the specific tracks, albums, playlists, and artists a user frequently engages with. Based on this data, the filters dynamically adjust the display of the library’s content. The user experiences a more refined and relevant view of their library, with recommendations that resonate with their musical tastes. The more the user interacts with the platform, the more sophisticated and accurate the filters become in reflecting their preferences.
Types of Dynamic Filtering Options
Several types of dynamic filtering options are implemented to enhance the user experience. These options allow users to tailor the filtering to their exact needs. They include, but are not limited to:
- Genre-based filtering: This filter analyzes the genres of music a user frequently listens to and prioritizes related content within the library.
- Mood-based filtering: This filter examines the mood associated with the music a user typically enjoys, such as upbeat, relaxing, or energetic. The filter then displays music with similar moods.
- Tempo-based filtering: This filter analyzes the tempo (speed) of the music a user listens to. The system prioritizes music with similar tempos in the library’s display.
- Artist-based filtering: This filter focuses on the artists a user has a strong affinity for. It recommends albums and songs from similar artists.
These options provide a multi-faceted approach to refining the user’s musical experience. Each option focuses on a particular aspect of the user’s listening history to offer more targeted and accurate recommendations.
Potential Benefits for Users
Dynamic filters offer several potential benefits for users. They enhance the discovery of new music that aligns with their preferences, reduce the time spent searching for relevant content, and create a more personalized listening experience. The personalized nature of these filters fosters a stronger connection between the user and the platform’s content, increasing engagement and satisfaction.
Examples of Implementation
One example of implementation is a filter that shows songs from artists similar to those the user has frequently played. Another example involves a filter that displays music with similar moods to the user’s typical listening choices. Furthermore, the filter could display music with similar tempos, catering to specific listening preferences.
Filter Types and Functionalities
| Filter Type | Associated Functionality |
|---|---|
| Genre-based | Prioritizes music within the same genres as the user’s frequent listening. |
| Mood-based | Displays music with similar moods to the user’s preferred listening choices (e.g., upbeat, relaxing). |
| Tempo-based | Prioritizes music with tempos similar to the user’s typical listening patterns. |
| Artist-based | Recommends music from artists similar to those the user frequently listens to. |
User Experience Impact of Dynamic Filters: Spotify Your Library Ui Update Dynamic Filters
Spotify’s library UI update, incorporating dynamic filters, promises a significant leap forward in user experience. This shift is driven by the need to navigate increasingly vast music collections efficiently. Dynamic filters are not just a technical advancement; they represent a crucial step toward personalized music discovery and enhanced user satisfaction.Dynamic filters, by their very nature, adapt to user interactions and preferences in real-time.
This adaptive capability allows users to explore music in a more intuitive and tailored manner, leading to a richer and more rewarding listening experience. It’s a proactive approach to engagement, shifting from passive consumption to active exploration.
Potential Positive Impacts on User Experience
Dynamic filters offer several potential benefits. They enable users to quickly and precisely target their desired music based on criteria like mood, genre, artist, or even specific memories associated with the music. This precision reduces the time spent searching, enabling users to discover music more efficiently and engage with their library in a more focused way.
Enhanced User Engagement and Discovery
The dynamic nature of these filters fosters exploration. As users interact with the filters, the system learns their preferences and subtly suggests relevant content. This refined suggestion engine, integrated with the filters, promotes a more intuitive and engaging discovery process, potentially leading to new musical discoveries and a deeper connection with the platform.
Addressing User Pain Points in Music Discovery
One significant user pain point is the difficulty in finding music that aligns with their current mood or emotional state. Dynamic filters, adapting to real-time user input, directly tackle this problem by allowing users to narrow their search criteria in a manner that reflects their current feelings. This targeted approach makes the discovery process more relevant and rewarding.
Improved User Satisfaction Through Dynamic Filtering
The ability to precisely target desired music translates to a more satisfying user experience. By allowing users to filter music based on a wide range of criteria, Spotify enhances user control over their music library. This control leads to increased user satisfaction and promotes a sense of ownership and customization.
Successful Filter Implementations in Other Applications
Several applications have successfully implemented filters to enhance user experience. For instance, e-commerce platforms use filters to allow users to narrow down their product searches based on price, size, color, and other criteria. Similarly, social media platforms use filters to curate content based on user interests and connections. These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of filters in improving user satisfaction and engagement.
Comparison of User Experience Before and After Dynamic Filters
| Aspect | Before Dynamic Filters | After Dynamic Filters |
|---|---|---|
| Search Time | Often lengthy, requiring multiple steps | Rapid and precise, focusing on user preferences |
| Music Discovery | Limited to pre-set categories or searches | Adaptive and personalized, promoting serendipitous discoveries |
| User Engagement | Passive listening with limited interaction | Active exploration and discovery, tailored to user needs |
| User Satisfaction | Potentially frustrating due to limited control | Increased control and satisfaction due to personalized filtering |
Technical Aspects of Dynamic Filtering
Spotify’s dynamic filtering system, crucial for a seamless user experience, relies on sophisticated technical underpinnings. This system enables users to quickly and intuitively discover music based on a wide range of criteria, from artist genre to mood and even time of day. The complexity of these filters hides a powerful engine of data processing, algorithms, and data structures working in concert.The implementation of dynamic filters involves a multi-faceted approach, combining various technical components and sophisticated algorithms to provide a rich and responsive user experience.
This requires careful consideration of data structures and algorithms to ensure efficiency and scalability, as the amount of data Spotify handles is vast.
Data Structures for Filtering
Implementing dynamic filtering in a large-scale application like Spotify necessitates the use of efficient data structures. One critical structure is a highly optimized inverted index. This index maps s (like song titles, artist names, genres, and moods) to the corresponding song IDs. This allows for rapid retrieval of songs matching the user’s search criteria. Further, a tree-based structure, such as a B-tree, might be employed to organize the songs themselves, providing quick access to specific metadata.
Algorithms for Filtering
The filtering process relies on various algorithms to evaluate and categorize songs based on user preferences. One key algorithm is fuzzy matching. This enables users to find songs even when their search terms aren’t precise matches. Another algorithm, collaborative filtering, identifies songs that are popular among users with similar tastes, a crucial element in Spotify’s recommendation engine.
Data Processing for Filter Options
Generating dynamic filter options requires processing vast amounts of data. This includes user listening history, song metadata, and artist profiles. A critical step involves extracting relevant features from this data. For instance, natural language processing (NLP) techniques might be used to categorize songs by genre or mood. Furthermore, data mining techniques may uncover patterns and relationships in user listening habits to anticipate user preferences.
Performance Considerations, Spotify your library ui update dynamic filters
Dynamic filters must be implemented with performance in mind. As Spotify’s user base grows and its library expands, the system must maintain responsiveness. Caching frequently accessed data can significantly improve performance. Furthermore, utilizing distributed computing can handle the large dataset load more efficiently.
Examples of Filtering in Similar Applications
Several applications use similar filtering techniques. For example, e-commerce platforms utilize search algorithms and filters to display relevant products. Similarly, social media platforms leverage filtering mechanisms to present users with content tailored to their interests.
Data Flow for Dynamic Filter Generation
| Step | Description | Data Structures/Algorithms |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Data Ingestion | Collecting user listening history, song metadata, and artist profiles. | Databases, data pipelines |
| 2. Feature Extraction | Deriving relevant features (e.g., genre, mood) from song metadata. | Natural Language Processing (NLP), data mining |
| 3. Indexing | Creating an inverted index to quickly retrieve songs based on search criteria. | Inverted index, hash tables |
| 4. Filtering | Applying algorithms (e.g., fuzzy matching, collaborative filtering) to generate dynamic filters. | Fuzzy matching, collaborative filtering |
| 5. Presentation | Displaying filter options to the user. | UI framework |
Comparison with Other Music Platforms
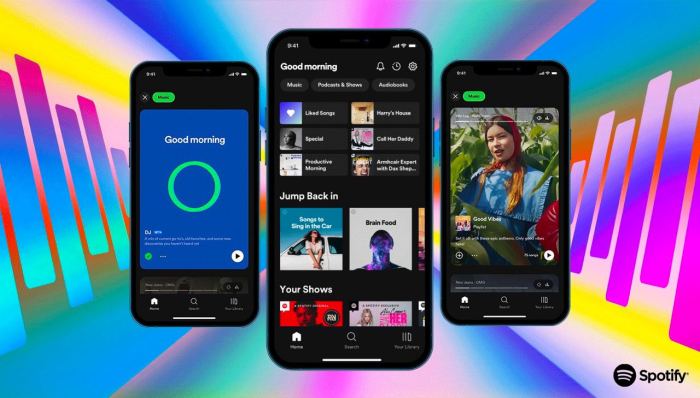
Spotify’s dynamic filtering in its library update represents a significant step forward in user experience. However, understanding its strengths and weaknesses requires a comparative analysis with other music platforms. This comparison will reveal how Spotify’s approach stacks up against existing solutions and potential areas for future innovation.The music streaming landscape is highly competitive, with various platforms vying for user attention.
Differing approaches to filtering and discovery mechanisms are crucial to a platform’s success. Comparing Spotify’s dynamic filters with those of its competitors allows us to identify best practices and potential areas where Spotify can refine its user interface and overall experience.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
A crucial aspect of evaluating Spotify’s dynamic filtering is understanding the approaches taken by its competitors. Different platforms have different strengths and weaknesses in their filtering methods, often reflecting their core target audiences and functionalities. Understanding these differences helps us assess the originality and potential impact of Spotify’s new dynamic filters.
Alternative Filtering Methods
Various music platforms utilize diverse filtering strategies. Apple Music, for example, heavily emphasizes curated playlists and artist-specific radio stations. These pre-defined categories offer a different approach to discovery compared to Spotify’s dynamic filtering, which is based on user interaction and evolving preferences. Other platforms might focus on collaborative filtering, suggesting songs based on friends’ listening habits, while others rely on explicit genre tags or s.
These diverse approaches showcase the variety in music platform design and the need to adapt filtering to individual user behaviors.
Key Differentiators
Spotify’s dynamic filtering, based on personalized algorithms and user interaction, is a key differentiator. This approach contrasts with competitors who might rely more heavily on pre-defined categories or collaborative filtering. A key differentiator lies in Spotify’s ability to adapt its recommendations in real-time, whereas other platforms might not provide this degree of responsiveness.
Comparison Table
| Platform | Filtering Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spotify | Dynamic, personalized filters based on user interaction and algorithms | Highly personalized, adaptable to user tastes, real-time adjustments | Complexity in algorithm, potential for “filter fatigue” if not managed effectively |
| Apple Music | Curated playlists, artist-specific radio stations | Pre-defined and structured approach, familiar experience | Less personalized than dynamic filters, might not adapt to evolving tastes as quickly |
| YouTube Music | Genre-based filtering, trending tracks, collaborative playlists | Clear categorization, discoverability based on popular trends | Might not provide a deep level of personalization as Spotify |
| Amazon Music | Genre tags, s, user reviews, curated stations | Wide range of search options, user-generated content considerations | Could lack the depth of personalization and dynamic adaptation of Spotify’s approach |
Potential for Innovation
Analyzing competitor practices reveals opportunities for Spotify to further enhance its dynamic filtering. For instance, incorporating collaborative filtering elements could provide richer insights into user preferences and create a more social listening experience. Combining pre-defined categories with dynamic filtering could offer a more accessible and user-friendly experience for new users.
Spotify’s new library UI update with dynamic filters is pretty cool, isn’t it? It’s definitely a step up from the old system. While I’m enjoying the improved searching, it makes me think about the ongoing controversies surrounding other tech giants, like the recent spacex elon musk sexual harassment lawsuit , which highlights the importance of ethical considerations in tech development.
Ultimately, I’m still really excited about the enhanced functionality of the Spotify library update.
Future Possibilities for Dynamic Filters
Spotify’s dynamic filters, a significant advancement in user experience, offer a glimpse into a future where music discovery is more personalized and intuitive. The current implementation demonstrates a powerful foundation for further development, allowing for deeper integration with existing features and expanding the scope of what’s possible. The potential for personalized listening experiences, tailored to specific moods or activities, is vast.
Potential Integrations with Other Spotify Features
Spotify’s ecosystem is rich with features, and dynamic filters can enhance many of them. Integration with the existing “Mood” feature, for example, could enable filters based on not just predefined moods, but also on dynamically detected emotional cues in a user’s listening history. This could lead to filters that adapt to a user’s current emotional state, suggesting music that complements their mood in real-time.
Similarly, filters based on user activity, such as exercise routines or work sessions, could suggest playlists or albums optimized for those specific tasks.
Innovative Use Cases for Dynamic Filters
Dynamic filters could also be instrumental in creating new listening experiences. Imagine filters that dynamically adjust based on the time of day, location, or even social context. For example, a user might have a filter that automatically suggests relaxing music for bedtime, or energetic tunes for a morning workout, all based on the current time and location. Filters based on social connections, such as discovering music popular among friends, or music often played during group events, could also be implemented.
Furthermore, the incorporation of user-generated tags and descriptions could create filters that respond to the specific nuances of individual music preferences.
Potential Areas for Improvement and Expansion
While dynamic filters have the potential to revolutionize music discovery, several areas warrant further development. Improving the algorithm’s ability to predict and adapt to user preferences in real-time is crucial. The system should also be designed to learn from user interactions with the filters, making future recommendations even more precise. Addressing potential biases in the algorithm’s data is also paramount to ensure a fair and unbiased music discovery experience.
Additionally, making the filter parameters more granular, allowing users to fine-tune their preferences, would further enhance personalization.
Spotify’s recent library UI update with dynamic filters is pretty cool, making it easier to find specific music. It’s fascinating how these updates in user interface design mirror the trends in other creative fields, like the defacement of Starman NFTs by artists inspired by Jim Henson and Shigeru Miyamoto. This creative reimagining of iconic figures in the digital space, explored in detail in this piece on defaced starman nft artist jim henson shigeru miyamoto crypto art starmaker , suggests a deeper connection between art, technology, and user experience, even impacting how we navigate our own music libraries.
Ultimately, it highlights how these design decisions in both Spotify and the NFT world are shaping how we engage with content.
Long-Term Implications for Music Discovery
The long-term implications of dynamic filtering are significant. It promises a future where music discovery is more personalized, efficient, and intuitive. Users will be able to find music that precisely matches their current mood, activity, or social context, leading to a richer and more fulfilling listening experience. This level of personalization could potentially redefine how users interact with music platforms, fostering deeper engagement and a more intimate relationship with their favorite genres and artists.
Table of Potential Future Integrations and Enhancements
| Feature | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Mood Filters | Filters adapt to real-time emotional cues from listening history. | Enhanced personalization, more relevant recommendations. |
| Activity-Based Filters | Filters adjust based on user activity (e.g., exercise, work). | Improved listening experience for specific tasks. |
| Social Context Filters | Filters suggest music based on social connections or group events. | Enhanced social listening experience, discover music with friends. |
| User-Generated Tag Filters | Filters utilize user-generated tags for greater personalization. | More nuanced and specific recommendations. |
| Time-of-Day Filters | Filters automatically adjust based on the time of day. | Improved contextual music discovery. |
Accessibility and Inclusivity Considerations
Spotify’s dynamic filtering system, while offering enhanced user experience, must prioritize accessibility and inclusivity. Ignoring these aspects can inadvertently exclude users with disabilities or diverse needs, diminishing the platform’s overall value and potential. A well-designed system caters to a wider audience, ensuring equitable access to the features and benefits.
Importance of Equitable Access
Dynamic filters, by their nature, are designed to streamline content discovery. However, if these filters aren’t accessible, they can become a barrier for users with disabilities. Ensuring equitable access means that everyone can utilize the filters to find music that resonates with their preferences, regardless of their abilities. This approach not only enhances user experience but also reflects a commitment to inclusivity.
Accommodating Diverse User Needs
Designing for diverse needs requires a nuanced approach. Users with visual impairments may require alternative text descriptions for filter options, while users with auditory processing differences might need adjustable audio cues. Considering cognitive differences is also vital, with clear and concise filter descriptions. Accessibility is not just about functionality; it’s about user-friendliness and ease of navigation for all.
Inclusive Design Considerations for Filtering Systems
Several key aspects should be considered for an inclusive filtering system:
- Alternative Text for Visual Elements: All visual elements within the filter interface should have comprehensive alternative text descriptions, providing context and meaning for screen reader users. For example, a filter option labeled “Pop Music” should have alternative text that clarifies the musical genre. This detail is crucial for accessibility and understanding.
- Adjustable Audio Cues: Provide adjustable audio cues or visual indicators for filter selections. This allows users with hearing impairments or sensory processing differences to understand filter actions. Think of visual highlighting, along with distinct audio cues, for filter selection.
- Clear and Concise Language: Employ clear, concise, and straightforward language in filter descriptions. Avoid jargon or complex terminology. Consider using simple and universally understandable language to enhance comprehension for all users.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure all filter functions are navigable using only a keyboard. This accommodates users who may not be able to use a mouse or trackpad. The entire filtering process should be entirely keyboard-driven, including selecting and adjusting filters.
Examples of Inclusive Design Considerations
Consider a filter for “Mood.” Instead of using abstract terms like “upbeat,” provide concrete options like “energetic,” “happy,” or “focused.” This makes the filter more accessible to a wider range of users, particularly those with cognitive differences. Similarly, a filter for “Artist” should allow for searches and phonetic searches, facilitating discovery for users with different access methods.
Suggestions for Making Dynamic Filters More Accessible
Implementing these suggestions will contribute to making dynamic filters more accessible for all users:
- User Testing with Diverse Groups: Conduct thorough user testing with individuals from diverse backgrounds and abilities. This iterative feedback is essential to identify and address any usability issues that may emerge. A diverse user group ensures that the filter system effectively caters to the widest possible range of needs.
- Accessibility Audits: Regularly perform accessibility audits on the filter interface to identify and fix any potential barriers. These audits can be automated or manual, ensuring that the system adheres to accessibility guidelines.
- Accessibility Guidelines Compliance: Adhere to industry-standard accessibility guidelines (e.g., WCAG) throughout the design and development process. This adherence ensures compliance and improves the overall accessibility of the filter system.
Accessibility Options for Users with Disabilities
| Disability | Accessibility Option | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Impairment | Screen reader compatibility | Alternative text for images, keyboard navigation, adjustable font sizes. |
| Auditory Impairment | Adjustable audio cues, visual indicators | Visual highlighting for filter selections, distinct audio cues for filter actions. |
| Cognitive Impairment | Clear and concise language, simplified interface | Concrete options for abstract terms, avoiding jargon, clear and concise filter descriptions. |
| Motor Impairment | Keyboard navigation, alternative input methods | Keyboard-only navigation for filter selection and adjustments. |
Last Word
In conclusion, Spotify’s library UI update with dynamic filters presents a compelling evolution in music discovery. The implementation of dynamic filters promises a more personalized and efficient experience, potentially revolutionizing how users interact with their music collections. The future of music discovery seems to be in the hands of sophisticated algorithms and tailored filtering options, and Spotify appears to be at the forefront of this exciting evolution.
We’ve explored the potential benefits, technical aspects, and potential pitfalls of this new feature. The impact on user experience and future developments will be crucial to watch.