Pan os ha clustering – PAN-OS HA clustering provides a robust and reliable solution for network security. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the intricacies of PAN-OS HA clustering, exploring its fundamental concepts, components, implementation, and security considerations. We’ll examine how it handles failovers, scales to different network environments, and ensures business continuity. Get ready to understand the power and flexibility of this vital network security feature.
From defining high availability and active/passive configurations to troubleshooting common issues, this guide walks you through every step. We’ll also explore the hardware and software requirements, best practices, and use cases for a secure and scalable PAN-OS HA cluster deployment.
Introduction to PAN-OS HA Clustering
PAN-OS High Availability (HA) clustering is a crucial feature for enhancing the resilience and performance of your Palo Alto Networks firewall deployments. It provides a redundant and fault-tolerant infrastructure, ensuring uninterrupted network operations even if one firewall in the cluster experiences a failure. This robust system minimizes downtime and maximizes network availability.HA clustering leverages the power of multiple firewalls working together, offering a high degree of protection against hardware failures, software glitches, and other unforeseen circumstances.
This collaborative approach guarantees seamless network traffic handling, ensuring critical business functions remain operational at all times.
Fundamental Concepts
PAN-OS HA clustering relies on fundamental concepts that contribute to its robust and reliable nature. Redundancy is paramount, with multiple firewalls acting as backups for each other. Failover mechanisms ensure a seamless transition to the backup firewall if a primary firewall fails. This seamless transition minimizes downtime and ensures continuous network operation. Active/passive configurations are employed where one firewall actively handles traffic while the other passively monitors and prepares to take over.
This arrangement maximizes performance and availability.
Benefits of Deploying PAN-OS HA Clustering
Implementing PAN-OS HA clustering yields significant benefits for network environments. Reduced downtime is a primary advantage, minimizing the impact of unexpected hardware or software issues. Enhanced network availability ensures continuous operation, preventing service disruptions and maintaining business continuity. Improved performance is also realized, as traffic can be distributed across multiple firewalls, leading to faster processing speeds and enhanced responsiveness.
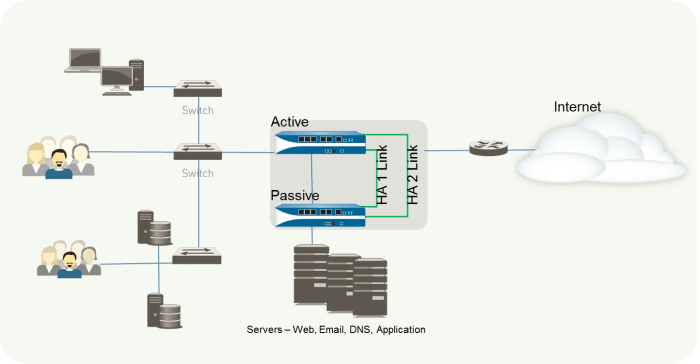
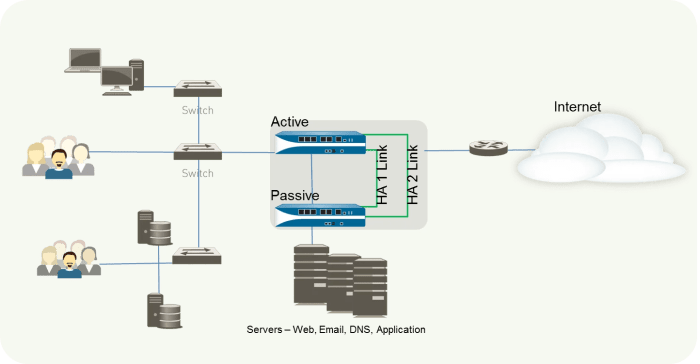
Network Diagram of a PAN-OS HA Cluster
A simplified network diagram illustrates the basic structure of a PAN-OS HA cluster.
Internet
|
|
+---+---+
| | |
| Firewall A (Active) |
| | |
+---+---+ +---+---+
| |
| |
+---+---+ +---+---+
| | | | | |
| Firewall B (Passive) |
| | |
+---+---+
|
|
+---+---+
| | |
| Network |
| Devices |
| | |
+---+---+
In this diagram, Firewall A is actively processing network traffic, while Firewall B is in a standby mode, monitoring and preparing to take over if necessary.
The network devices represent the computers, servers, and other devices connected to the firewall cluster. The arrows depict the flow of data through the network. This simple diagram showcases the basic architecture of a PAN-OS HA cluster.
Components of a PAN-OS HA Cluster: Pan Os Ha Clustering
High Availability (HA) in Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted network security. A well-designed HA cluster ensures continuous operation even if one device fails, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency. This robust architecture is built upon several key components, each playing a specific role in the cluster’s functionality.
Understanding these components is essential for configuring and managing a PAN-OS HA deployment effectively. The correct configuration of hardware and software, coupled with an appropriate understanding of the components’ roles, is paramount for successful HA implementation.
Key Components
The core components of a PAN-OS HA cluster are the physical devices and the software that governs their interaction. These components work in concert to provide high availability and resilience. The two primary devices are the primary and secondary units, with the primary unit handling active operations.
- Primary Unit: The primary unit acts as the active controller, handling all traffic and security policies. It is responsible for all network management tasks, such as policy enforcement, device configuration, and user authentication.
- Secondary Unit: The secondary unit acts as a standby unit. It continuously monitors the primary unit and is prepared to take over immediately in case of a failure. The secondary unit maintains a synchronized copy of the primary unit’s configuration and state data, ensuring a smooth failover process.
Hardware Requirements
The hardware requirements for a PAN-OS HA cluster depend on the scale and complexity of the network being protected. Factors such as the number of users, the volume of network traffic, and the security policies being implemented all influence the hardware selection. Generally, both units should be identical to ensure seamless operation.
- Identical Hardware: For optimal HA performance, both the primary and secondary units should be identical in terms of hardware specifications. This ensures consistency in processing capabilities and minimizes potential conflicts during failover.
- Sufficient Resources: The hardware should possess sufficient processing power, memory, and storage capacity to handle the anticipated workload. Underestimating these needs can lead to performance bottlenecks and instability.
- Redundant Power Supplies: Redundant power supplies are crucial for ensuring uninterrupted operation. This minimizes the risk of downtime due to power failures.
- Network Connectivity: Reliable network connectivity between the units is essential for communication and synchronization. High-bandwidth connections are recommended to prevent performance bottlenecks during failover.
Software Requirements
PAN-OS software manages the cluster’s functionality. Specific versions are required for compatibility and optimal performance.
- Compatible PAN-OS Version: Both units must run the same PAN-OS version to guarantee compatibility. Upgrading the software on the primary unit will typically require a similar upgrade on the secondary unit to avoid potential conflicts and ensure a smooth transition.
- Licensing Considerations: The licensing model for the PAN-OS software must support the HA cluster configuration. Ensure that the license allows for the HA functionality.
Configuration Options
PAN-OS HA clusters can be configured in various ways to meet specific needs. Different configurations can offer different levels of redundancy and performance.
- Two-Unit Cluster: The standard configuration consists of two units, offering a basic level of HA protection. This is a common choice for smaller networks where the added cost of additional units is not a major concern.
- Multi-Unit Clusters: For larger networks with high traffic demands, multi-unit clusters can be deployed. These provide additional redundancy and resilience in the event of multiple unit failures.
Implementation and Configuration of a PAN-OS HA Cluster
Setting up a high-availability (HA) cluster for Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS security appliances ensures continuous operation and enhanced resilience against failures. Proper implementation and configuration are crucial for realizing the full benefits of this feature. This involves careful consideration of network topology, device specifications, and configuration parameters.
The process of implementing a PAN-OS HA cluster involves several key steps, including selecting appropriate hardware, configuring the network infrastructure, and setting up the cluster itself. Each step requires careful attention to detail to ensure a stable and reliable deployment. Crucially, understanding the configuration parameters for each component within the cluster is vital for optimal performance and fault tolerance.
Hardware Requirements and Network Considerations
For a robust HA cluster, ensure the participating devices meet the minimum hardware specifications Artikeld in the PAN-OS documentation. Compatibility is critical. Consider factors such as CPU, memory, and storage capacity to support the anticipated traffic load. Proper network connectivity is fundamental. The devices within the cluster must be able to communicate with each other over a dedicated, high-bandwidth network link.
Use dedicated network interfaces for HA communication to isolate this traffic from other network traffic.
Configuring the PAN-OS HA Cluster
Configuring the PAN-OS HA cluster involves several steps. First, the participating firewalls need to be identified and assigned roles (e.g., primary and secondary). This involves specifying the IP addresses and network interfaces of the firewalls. Next, the devices are configured for communication using a private, dedicated network link. This network should be configured with sufficient bandwidth to handle the HA traffic without impacting regular network operations.
Configuration Parameters for Each Component
Several parameters need to be configured for each firewall in the HA cluster. These parameters include the following:
- Virtual IP Address (VIP): The VIP is a single IP address that represents the HA cluster to the outside world. This address is essential for external communication. The VIP should be assigned to an interface on each firewall.
- HA Interface: This interface is specifically dedicated to HA communication between the firewalls. Ensure this interface is configured with a static IP address, assigned to a dedicated network. It’s vital for reliable communication between the primary and secondary devices.
- Synchronization Interval: This parameter defines how often the firewalls synchronize their configurations. A shorter interval ensures faster recovery in case of failure but might increase network traffic. A longer interval reduces network traffic but may increase recovery time. Choose a balance based on the network bandwidth and the desired level of synchronization.
- Clustering Authentication: Secure the communication between the firewalls by using a strong password for authentication. This ensures that only authorized devices can join the cluster.
Proper configuration of these parameters is essential for ensuring the HA cluster functions correctly and efficiently. Careful consideration of the synchronization interval, network bandwidth, and security measures is important for a stable cluster.
Verification of HA Cluster Functionality
Validating the functionality of the HA cluster is crucial after configuration. This involves a series of steps to verify that the cluster is operating correctly.
- Ping the VIP: Verify that the VIP responds to ping requests from external devices. This confirms that the cluster is reachable and responding correctly.
- Verify Device Responsiveness: Attempt to connect to services hosted on the firewalls using the VIP. This confirms that the cluster is providing the expected services.
- Simulate Failure: Intentionally take one of the firewalls offline. Monitor the behavior of the cluster to ensure the remaining device takes over and the services remain available. This simulates a failure scenario.
- Monitor Logs: Review the logs on both devices to ensure no errors are reported. This helps identify any potential issues that may arise.
Thorough verification is essential to ensure a robust and reliable HA cluster. Regular monitoring and testing will ensure the cluster operates as expected.
Failover and Recovery Procedures
PAN-OS High Availability (HA) clustering is designed to ensure continuous operation even in the event of a failure in one of the cluster members. This robust architecture automatically transitions to the remaining device, minimizing downtime and maintaining service continuity. Understanding the failover mechanisms and recovery procedures is crucial for effectively managing a PAN-OS HA cluster.
The PAN-OS HA cluster dynamically monitors the health of both devices. If one device experiences a critical failure, the remaining device seamlessly takes over all functions, ensuring uninterrupted network security. This automatic failover is a key advantage of the HA architecture, providing high availability and resilience against failures.
Failover Scenarios
Failover in a PAN-OS HA cluster occurs when one device experiences a critical issue, such as a hardware malfunction, software corruption, or network connectivity loss. The remaining device is immediately designated as the active unit, assuming all security functions. This process is transparent to end-users, ensuring minimal disruption to network traffic.
Recovery Procedures
The recovery process in a PAN-OS HA cluster involves restoring the failed device to operational status. This process typically includes verifying the hardware integrity, reinstalling the PAN-OS software, and synchronizing configuration with the active device. Once the failed device is operational and healthy, it can be integrated back into the cluster.
Monitoring the HA Cluster Health
Monitoring the health of a PAN-OS HA cluster is essential for proactive management. The system continuously checks for critical issues, such as device failures or performance degradation. Tools like the PAN-OS management interface provide real-time information on the health of each device and the overall cluster.
Role of Logs and Alerts, Pan os ha clustering
Detailed logs and alerts are vital for understanding and addressing issues in the HA cluster. These logs capture events, errors, and warnings, providing valuable insights into the performance and stability of the cluster. Alerts, triggered by specific events, immediately notify administrators of potential problems, allowing for swift intervention and resolution. Regularly reviewing logs and alerts is critical for maintaining the health and stability of the PAN-OS HA cluster.
Alerting mechanisms provide a rapid response to potential failures and support efficient problem-solving. For example, an alert triggered by a high CPU utilization rate on one of the devices allows administrators to investigate the cause and implement corrective actions.
Security Considerations in PAN-OS HA Clustering
High availability (HA) clustering in Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS enhances system resilience and uptime, but it introduces new security considerations. Proper configuration and ongoing vigilance are crucial to maintain the integrity and security of the clustered environment. These security considerations are essential to mitigating potential risks and ensuring the continued safety of the network resources managed by the PAN-OS cluster.
Pan OS HA clustering is all about high availability and redundancy, ensuring your network keeps running smoothly. This resilience mirrors the sophisticated strategies used in AI, like those employed by DeepMind’s AI in chess, shogi, and Go, particularly in the area of deepmind ai chess alphazero shogi go. Ultimately, both aim for optimal performance and fault tolerance, just on very different scales.
Understanding these parallels can lead to more robust and efficient network designs.
Implementing HA clustering requires careful planning and execution to maintain security throughout the lifecycle of the system. This includes choosing the right components, configuring them securely, and understanding the implications of failover and recovery procedures. Security vulnerabilities can be introduced if these aspects are not carefully addressed. Understanding the potential risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies are key to maintaining a secure HA cluster.
Security Implications of HA Clustering
The interconnected nature of HA clusters introduces new security vectors. If a compromised node in the cluster gains access to shared resources, it could potentially compromise the entire system. Data breaches and unauthorized access to critical network resources are serious risks. Ensuring secure communication channels between nodes and implementing robust authentication mechanisms are essential to mitigating these risks.
Security Best Practices for PAN-OS HA
Maintaining a secure PAN-OS HA environment requires a multi-faceted approach. Regular security audits, proactive vulnerability scanning, and continuous monitoring of system logs are crucial.
- Secure Communication Channels: Encrypting communication between the nodes is paramount. Utilize strong encryption protocols to protect data exchanged between the cluster members. This prevents unauthorized access and eavesdropping on critical communication paths.
- Robust Authentication: Implement strong authentication mechanisms for user accounts and system access. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be enforced for all critical accounts to add another layer of security. Regularly review and update account privileges to limit the potential impact of compromised accounts.
- Network Segmentation: Segment the network to isolate the HA cluster from other parts of the network. This minimizes the impact of a potential breach to the rest of the network. Properly configure firewalls to control traffic flow and restrict access to the cluster from untrusted sources.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and remediate vulnerabilities. This includes assessing the effectiveness of the implemented security controls and looking for potential weaknesses. Use penetration testing to evaluate the security posture of the HA cluster.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor the system logs and security alerts for any suspicious activity. This enables quick detection and response to security incidents. Implement a robust security information and event management (SIEM) system to analyze logs and identify potential threats.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Several potential vulnerabilities can emerge in a PAN-OS HA cluster. Properly addressing these vulnerabilities is essential to maintaining a secure environment.
- Node Compromise: A compromised node can potentially expose sensitive data and grant unauthorized access to the entire cluster. Implement robust security controls on each node to minimize the risk of compromise. Employ regular patching and updates to address known vulnerabilities.
- Shared Resource Attacks: If shared resources are not properly secured, they can be exploited by attackers. Ensure that access to shared resources is controlled and restricted to authorized personnel only. Use access control lists (ACLs) and other security mechanisms to limit access to sensitive data.
- Misconfigurations: Improper configurations of HA components can introduce security vulnerabilities. Thoroughly review and validate all configurations to ensure compliance with security best practices. Consult PAN-OS documentation for recommended configurations.
- Network Attacks: The cluster’s network interface(s) can be vulnerable to various network attacks. Configure robust network security measures such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to detect and mitigate network attacks. Use strong network segmentation to limit the impact of a potential compromise.
Secure Configurations for HA Clusters
Implementing secure configurations is crucial for a robust HA environment. The following examples demonstrate secure configurations for PAN-OS HA clusters.
- Firewall Policies: Implement strict firewall policies to control access to the cluster from outside and between the cluster members. This limits potential points of entry for attackers. Use granular access controls based on roles and responsibilities.
- User Access Controls: Restrict access to the cluster to authorized users only. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign appropriate privileges. Implement MFA for all critical accounts.
- Regular Backups: Regular backups of the cluster’s configuration and data are essential for disaster recovery. This allows for quick recovery in case of data loss or system failure.
High Availability (HA) Clustering in Different Network Environments
High Availability (HA) clustering is a crucial aspect of network security, enabling organizations to maintain continuous operation even in the face of hardware or software failures. Understanding how HA clustering adapts to various network environments is essential for selecting the appropriate configuration. This section explores the adaptability of PAN-OS HA clustering across diverse network topologies.
PAN-OS HA clustering is designed to provide fault tolerance and high availability, distributing workload and ensuring uninterrupted network access. Its scalability allows organizations to tailor the clustering solution to their specific needs, from small offices to large enterprises. The effectiveness of HA clustering depends on a suitable design that addresses the unique characteristics of the network environment.
Comparing HA Clustering in Different Network Topologies
Different network topologies present unique challenges and opportunities for HA clustering implementation. A small office network, for example, might require a simpler configuration than a large enterprise network. The key considerations include the number of devices, the volume of traffic, and the criticality of applications running on the network.
PAN-OS HA Cluster Scalability
The scalability of a PAN-OS HA cluster directly impacts its ability to handle the demands of different network environments. The table below provides a general guideline for the appropriate HA cluster size based on network characteristics. It is crucial to consider the specific needs of each network environment and to consult with network specialists to ensure optimal configuration.
| Network Topology | Number of devices | Number of users | HA Cluster Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small office | 1-5 | 50-100 | 2-3 |
| Mid-sized company | 5-15 | 100-500 | 3-5 |
| Large enterprise | >15 | >500 | 5+ |
Impact of Network Traffic on HA Clustering
The volume of network traffic significantly influences the optimal HA cluster size. High traffic loads necessitate more powerful and resilient clustering configurations. A large enterprise network with thousands of users and substantial data exchange will require a larger HA cluster to handle the increased processing demands.
Factors Affecting HA Cluster Configuration
Several factors influence the optimal HA cluster configuration. The types of applications running on the network, the criticality of network services, and the availability requirements all play a role. For instance, a financial institution with critical transactions will likely demand a higher level of availability and a more robust HA cluster than a small business.
Security Considerations in Different Environments
Security considerations are paramount in all network environments, but they become even more critical when deploying HA clustering. The shared resources and increased attack surface must be addressed effectively. Implementing robust security measures at the cluster level, including access controls and regular security audits, is essential.
Performance and Scalability
PAN-OS HA clusters are designed for high availability, but their performance and scalability are equally critical considerations. A well-configured cluster can handle a significant volume of traffic while maintaining low latency. Understanding the performance characteristics and scalability factors allows for informed decisions in deployment and optimization. This section delves into the metrics for evaluating performance, factors influencing scalability, and strategies for optimizing PAN-OS HA cluster performance.
Performance Characteristics of PAN-OS HA Clusters
PAN-OS HA clusters leverage the power of two or more firewalls working together to provide redundancy and increased throughput. This collaborative approach distributes processing tasks across the cluster members, resulting in improved overall performance compared to a single firewall. Key performance characteristics include faster processing speeds for security policies, increased throughput for network traffic, and reduced latency in response times.
The degree of improvement depends on the specific workload and the configuration of the cluster.
Metrics for Evaluating PAN-OS HA Cluster Performance
Several metrics are crucial for evaluating the performance of a PAN-OS HA cluster. These metrics provide insights into the health and efficiency of the system. Key metrics include:
- Throughput: This measures the volume of network traffic processed by the cluster per unit of time (e.g., Mbps). High throughput indicates efficient handling of network traffic, while low throughput suggests potential bottlenecks.
- Latency: This measures the time taken for a packet to traverse the cluster. Low latency ensures minimal delays in network communication, critical for applications requiring quick responses.
- CPU Utilization: This represents the percentage of CPU resources utilized by the cluster. High CPU utilization indicates potential resource constraints and may necessitate adjustments to the configuration or hardware.
- Memory Usage: Similar to CPU utilization, this metric tracks the percentage of memory utilized by the cluster. High memory usage can lead to performance degradation and should be monitored.
- Policy Processing Time: This metric measures the time taken for the cluster to process security policies. High processing times indicate potential bottlenecks and require investigation into the policy configuration or the cluster’s capacity.
Factors Influencing Scalability of PAN-OS HA Clusters
Several factors influence the scalability of PAN-OS HA clusters, impacting their ability to handle increasing network traffic and security demands.
Pan-OS HA clustering is all about high availability, ensuring your network keeps running smoothly. It’s a fascinating technology, but honestly, sometimes I find myself thinking about the latest Nintendo Switch indie world showcase, specifically the Axiom Verge 2 Boyfriend Dungeon game. This showcase is pretty cool, and it reminds me that even complex network configurations can be pretty engaging.
Back to Pan-OS HA clustering, the reliable redundancy and seamless failover are truly impressive features.
- Hardware Resources: The processing power, memory, and network interface cards (NICs) of the firewall devices in the cluster directly affect the scalability. More powerful hardware allows for greater throughput and handling of a larger volume of traffic.
- Number of Cluster Members: Adding more firewalls to the cluster increases the processing capacity and can significantly enhance scalability. However, optimal performance is achieved when the cluster size is appropriately matched to the workload.
- Network Infrastructure: The bandwidth and stability of the network connecting the cluster members influence the efficiency of data exchange between them. Adequate network bandwidth is essential for high performance.
- Security Policies: Complex security policies that involve many rules or deep packet inspection can impact the processing load on the cluster. Simplified policies reduce the processing time and enhance scalability.
- Number of Concurrent Connections: A high number of concurrent connections can strain the cluster’s resources, potentially impacting performance and scalability.
Optimizing Performance in a PAN-OS HA Cluster
Several strategies can optimize the performance of a PAN-OS HA cluster, ensuring efficient handling of increasing network traffic.
- Monitoring and Tuning: Regular monitoring of key performance metrics is crucial for identifying potential bottlenecks. Tuning security policies and configurations to reduce processing load can significantly improve performance.
- Hardware Upgrades: Upgrading the hardware resources of the cluster members, such as adding more RAM or faster CPUs, can significantly enhance the cluster’s capacity to handle increasing traffic loads.
- Policy Optimization: Refining security policies to eliminate unnecessary rules or improve their efficiency can free up resources and enhance performance. Using advanced techniques like traffic shaping can prioritize and streamline network traffic processing.
- Network Optimization: Ensuring sufficient network bandwidth and stability between cluster members is essential. Addressing network bottlenecks can improve the efficiency of data exchange.
- Cluster Size Optimization: Carefully consider the appropriate number of firewalls in the cluster based on the expected workload. Over-provisioning can lead to wasted resources, while under-provisioning can result in performance bottlenecks.
Management and Monitoring of PAN-OS HA Clusters
Managing a high-availability (HA) PAN-OS cluster requires dedicated tools and techniques to ensure optimal performance and security. Effective management encompasses not only the initial configuration but also ongoing monitoring, logging, and troubleshooting. This crucial aspect allows administrators to maintain a resilient and efficient security infrastructure.
Tools and Techniques for Management
The primary tool for managing PAN-OS HA clusters is the Panorama management console. This centralized platform provides a comprehensive view of the entire security infrastructure, including all firewalls in the cluster. Beyond the Panorama console, various command-line interfaces (CLIs) and scripting capabilities are available for advanced configurations and automation. These tools allow administrators to perform tasks like configuring policies, managing users, and monitoring system logs efficiently.
Sophisticated tools are vital for ensuring that the PAN-OS HA cluster remains stable and secure.
Monitoring Cluster Health and Performance
Monitoring the health and performance of a PAN-OS HA cluster is critical for proactive issue resolution. Real-time dashboards within the Panorama console provide a visual representation of key metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network throughput for each firewall device. These metrics provide valuable insights into the overall health of the cluster. Regular monitoring enables identification of potential bottlenecks and performance degradation before they escalate into significant problems.
These monitoring capabilities enable rapid response to potential issues, enhancing the overall resilience of the cluster.
Pan OS HA clustering is all about redundancy and high availability, ensuring network services keep running smoothly. This concept is crucial for reliable operations, especially in a modern networking environment. Interestingly, recent leaks about the Huawei Nova 2s, particularly its home button and thin bezels, huawei nova 2s home button thin bezels leaks china , highlight the ongoing evolution in mobile technology.
Ultimately, Pan OS HA clustering is about providing stability and resilience in network infrastructure, a similar goal to the constant innovation in mobile design.
Importance of Logging and Auditing
Comprehensive logging and auditing are essential for maintaining a secure and reliable PAN-OS HA cluster. Detailed logs capture all events and activities within the cluster, providing a historical record for troubleshooting, compliance audits, and security analysis. The logs offer a detailed account of user actions, policy changes, and security events, allowing for a thorough understanding of the cluster’s behavior.
Robust logging and auditing mechanisms are paramount for detecting anomalies and responding to security incidents promptly.
Panorama Management Console Overview
The Panorama management console is the central point of control for the entire PAN-OS HA cluster. It offers a unified view of all firewalls in the cluster, allowing administrators to manage policies, users, and configurations centrally. The console’s intuitive interface simplifies tasks such as creating and managing security policies, configuring user accounts, and monitoring device health. Advanced features such as reporting and analysis capabilities are also available to gain further insight into cluster performance and security posture.
- Centralized Management: The Panorama console provides a single pane of glass for managing all firewalls within the HA cluster, streamlining configuration and maintenance.
- Policy Management: Create, edit, and deploy security policies across all firewalls in the cluster, ensuring consistent security across the network.
- User Management: Manage user accounts, permissions, and access controls for the entire cluster, enhancing security and control.
- Reporting and Analysis: Generate reports on various aspects of the cluster’s performance, security posture, and user activity. This allows for in-depth analysis and proactive issue resolution.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in PAN-OS HA Clusters
Troubleshooting PAN-OS HA clusters is crucial for maintaining network security and performance. Effective troubleshooting requires a methodical approach, understanding potential issues, and possessing the right tools. This section details common problems and provides practical steps for resolution.
Understanding the interconnected nature of high-availability clusters is key to successful troubleshooting. A failure in one device can cascade to the other, requiring a comprehensive approach to diagnose and resolve issues.
Failover Issues
Failover issues in PAN-OS HA clusters often stem from communication problems between the devices. The primary symptom is the non-responsive state of one or both devices.
- Verify network connectivity between the two devices. Using tools like ping or traceroute can quickly determine if there are network interruptions. Ensure the configured interfaces and IP addresses are correct and functioning as expected.
- Examine the system logs on both devices for any error messages. Error messages often provide crucial clues regarding the root cause of the failure. Specific log entries can indicate issues with the HA configuration, such as mismatched licenses or faulty synchronization processes.
- Check the status of the HA cluster using the PAN-OS management interface. This interface provides an overview of the cluster’s health and identifies any discrepancies in the devices’ status. Observe if there are any alerts or warnings indicating issues.
Performance Bottlenecks
Performance issues in a PAN-OS HA cluster can manifest as slow response times, increased latency, or high CPU utilization. Identifying the bottleneck is crucial to effective resolution.
- Analyze the system resources on both devices. Monitor CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O to pinpoint any resource-intensive processes. High CPU usage on one or both devices can indicate excessive traffic, misconfigured policies, or performance-intensive applications.
- Review the firewall policies to ensure they are optimized. Redundant or overly complex rules can significantly impact performance. Identify and streamline policies to remove unnecessary rules or configurations.
- Assess the network traffic patterns. Heavy traffic volumes can overwhelm the cluster’s capacity. Analyze traffic logs and identify patterns to pinpoint potential bottlenecks. If possible, monitor network bandwidth utilization and ensure adequate bandwidth to handle the traffic load.
Security Breaches
Unauthorized access to the PAN-OS HA cluster can compromise the entire network. Security breaches are serious and require immediate investigation.
- Examine security logs for suspicious activity. Log analysis is critical in detecting unauthorized access attempts. Specific patterns in the logs can point to malicious actors or misconfigurations.
- Review access controls and user permissions. Ensure only authorized personnel have access to the HA cluster. Regularly review and update access control lists to maintain security posture.
- Implement robust security controls, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) or security information and event management (SIEM) solutions. Implementing such systems can provide proactive detection and response to security threats.
Troubleshooting Table
| Issue | Symptoms | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Failover Issues | Device not responding | Check connectivity, logs, and cluster status; review HA configuration. |
| Performance Bottlenecks | Slow response times | Analyze system resources, review policies, and assess network traffic. |
| Security Breaches | Unauthorized access | Review logs, strengthen access controls, and implement security controls. |
Use Cases for PAN-OS HA Clustering
PAN-OS High Availability (HA) clustering offers significant advantages for enhancing network security and reliability. This robust feature provides critical redundancy and failover capabilities, protecting businesses from downtime and ensuring continuous operation. By understanding the various use cases where HA clustering is beneficial, organizations can make informed decisions about implementing this technology.
Benefits of PAN-OS HA Clustering
PAN-OS HA clustering delivers numerous benefits that enhance network resilience and reliability. These features are crucial for maintaining business continuity and minimizing potential disruptions. The key benefits include:
- Enhanced Availability: HA clustering ensures continuous operation by automatically switching to the backup firewall in case of a failure, minimizing downtime. This is essential for critical applications and services that cannot tolerate any interruption.
- Improved Reliability: The redundant configuration of the PAN-OS cluster reduces the risk of single points of failure. This robust design safeguards against hardware malfunctions, software glitches, and other potential disruptions, ensuring that the network remains operational.
- Increased Security: By providing continuous protection, the HA cluster contributes to a more secure network environment. This consistent availability prevents malicious actors from exploiting any downtime.
- Simplified Management: HA clustering simplifies the management of firewall configurations and policies, allowing administrators to focus on maintaining the security posture rather than managing multiple devices.
Critical Business Continuity Scenarios
HA clustering is crucial for business continuity in numerous scenarios. Understanding these situations is essential for recognizing the value of HA clustering in maintaining essential operations.
- 24/7 Operations: For businesses with 24/7 operations, such as online retailers, financial institutions, or e-commerce platforms, network downtime can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage. HA clustering ensures that services remain uninterrupted, maintaining customer trust and operational efficiency.
- Mission-Critical Applications: For organizations with mission-critical applications, such as those handling sensitive data or supporting crucial business processes, HA clustering is vital. The uninterrupted operation of these applications is paramount to maintain productivity and operational integrity.
- Compliance Requirements: In industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as healthcare or finance, HA clustering plays a significant role in maintaining compliance by ensuring continuous availability of critical systems and data. The ability to meet uptime requirements is often crucial for compliance.
Financial Institution Use Case
A financial institution, handling high-volume transactions and sensitive customer data, requires a highly available network infrastructure. Deploying PAN-OS HA clustering is crucial to protect their network.
| Scenario | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| High-volume online transactions | Downtime can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage. | PAN-OS HA clustering ensures uninterrupted transaction processing, minimizing downtime and financial impact. |
| Data security and compliance | Breaches can lead to regulatory fines and loss of customer trust. | PAN-OS HA clustering protects against potential downtime, ensuring data security and compliance with regulatory requirements. |
| Disaster recovery | Data loss due to disasters can cripple the institution. | HA clustering allows for quick failover to the secondary cluster, ensuring business continuity and minimizing data loss. |
“By leveraging PAN-OS HA clustering, the financial institution can maintain continuous operations, protect sensitive customer data, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, safeguarding its reputation and financial stability.”
Last Word
In conclusion, PAN-OS HA clustering offers a powerful solution for enhancing network resilience and reliability. By understanding the components, implementation, failover procedures, and security considerations, you can effectively deploy and manage a high-availability cluster for your network. This guide provides a complete overview of this critical technology, ensuring a solid understanding of its capabilities and practical applications.