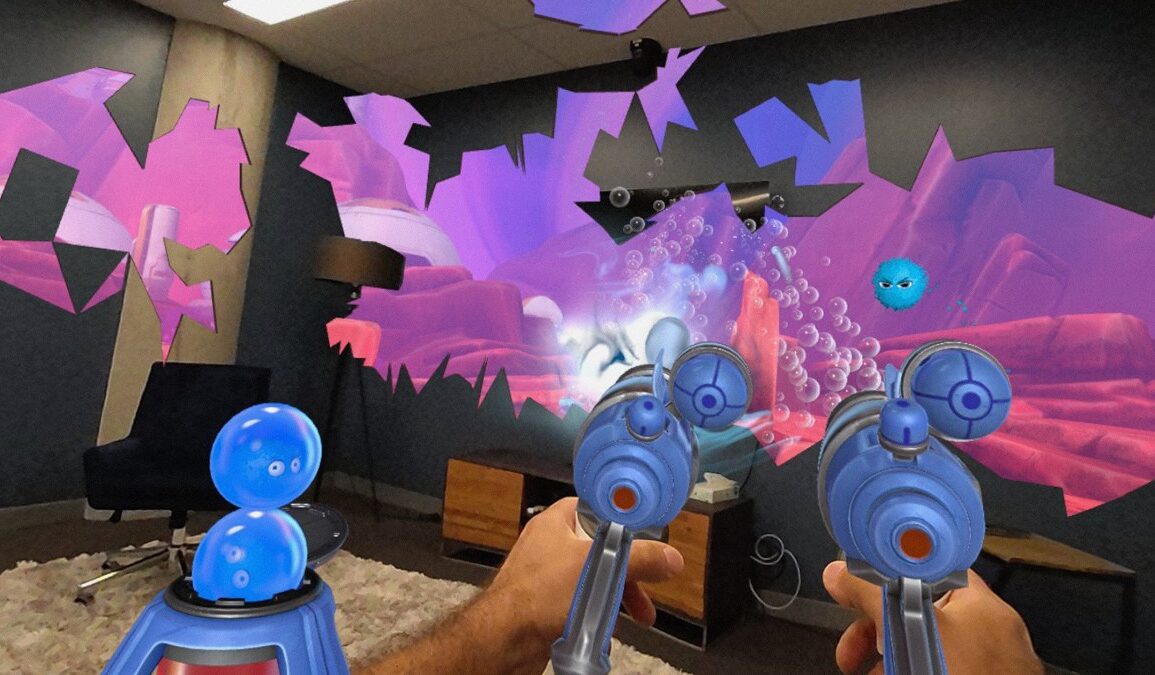
Meta Quest 3 mixed reality chores offer a fascinating glimpse into the future of household tasks. Imagine tackling cleaning, organizing, or maintenance with the help of virtual tools and a sophisticated interface. This exploration delves into the potential of VR for everyday chores, examining the Meta Quest 3’s capabilities, user experience, and potential challenges.
This innovative approach combines the physical world with digital elements, allowing for a new way to approach everyday tasks. The Meta Quest 3’s powerful processing capabilities and intuitive controls could streamline chores, making them less tedious and potentially even more enjoyable. We’ll analyze how virtual assistants and tools can enhance efficiency and precision in these tasks, creating a truly immersive and interactive experience.
Introduction to Mixed Reality Chores
Mixed reality chores represent a novel approach to household and personal tasks, leveraging the seamless integration of virtual and physical spaces. This emerging technology promises to revolutionize how we approach daily activities, enhancing efficiency and potentially even making certain chores more enjoyable. The core concept revolves around overlaying digital information and tools onto the real world, guiding users through tasks in a more intuitive and interactive way.The core concept behind mixed reality chores is the combination of physical space with digital elements, creating a hybrid environment for performing tasks.
This approach offers a significant departure from traditional methods, enabling more precise and guided actions, thereby potentially reducing errors and improving overall efficiency. By merging the tangible with the virtual, mixed reality chores aim to simplify complex tasks and make everyday chores less tedious.
Potential Advantages of VR for Everyday Tasks
VR applications in everyday tasks offer numerous advantages. Increased precision and efficiency are key benefits. Visual aids and step-by-step instructions provided by the VR environment can lead to fewer errors and faster completion times. The immersive nature of VR can also make tasks less tedious, transforming mundane chores into engaging experiences. For example, virtual guidance during complex maintenance tasks can improve safety and prevent damage to physical assets.
Cleaning your house with the Meta Quest 3’s mixed reality features is surprisingly fun! While you’re tackling those virtual chores, you might want to check out some awesome deals on tech like the Microsoft Surface Headphones 2, Apple iPads, and Amazon Echo Show 8. This site has a great roundup of current sales on various electronics, including LG and Lenovo products, perfect for enhancing your mixed reality experience.
Ultimately, the Meta Quest 3’s mixed reality chores are a unique way to enjoy home tasks!
Types of Chores Suitable for Mixed Reality
A wide range of chores can be enhanced or even completely transformed through mixed reality. From simple cleaning tasks to intricate maintenance procedures, VR can streamline and improve various aspects of our daily routines. The ability to visualize the entire task from a digital perspective can be incredibly beneficial in certain scenarios.
Table of Chores and VR Implementations
| Chore Type | VR Tools/Techniques | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning | Interactive 3D models of rooms, augmented reality overlays for cleaning schedules, virtual assistants for task guidance. | Improved cleaning efficiency, visualization of hard-to-reach areas, tailored cleaning strategies. |
| Organizing | Virtual storage solutions, interactive room layouts, augmented reality tools for identifying missing items. | Improved organization, efficient space utilization, reduced time spent searching for items. |
| Maintenance | 3D models of appliances and structures, interactive tutorials for repairs, virtual tools for dismantling and reassembling. | Improved safety during repairs, precise instructions for troubleshooting, reduced risk of damage. |
| Gardening | Virtual tools for planting and pruning, interactive guides for plant care, 3D models of gardens. | Personalized gardening plans, precise measurements and guidance, enhanced safety when using tools. |
Meta Quest 3 Capabilities
The Meta Quest 3, a standalone virtual reality (VR) headset, is increasingly relevant for mixed reality (MR) applications, including chores. Its advanced hardware and software provide a compelling platform for executing and enhancing various tasks within a combined virtual and physical environment. This exploration delves into the key features that support mixed reality chores, comparing its capabilities with other VR/AR headsets and outlining its specifications.The Meta Quest 3’s ability to seamlessly blend virtual elements with the real world is crucial for successful mixed reality chore execution.
This integration allows for intuitive interaction with digital objects and tools, enabling users to perform tasks efficiently and accurately within their physical space.
Key Hardware Features
The Quest 3’s superior processing power, enhanced visuals, and improved tracking contribute significantly to a smoother and more immersive mixed reality experience. This, in turn, directly impacts the user’s ability to perform chores in a virtual environment overlaid onto the real world. The increased resolution and refresh rate, combined with improved eye-tracking and hand-tracking, contribute to a more refined and natural interaction with the virtual environment, leading to greater accuracy and efficiency in mixed reality chore completion.
Software Support for Chores
The Quest 3’s software platform, specifically designed for VR applications, provides a rich ecosystem of tools and functionalities tailored for mixed reality chores. This includes applications and APIs that allow developers to create experiences for various tasks. These functionalities, combined with the hardware, offer opportunities to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in handling chores. Integration with other platforms, including cloud-based services, can facilitate task management, collaboration, and remote assistance, potentially improving the overall workflow.
I’ve been experimenting with Meta Quest 3’s mixed reality chores, and it’s surprisingly intuitive. While navigating those virtual environments, I was reminded of how exciting it is to see older phones like Verizon’s Moto G7 Play and G7 Power finally get Android 10, a significant update that opens up a whole new world of possibilities for users.
It got me thinking, how will these advancements in mobile technology impact the future of mixed reality experiences on the Quest 3?
Comparative Analysis with Other VR/AR Headsets
Compared to other VR/AR headsets, the Quest 3 stands out for its balance of affordability, performance, and ease of use. Its relatively lower price point makes it accessible to a wider range of users, while its impressive processing power allows for more demanding MR experiences. Other headsets might excel in specific areas like specialized tracking or advanced spatial computing, but the Quest 3 offers a comprehensive package suitable for a broader range of mixed reality chore applications.
I’ve been exploring the possibilities of Meta Quest 3 mixed reality chores, and it’s fascinating how these virtual environments could streamline tasks. However, the news about Apple hiring anti-union lawyers from Littler Mendelson to fight the CWA unionization effort really highlights the complex relationship between tech companies and their workforce. This raises some serious questions about worker rights and the future of work in VR. Ultimately, I’m still excited about the potential of Meta Quest 3 for everyday chores, but the larger societal implications are definitely something to consider.
For example, while some high-end AR headsets provide advanced object recognition, the Quest 3 offers a practical solution for a broader range of users who want to integrate virtual elements into their daily lives.
Meta Quest 3 Specifications
| Feature | Description | Impact on Chores |
|---|---|---|
| Display | High-resolution, high refresh rate displays | Improved visual clarity and responsiveness, enabling precise interactions with virtual objects during tasks. |
| Tracking | Advanced eye and hand tracking | Enhanced accuracy and intuitiveness in manipulating virtual tools and objects, leading to greater efficiency in chore completion. |
| Processing Power | Powerful processor for real-time rendering | Smooth and responsive virtual environment, enabling complex interactions without lag, crucial for various chore scenarios. |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity | Facilitates seamless communication and integration with other devices, essential for certain chore workflows and remote assistance. |
| Controllers | Intuitive controllers for manipulation | Enables precise control over virtual objects and tools, contributing to improved accuracy and speed in chore execution. |
User Experience and Interface Design
The user experience (UX) is paramount for a successful mixed reality cleaning chore application. A well-designed interface will guide users intuitively through tasks, making the experience engaging and efficient. This section delves into the crucial aspects of designing a user-friendly interface for a Meta Quest 3-based cleaning application, focusing on the interaction between virtual and real-world elements.
Virtual Cleaning Tools and Object Interaction
A key element of the interface is the design of virtual cleaning tools. These tools need to feel natural and intuitive to use in the mixed reality environment. Users should be able to pick up, manipulate, and use these tools seamlessly within the real world context. For example, a virtual mop should be easily grasped and moved around a virtual representation of a floor.
Similarly, a virtual spray bottle should allow for realistic spraying actions, and a dustpan should permit easy picking up of virtual debris.
- Intuitive Controls: Virtual tools should respond to natural hand gestures. For instance, a swipe gesture could simulate spraying a cleaning solution, and a pinching gesture could pick up virtual debris. Voice commands can provide an alternative, especially when users are wearing gloves or have limited hand dexterity.
- Haptic Feedback: Adding haptic feedback to the interaction with virtual tools can further enhance the realism and user experience. The virtual mop could provide resistance when encountering virtual dirt, while the spray bottle could simulate the feel of pressure when spraying.
- Visual Cues: Visual cues, such as highlighting dirty areas, or indicating the progress of a cleaning task, will help users stay engaged and informed. A virtual ‘dirty spot’ marker could visually guide the user toward the specific area that needs attention.
Mixed Reality Task Guidance
The application should guide users through the cleaning task in a clear and unambiguous manner. This is crucial for both new and experienced users.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: The interface should provide clear step-by-step instructions within the mixed reality environment. These instructions could be displayed as holographic overlays or as text projected onto surfaces.
- Spatial Guidance: The application can use virtual arrows or other visual aids to guide the user’s movement and placement of cleaning tools in the real world. A virtual arrow could point toward a specific area of a room that needs cleaning.
- Interactive Room Models: A virtual representation of the room could be interactive, highlighting specific areas needing cleaning, showing the progress of the cleaning task, or even displaying detailed cleaning instructions in relation to the real-world room.
Interface Design Comparison
Different interface designs offer varying strengths and weaknesses. A comparative analysis helps in selecting the optimal approach.
| Interface Design | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Holographic Overlays | Intuitive, immersive, and clear visual cues. | Can be distracting if overly complex. May require more processing power. |
| Projected Instructions | Easy to understand, less immersive. | May not be suitable for all types of cleaning tasks. |
| Virtual Room Models | Allows for comprehensive cleaning task guidance and monitoring. | Requires more processing power and potentially more complex interaction design. |
Challenges and Limitations
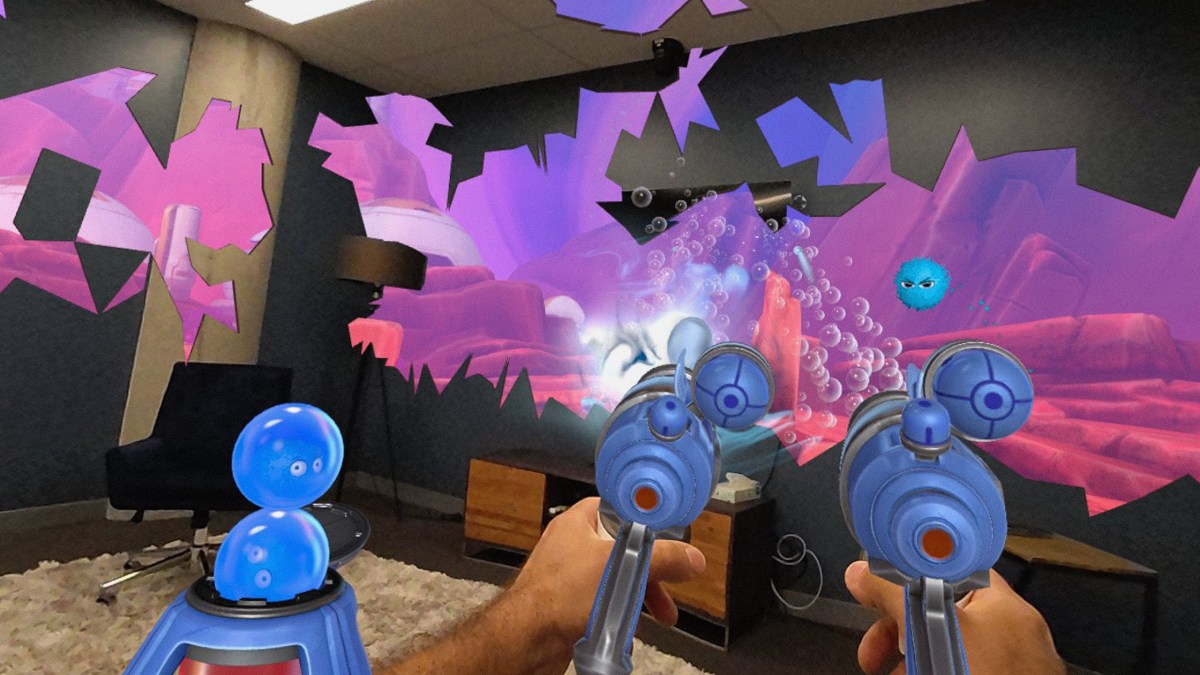

Mixed reality chores on the Meta Quest 3, while promising, face inherent technical and user experience hurdles. Careful consideration of these limitations is crucial for successful development and adoption. This section delves into potential challenges, outlining possible solutions, and highlighting critical security and privacy concerns.
Technical Limitations
The Meta Quest 3, while powerful, has limitations impacting mixed reality chore applications. Processing power, sensor accuracy, and the complexity of environmental interaction are key factors. Real-time tracking and rendering of virtual objects within the physical environment can be computationally demanding. Insufficient processing power could lead to lag or visual glitches, impacting the user’s experience. Furthermore, the accuracy of the sensors used for depth perception and object recognition might not be perfect in all scenarios, leading to inaccuracies in virtual object placement or tracking.
User Experience Challenges
User experience is paramount in the adoption of mixed reality chores. Intuitive interfaces and natural interaction methods are vital. The learning curve for new users can be significant. Providing clear instructions, intuitive controls, and comprehensive tutorials can mitigate this issue. Users might find the task itself too complex, or the environment too demanding for certain chores.
Tailoring the application to specific user skill levels and task complexity is a critical aspect of design.
Security and Privacy Concerns, Meta quest 3 mixed reality chores
Security and privacy are paramount when handling personal data within mixed reality chores. Data encryption and secure storage of user data are essential. Data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information could have significant repercussions. Clear data usage policies and user consent procedures are crucial for building trust. Implementing robust authentication protocols, access controls, and secure data transmission channels is critical.
Real-World Problems and Technological Solutions
Many real-world scenarios benefit from mixed reality chore applications. For instance, elderly care can leverage mixed reality to guide users through exercises or provide reminders. This technology can assist in maintenance tasks, ensuring accuracy and efficiency. In construction, virtual overlays can guide workers through complex procedures, minimizing errors and ensuring safety. Similarly, home maintenance can be improved with clear virtual instructions overlaid on physical spaces.
Table of Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Description | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Computational Demands | Real-time tracking and rendering can be computationally intensive, leading to lag and glitches. | Optimizing algorithms, utilizing cloud-based processing, and prioritizing visual fidelity based on task requirements. |
| Sensor Accuracy | Depth perception and object recognition sensors might not be perfect, resulting in inaccuracies. | Utilizing multiple sensor types, implementing advanced calibration routines, and employing error correction algorithms. |
| User Experience Complexity | Users might struggle with complex interactions or a steep learning curve. | Intuitive interface design, clear instructions, detailed tutorials, and customizable difficulty settings. |
| Security and Privacy | Data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information are potential risks. | Implementing robust encryption, secure data storage, and clear data usage policies with user consent. |
Future Trends and Applications: Meta Quest 3 Mixed Reality Chores
Mixed reality chores, particularly on platforms like Meta Quest 3, are poised for significant expansion beyond their current applications. The potential for integration across various sectors is immense, promising to reshape how tasks are performed and managed. This section explores the future applications of mixed reality chore systems, emphasizing advancements in technology and practical use cases.The transformative power of mixed reality in chores lies in its ability to overlay digital information onto the physical world.
This augmentation enhances efficiency and reduces the margin for error. As technology matures and user interfaces become more intuitive, we can anticipate a wider adoption of mixed reality chore applications across diverse industries.
Potential Sectors for Adoption
Mixed reality chore applications have the potential to revolutionize several sectors. Their ability to provide real-time guidance and feedback is particularly valuable in environments where precision and safety are paramount.
- Construction and Engineering: Mixed reality can guide workers through complex assembly procedures, highlighting critical steps and providing real-time feedback on alignment and measurements. This precision can reduce errors, minimize rework, and improve safety on job sites. For instance, a construction worker could use mixed reality to visualize and align prefabricated components in a building, ensuring accurate placement and structural integrity.
- Manufacturing and Assembly: Mixed reality can streamline assembly lines by providing workers with step-by-step instructions overlaid on the components they are working with. Real-time instructions, alongside interactive 3D models, can improve accuracy and reduce errors, leading to higher productivity and reduced training times. For example, a worker assembling a complex electronic device can receive precise guidance on connecting wires and components, visualized directly within the device.
- Healthcare: Surgical procedures could benefit from mixed reality overlays, guiding surgeons through intricate anatomical structures and providing real-time feedback on their actions. This precision and support can lead to more accurate procedures, reducing complications and improving patient outcomes. Imagine a surgeon using mixed reality to see a patient’s anatomy overlaid on their body during a delicate operation.
- Home Maintenance and Repair: Users can access step-by-step instructions and interactive tutorials for home repairs, enabling them to tackle tasks with confidence and accuracy. This can reduce reliance on professionals for minor repairs and encourage DIY approaches. A homeowner could use mixed reality to visualize the placement of electrical components during a home renovation, ensuring correct wiring and preventing electrical hazards.
Technological Advancements
Further advancements in mixed reality technology, particularly in areas like haptics and gesture recognition, will significantly enhance the functionality of these applications.
- Improved Haptic Feedback: Enhanced haptic feedback systems will allow users to experience more realistic and intuitive interactions with virtual objects and environments. This improved tactile sensation will make mixed reality chores feel more natural and less like a disembodied experience.
- Enhanced Gesture Recognition: More accurate and responsive gesture recognition systems will improve user experience, allowing users to control and manipulate virtual objects with greater precision and ease. This could reduce the need for complex controllers, leading to a more intuitive interaction paradigm.
- Integration with IoT Devices: Seamless integration with IoT devices can allow mixed reality chore applications to monitor and adjust to real-time conditions. This enables more dynamic and adaptable workflows, especially in environments with changing parameters.
Future Use Cases
The potential applications extend beyond the described sectors, and we can anticipate further innovations in the future.
- Virtual Training and Simulation: Mixed reality chore applications can provide realistic simulations of complex procedures, allowing users to practice and refine their skills in a safe and controlled environment. This can be invaluable for training professionals in various fields, from construction to medicine.
- Remote Assistance: Experts can remotely guide technicians or users through complex tasks, providing real-time support and guidance. This can prove useful in situations where specialized expertise is needed, and travel is not practical.
- Interactive Maintenance: Mixed reality can provide real-time feedback and guidance during maintenance tasks, allowing users to identify and fix issues quickly and efficiently. Imagine a mechanic using mixed reality to visualize the inner workings of a complex engine and identify faults or required repairs.
Illustrative Examples of Mixed Reality Chores
Mixed reality chores offer exciting possibilities for simplifying and enhancing everyday tasks. This section explores a specific scenario of virtual furniture assembly, showcasing how mixed reality can interact with the real world to make complex tasks more intuitive and efficient.The virtual augmentation of physical space allows users to experience tasks in a more interactive and engaging manner than traditional methods.
This improved user experience is crucial for mixed reality chore applications, as users need to feel comfortable and confident in using these new tools.
Virtual Furniture Assembly Scenario
This scenario details a step-by-step process for assembling a virtual bookshelf using the Meta Quest 3. The experience leverages the device’s spatial awareness and hand tracking capabilities.
The user interface presents a 3D model of the bookshelf, overlaid onto the real-world environment. The virtual components of the bookshelf are clearly labeled and color-coded. Intuitive interaction tools, such as hand gestures and voice commands, are available for manipulating the virtual parts.
Step-by-Step Assembly Guide
- Initial Setup: The user initiates the assembly by activating the mixed reality application on their Meta Quest 3. The application scans the room using the device’s sensors and projects the virtual bookshelf model onto the chosen wall. The user can adjust the position and orientation of the virtual bookshelf using hand gestures.
- Component Selection: The user selects the necessary virtual components from a virtual inventory. The components appear as translucent holograms, allowing the user to visualize how they fit together before physical placement.
- Component Placement: The user uses hand gestures to precisely position each component on the virtual bookshelf. Visual cues and haptic feedback confirm proper alignment. The application will provide an audio cue and a visual confirmation when the piece is properly placed.
- Connection and Locking: Once all the components are in place, the application guides the user through the connection and locking process. The user interacts with virtual connection points on the components using hand gestures, and the application visually highlights the necessary steps and provides audio instructions.
- Verification and Completion: After the final component is in place, the user verifies the complete assembly using a virtual checkmark. The application confirms the successful completion of the assembly and displays the assembled bookshelf in a more solid, non-translucent state.
Interaction between Virtual and Real Worlds
The mixed reality environment seamlessly blends virtual and real elements. The virtual bookshelf model is anchored to the user’s real-world environment, enabling the user to manipulate the components within that environment. The real-world surface the bookshelf is to be placed on, along with the real-world lighting and shadows, influences the display of the virtual components. The virtual bookshelf model is anchored to the real-world environment through the use of augmented reality markers and spatial mapping technology.
Real-world objects are not obstructed by the virtual model, and the user can still interact with physical objects around the virtual bookshelf.
Mixed Reality Chore Environment Illustration
Imagine a living room. On a wall, a virtual bookshelf is displayed. The virtual bookshelf’s components are translucent, allowing the user to see the real wall beneath. The components of the bookshelf are brightly colored and easily identifiable. The real-world furniture and objects remain visible and interactive, not obstructed by the virtual bookshelf.
The user’s hands are tracked, and their movements precisely position the virtual components, with clear visual and auditory feedback. The real-world lighting and shadows cast by the real-world objects are visible through the virtual components, creating a seamless blend of the two realities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mixed reality chores, particularly those implemented via Meta Quest 3, offer intriguing possibilities for reducing our environmental footprint. While the technology itself has an energy consumption profile, careful design and application can lead to significant positive impacts on resource use and waste generation. The potential for reducing physical labor, optimizing material use, and promoting sustainable practices is substantial.The core benefit lies in the ability to virtually simulate tasks, optimize processes, and reduce the need for physical materials and energy-intensive procedures.
This virtual realm can serve as a powerful tool for promoting more sustainable approaches to everyday chores. By understanding the environmental impact of these virtual tools and processes, we can assess the true sustainability benefits and ensure responsible implementation.
Environmental Impact of Physical Chores
Traditional chore methods, often relying on physical materials and energy-consuming processes, have a substantial environmental footprint. Consider the energy consumption associated with transportation to the hardware store, the manufacturing processes for physical tools and supplies, and the disposal of materials. Furthermore, physical labor often involves significant energy expenditure, adding to the overall carbon footprint.
Potential for Reduced Energy Consumption
Mixed reality chores can significantly reduce energy consumption through several mechanisms. Virtual planning and optimization can lead to more efficient material use and reduce waste. For example, a virtual layout of a room allows for a more precise measurement of materials needed, minimizing waste and reducing the need for multiple trips to the hardware store. Virtual simulations can also optimize energy usage during physical tasks, allowing for the most efficient methods to be employed.
Furthermore, remote assistance, where a virtual expert can guide a user through a task, can minimize the need for physical travel or physical tool use, thus decreasing the overall energy expenditure.
Potential for Reduced Material Waste
The virtual nature of mixed reality chores allows for significant reductions in material waste. Virtual simulations enable precise measurements and estimations, reducing the amount of material ordered or purchased. For instance, a virtual paint job allows for a precise calculation of the required paint, preventing over-ordering and subsequent waste. The reduction in physical tools and materials also translates to a smaller environmental impact from manufacturing, transportation, and disposal.
Virtual simulations can also identify potential waste in the process and guide users to more sustainable methods, potentially reducing the need for specific physical materials entirely.
Sustainable Aspects of the Technology
The sustainable aspects of mixed reality chores extend beyond reduced material and energy consumption. Virtual training and tutorials, integrated into the mixed reality experience, can foster a greater understanding of sustainable practices. This understanding can be applied to physical chores, promoting a shift toward environmentally conscious habits. Additionally, virtual tools can provide feedback and guidance, ensuring that users employ the most sustainable approaches.
For example, a virtual tool that calculates the optimal route for recycling can incentivize and guide users towards environmentally friendly behaviors.
Examples of Sustainable Applications
Virtual gardening applications can help users understand plant care and water usage. Virtual home maintenance tools can assist in understanding the most efficient approaches to maintenance, including the use of eco-friendly products and techniques. Similarly, a virtual construction tool can help plan projects with a focus on sustainable materials and methods.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the integration of Meta Quest 3 with mixed reality chores presents a promising future. While challenges remain, the potential for improved efficiency, user experience, and even sustainability is significant. From cleaning to complex repairs, the potential applications are vast, hinting at a paradigm shift in how we approach everyday tasks. The future of home management might be more interactive, engaging, and even enjoyable than we previously imagined.












