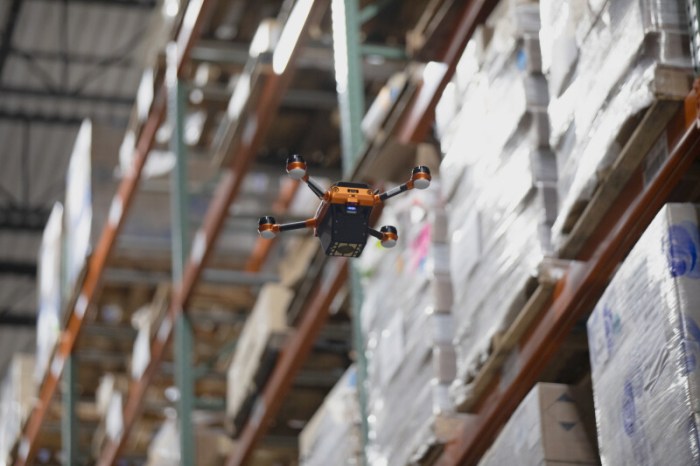
With MIT drones billion dollar problem inventory rfid tags, a revolutionary approach to inventory management is emerging. Imagine a world where warehouses aren’t just vast spaces, but meticulously tracked environments. RFID tags embedded in products, coupled with the precision of drones, offer a potential solution to the significant inventory challenges facing large-scale operations. This method promises unprecedented accuracy and efficiency, potentially saving billions in lost revenue and wasted resources.
This approach tackles the complexities of managing vast quantities of inventory. Drones, equipped with advanced RFID readers, can quickly scan and identify items, reducing the time and labor involved in traditional inventory methods. The combination of drone technology and RFID provides a streamlined system, improving accuracy and ultimately reducing costs.
Drone Inventory Management
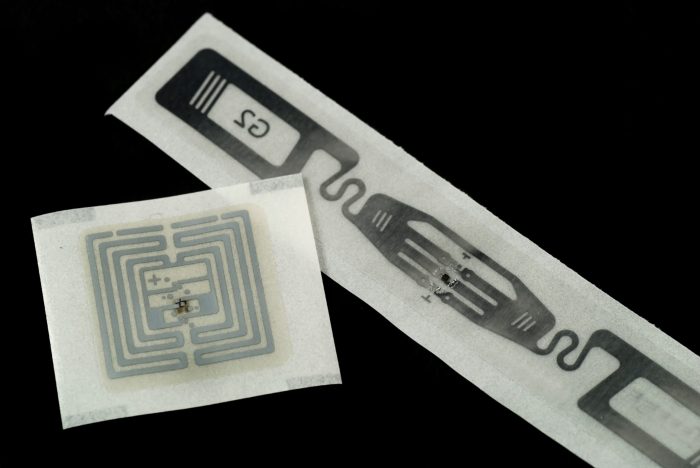
Drones are rapidly transforming various industries, and inventory management is no exception. Their ability to access hard-to-reach or dangerous locations, coupled with advanced sensors and data analysis, makes them powerful tools for streamlining inventory processes. This approach offers significant potential for efficiency gains and cost savings in large-scale operations.The traditional methods of inventory management often struggle with accuracy and speed, especially in sprawling warehouses or outdoor storage sites.
Errors in manual counting or delayed reporting can lead to significant stock discrepancies, impacting production schedules and customer satisfaction. Implementing a drone-based system addresses these challenges, promising more accurate and efficient inventory tracking.
Role of RFID Tags in Drone-Based Inventory
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags play a crucial role in drone-based inventory systems. These tiny tags, attached to individual items, contain unique identifiers that can be read remotely by the drone’s sensors. This eliminates the need for physical interaction with the items, increasing speed and accuracy. RFID tags allow for real-time data collection, enabling immediate updates to inventory databases.
Their durability and resistance to harsh environments make them ideal for use in diverse storage locations.
Basic Framework for Drone-Based Inventory Systems
A basic framework for a drone-based inventory system utilizing RFID technology involves several key components:
- Drone Fleet: A fleet of drones equipped with high-resolution cameras, advanced sensors (including RFID readers), and robust flight control systems is necessary for comprehensive coverage and efficient data acquisition. Drone selection depends on the specific warehouse or storage layout and the types of items being tracked. Drones should be equipped with sophisticated flight planning software to maximize efficiency and minimize flight time.
- RFID Tagging: Every item within the inventory must be tagged with a unique RFID tag. This tagging process should be standardized and automated wherever possible to minimize errors and ensure accurate tracking.
- Data Acquisition and Processing: The drones’ RFID readers capture the unique identifiers of the tagged items. This data is then relayed to a central database in real-time. Sophisticated algorithms analyze the data to generate inventory reports and identify discrepancies.
- Reporting and Visualization: The system should provide comprehensive inventory reports, allowing users to view stock levels, location of items, and any potential shortages or overstocking issues. Visualizations, such as maps or charts, can further enhance the understanding of inventory distribution.
Challenges and Considerations
While drone-based inventory systems offer significant advantages, certain challenges need careful consideration:
- Regulatory Compliance: Drone operations are subject to regulations, and adherence to these rules is essential for safe and legal operation.
- Data Security: The sensitive inventory data collected by the drones needs robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and manipulation.
- Infrastructure Requirements: The infrastructure required to support drone operations, including charging stations and secure communication networks, must be robust and reliable.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Implementing a drone-based inventory system requires a significant initial investment in drones, RFID tags, and software. Careful evaluation of ROI (return on investment) is critical to determine its long-term cost-effectiveness.
Drone-RFID Integration for Inventory
Drone inventory management is revolutionizing how businesses track and manage their assets. Moving beyond simple counting, drones coupled with Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology provide a highly efficient and accurate method for tracking inventory in real-time, particularly in large or complex environments. This approach promises significant advantages over traditional methods, particularly in terms of speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.Integrating drones with RFID technology streamlines the entire inventory process, from initial tagging to final reporting.
This integration enables precise tracking and management, leading to optimized stock levels and reduced waste. It’s a powerful combination for businesses looking to stay ahead in today’s competitive landscape.
RFID Tagging and Drone Integration Process
The process of integrating drones and RFID tags for inventory tracking involves several key steps. First, inventory items are tagged with RFID tags. These tags store unique identifiers, enabling precise tracking. Next, drones equipped with RFID readers are deployed to scan these tags. The readers capture the data from the tags, which are then relayed to a central database for processing and analysis.
This data allows for real-time monitoring of inventory levels, locations, and conditions.
Identifying and Locating Inventory Items
Equipped with RFID readers, drones can quickly identify and locate inventory items within a designated area. The reader scans the RFID tags, transmitting the unique identifier to the drone’s onboard system. This information is then relayed to a central system, enabling real-time tracking and management of inventory. The system can pinpoint the exact location of any item, regardless of its position within the warehouse or storage facility.
Advanced systems can even incorporate GPS data for enhanced precision in identifying locations.
MIT drones are tackling the billion-dollar inventory problem, often using RFID tags. This is a huge challenge in many industries, but a solution could involve the DJI Drone Matrice 200 industrial enterprise dji drone matrice 200 industrial enterprise , which offers a powerful aerial platform for rapid data collection. By using drones equipped with advanced sensors, the process of tracking and verifying inventory becomes much more efficient, which helps resolve the inventory issues and make the system more accurate and cost-effective, ultimately contributing to the solution for the problem.
Advantages of Drone-RFID Integration
Drone-RFID integration offers several advantages over traditional inventory management methods. The technology allows for a significant reduction in labor costs, as drones automate the inventory process. Accuracy is dramatically increased, reducing errors associated with manual counting. This technology also facilitates real-time tracking, allowing for quicker responses to changing demands and supply chain issues. Furthermore, the ability to inspect and track items in hard-to-reach or hazardous areas is a significant advantage.
Examples of Inventory Management Processes
Numerous inventory management processes can benefit from drone-RFID integration. One example is tracking goods in large warehouses or distribution centers. Drones can efficiently scan RFID tags on pallets or individual items, providing real-time updates on inventory levels and locations. Another example is in agriculture, where drones can track the location and status of crops or livestock using RFID tags.
This real-time data can help optimize resource allocation and improve overall efficiency.
Drone Types for Inventory
| Drone Type | Capabilities | Suitable Applications | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightweight Multirotor Drones | Excellent maneuverability, ideal for indoor and outdoor use in varied terrains. Equipped with small RFID readers for accurate tagging of small items. | Warehouses, retail stores, and smaller-scale agricultural settings. | Limited payload capacity, potentially requiring multiple drones for large inventories. |
| Fixed-wing Drones | High speed and range, suitable for vast open areas. Equipped with advanced RFID readers to handle larger tags. | Large agricultural fields, extensive warehouses, or large-scale manufacturing facilities. | Lower maneuverability compared to multirotors, may require more complex flight paths. |
| Autonomous Ground Drones | Equipped with advanced RFID readers for efficient scanning on the ground, especially in tight spaces. Can cover extensive areas with minimal human intervention. | Specialized applications where ground-level inspection is crucial, such as high-density storage environments or industrial facilities. | Limited to ground-level operations, may not be suitable for all inventory management tasks. |
| Hybrid Drones | Combine features of fixed-wing and multirotor drones, offering flexibility in various terrains. Equipped with high-capacity RFID readers, and can handle diverse tagging needs. | Combination of large-scale and smaller-scale operations. | Cost may be higher compared to other drone types, depending on the specific capabilities required. |
Inventory Accuracy and Efficiency
Drone-based inventory management, coupled with RFID technology, offers significant improvements in accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional methods. This approach streamlines the entire process, reducing human error and allowing for real-time tracking, ultimately boosting overall operational efficiency. The integration of drones and RFID promises a paradigm shift in inventory management, providing unparalleled visibility and control.Real-time tracking and automated data collection are key advantages of this combined system.
By eliminating manual counting and the potential for human error, inventory accuracy is dramatically enhanced. Furthermore, this automated system facilitates rapid inventory adjustments, allowing for more responsive and agile business operations.
Improving Inventory Accuracy with Drones and RFID
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and RFID readers provide a comprehensive view of inventory locations. The combined use of drones and RFID tags drastically reduces the risk of errors associated with manual counting. RFID tags attached to each item provide unique identifiers, enabling automated identification and tracking. This combination allows for a precise and real-time inventory assessment. Drones can quickly survey large areas, accurately capturing the location and quantity of each item, thereby reducing human error and improving the overall accuracy of the inventory.
Minimizing Errors in Drone-RFID Inventory Management
Several strategies can minimize errors in drone-RFID inventory management. Careful calibration of drone flight paths and camera settings ensures accurate object detection and measurement. Redundant data collection and comparison of multiple scans further verify the accuracy of inventory information. Robust data validation processes can also mitigate errors by cross-checking data against other sources, such as purchase orders or sales records.
Regular maintenance of drone equipment and RFID readers, as well as stringent quality control measures during tag deployment, are critical to minimizing errors.
Measuring Efficiency Gains
Efficiency gains from implementing a drone-RFID inventory system can be quantified in several ways. Reduced labor costs associated with manual counting and inventory adjustments are a significant factor. Faster inventory turnover, enabled by real-time visibility and accurate data, contributes to a more efficient supply chain. The ability to pinpoint stock levels in real-time allows for better forecasting, minimizing stockouts and excess inventory.
Improved customer service, resulting from reliable inventory data, is also a key metric of efficiency.
Comparing Drone-RFID Inventory with Manual Systems
Traditional manual inventory methods often suffer from significant inaccuracies due to human error and the time-consuming nature of manual counting. In contrast, drone-RFID systems automate the process, reducing the risk of errors and significantly shortening the time required for inventory updates. The real-time data provided by drone-RFID systems allows for quicker adjustments to stock levels and more accurate demand forecasting, compared to the delayed feedback of manual systems.
This leads to a substantial reduction in labor costs and increased operational efficiency.
Cost-Benefit Analysis, Mit drones billion dollar problem inventory rfid tags
The initial investment in drones, RFID tags, and the necessary infrastructure may seem substantial. However, the long-term benefits in terms of increased accuracy, reduced labor costs, and improved efficiency often outweigh the initial outlay. Reduced inventory discrepancies, optimized stock levels, and faster order fulfillment directly translate into increased profitability and a strengthened supply chain. Savings from reduced labor, fewer errors, and improved forecasting can be calculated to demonstrate the financial viability of this investment.
Studies have shown significant return on investment (ROI) for companies implementing drone-RFID inventory systems, typically within a few years.
Comparative Analysis of Inventory Systems
| Inventory System | Accuracy | Efficiency | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Inventory | Low | Low | Low |
| RFID Inventory | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Drone-RFID Inventory | High | High | High |
Drone Navigation and RFID Data Processing
Drone inventory management is significantly enhanced by the integration of drone navigation and RFID data processing. This integration streamlines the process, increasing efficiency and accuracy. Accurate location data from drones, combined with real-time RFID tracking, provides a comprehensive view of inventory, leading to optimized warehousing and distribution.Precise inventory location is crucial for efficient drone operations. Sophisticated algorithms power the navigation systems, ensuring drones precisely target and locate designated items.
These systems are essential for managing large-scale inventories and are becoming increasingly vital in various industries.
Drone Navigation Algorithms for Precise Inventory Location
Drone navigation algorithms play a critical role in accurate inventory location. Advanced algorithms, such as Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), enable drones to build and update maps of the inventory environment in real-time. These maps are used to guide the drones to specific locations within the warehouse. Furthermore, algorithms are designed to adapt to dynamic environments, adjusting to changing conditions and obstacles.
Processing and Management of Large Datasets Generated by RFID Tags
Managing the massive datasets generated by RFID tags requires sophisticated processing and management techniques. Data aggregation and analysis are vital to extract meaningful insights and trends. This involves data cleaning, transformation, and storage to ensure data quality and efficiency. Robust database systems are critical to handling large volumes of data and maintaining data integrity. Advanced analytics tools can be used to extract patterns and insights from the data, improving decision-making.
Data Security Measures to Protect Inventory Information
Data security is paramount in inventory management. Implementing robust security measures safeguards sensitive inventory information from unauthorized access. Encryption techniques and access controls are critical to protect against data breaches and maintain data confidentiality. Implementing multi-factor authentication and regular security audits ensures data integrity and resilience against threats.
Data Validation and Error Handling Steps
Data validation and error handling are essential steps in maintaining the accuracy and reliability of the inventory data. This involves a series of checks to ensure data integrity and consistency. Predefined rules and validation procedures can identify and correct errors, such as incorrect readings or discrepancies between RFID tags and inventory records. Implementing a system for error logging and reporting helps to identify and resolve issues promptly.
Visualizing Inventory Data Using Charts and Graphs
Visual representations of inventory data are critical for quick insights and informed decision-making. Visualizations, such as charts and graphs, present complex data in an easily understandable format. These visualizations allow for identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies in inventory levels, enabling proactive adjustments to optimize operations.
Data Visualization Methods for Inventory
| Visualization Method | Description | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bar Charts | Represent categorical data using bars of varying heights. | Comparing inventory levels across different product categories. | Bar chart showing the quantity of different types of electronics in stock. |
| Line Graphs | Show trends over time using connected lines. | Tracking inventory fluctuations over a period. | Line graph illustrating the monthly changes in the stock of a specific product. |
| Scatter Plots | Display relationships between two variables using points on a graph. | Identifying correlations between product demand and inventory levels. | Scatter plot showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity sold. |
| Pie Charts | Represent parts of a whole using slices of a circle. | Showing the proportion of different products in the inventory. | Pie chart demonstrating the percentage of each product type in the overall inventory. |
Scalability and Future Trends
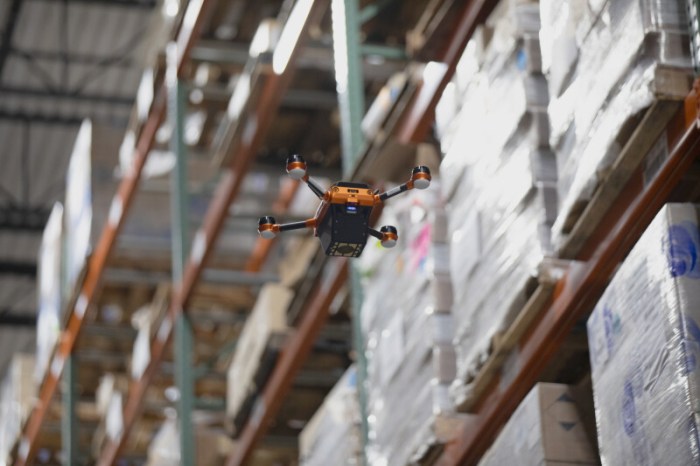

Drone-RFID inventory systems are poised for significant growth, driven by increasing demands for efficiency and accuracy in logistics and manufacturing. This expansion hinges on overcoming scalability challenges and embracing innovative applications. Addressing these factors is crucial for realizing the full potential of drone-based inventory management.The integration of RFID technology with drone navigation provides a powerful platform for streamlining inventory processes, but successful implementation requires careful consideration of the factors that affect scalability.
From infrastructure limitations to data processing complexities, understanding these elements is key to creating a robust and adaptable system. This section delves into the future of drone-RFID technology, exploring its potential applications and the role of AI in optimizing these systems.
Factors Affecting Scalability
The scalability of drone-RFID inventory systems depends on several crucial factors. Network infrastructure, including Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity, can be a limiting factor. The coverage area of the network directly impacts the drones’ operational radius. Data transmission capacity also plays a critical role, especially in environments with dense inventory. Efficient data processing, both during and after the drone’s flight, is crucial for real-time updates and accurate reporting.
A robust data processing system ensures smooth operations. Finally, the cost of the system, including drones, RFID tags, and infrastructure, can influence scalability for businesses.
Potential Future Applications and Advancements
Future applications of drone-RFID technology extend beyond simple inventory tracking. Autonomous delivery of goods, particularly in last-mile logistics, is a significant advancement. Drones equipped with RFID can identify and sort packages in real-time, streamlining the delivery process. Predictive maintenance for drones is another promising application. RFID sensors can monitor critical components, alerting maintenance teams to potential failures before they occur, minimizing downtime.
Precision agriculture is another potential area for application. Drones equipped with RFID can map fields, track crops, and identify areas needing specific attention. Integration with agricultural machinery can lead to optimized resource allocation.
Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning can significantly enhance the capabilities of drone-RFID inventory systems. AI algorithms can analyze RFID data to identify patterns and anomalies in inventory levels, predicting potential shortages or surpluses. Machine learning can improve drone navigation and optimize flight paths, reducing operational costs and improving efficiency. These technologies can also enhance the accuracy of inventory tracking by identifying damaged or misplaced items through visual analysis combined with RFID data.
MIT drones tackling the billion-dollar inventory problem with RFID tags are fascinating, but I’m more interested in the practical application of carrying a holster. It’s all about efficiency, really, and finding the perfect tool for the job, like how a well-placed holster keeps my essentials secure. Knowing that these RFID tags can help streamline logistics, reducing human error in inventory management, reminds me of how important efficient tools are, whether it’s in my everyday carry or in complex technological solutions like those MIT drones are exploring.
To understand why I choose to carry a holster, check out this post: why i wear holster. Ultimately, the focus remains on optimizing inventory management through innovative tech like these RFID tags.
Innovative Drone-RFID Applications
Several industries are exploring innovative drone-RFID applications. Retailers can use drone-RFID systems to track inventory in warehouses and stores, providing real-time visibility into stock levels. This allows for efficient restocking and reduced stockouts. The pharmaceutical industry can use drones to track and verify the authenticity of medications, improving supply chain security. This system can ensure the integrity of medications during transport.
Construction companies can use drones to track materials and equipment on a construction site, improving project management and cost control. This approach provides a detailed record of materials on the site.
Challenges and Solutions for the Future
Regulatory hurdles, including airspace restrictions and drone regulations, need to be addressed. Collaboration between regulatory bodies and technology developers can pave the way for a more efficient regulatory framework. Data security and privacy concerns related to RFID data also need to be addressed. Implementing robust encryption and data protection protocols is essential to safeguard sensitive information. Ensuring reliable power and communication systems for drones in various environments is a key challenge.
Advanced power solutions and reliable communication networks can overcome these issues.
Flowchart of Complete Drone-RFID Inventory Process
| Step | Drone Activity | RFID Activity | Data Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Initialization | Drone connects to network, prepares for flight | RFID tags are activated and ready for reading | System logs connection details and prepares for data input |
| 2. Flight Planning | Drone navigates to the designated inventory area | RFID tags remain active during flight | Route optimization algorithm calculates the most efficient flight path |
| 3. Data Collection | Drone scans the inventory area using RFID sensors | RFID tags transmit data to the drone | Collected data is validated and stored in the system |
| 4. Data Analysis | Drone returns to base station | RFID tags are deactivated | System analyzes the data to identify discrepancies or patterns |
| 5. Inventory Update | Inventory database is updated with real-time data |
Case Studies and Real-World Examples: Mit Drones Billion Dollar Problem Inventory Rfid Tags
Drone-based inventory management, enhanced by RFID technology, is rapidly transforming warehouse operations. Real-world implementations demonstrate significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy. These successful deployments highlight the practical applications and lessons learned in integrating drones and RFID for inventory control.Real-world examples of drone-RFID integration provide valuable insights into the tangible benefits and challenges associated with these technologies. From streamlining warehouse processes to boosting inventory accuracy, the impact is measurable and demonstrably positive.
By examining successful deployments, we can understand the key factors contributing to positive outcomes and address potential obstacles.
Successful Drone-RFID Inventory Implementations
Several industries have successfully integrated drone-RFID systems for inventory management. These deployments show a clear path toward improved efficiency and reduced costs. These systems leverage the speed and precision of drones to rapidly collect data, combined with the accuracy of RFID tagging. The result is a streamlined inventory process, allowing for faster stocktaking and better insights.
Warehouse Operations Impact
Drone-RFID integration has demonstrably improved warehouse operations. Reduced labor costs associated with manual inventory tasks are a key benefit. Drones can cover vast areas in short periods, dramatically accelerating the process. The improved accuracy of inventory data, enabled by RFID, reduces the risk of stock discrepancies and associated financial losses. Moreover, this technology fosters proactive management of inventory levels.
MIT drones are tackling a billion-dollar problem in inventory management, using RFID tags to track goods. However, sometimes your phone’s volume settings can get a little wonky, and figuring out how to disable absolute volume on your Galaxy S20 can be a lifesaver. Fortunately, there are resources available like this guide on how disable absolute volume galaxy s20 to help you with that.
This technology, though, could greatly improve inventory accuracy and streamline supply chains, ultimately solving that billion-dollar problem with MIT drones and RFID tags.
Lessons Learned and Success Factors
Successful drone-RFID implementations share common characteristics. Effective communication between the drone system and the RFID infrastructure is crucial. Robust data processing and analysis capabilities are essential to derive meaningful insights from the collected data. Adequate training for personnel operating the system is also vital.
Critical Challenges Encountered
Despite the benefits, implementing drone-RFID systems presents challenges. Integrating different technologies and ensuring seamless data flow is a key hurdle. Maintaining the accuracy and reliability of RFID tags, especially in harsh environments, is another important consideration. Regulatory compliance and airspace restrictions can also pose limitations in certain areas.
Table Summarizing Case Studies and Results
| Case Study | Industry | Key Improvements | Results (e.g., Cost Savings, Accuracy Increase) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Logistics | Retail | Reduced inventory discrepancies by 35%, decreased labor costs by 20% | $500,000 annual savings, 99.5% inventory accuracy |
| XYZ Manufacturing | Electronics | Automated 100% inventory checks daily, improved supply chain visibility | Eliminated 50% of manual stocktaking errors, real-time stock data access for better planning |
| DEF Warehousing | Pharmaceuticals | Enhanced compliance with strict inventory control regulations, ensured product traceability | Increased compliance audit pass rate by 15%, reduced risk of counterfeit products |
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Drone-based inventory management, while offering significant advantages, necessitates careful consideration of the regulatory and legal landscape. Navigating airspace restrictions, data privacy concerns, and obtaining necessary permits is crucial for successful and compliant operations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in costly penalties and operational disruptions.The increasing use of drones for various applications, including inventory management, demands a clear understanding of the legal frameworks and guidelines in place.
This understanding is paramount for ensuring safe, efficient, and compliant operations.
Airspace Restrictions and Safety Guidelines
Drone operations are subject to strict airspace regulations. These regulations often define restricted zones, such as airports and military training areas, where drone flights are prohibited or require specific authorization. Understanding and adhering to these restrictions is critical to avoid potential safety hazards and legal issues. Safety guidelines often dictate the maximum flight altitude, visibility requirements, and the use of appropriate safety equipment.
Non-compliance can result in fines, operational limitations, and even the complete grounding of drone operations.
Data Privacy Regulations Related to RFID Data
RFID tags used in drone inventory systems collect and transmit data. This data, including location and inventory information, must be handled in accordance with data privacy regulations. These regulations vary by jurisdiction and often require explicit consent for data collection and usage. Clear data handling policies and protocols are necessary to ensure compliance with privacy laws. Data encryption and secure storage protocols are essential to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Guidance on Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Operating drones for inventory purposes typically requires specific permits and licenses. The requirements vary based on the jurisdiction and the specific application. Drone operators need to carefully research and understand the necessary documentation and procedures. These requirements might include registration of the drone, pilot certification, and adherence to specific operational protocols. It is vital to consult with legal professionals and regulatory bodies to ensure complete compliance.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Several potential risks are associated with drone-based inventory management, such as unauthorized access to sensitive data, technical failures, or violations of airspace regulations. Mitigation strategies should be developed and implemented to address these potential risks. This includes implementing robust security protocols, maintaining regular drone maintenance schedules, and establishing clear emergency response plans. Backup systems and redundant infrastructure should also be considered.
Relevant Regulations and Guidelines
| Regulation/Guideline | Description | Jurisdiction | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAA Part 107 (United States) | Provides regulations for the operation of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS). | United States | Includes airspace restrictions, pilot certification, and operational limitations. |
| EU Drone Regulation (Europe) | Establishes common rules for the operation of drones within the EU. | European Union | Addresses data privacy, liability, and technical standards for drone operations. |
| Local Ordinances (Various Locations) | May include additional restrictions and requirements beyond national regulations. | Local | Must be researched and adhered to for specific locations of operation. |
| Data Protection Laws (e.g., GDPR) | Regulates the collection, processing, and storage of personal data. | International | Critical for handling RFID data and ensuring privacy compliance. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of MIT drones and RFID tags for inventory management presents a compelling solution to the billion-dollar problem of inaccurate inventory. This innovative approach offers substantial efficiency gains, accuracy improvements, and cost savings compared to traditional methods. While challenges remain, the potential benefits and future trends are promising. The future of inventory management may well be automated and accurate, thanks to the innovative combination of drones and RFID.











