Latin America malware update reveals a complex cybersecurity landscape. This in-depth analysis explores the evolving threats, impact on economies, and cybersecurity measures employed across the region. From prevalent malware types and attack vectors to the financial consequences and mitigation strategies, this comprehensive overview provides critical insights into the current state of digital security in Latin America.
The report examines recent malware trends, analyzing the most common types, tactics, and attack vectors targeting various sectors. It delves into the economic ramifications, including financial losses, reputational damage, and the erosion of public trust. The report further assesses the cybersecurity infrastructure of different Latin American countries, highlighting strengths and weaknesses in their policies and practices.
Recent Malware Trends in Latin America: Latin America Malware Update
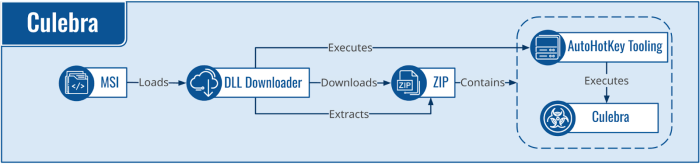
Latin America has seen a concerning surge in malware activity over the past year, highlighting the region’s vulnerability to evolving cyber threats. This increase is driven by factors like a growing digital infrastructure, coupled with a sometimes less robust cybersecurity posture in various sectors. Understanding these trends is crucial for proactive defense strategies.The prevalent malware types, tactics employed, and attack vectors used against different sectors are detailed below.
This analysis aims to provide insights into the current threat landscape and aid in developing more effective security measures.
Prevalence of Malware Types
The following table summarizes the frequency of various malware types impacting Latin America in the past year. Data sources include reports from cybersecurity firms, incident response teams, and government agencies. While precise figures are often difficult to obtain due to reporting inconsistencies, the data presented provides a general overview of the situation.
| Malware Type | Frequency | Sector Targeted | Attack Vector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware | High | Finance, Healthcare, Government | Phishing emails, exploit kits, vulnerable software |
| Trojan Horses | Moderate | Finance, Government | Malicious attachments, compromised websites, social engineering |
| Spyware | Moderate | Finance, Healthcare | Malicious websites, infected software, compromised devices |
| Keyloggers | Low | Finance | Phishing attacks, malicious websites, compromised devices |
| Banking Trojans | High | Finance | Phishing attacks, malicious websites, infected software |
Malware Tactics Against Specific Sectors, Latin america malware update
Malware tactics vary significantly across different sectors. The finance sector, for instance, often faces targeted attacks with sophisticated ransomware campaigns designed to extort financial gains. Attackers frequently use phishing emails disguised as legitimate banking communications to gain initial access. In healthcare, malware can disrupt critical operations, leading to patient data breaches and potential harm. Government sectors are also vulnerable, with attackers seeking to disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, or cause reputational damage.
The tactics employed often involve exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated systems or employing social engineering to manipulate individuals.
Attack Vectors Employed in Latin America
Cybercriminals targeting Latin America frequently utilize common attack vectors. Phishing emails remain a prevalent method, capitalizing on the region’s unique linguistic and cultural nuances. Compromised websites, often used to distribute malware, pose a significant threat. Vulnerabilities in outdated software, which are often deployed in Latin American institutions, are commonly exploited. Social engineering tactics, leveraging trust and human error, are increasingly used to gain access to sensitive data.
Specific Examples of Recent Attacks
A notable recent attack involved a large financial institution in Brazil being hit with a ransomware attack. The attackers encrypted critical systems and demanded a substantial ransom for their release. Similarly, a major healthcare provider in Mexico suffered a data breach due to a sophisticated phishing campaign that targeted employees. These examples underscore the critical need for stronger security measures across all sectors.
Impact of Malware on Latin American Economies
Malware attacks are no longer a niche problem confined to large corporations. They are a significant threat to the economies of Latin American countries, impacting businesses of all sizes, from small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to multinational corporations. The financial repercussions, reputational damage, and erosion of public trust are substantial and far-reaching.
Financial Repercussions of Malware Attacks
Malware attacks often result in significant financial losses for Latin American businesses. These losses can stem from direct costs associated with recovery, such as data restoration, forensic analysis, and legal fees. Indirect costs, such as lost productivity, decreased sales, and disruption of supply chains, can be equally, if not more, damaging. The disruption of critical infrastructure, like energy grids or financial systems, can have devastating cascading effects on the entire economy.
Estimates vary widely, but the potential for substantial financial damage is a critical concern for businesses across Latin America.
Data Breaches and Damaged Company Reputation
Data breaches, often a consequence of malware attacks, can irreparably harm the reputation of Latin American companies. The theft or compromise of sensitive customer data, such as financial information or personal details, can lead to a loss of consumer trust and damage brand image. This reputational damage can be particularly severe in sectors that deal directly with personal information, like banking and healthcare.
Companies may face lawsuits, regulatory fines, and difficulty attracting and retaining customers.
Consequences of Malware Attacks on Public Trust
Malware attacks can erode public trust in digital services. When individuals or businesses experience financial losses or data breaches, their faith in the security and reliability of digital platforms can be shaken. This loss of public trust can negatively affect the adoption of digital technologies and hamper economic development. Instances of attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power grids, can cause widespread panic and social unrest.
Specific Instances of Malware Attacks and Economic Impacts
Unfortunately, specific examples of malware attacks and their precise economic impacts in Latin America are often not publicly reported due to privacy concerns or for competitive reasons. However, news reports frequently detail attacks on financial institutions and other critical sectors, highlighting the potential for significant economic disruption. The impact of these attacks is often multifaceted, involving direct financial losses, reputational damage, and a reduction in public confidence in digital platforms.
Latin America’s malware situation is definitely concerning. Recent updates highlight a surge in sophisticated attacks, potentially linked to geopolitical tensions like the complex trade disputes between the US and China, including the trump tim cook tariffs samsung china trade war. These global economic battles seem to be creating fertile ground for cybercriminals, impacting digital security in the region and beyond.
The region’s digital defenses need urgent bolstering.
| Sector | Financial Impact (Estimated) | Data Breach Impact | Reputation Damage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Institutions | Millions to billions of dollars in losses | Loss of customer trust, potential for fraud, and regulatory penalties | Significant damage to brand image, difficulty attracting new customers |
| Healthcare | Significant costs for data restoration and legal fees | Compromised patient records, potential for identity theft | Erosion of patient trust, legal repercussions, difficulty in attracting new patients |
| Retail | Lost sales, potential for fraud, and operational disruption | Exposure of customer credit card details, leading to potential financial losses for customers | Reduced customer confidence, potential for brand boycotts |
| Government Agencies | Disruption of services, loss of public trust | Compromise of sensitive government data, potential for corruption and abuse of power | Loss of public confidence in government institutions, negative impact on democratic processes |
Cybersecurity Measures in Latin American Countries
Latin America faces a complex cybersecurity landscape, characterized by varying levels of technological advancement and economic disparities. While some nations have made strides in establishing robust cybersecurity frameworks, others grapple with significant gaps in policies and resources. This uneven playing field leaves the region vulnerable to sophisticated cyber threats, impacting both individuals and national economies.Cybersecurity infrastructure in Latin America demonstrates a diverse range of approaches.
Some countries have established dedicated cybersecurity agencies and implemented national strategies, while others rely more heavily on industry initiatives and international collaborations. This variation in approach highlights the unique challenges and priorities faced by each nation.
Cybersecurity Policies and Practices Across Latin America
Latin American countries vary significantly in their cybersecurity policies and practices. Factors such as economic development, political stability, and the level of digital penetration influence the extent and effectiveness of cybersecurity measures. This diversity presents both opportunities and challenges in fostering a coordinated regional approach to cyber threats.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Cybersecurity Strategies
| Country | Cybersecurity Policies | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Brazil has a National Cybersecurity Strategy, with dedicated agencies like the National Security Council (NSC) responsible for policy and enforcement. | Well-defined national strategy, strong presence of cybersecurity agencies, significant investment in research and development. | Implementation challenges, potential for bureaucratic inefficiencies, limited resources for smaller businesses and regions. |
| Mexico | Mexico has a growing awareness of cybersecurity, with policies and strategies aimed at protecting critical infrastructure and promoting cybersecurity awareness. | Growing emphasis on cybersecurity in recent years, focus on critical infrastructure protection, increased awareness campaigns. | Lack of consistent enforcement, need for stronger collaboration between government agencies, insufficient resources for smaller businesses and municipalities. |
| Chile | Chile has implemented cybersecurity policies and strategies to address vulnerabilities in digital infrastructure. | Strong emphasis on international cooperation, advanced digital infrastructure, proactive approach to cybersecurity threats. | Limited resources for public awareness programs, potential for policy gaps in specific sectors, need for consistent enforcement mechanisms. |
| Argentina | Argentina has recognized the need for cybersecurity measures, though the implementation of policies and strategies may be less developed than in other countries. | Increasing emphasis on cybersecurity, collaborations with international organizations, commitment to improving infrastructure. | Limited resources for cybersecurity professionals and training, potential gaps in policy enforcement, inconsistent application of cybersecurity standards across sectors. |
| Colombia | Colombia has demonstrated a commitment to strengthening cybersecurity, but the level of implementation varies depending on the specific sector. | Active engagement with international cybersecurity communities, increasing awareness among businesses, focus on critical infrastructure protection. | Lack of specialized cybersecurity personnel, need for improved coordination among government agencies, limited resources to support smaller organizations. |
The table above provides a snapshot of cybersecurity strategies across several Latin American nations. It’s crucial to note that this is not an exhaustive list and the cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving. Further research into specific policies and initiatives within each country is recommended for a more comprehensive understanding. The presented data serves as a starting point for a deeper dive into the specifics of each nation’s approach.
Latin America is seeing a concerning spike in malware activity lately. While the specifics are still emerging, it’s a worrying trend. This recent surge in malicious software is particularly troubling, considering the potential impact on critical infrastructure, and the ongoing efforts to secure EV battery technology, like the Stellantis Samsung DOE ATVM EV battery loan program, which is aiming to boost the adoption of electric vehicles.
The malware situation in Latin America warrants continued vigilance and proactive measures.
Malware Mitigation Strategies for Latin America
Latin America faces a complex cybersecurity landscape, where malware threats are constantly evolving and adapting to vulnerabilities in both organizations and individuals. Effective mitigation strategies are crucial for safeguarding critical infrastructure, protecting sensitive data, and fostering economic stability. This requires a multi-faceted approach that goes beyond simple technical solutions to encompass cultural shifts in awareness and education.Addressing the specific challenges faced by Latin American countries necessitates a tailored approach.
The varying levels of digital literacy, economic disparities, and regulatory frameworks influence the effectiveness of different security measures. A unified strategy must consider these nuances while remaining adaptable to emerging threats.
Strengthening Security Protocols
Robust security protocols are the foundation of any successful malware mitigation strategy. These protocols should be comprehensive, encompassing a variety of preventative measures. Implementing strong passwords, employing multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating software are essential elements. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify potential vulnerabilities and address them proactively.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple verification methods (e.g., password, code from a mobile device) to access accounts. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if a password is compromised. Examples include authenticator apps and security tokens. Failure to implement MFA can expose systems to phishing and credential stuffing attacks.
- Regular software updates: Malware often exploits vulnerabilities in outdated software. Ensuring that operating systems, applications, and security software are up-to-date with the latest patches is crucial. Scheduled automated updates can streamline this process and minimize the window of vulnerability.
- Strong password policies: Creating and enforcing strong password policies is vital. These policies should mandate the use of complex passwords, encourage frequent password changes, and discourage the reuse of passwords across multiple accounts. Password managers can help users create and manage strong, unique passwords.
- Employee training programs: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices is crucial. Training programs should cover topics like phishing awareness, safe browsing habits, and recognizing suspicious emails and attachments. Regularly updating these training programs is critical to address evolving threats and tactics.
Promoting Cybersecurity Awareness and Education
A significant portion of malware infections stem from user errors, particularly those related to phishing and social engineering attacks. Raising cybersecurity awareness and education levels across the region is paramount. Tailored educational programs that cater to diverse literacy levels and cultural backgrounds are essential.
- Targeted awareness campaigns: Public awareness campaigns can reach a broad audience, especially those with limited digital literacy. These campaigns can use various media, including social media, radio, and television, to disseminate key cybersecurity messages.
- Community outreach programs: Engaging with local communities through workshops, seminars, and interactive sessions can foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness. This approach is particularly beneficial for underserved populations.
- Educational resources for schools and businesses: Integrating cybersecurity education into school curricula and workplace training programs is essential. This will instill a culture of cybersecurity awareness from an early age.
Protecting Businesses and Individuals
Businesses and individuals can implement several proactive measures to protect themselves from malware attacks. This includes employing robust antivirus software, regularly backing up data, and using secure networks.
- Robust antivirus software: Employing up-to-date antivirus and anti-malware software is crucial for detecting and removing malicious software from devices. Real-time scanning and regular virus definition updates are key features.
- Regular data backups: Regularly backing up important data to an external hard drive or cloud storage ensures data recovery in case of infection or device failure. This is especially important for critical business data.
- Secure networks: Using strong Wi-Fi passwords, avoiding public Wi-Fi when possible, and using a virtual private network (VPN) can enhance network security.
International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential in addressing regional malware threats. Sharing information, best practices, and resources across borders can help Latin American countries develop more robust cybersecurity defenses.
- Information sharing agreements: Establish agreements between countries to facilitate the exchange of threat intelligence, allowing for quicker responses to emerging threats.
- Joint cybersecurity exercises: Conduct joint exercises and training programs to improve coordination and collaboration between different countries in responding to large-scale cyberattacks.
- Capacity building programs: Supporting the development of cybersecurity skills and infrastructure in Latin American countries through international partnerships can enhance regional resilience.
Emerging Malware Threats in Latin America
Latin America’s rapidly evolving digital landscape presents a unique set of challenges for cybersecurity. As economies become more reliant on technology, the potential for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities increases. This necessitates a proactive approach to understanding emerging threats and adapting security strategies accordingly.The digitalization of Latin American economies has fostered the growth of new and sophisticated malware, requiring a comprehensive understanding of the evolving landscape to effectively counter these threats.
Latin America is seeing a surge in malware, a worrying trend. While this is concerning, it’s important to consider the broader digital landscape. Parents’ concerns about TikTok’s content, especially given the recent news about TikTok’s warning labels won’t ease parental concerns over app content , highlight a larger issue of online safety. Ultimately, staying vigilant about online threats in Latin America remains crucial.
Emerging Malware Trends
The malware landscape in Latin America is shifting, with new threats emerging and existing ones adapting. These evolving threats often leverage the region’s specific technological infrastructure and economic conditions. Sophisticated attacks are becoming increasingly common, highlighting the need for robust security measures and proactive threat intelligence.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): The rise of RaaS platforms allows even less-skilled actors to launch sophisticated ransomware campaigns. This democratization of attack tools has led to an increase in targeted ransomware attacks against businesses and critical infrastructure. For instance, attacks on healthcare facilities and financial institutions are becoming more common, causing significant disruptions and financial losses.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Latin American businesses are increasingly vulnerable to supply chain attacks. Malicious actors can infiltrate software or hardware components supplied to organizations, potentially gaining access to sensitive data or causing widespread disruptions. These attacks often exploit the lack of robust security protocols in supply chains.
- Targeted Phishing Campaigns: Sophisticated phishing campaigns are designed to target specific individuals or organizations within Latin America. These attacks often leverage social engineering techniques and exploit regional cultural nuances to increase success rates. This requires businesses to educate employees on recognizing and avoiding phishing scams.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
The digitalization of Latin American economies, while bringing opportunities, also presents new vulnerabilities. The proliferation of interconnected devices, coupled with the often-limited cybersecurity resources of smaller businesses, creates an environment ripe for exploitation. Malware can leverage these vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive data, disrupt operations, or cause significant financial losses.
- Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness: Limited cybersecurity awareness among users and organizations remains a significant vulnerability. Malware often relies on human error, and effective security strategies must address this critical weakness. Training and awareness programs are essential to mitigating this risk.
- Limited Cybersecurity Resources: Many smaller businesses and organizations in Latin America may lack the resources to implement comprehensive cybersecurity measures. This makes them particularly susceptible to attacks, and collaborative efforts to provide support and resources are essential.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Limited internet infrastructure and digital literacy in some areas can contribute to vulnerabilities. Malware can target these gaps to spread rapidly and gain access to networks. Strengthening infrastructure and promoting digital literacy can help mitigate this vulnerability.
Comparison with Historical Patterns
Historical malware trends in Latin America often focused on simpler, mass-scale attacks. However, the sophistication and targeting of recent threats are markedly different. Today’s malware is often designed to target specific vulnerabilities within individual organizations, leveraging more sophisticated techniques. This shift demands a more proactive and targeted security approach.
Impact of Digitalization
The digitalization of Latin American economies has dramatically increased the potential for new malware types. As more businesses and individuals adopt digital services, the attack surface grows exponentially. This necessitates a shift from reactive to proactive cybersecurity measures.
Example: A sophisticated ransomware targeting specific industries, such as financial institutions, is a significant emerging threat. This type of attack often leverages advanced techniques to bypass traditional security measures and encrypt sensitive data, demanding substantial payments for decryption.
Case Studies of Latin American Malware Attacks
Latin America, a region with a rapidly growing digital landscape, is increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated malware attacks. These attacks, ranging from targeted ransomware campaigns to widespread phishing scams, have significant economic and societal consequences. Understanding these attacks, their motivations, and the responses of affected organizations is crucial for building stronger cybersecurity defenses.Malware attacks in Latin America often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated systems, a lack of cybersecurity awareness among users, and the complexity of regulatory frameworks.
The motivations behind these attacks can vary from financial gain to political or ideological objectives. This section examines notable cases, focusing on the tactics employed, the financial impact, and the effectiveness of recovery strategies.
Recent Notable Malware Attacks
Several recent malware attacks have targeted organizations across Latin America. These incidents demonstrate the evolving tactics of cybercriminals and the need for proactive cybersecurity measures. Attacks frequently involve exploiting known vulnerabilities in software, leading to widespread infections and data breaches.
Motivations and Tactics of Attackers
Attackers’ motivations vary, but financial gain is a primary driver. Ransomware attacks, for example, often target organizations with critical infrastructure or sensitive data, aiming to extort substantial sums of money. Phishing campaigns, which aim to trick users into revealing sensitive information, often target specific demographics, leveraging social engineering tactics.
Responses and Recovery Strategies
The responses of affected organizations to these attacks vary significantly. Some organizations prioritize immediate data recovery, often paying ransom demands. Others focus on incident response, implementing security measures to prevent future attacks. This includes conducting forensic investigations, patching vulnerabilities, and educating employees on cybersecurity best practices. Effective incident response plans are essential for mitigating the impact of an attack and minimizing long-term damage.
Financial Losses Incurred
The financial losses incurred by organizations due to these attacks can be substantial. Ransom payments, recovery costs, legal fees, and lost productivity can cripple smaller businesses and significantly impact larger organizations. Data breaches can also result in significant fines under data protection regulations, adding to the financial burden. Quantitative data on these losses is often difficult to obtain, making it challenging to fully assess the scale of the problem.
For instance, in a recent case of a large retail chain in Brazil, ransomware attackers demanded a considerable sum to unlock encrypted data. This incident illustrates the considerable financial strain that ransomware attacks can impose.
Example: Ransomware Attack on a Brazilian Bank
In 2023, a major Brazilian bank faced a ransomware attack. The attackers encrypted critical systems, demanding a substantial ransom for decryption. The bank initially considered paying the ransom, but instead prioritized a robust incident response plan. This included isolating the infected systems, restoring data from backups, and implementing enhanced security measures. The bank engaged cybersecurity experts to assess the attack and implement long-term solutions.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the Latin America malware update paints a concerning but actionable picture of the region’s digital security challenges. While the evolving malware landscape presents significant threats, the report also underscores the importance of proactive mitigation strategies, robust cybersecurity policies, and international cooperation. By understanding the emerging threats and implementing effective countermeasures, Latin American nations can fortify their digital defenses and safeguard their economies.