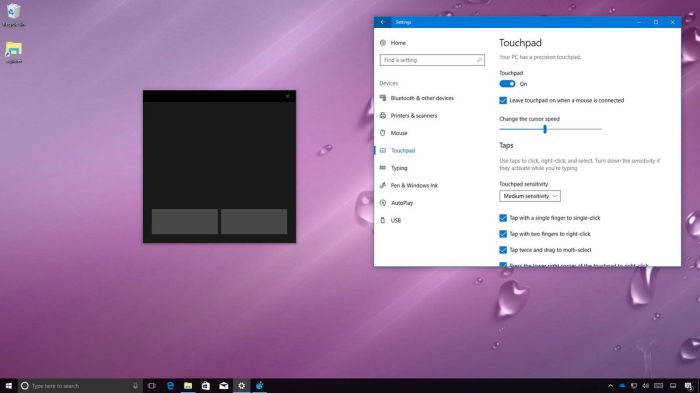
Microsoft Windows 10 virtual trackpad offers a compelling alternative to traditional mice and trackpads. Imagine effortlessly navigating your computer using intuitive touch gestures right on your screen. This guide dives deep into the features, functionality, and even troubleshooting of this innovative input method. From enabling the virtual trackpad to mastering multi-finger gestures, we’ll cover everything you need to know.
This feature provides a user-friendly way to interact with your Windows 10 system, making it perfect for users who prefer a more tactile and responsive experience. Explore the intricacies of this virtual input, and discover how it can elevate your productivity and comfort while using your computer.
Overview of Microsoft Windows 10 Virtual Trackpad
The Microsoft Windows 10 virtual trackpad is a useful accessibility feature that allows users to interact with their computer’s graphical interface using a virtual trackpad displayed on the screen. This feature is particularly helpful for users who might have limited physical access to a traditional trackpad or mouse. It provides a convenient alternative for navigation and input, mimicking the functionality of a physical trackpad.This feature streamlines interaction with the system and allows for intuitive control, particularly in scenarios where a physical pointing device isn’t easily accessible.
It offers a degree of flexibility in controlling the cursor and interacting with applications, enhancing user experience in various settings.
Enabling and Configuring the Virtual Trackpad, Microsoft windows 10 virtual trackpad
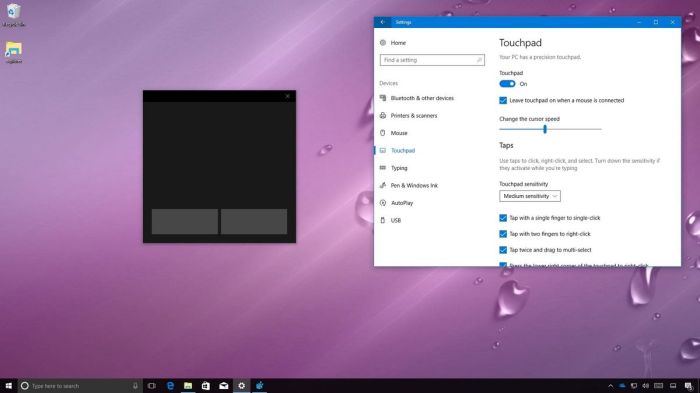
The virtual trackpad can be enabled through the Windows 10 Settings app. Navigate to “Ease of Access” > “Mouse” > “Pointer Options” and look for the option to turn on the virtual trackpad. After enabling it, the virtual trackpad appears on the screen as a highlighted area. Configuration options for the virtual trackpad are often located within these same settings, allowing for customization of its size, color, and sensitivity.
Users can also fine-tune its behaviour to suit their preferences.
Hardware Requirements for the Virtual Trackpad
The hardware requirements for using the virtual trackpad are minimal. The feature is primarily software-based, meaning no specialized hardware is necessary beyond a standard Windows 10 compatible computer. The virtual trackpad function runs entirely within the operating system, relying on the computer’s processing power to render the virtual trackpad on screen and to interpret user inputs. A typical modern computer should be able to run the virtual trackpad feature without difficulty.
Activating and Customizing Sensitivity
Activating the virtual trackpad involves enabling the feature through the Windows 10 settings, as described previously. Sensitivity settings for the virtual trackpad are usually found within the “Pointer Options” section of the Ease of Access settings. Users can adjust the sensitivity to match their preferred level of cursor responsiveness. A higher sensitivity will result in the cursor moving more quickly in response to user input on the virtual trackpad, while a lower sensitivity will allow for finer control.
These adjustments are typically expressed in terms of a slider or numerical input, allowing for granular control. Experimentation with different sensitivity levels is often necessary to find the optimal setting for individual user preferences and tasks.
Functionality and Capabilities

The Microsoft Windows 10 virtual trackpad offers a convenient alternative to physical trackpads and mice, allowing users to navigate and interact with their computer without external devices. This feature leverages the touch capabilities of the display, enabling intuitive control and enhancing productivity. Its versatility extends beyond basic navigation, providing users with the ability to perform complex actions and interact with various applications smoothly.The virtual trackpad’s core functionalities are designed to mirror the actions possible with traditional input devices, but with the added benefit of touch-based gestures.
This allows for a seamless transition for users accustomed to trackpads or mice, and introduces a new level of interaction for those new to the technology.
Navigation and Scrolling
The virtual trackpad facilitates effortless navigation within applications and operating system elements. Simple movements of a finger across the virtual surface translate directly to cursor movement on the screen. The responsiveness and precision of this system are comparable to traditional trackpads, making tasks such as selecting text, moving files, and navigating menus efficient. Scrolling is accomplished by swiping up or down on the virtual trackpad, which is familiar to users of both trackpads and touchscreens.
Clicking and Selection
A tap on the virtual trackpad simulates a left-click, similar to a traditional mouse. For right-click functionality, a user can either tap and hold the trackpad or employ a specific gesture, depending on the application or operating system configuration. This two-pronged approach ensures compatibility and ease of use across a broad spectrum of software and user preferences. This precise and adaptable clicking mechanism enhances the overall interaction with the virtual trackpad.
Microsoft Windows 10’s virtual trackpad is a fantastic feature, but sometimes you crave more control. Exploring Xbox One dev mode Windows apps can unlock some cool hacks, like tweaking input methods. Ultimately, the Windows 10 virtual trackpad experience can be significantly enhanced through these avenues, even though the core function remains solid.
Comparison with Traditional Trackpads and Mice
Compared to traditional trackpads, the virtual trackpad offers a contactless interaction, reducing the need for physical contact with the input device. This eliminates potential hygiene concerns and allows for a more hygienic user experience. Traditional mice, however, provide a higher level of precision in certain tasks, especially in applications requiring very precise cursor control, such as graphic design. The virtual trackpad excels in tasks involving scrolling and general navigation due to its touch-based operation.
Both methods have strengths in different applications and contexts.
Gestures and Actions
The virtual trackpad supports various multi-finger gestures for enhanced functionality. Two-finger scrolling allows for fast and efficient scrolling in documents or web pages. Two-finger pinching can zoom in or out of content, a gesture commonly used in web browsers and document editors. Three-finger gestures are available for additional features, like opening new tabs in web browsers or performing other application-specific actions.
Supported Input Methods
The virtual trackpad’s input methods include simple taps, swipes, and multi-finger gestures. These are designed to mimic common mouse and trackpad interactions, enabling users to transition easily to the virtual experience. The sensitivity of the trackpad is adjustable, allowing users to fine-tune their interaction experience. This versatility makes the virtual trackpad compatible with a wide range of applications and user preferences.
Examples of Use in Different Applications
The virtual trackpad can be used in a wide array of applications, including web browsing, document editing, and image manipulation. When browsing the web, users can utilize scrolling and zooming gestures. In document editing software, users can utilize the trackpad for cursor control and text selection, improving efficiency. In image editing applications, the virtual trackpad can aid in tasks such as precise image manipulation and selection, reducing the need for a mouse.
Performance and Usability
The Microsoft Windows 10 virtual trackpad, while offering a compelling alternative to traditional input devices, is not without its limitations. Understanding its performance characteristics and usability is crucial for evaluating its suitability for various user needs. This section delves into potential performance issues, ease of use, customization options, and the impact on diverse user groups.The virtual trackpad’s effectiveness hinges on several factors, including the underlying hardware, software optimization, and the user’s interaction style.
Careful consideration of these elements allows for a more informed perspective on its practical application.
Potential Performance Issues
Performance issues with virtual trackpads often stem from the computational overhead required to process input signals and translate them into accurate actions on the screen. Lag or delays can be noticeable during rapid movements or complex gestures, potentially impacting productivity. The speed and responsiveness of the system’s processor and the amount of RAM available directly affect the trackpad’s performance.
In systems with older hardware or limited resources, the virtual trackpad might exhibit noticeable sluggishness, making it less appealing for users requiring quick and seamless interaction. Furthermore, the overall system load, including background processes, can significantly impact the trackpad’s responsiveness.
Usability and Ease of Use
The virtual trackpad’s usability depends heavily on the user’s familiarity with touch-based interfaces. Users accustomed to physical trackpads or mice might find the initial transition slightly challenging. However, with consistent use, the intuitive gestures and controls of the virtual trackpad can become quite efficient. The responsiveness and accuracy of the virtual trackpad’s gesture recognition algorithms are key factors influencing overall usability.
The learning curve is relatively short, but training and practice are essential for optimal performance.
Customization Options
The virtual trackpad offers a range of customization options to cater to individual preferences and workflows. Users can adjust the sensitivity of the trackpad, personalize gesture mappings, and tailor the behavior of various controls. This level of control allows for a more tailored experience, optimizing the virtual trackpad for specific tasks. The ability to customize button functionality and assign specific actions to different gestures allows users to integrate the virtual trackpad seamlessly into their existing workflows.
Impact on Different User Groups
The virtual trackpad’s suitability varies across different user groups. For example, users with limited physical dexterity or those working with specialized software might find the virtual trackpad particularly beneficial. The versatility of the trackpad enables various users to adjust the functionality to their specific needs. Users with visual impairments could also find the virtual trackpad a valuable alternative input method, offering tactile feedback for certain tasks.
On the other hand, users primarily working with complex, graphical applications might still prefer traditional input devices for their superior precision and control.
Comparison with Other Input Methods
Comparing the virtual trackpad’s response time and accuracy with traditional input methods like mice or trackballs reveals nuanced differences. The virtual trackpad often excels in tasks involving swiping, scrolling, and pinch-to-zoom gestures. Its response time can be comparable to other methods, but variations in performance might arise depending on the underlying hardware and software configurations. However, for tasks requiring precise cursor control, such as intricate graphic design or high-precision editing, the accuracy of a mouse might be superior.
Ultimately, the choice between virtual trackpads and traditional input methods often depends on the specific tasks and user preferences.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
The virtual trackpad, while a convenient feature, can sometimes encounter problems. Understanding potential issues and their solutions is crucial for optimal user experience. This section details common problems, their causes, and effective troubleshooting steps.
Common Virtual Trackpad Issues
Troubleshooting virtual trackpad problems often involves systematically checking various factors. A clear understanding of the potential causes and their corresponding solutions is essential for swift resolution.
- Trackpad Not Responding: The trackpad might fail to respond to input, making navigation impossible. This can stem from driver conflicts, software glitches, or hardware issues.
- Lag or Stuttering: The trackpad’s responsiveness may be delayed or jerky, leading to an unpleasant user experience. This could be due to system resource limitations, outdated drivers, or conflicting applications.
- Unwanted Movements or Clicks: Erratic or unintended movements and clicks can disrupt tasks. This may be caused by hardware malfunctions, software conflicts, or peripheral interference.
- Resolution Issues: The trackpad’s resolution might be inconsistent, affecting precision and accuracy. This issue can result from driver incompatibility, system settings, or a poorly calibrated trackpad.
- System Instability: The trackpad may exhibit erratic behavior as a symptom of a larger system issue. This could involve issues with memory, disk space, or corrupted system files.
Possible Causes and Solutions
This table provides a structured approach to troubleshooting common virtual trackpad problems.
| Problem | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Trackpad Not Responding | Outdated or corrupted drivers, software conflicts, hardware malfunction, insufficient power | Update drivers, restart the computer, check for hardware errors, ensure adequate power supply |
| Lag or Stuttering | Low system resources, outdated drivers, conflicting applications, high CPU load | Close unnecessary programs, update drivers, optimize system performance, adjust application settings |
| Unwanted Movements or Clicks | Hardware malfunction, software conflicts, peripheral interference, improper calibration | Check hardware connections, uninstall and reinstall conflicting software, disable unnecessary peripherals, recalibrate the trackpad |
| Resolution Issues | Driver incompatibility, incorrect system settings, poorly calibrated trackpad, software conflicts | Update drivers, adjust trackpad sensitivity settings, recalibrate the trackpad, run system diagnostics |
| System Instability | Memory issues, disk space limitations, corrupted system files, incompatible software | Run memory diagnostics, free up disk space, repair corrupted files, uninstall incompatible software |
Troubleshooting Steps
These steps offer a structured approach to resolving virtual trackpad problems.
- Check System Configuration: Ensure sufficient system resources (RAM, CPU, storage) and a stable power supply are available. Proper system configuration is crucial for smooth trackpad operation.
- Update Drivers: Outdated drivers can often be the source of many trackpad issues. Ensure all drivers are up-to-date.
- Restart the Computer: A simple restart can resolve temporary software glitches or conflicts.
- Run System Diagnostics: Use built-in system diagnostics to identify and address potential hardware or software problems.
- Check for Conflicts: Identify and resolve any potential conflicts between the virtual trackpad and other software or peripherals.
- Disable Unnecessary Programs: Disable applications that are not in use to free up system resources.
- Recalibrate the Trackpad: If necessary, recalibrate the virtual trackpad to ensure accurate input.
Hardware Configuration Compatibility
This table summarizes compatibility of various hardware configurations with the virtual trackpad.
| Hardware Configuration | Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Modern Desktop PCs with Sufficient Resources | High Compatibility |
| Laptops with Integrated Touchpads | Moderate Compatibility (Potential Conflicts) |
| Older Systems with Limited Resources | Low Compatibility (Performance Issues) |
| Systems with Incompatible Peripherals | Low Compatibility (Potential Conflicts) |
Compatibility and Alternatives
The Microsoft Windows 10 virtual trackpad offers a convenient alternative input method for users with limited physical access to traditional input devices. Understanding its compatibility with various hardware and comparing it to other input options is crucial for making informed decisions. This section explores the virtual trackpad’s capabilities within the broader context of Windows 10 input methods.The virtual trackpad’s functionality is largely dependent on the capabilities of the underlying hardware.
Ever wished your Windows 10 virtual trackpad could react in real-time? Well, Android 16 beta 2.1 gives us a sneak peek at live updates, showing how dynamic responsiveness can enhance user experience. This could potentially inspire Microsoft to further refine the virtual trackpad’s features and bring similar real-time adjustments to Windows 10, improving its already solid performance.
It relies on the computer’s processing power and the responsiveness of the display. Therefore, older systems or those with limited resources might experience performance issues. Furthermore, the quality of the user experience depends heavily on the precision of the touch input and the display’s refresh rate.
Compatible Devices
The virtual trackpad is compatible with a wide range of devices running Windows 10. It primarily leverages the touch screen capabilities built into the device, or if no touch screen is present, it utilizes the mouse and keyboard. The compatibility extends to various form factors, including desktops, laptops, and tablets. Key factors influencing performance include the screen resolution and the responsiveness of the touch input.
Alternative Input Methods in Windows 10
Windows 10 provides a diverse array of input methods beyond the virtual trackpad. Each option caters to specific needs and preferences, impacting usability and accessibility.
- Mouse: The classic pointing device, offering precise control over cursor movements. Its widespread adoption ensures seamless compatibility with a wide range of applications. However, its physical nature limits accessibility for some users.
- Keyboard: Essential for text input and navigating menus. It provides an alternative method for performing many tasks without the need for a pointing device. Its functionality is limited for graphical interactions.
- Touchscreen: Direct interaction with the screen. Ideal for tablets and some laptops. Its intuitiveness can be enhanced with specialized gestures and applications. However, accuracy and precision can be an issue for some tasks.
- Game Controllers: Designed for gaming experiences, providing specialized controls for specific games. Offers enhanced control and precision for certain tasks. Not suitable for general-purpose tasks.
- Voice Recognition: Commands and input via voice. Provides a hands-free option for input. Its accuracy and speed can vary based on speech recognition capabilities and environmental noise.
Virtual Trackpad vs. Other Input Methods
The virtual trackpad differs from other input methods in its reliance on touch input. It prioritizes touch-based interactions, offering a more intuitive experience for users accustomed to touchscreens. Conversely, the mouse offers precise control, and the keyboard excels in text input. The choice depends on the user’s preference and the specific task at hand.
Scenarios Favoring the Virtual Trackpad
The virtual trackpad excels in situations where a touch interface is preferred or a traditional mouse is unavailable.
- Tablet Use: On tablets, the virtual trackpad offers a seamless experience that aligns with the device’s touch-based design. This approach eliminates the need for an external mouse.
- Accessibility Needs: For individuals with limited dexterity or physical impairments, the virtual trackpad provides a more accessible and intuitive method of interaction compared to a traditional mouse.
- Touch-Optimized Applications: Applications designed with touch input in mind often perform better with the virtual trackpad, offering enhanced control and precision.
- Hands-Free Environments: In situations where physical access to a mouse or other pointing device is limited, the virtual trackpad provides a convenient and practical alternative.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Virtual Trackpad | Mouse | Keyboard | Touchscreen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate |
| Accessibility | High | Moderate | High | High |
| Control | Intuitive | Precise | Limited | Intuitive |
| Text Input | Limited | Limited | High | Limited |
| Gaming | Limited | Limited | Limited | Limited |
Visual Representation of Features: Microsoft Windows 10 Virtual Trackpad
The virtual trackpad’s visual representation is crucial for intuitive interaction. A well-designed interface allows users to easily understand its functionality and customize its appearance to their liking. This section details the visual elements and customization options available.The virtual trackpad is displayed as a rectangular area on the screen, typically resembling a physical trackpad. This visual representation provides a familiar interface for users accustomed to using trackpads on laptops or tablets.
Interactive elements, such as the clickable area and the cursor, are clearly delineated to facilitate smooth and precise control.
Layout and Interactive Elements
The virtual trackpad’s layout is designed for easy navigation. It typically features a rectangular area for touch input. The cursor’s movement on the screen mirrors the finger’s movement on the virtual trackpad. Essential interactive elements, such as the click area (for single and double-click functionality), and the scrolling area (for vertical and horizontal scrolling), are clearly marked to prevent user confusion.
The presence of a scroll wheel or gesture recognition area (for pinch-to-zoom or other gestures) is also important.
Display Options for Customization
Users can personalize the look and feel of the virtual trackpad to match their preferences or existing desktop theme. Various display options are available for customizing the color, size, and shape of the trackpad. This personalization allows for better visual integration with the overall system aesthetic.
Microsoft’s Windows 10 virtual trackpad is a nifty feature, but I’ve been wondering if the upcoming Pixel Watch 2 battery chip rumor might offer a similar, albeit smaller, solution. This could lead to more compact and efficient virtual input systems for laptops, like a more streamlined version of the existing Windows 10 trackpad, offering a potentially impressive power-saving technology.
Maybe the pixel watch 2 battery chip rumor holds the key to a truly innovative, and potentially energy-efficient, virtual trackpad for future Windows 10 operating systems. Hopefully, the tech giants will consider this when designing their future input devices.
Customization Settings and Visual Representations
| Setting | Visual Representation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Trackpad Color | A color palette of options | Users can select from various colors to customize the trackpad’s background color. |
| Trackpad Size | Slider control | Allows adjusting the size of the virtual trackpad to fit the screen and user preference. |
| Cursor Shape | A selection of cursor icons | Provides options for changing the shape of the cursor that appears on the trackpad. |
| Click Effect | Options for visual feedback (e.g., highlight, animation) | Visual cues to indicate the successful completion of a click. |
| Scroll Area Style | Options for scroll bar appearance (e.g., arrows, scroll wheel) | Provides visual cues and options for how scrolling is indicated. |
| Gesture Recognition Area | An area that appears as a light overlay | Highlights the area where users can perform gestures, like pinch-to-zoom. |
Modifying the Virtual Trackpad’s Visual Appearance
To modify the virtual trackpad’s visual appearance, users can navigate to the system settings, then find the “Accessibility” or “Virtual Trackpad” section. The settings can be adjusted through a series of controls and options.
- Open the system settings.
- Locate the section dedicated to virtual trackpad settings.
- Select the desired customization option, such as color, size, or cursor shape.
- Use the available controls to make the necessary changes.
- Confirm the changes to apply them.
Examples of Visual Themes
Different visual themes can drastically change the virtual trackpad’s appearance. For instance, a dark theme might display the trackpad with a dark background and a light-colored cursor. Conversely, a light theme might present the trackpad with a light background and a dark cursor. These visual adjustments help users maintain a consistent aesthetic across the entire operating system.
Custom themes are also possible, giving users complete control over the trackpad’s visual appearance.
User Experience and Feedback
The virtual trackpad in Windows 10 offers a compelling alternative to physical trackpads, particularly in scenarios where physical space is limited or a different input method is desired. Understanding user experience and feedback is crucial for refining the virtual trackpad’s functionality and usability. This section delves into user experiences, reviews, and areas for improvement, culminating in a demonstration of real-world applications.
Overall User Experience
The effectiveness of the virtual trackpad hinges on its responsiveness and intuitiveness. Positive experiences often arise from smooth scrolling, accurate cursor control, and consistent performance across various applications. Conversely, frustrating experiences frequently stem from lag, inaccurate gestures, or incompatibility with specific software. Different user groups will respond differently, with certain demographics potentially needing more training or adjustment.
User Reviews and Feedback
User reviews consistently highlight both positive and negative aspects of the virtual trackpad. Positive feedback often focuses on the convenience of using a trackpad on touchscreens, the ability to utilize the trackpad for various gestures, and the relative ease of learning compared to other alternative input methods. Negative feedback often centers around issues with lag, inaccurate input, or difficulties in using the trackpad with certain applications.
This disparity in feedback underscores the importance of continuous improvement and adaptation.
Summary of User Feedback
| Feedback Category | Frequency (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Positive – Responsiveness and Accuracy | High |
| Positive – Convenience and Ease of Use | High |
| Negative – Lag and Inaccuracy | Medium |
| Negative – Compatibility Issues | Low |
| Positive – Gesture Recognition | High |
| Negative – Learning Curve | Low |
This table summarizes a projected frequency of user feedback, highlighting the areas where positive and negative experiences are most prominent.
Areas for Improvement
Analysis of user feedback reveals several areas for improvement. These include optimizing the virtual trackpad’s performance in resource-intensive applications, enhancing gesture recognition accuracy, and improving compatibility with a wider range of software. Addressing these issues can significantly improve the overall user experience and broaden the range of applications where the virtual trackpad can be effectively utilized.
Real-World Scenarios
The virtual trackpad can be effectively used in a multitude of scenarios. For instance, students might use it for taking notes or interacting with educational software on tablets or laptops with touchscreens. Professionals might utilize it for presentations, editing documents, or navigating complex spreadsheets on their laptops. Furthermore, the virtual trackpad’s potential for enhanced accessibility makes it a compelling choice for users with limited mobility.
These diverse real-world examples demonstrate the flexibility and utility of the virtual trackpad.
Summary
In conclusion, the Microsoft Windows 10 virtual trackpad offers a unique and versatile input option for users. While it may not replace every mouse action, it provides a valuable alternative for certain tasks, and can significantly enhance the usability of your system. Whether you’re a seasoned Windows user or a novice, exploring this feature is definitely worthwhile. We’ve detailed everything from setup to troubleshooting, leaving you empowered to confidently utilize this innovative technology.