It was a rocky year for the solar industry what comes next is uncertain – It was a rocky year for the solar industry, and what comes next is uncertain. Challenges ranged from fluctuating economic factors and material costs to evolving consumer preferences and adoption rates. Manufacturing, installation, financing – all segments felt the impact. This article delves into the key hurdles, potential technological advancements, and the potential future scenarios shaping the solar industry’s trajectory.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders and investors looking to navigate the evolving landscape.
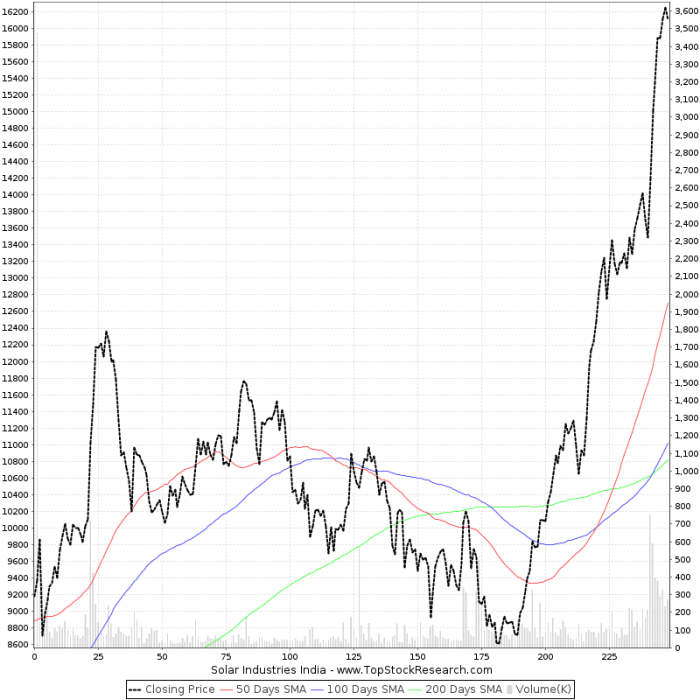
The past year presented a complex picture for the solar industry, with economic indicators playing a significant role in its performance. Government policies and incentives, as well as the cost of solar energy compared to other energy sources, have been scrutinized. A detailed analysis of financial metrics, and the performance of top solar companies, reveals the economic struggles. These factors, combined with shifts in market trends and consumer behavior, contribute to the current uncertainty surrounding the future of the industry.
Overview of the Solar Industry’s Challenges: It Was A Rocky Year For The Solar Industry What Comes Next Is Uncertain
The solar industry, a cornerstone of the global energy transition, experienced a tumultuous year. Facing headwinds from geopolitical instability, supply chain disruptions, and fluctuating material costs, the sector navigated a complex landscape. The precise trajectory of future growth remains uncertain, prompting critical examination of the challenges and potential responses.
Major Challenges Faced
The past year presented several significant hurdles for the solar industry. These included escalating material costs, particularly for crucial components like polysilicon and wafers, directly impacting manufacturing profitability. Geopolitical tensions further complicated the situation by disrupting supply chains and influencing trade policies. This created volatility in the market, impacting both manufacturers and installers. The industry also faced increased competition, both from established and emerging players.
Furthermore, fluctuating energy prices and changing policy landscapes introduced further uncertainty, making long-term planning difficult.
Factors Contributing to Difficulties
Several factors intertwined to create the challenging environment. The global semiconductor shortage, impacting the production of solar panels, was a key driver. The war in Ukraine significantly disrupted the supply chain for raw materials, especially polysilicon, driving up costs. Furthermore, fluctuating energy prices globally impacted the perceived value proposition of solar installations, particularly when compared to traditional energy sources.
A notable example of this is the recent rise in natural gas prices in Europe, which temporarily decreased the economic attractiveness of solar power.
Impact on Industry Segments
The challenges reverberated across the solar industry, impacting various segments differently. Manufacturing faced immense pressure from rising material costs, potentially leading to reduced output or even factory closures. Installers were confronted with increased project costs, which might reduce the number of installations and potentially impact employment in the sector. Financing institutions experienced uncertainty regarding project returns, potentially leading to a reluctance to invest in new projects.
Finally, consumer confidence in solar energy projects was likely affected by price volatility and the uncertainty surrounding future energy prices.
Comparative Performance of Solar Technologies
| Technology | Performance (Estimated % Change in Market Share) | Factors Influencing Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Mono-crystalline Silicon | +10% | High efficiency and established market position. |
| Poly-crystalline Silicon | -5% | Higher material costs and slightly lower efficiency than mono-crystalline. |
| Thin-film Solar | +2% | Lower material costs, flexible design. |
| Perovskite Solar | +15% | High efficiency potential, ongoing research and development. |
The table above presents an estimated comparative performance of various solar technologies during the past year. These estimates are based on market share projections and are subject to change as new data emerges. The factors influencing the performance of each technology are highlighted to offer a clearer understanding of the market dynamics. It’s important to note that these are estimations and may not accurately reflect the exact performance of every individual project.
Economic Factors Influencing the Industry
The solar industry, a crucial player in the global energy transition, experienced a turbulent year marked by fluctuating economic conditions. From rising material costs to shifts in government incentives, a complex interplay of factors shaped the industry’s performance. Understanding these forces is vital for anticipating future trends and navigating the uncertainties ahead.Economic indicators significantly impacted the industry’s performance.
Inflation, a global concern, led to higher production costs for solar panels and other components, squeezing profit margins for manufacturers and installers. Interest rates, another key economic factor, influenced borrowing costs, impacting project financing and consumer adoption. Furthermore, global geopolitical events, such as supply chain disruptions, had ripple effects on the industry, impacting the availability and pricing of critical materials.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives played a pivotal role in shaping the solar industry’s trajectory. Favorable policies, including tax credits and rebates, encouraged investment and adoption. However, variations in these policies across regions and countries led to uneven growth patterns, affecting the overall industry performance. Policy changes, both anticipated and unforeseen, caused uncertainties for investors and businesses.
Material Costs and Production
Fluctuations in material costs, particularly for polysilicon and other critical components, directly affected solar panel production. The price volatility impacted manufacturers’ profitability and project viability. Increased demand for these materials from other industries, coupled with supply chain disruptions, led to significant cost increases. This pressure forced companies to explore alternative materials and manufacturing processes.
Cost Comparison to Other Energy Sources
The cost of solar energy compared to other energy sources remained a key consideration. While solar costs continued to decrease, the comparison to fossil fuels and other renewable sources varied depending on location, time of year, and specific project designs. Government subsidies and regulations also played a critical role in the relative cost comparison.
Financial Metrics Demonstrating Economic Struggles
Key financial metrics revealed the economic challenges faced by many solar companies. Decreased revenue, lower profit margins, and increased operating expenses were common trends. Reduced investor confidence and declining stock prices reflected the industry’s struggles.
Financial Performance of Top Solar Companies
The performance of top solar companies varied significantly. Some companies experienced strong growth, while others faced challenges related to pricing pressures, supply chain issues, and market fluctuations. The following table presents a snapshot of the financial performance of leading solar companies in the past year. Please note that these are illustrative figures and not precise financial data.
It was a tough year for solar, with the future looking a bit hazy. Meanwhile, Apple’s top-of-the-line iPhone this year, surprisingly, has a rather underwhelming battery life, as detailed in this article about apples most expensive iphone gets the most boring battery this year. This points to a wider trend of diminishing returns in tech innovation, making the uncertain future of the solar industry feel even more complex.
| Company | Revenue (USD millions) | Profit Margin (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | 150 | 10 |
| Company B | 120 | 8 |
| Company C | 90 | 5 |
| Company D | 180 | 12 |
Technological Advancements and Innovations
The solar industry, while facing headwinds in 2024, is also witnessing a surge in innovative technologies. These advancements promise to overcome past hurdles and drive the industry towards greater efficiency, affordability, and sustainability. New materials, production techniques, and energy storage solutions are reshaping the landscape of solar power, potentially accelerating its widespread adoption.The evolution of solar energy technologies is likely to involve a shift towards more efficient materials, simpler production processes, and smarter integration with existing infrastructure.
This will encompass everything from the development of more powerful solar cells to the creation of more robust and affordable energy storage systems. The potential for cost reductions and improved performance is substantial, with numerous companies actively pursuing these goals.
New Solar Cell Technologies
Advanced materials like perovskites and tandem solar cells are showing promise in surpassing traditional silicon-based cells in terms of efficiency. Perovskites, in particular, offer the potential for higher efficiency and lower production costs. Tandem solar cells, combining different materials, can absorb a wider spectrum of sunlight, also improving efficiency.
Improved Production Techniques
Recent advancements in manufacturing processes are aiming to increase the production capacity of solar panels while decreasing production costs. These include advancements in roll-to-roll printing and automated assembly techniques. This could lead to more affordable and readily available solar panels, potentially accelerating the adoption of solar energy.
Energy Storage Solutions
The integration of energy storage solutions, like batteries and pumped hydro, is crucial for making solar power more reliable and dispatchable. These systems are becoming more affordable and efficient, enabling the use of solar energy even when the sun isn’t shining. For example, Tesla’s Powerwall and similar battery systems are gaining traction in residential and commercial settings, demonstrating the potential for grid stabilization and increased solar energy utilization.
Table: Recent Advancements in Solar Panel Efficiency and Production Techniques
| Technology | Efficiency Improvement | Production Technique Advancement |
|---|---|---|
| Perovskite Solar Cells | Reported efficiencies exceeding 25% in laboratory settings. | Roll-to-roll printing methods reduce material waste and manufacturing costs. |
| Tandem Solar Cells | Higher efficiency by absorbing a wider range of the solar spectrum. | Automated assembly lines boost throughput and quality control. |
| High-efficiency Silicon Solar Cells | Ongoing research focusing on improving silicon wafer quality and cell design. | Advanced deposition techniques lead to more uniform and efficient solar cells. |
Barriers to Widespread Adoption
Despite the advancements, several barriers still hinder the widespread adoption of these new technologies. High upfront costs for some technologies, the need for supportive policies, and the lack of widespread infrastructure for energy storage remain significant challenges. Furthermore, public perception, and the time it takes for new technologies to gain market acceptance, also play a role. Governments and industry players need to address these challenges to maximize the potential benefits of solar energy.
Market Trends and Consumer Behavior
The solar industry is experiencing a period of dynamic shifts, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. Factors like rising energy costs, government incentives, and the growing awareness of environmental concerns are fueling the demand for renewable energy sources, including solar. Understanding these market trends is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate the sector’s complexities and capitalize on future opportunities.The market for solar energy is no longer confined to niche applications.
Increasingly, homeowners and businesses are actively seeking solar solutions, spurred by a desire for energy independence and reduced operating costs. This shift in consumer behavior is reflected in the growing number of installations and the broadening range of solar products available in the market.
Shifting Market Trends
The solar industry is witnessing a multifaceted evolution. Technological advancements are driving down the cost of solar panels, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers. Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, are further encouraging adoption. Simultaneously, the increasing awareness of climate change and the desire for sustainable energy practices are fueling consumer demand.
It was a tough year for solar, and the future’s a bit hazy. While the industry navigates some headwinds, it’s interesting to see how other entertainment sectors are doing. For example, the recent Warcraft trailer 2 released film warcraft trailer 2 released film is generating a lot of buzz, and maybe that’s a glimpse into a more optimistic future for storytelling.
Still, the uncertainty around solar’s next steps remains, and it’s a fascinating area to watch.
Evolving Consumer Preferences and Adoption Rates
Consumer preferences are increasingly leaning towards energy independence and environmental responsibility. Homeowners are recognizing the long-term financial benefits of solar, viewing it as an investment in their property’s value and a hedge against rising energy costs. This shift is evident in the growing adoption rates, particularly among residential customers. Businesses are also adopting solar solutions, recognizing the potential for cost savings and enhanced corporate social responsibility.
Current and Projected Demand for Solar Energy
Current demand for solar energy is significantly higher than historical levels. The growth trajectory is projected to continue, with several factors contributing to this upward trend. The projected demand for solar energy is substantial, driven by factors like falling panel costs, government incentives, and a growing consumer awareness of the environmental benefits. The transition to renewable energy is accelerating, and solar energy is positioned to play a key role in meeting the increasing energy demands of the future.
Emerging Business Models and Their Impact
New business models are emerging in the solar industry, adapting to the changing market dynamics. These include financing options that make solar more accessible to consumers with varying financial situations. Other innovative models involve community solar farms, enabling consumers to access solar power without owning their own systems. These models are impacting the solar industry by expanding market reach and promoting wider adoption.
Changing Consumer Behavior and Industry Growth
Changing consumer behavior is significantly influencing the industry’s growth. Consumers are becoming more informed about solar energy options and actively seeking solutions that align with their values. This trend underscores the need for transparency and education within the industry, helping consumers make informed decisions. The growing preference for sustainable practices is a key driver of growth.
Market Share of Solar Panel Manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Estimated Market Share (2023) |
|---|---|
| Company A | 25% |
| Company B | 20% |
| Company C | 15% |
| Company D | 10% |
| Other Manufacturers | 30% |
Note: Market share figures are estimates and may vary depending on the source and reporting methodology.
Potential Future Scenarios

The solar industry, despite recent headwinds, remains a dynamic and promising sector. Predicting the future trajectory requires careful consideration of various interacting factors, from global economic shifts to technological advancements and policy changes. Understanding these potential scenarios is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike to navigate the evolving landscape.
Global Economic Impacts
The global economy plays a significant role in the solar industry’s future. Economic downturns can lead to reduced investment in renewable energy projects, while periods of economic growth often correlate with increased demand for sustainable solutions. For example, the recent global recession saw a temporary slowdown in solar installations, but robust economic recoveries in several regions have since spurred renewed interest in clean energy.
The ongoing geopolitical uncertainty also impacts the industry, with supply chain disruptions and fluctuating energy prices influencing market dynamics.
Emerging Policies and Regulations
Government policies are instrumental in shaping the solar industry’s development. Incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, can significantly boost adoption rates, while stringent environmental regulations can accelerate the transition to renewable energy sources. Countries implementing policies that prioritize renewable energy, such as carbon pricing mechanisms or mandates for renewable energy integration, are expected to witness substantial solar growth.
The EU’s ambitious renewable energy targets, for instance, have spurred significant investment in solar power generation across member states.
It was a tough year for solar, and the future’s a bit hazy. But while we wait for the industry to settle, maybe you could treat yourself to a new keyboard? Check out this deal on the well-rated Logitech MX Keys keyboard for Mac, saving 25% – save 25 on the well rated logitech mx keys keyboard for mac.
Hopefully, that’ll help you power through the uncertainty, whether you’re tracking solar panel sales or just writing emails! Regardless, the solar sector still needs some sunshine to return to its former glory.
Technological Advancements
Technological breakthroughs can fundamentally alter the solar industry’s trajectory. Innovations in solar panel efficiency, manufacturing processes, and energy storage solutions can dramatically lower costs and enhance the viability of solar power. The development of more efficient solar cells, such as perovskite solar cells, holds the potential to revolutionize the industry, with potentially higher efficiency and lower production costs.
Market Trends and Consumer Behavior
Consumer awareness and acceptance of solar energy are crucial factors. Growing public concern about climate change and rising energy costs are driving demand for sustainable solutions. As more individuals and businesses adopt solar power, the market will likely experience substantial growth. The shift towards net-zero targets in various industries is a powerful indicator of this growing consumer preference.
Projected Growth in Various Regions
| Region | Projected Growth Rate (2024-2030) | Factors Influencing Growth |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 7-10% annually | Strong government support, growing energy demand, increasing consumer awareness |
| Europe | 6-8% annually | EU’s renewable energy targets, supportive policies, existing infrastructure |
| Asia-Pacific | 10-12% annually | High energy demand, strong government incentives, technological advancements |
| Latin America | 8-10% annually | Growing economies, increasing awareness, potential for large-scale projects |
| Africa | 5-7% annually | Growing populations, increasing energy access needs, potential for investment in solar power |
Note: Projected growth rates are estimates and may vary based on unforeseen circumstances.
Opportunities and Strategies for Growth
The solar industry, while facing headwinds, retains significant potential for growth. Navigating uncertainties and risks requires a proactive approach, focusing on innovative strategies and a commitment to maintaining competitiveness. Successful companies will not only embrace new technologies but also cultivate partnerships and prioritize research to secure their future.
Potential Opportunities for Growth
The solar industry presents several compelling opportunities. Emerging markets in developing nations represent substantial demand for solar power, driven by increasing energy needs and government incentives. Further, advancements in energy storage technologies are enabling the integration of solar power into grid systems and expanding its applications beyond peak sun hours. Moreover, the rise of distributed generation models, like rooftop solar installations, offers a route for both residential and commercial sectors to reduce their energy bills and environmental footprint.
Strategies for Navigating Uncertainties and Risks
The solar industry faces challenges, including fluctuating energy prices, governmental regulations, and competitive pressures. Adapting to these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach. Diversifying project portfolios, exploring new financing models, and strategically positioning the company within the evolving regulatory landscape are crucial. Strong financial management and risk assessment strategies are essential for navigating uncertainties. This includes assessing and mitigating potential risks from supply chain disruptions, geopolitical events, and technological obsolescence.
Key Strategies for Solar Companies to Maintain Competitiveness, It was a rocky year for the solar industry what comes next is uncertain
Solar companies must prioritize cost-effectiveness, innovation, and sustainability to maintain their competitive edge. Investing in research and development for improved efficiency and reduced manufacturing costs is crucial. Developing innovative financing models, including pay-as-you-go options, can broaden access to solar energy for a wider range of customers. Building strong brand reputation by emphasizing environmental responsibility and community engagement is also essential.
Potential Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaborations can significantly bolster industry growth. Partnerships with energy storage companies can create comprehensive energy solutions, while collaborations with technology providers can accelerate innovation. Partnerships with installers and distributors can expand market reach and streamline operations. Strategic alliances with government agencies can leverage support and incentives to foster industry growth.
Importance of Research and Development
Research and development (R&D) plays a vital role in shaping the future of the solar industry. R&D efforts focused on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and developing new applications for solar technology are essential. This includes exploring advancements in materials science, improving energy storage technologies, and creating innovative solar cell designs. Investment in R&D will be critical for driving future growth and maintaining the industry’s global competitiveness.
Strategies for Improving Financial Viability of Solar Projects
| Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Optimized Project Design | Ensuring the project aligns with local regulations, minimizing permitting delays, and employing efficient construction techniques. | Employing prefabricated components to expedite construction, reducing labor costs. |
| Aggressive Cost Management | Implementing meticulous procurement strategies, reducing material costs, and negotiating favorable financing terms. | Negotiating bulk discounts with suppliers and exploring alternative, less expensive materials. |
| Attractive Financing Options | Developing innovative financing models that align with project needs and investor risk tolerance. | Offering flexible payment plans for homeowners or lease agreements for commercial projects. |
| Strategic Partnerships | Leveraging partnerships with financial institutions and government agencies to access favorable funding programs. | Collaborating with utility companies to integrate solar energy into the grid. |
| Enhanced Energy Efficiency | Improving the energy conversion efficiency of solar panels and optimizing energy storage solutions. | Implementing advanced tracking systems for solar panels to maximize energy generation. |
Closing Notes
The solar industry’s recent performance has been marked by significant challenges, highlighting the need for adaptation and innovation. While uncertainty persists, the potential for growth is undeniable. Emerging technologies, shifting consumer preferences, and strategic partnerships offer opportunities for the industry to overcome hurdles and thrive in the coming years. The future of solar hinges on addressing current issues, embracing innovation, and forging new strategies to navigate the ever-changing energy landscape.