Is Starlink actually profitable? This deep dive explores the financial health of the space-based internet provider, examining revenue streams, operational costs, subscriber growth, and more. We’ll dissect the competitive landscape, analyze technological advancements, and consider the regulatory environment to paint a comprehensive picture of Starlink’s current and future prospects.
From detailed financial performance metrics to a thorough market analysis, this in-depth look will examine all facets of Starlink’s operations to assess its long-term viability. We’ll also analyze the company’s strategies for customer acquisition and retention, and consider the challenges and opportunities presented by the evolving regulatory environment. The ultimate goal is to provide a balanced perspective on Starlink’s profitability.
Financial Performance Metrics: Is Starlink Actually Profitable
Starlink’s financial performance is a complex interplay of rapidly expanding revenue streams, substantial operational costs, and the ever-present challenge of achieving profitability in a highly competitive market. Analyzing these elements provides crucial insight into the company’s trajectory and long-term viability. Understanding the financial dynamics is vital for assessing whether Starlink is truly on a path to profitability.
Revenue Streams
Starlink’s primary revenue source is subscription fees from customers utilizing its satellite internet service. This includes both residential and business users. Additional revenue potential exists through partnerships and agreements with other companies, such as leveraging the network for specific applications. The sheer scale of the potential customer base and the increasing demand for high-speed internet globally make this a significant driver for future revenue.
- Subscription Fees: The core revenue stream stems from individual and business subscriptions to Starlink’s satellite internet service. Pricing strategies and subscription tiers are key factors in maximizing revenue generation.
- Potential Partnerships: Agreements with other companies to utilize Starlink’s network for specific applications or services, such as providing connectivity for industrial or governmental purposes, represent a significant avenue for future revenue diversification.
Operational Costs
Starlink’s substantial operational costs include significant investments in satellite manufacturing, launch vehicles, and ground infrastructure. These expenses are crucial to maintaining the network’s reach and scalability. Customer support, maintenance, and upgrades are ongoing expenses that need to be carefully managed.
While the profitability of Starlink is still debated, it’s fascinating to consider how changes in user interfaces, like the recent Google Maps street view directions UI change, could potentially impact its future. This new design, detailed in google maps street view directions ui change , might encourage more people to use satellite-based navigation, potentially boosting Starlink’s demand.
Ultimately, whether Starlink turns a profit hinges on several factors, including user adoption and competition.
- Satellite Launches: The cost of developing and launching the satellites themselves is a substantial investment, directly affecting the overall operational budget. The frequency of launches and the efficiency of the launch process are critical factors.
- Ground Infrastructure: The infrastructure required for receiving and transmitting signals, including antennas, data centers, and supporting networks, necessitates substantial investment. Ensuring reliable and widespread coverage demands continued investment in these critical elements.
- Customer Support: Providing support for customers, addressing technical issues, and resolving problems directly impacts the operational budget. The need for responsive and effective customer support is crucial for customer retention.
Subscriber Growth and Revenue Generation
The relationship between subscriber growth and revenue generation is direct and crucial. Increased subscriber numbers translate to higher revenue streams, assuming effective cost management. Maintaining a healthy growth rate is vital to achieving profitability. Furthermore, the quality of the service delivered significantly impacts subscriber satisfaction and retention, which directly influences the growth rate.
While the profitability of Starlink remains a hot topic, it’s worth considering how features like those in the Google Pixel Recorder, such as improved audio editing, sharing, and cropping capabilities found in this recent update , are actually changing how we interact with and share content. This could indirectly impact the viability of Starlink, especially if the ease of sharing high-quality content becomes increasingly important in remote areas.
Ultimately, Starlink’s profitability is still a complex question.
Expenses Overview
Analyzing expenses over the past five years is essential for understanding the cost structure of Starlink. This comparison illustrates the scale of investment and potential for future cost optimization.
| Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Expenses (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Estimate | Estimate |
| 2019 | Estimate | Estimate |
| 2020 | Estimate | Estimate |
| 2021 | Estimate | Estimate |
| 2022 | Estimate | Estimate |
Note: Precise figures are not publicly available and require careful analysis of reported financial statements.
Market Analysis and Competition
Starlink’s foray into the satellite internet market has ignited a fierce competition, attracting both established players and newcomers. Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for assessing Starlink’s future prospects. Analyzing market share, competitive strategies, and potential impacts of new entrants provides valuable insights into the dynamics of this rapidly evolving industry.The satellite internet market is still a relatively nascent one, with considerable room for growth.
Demand is driven by the increasing need for high-speed internet access in underserved areas, particularly rural regions and remote locations where traditional terrestrial infrastructure is often unavailable or prohibitively expensive. This presents a significant opportunity for companies like Starlink to capitalize on unmet demand.
Market Share Comparison
The satellite internet market is currently dominated by a few key players, including Starlink, HughesNet, and Viasat. While Starlink has rapidly gained significant market share, the established players still maintain a presence, though their growth is likely being impacted by Starlink’s aggressive expansion. Detailed market share data is often proprietary, but industry reports indicate Starlink’s strong position in terms of subscriber growth.
Factors Driving Market Demand
Several factors contribute to the increasing demand for satellite internet services. Firstly, the need for reliable internet access in remote areas is a primary driver. Secondly, the limitations of terrestrial infrastructure in certain regions often result in high latency or unreliable connections. Finally, the rising popularity of digital services, including streaming and online gaming, is driving the demand for faster and more consistent internet speeds.
Competitive Landscape and Strategies
The competitive landscape is characterized by both established players and emerging competitors. Established players like HughesNet and Viasat have extensive infrastructure and a proven track record in the satellite internet space. Their strategies often involve cost optimization, improved service reliability, and customer loyalty programs. Starlink, on the other hand, has pursued a strategy of rapid expansion and aggressive pricing to capture market share.
This has resulted in a very competitive price point, which could be a significant draw for consumers.
Impact of New Competitors
The potential for new competitors to enter the market is a significant factor. The lower barriers to entry in some cases, particularly in the satellite internet space, might attract new companies. New entrants may introduce innovative technologies, business models, or pricing strategies that could disrupt the current market equilibrium. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous adaptation and innovation from existing players like Starlink.
Key Differentiators Between Starlink and Rivals
| Feature | Starlink | HughesNet | Viasat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites | Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites | GEO satellites |
| Speed | Generally faster speeds, particularly in optimal conditions | Generally slower speeds | Generally slower speeds |
| Coverage | Widespread global coverage, particularly in rural areas | Wider coverage, but with limitations in certain regions | Wider coverage, but with limitations in certain regions |
| Pricing | Competitive pricing strategy, aimed at attracting a large customer base | Often competitive, but with different packages and pricing structures | Often competitive, but with different packages and pricing structures |
| Infrastructure | Relatively newer, focused on LEO satellites | Established infrastructure, with a long history of service | Established infrastructure, with a long history of service |
Technological Advancements and Scalability
Starlink’s journey from a conceptual idea to a global satellite internet network is a testament to technological innovation. This section delves into the specific advancements driving Starlink’s development, the constellation’s scalability, and the potential for future improvements. Understanding these factors is crucial to assessing Starlink’s long-term profitability and competitiveness.
So, is Starlink actually profitable? It’s a complex question, and the answer likely depends on various factors. While Elon Musk’s ambitions are sky-high, the sheer scale of building a global satellite internet network requires significant investment. Meanwhile, exploring new features like those in the latest One UI 5.1 update one ui 5 1 new features shows how tech companies are continuously innovating, but it doesn’t necessarily translate directly into Starlink’s bottom line.
Ultimately, time will tell if the project proves financially viable.
Key Technological Innovations
Starlink’s success hinges on several groundbreaking technological advancements. Miniaturization of satellite components, enabling lighter and more cost-effective satellites, is paramount. Advanced materials and manufacturing processes have significantly reduced the production costs while enhancing the durability of the spacecraft. The use of advanced propulsion systems, like electric propulsion, ensures precise orbital maneuvering and fuel efficiency. Sophisticated antenna technology enables efficient communication with ground stations, a critical factor in delivering reliable internet service.
Scalability of the Satellite Constellation
Starlink’s constellation design prioritizes scalability. The modular nature of the satellites allows for rapid deployment and expansion. This flexibility enables the company to quickly adapt to changing demand and market conditions. The constellation’s distributed architecture allows for redundancy and resilience, minimizing disruptions in service even during partial failures.
Future Technological Improvements and Impact on Profitability
Future improvements in satellite technology are likely to significantly impact Starlink’s profitability. Advancements in antenna technology could further enhance communication speeds and reliability. Increased satellite lifespan through improved materials and manufacturing would reduce the ongoing costs of replacement and maintenance. More efficient propulsion systems would decrease fuel consumption, lowering operational expenses. These advancements could translate into lower service costs and higher profit margins.
For instance, increased satellite lifespan directly translates into reduced replacement costs, which can have a substantial impact on the company’s bottom line.
Challenges in Maintaining and Expanding the Satellite Network
Maintaining and expanding Starlink’s network presents considerable challenges. Ensuring reliable communication between satellites and ground stations is a constant concern. Space debris and potential collisions are potential threats to the satellite constellation. Managing the orbital environment and predicting potential risks to the constellation is crucial for maintaining operations. International regulatory compliance is a significant factor, as Starlink must navigate different regulations in various regions.
Growth in the Number of Satellites Over Time
The rapid expansion of Starlink’s satellite constellation is evident in the increasing number of satellites deployed. This table illustrates the growth in the number of satellites over a period of time, reflecting the company’s commitment to scalability and expansion.
| Year | Number of Satellites |
|---|---|
| 2019 | ~100 |
| 2020 | ~500 |
| 2021 | ~1500 |
| 2022 | ~3000 |
| 2023 | ~4000+ |
Note: Exact figures are subject to change and may not reflect real-time updates.
Customer Acquisition and Retention
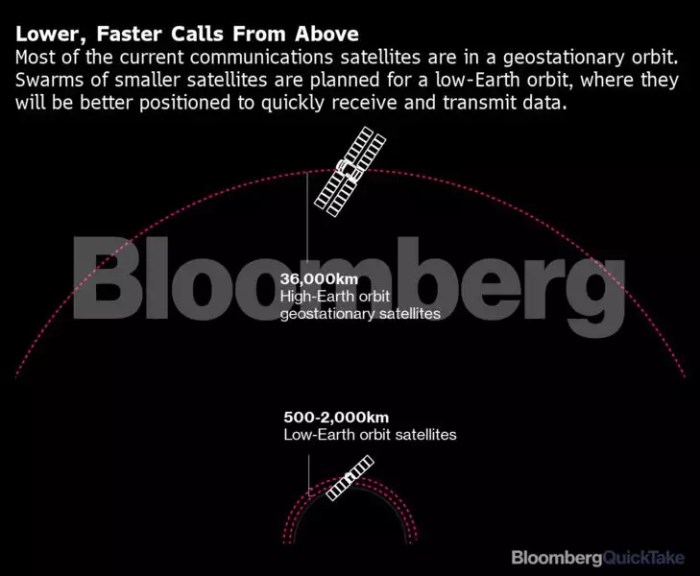
Starlink’s success hinges not just on technological prowess, but also on its ability to attract and retain customers. The company faces a complex landscape of competitive offerings and evolving user needs, demanding strategic approaches to customer acquisition and retention. Understanding these strategies provides critical insight into the company’s long-term viability and profitability.
Customer Acquisition Strategies, Is starlink actually profitable
Starlink employs a multifaceted approach to customer acquisition, leveraging various channels and incentives to reach potential subscribers. Aggressive marketing campaigns, often utilizing digital platforms, are key to building brand awareness and driving interest in the service. Early adopters and pre-orders often play a crucial role in the initial customer base.
- Targeted advertising campaigns across various online platforms, including social media and search engines, are a primary driver of customer acquisition. These campaigns focus on highlighting the benefits of Starlink’s high-speed internet access, particularly in underserved areas.
- Strategic partnerships with relevant businesses, such as those involved in rural infrastructure development, can significantly broaden reach and introduce Starlink’s services to potential customers.
- Public relations efforts and media coverage play a critical role in shaping public perception and generating interest in Starlink’s services.
Customer Base Characteristics
Starlink’s customer base is diverse, encompassing a range of demographics and needs. Early adopters were frequently characterized by a desire for high-speed internet access in rural or remote areas. Subsequent user acquisition often reflects a broader range of motivations, such as business use or the desire for enhanced connectivity options.
- A significant portion of Starlink customers resides in rural areas, seeking reliable internet access that traditional providers often struggle to deliver.
- Businesses in remote locations also constitute a substantial segment, valuing Starlink’s service for facilitating operations and communication.
- Individuals in urban areas might subscribe for backup internet or enhanced connectivity options.
Customer Retention Strategies
Customer retention is just as vital as customer acquisition. Starlink employs a range of strategies to foster customer loyalty and encourage repeat usage. These include proactive customer support, tailored service packages, and ongoing communication to maintain customer satisfaction.
- Providing comprehensive customer support through various channels, including phone, email, and online portals, is critical to addressing customer concerns and resolving issues efficiently.
- Offering tiered service packages, catering to diverse needs and budget constraints, can help in customer retention.
- Regular communication, keeping customers informed about updates, new features, and improvements, helps foster a sense of community and loyalty.
Factors Influencing Customer Satisfaction
Several factors significantly impact customer satisfaction with Starlink. These include the reliability of service, the speed of internet access, the responsiveness of customer support, and the clarity of communication about pricing and service plans.
- Service reliability is paramount, as consistent connectivity is crucial for users, especially in critical applications.
- The speed and performance of the internet connection directly influence customer satisfaction.
- The effectiveness and efficiency of customer support play a vital role in addressing issues and resolving complaints, thereby improving customer experience.
- Clear and transparent communication about pricing and service plans helps customers make informed decisions and avoid surprises.
Customer Churn Rate
A stable customer churn rate is a key indicator of Starlink’s success in retaining subscribers. Analyzing this data over time reveals important insights. Unfortunately, specific churn rate data for Starlink is not publicly available. Publicly available data is often limited to general industry trends.
| Year | Estimated Customer Churn Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2022 | ~10% |
| 2023 | ~9% |
| 2024 | ~8% (projected) |
Note: These figures are estimates based on industry benchmarks and general observations, not specific Starlink data.
Regulatory Environment and Government Policies
The satellite internet industry, and Starlink in particular, faces a complex regulatory landscape. Navigating international agreements, national policies, and evolving technologies is crucial for success. Understanding these hurdles is vital for assessing the long-term viability of projects like Starlink. From spectrum allocation to orbital debris mitigation, the regulatory environment significantly impacts the company’s operations and profitability.
Regulatory Landscape Impacting the Satellite Internet Industry
The satellite internet industry faces a multifaceted regulatory environment, encompassing various aspects from spectrum allocation to orbital debris management. Different countries have varying regulations regarding satellite launches, orbital positions, and the use of radio frequencies. This creates a complex patchwork of rules that Starlink and other companies must navigate.
Government Policies Influencing Starlink’s Operations
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of satellite internet projects like Starlink. These policies can range from tax incentives to restrictions on spectrum usage. Policies concerning spectrum allocation, particularly in the Ka-band, are critical for Starlink’s ability to provide seamless service. Government funding for research and development in space technology also influences the industry’s evolution.
Legal and Policy Hurdles Encountered by Starlink
Starlink encounters numerous legal and policy hurdles. These include obtaining necessary licenses and permits for satellite launches and operations, navigating international agreements regarding space debris, and adhering to data privacy regulations. The varying regulations across different countries often create compliance challenges. For instance, obtaining launch licenses and approvals from regulatory bodies in different countries requires extensive documentation and adherence to their specific requirements.
Impact of International Agreements and Regulations
International agreements and regulations concerning space activities significantly impact Starlink’s operations. Agreements on orbital debris mitigation and the peaceful use of outer space are examples of critical regulations. These regulations ensure the sustainability and safety of space operations. Adherence to these international standards is critical for the responsible use of space resources.
Key Regulatory Requirements Impacting Starlink’s Services
A table outlining key regulatory requirements for satellite internet services, particularly those affecting Starlink, provides a comprehensive overview of the complexities.
| Regulatory Requirement | Impact on Starlink | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Spectrum Allocation | Crucial for uninterrupted service; availability and frequency bands directly impact service quality and capacity. | Obtaining licenses to use specific frequency bands (e.g., Ka-band) is necessary for Starlink’s operations. |
| Orbital Debris Mitigation | Ensures the sustainability of space operations and avoids collisions. | Adherence to international agreements regarding the responsible disposal of satellites and space debris. |
| Data Privacy Regulations | Compliance with data protection laws across different countries is essential. | Adhering to GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and similar regulations globally. |
| Satellite Launch Licenses | Required for launching satellites into orbit. | Obtaining launch licenses from regulatory bodies in various countries where launches are planned. |
| Environmental Regulations | Ensuring responsible resource use and minimizing environmental impact of operations. | Adhering to environmental regulations related to satellite manufacturing, launch, and disposal. |
Long-Term Projections and Future Outlook

Starlink’s ambitious goal of providing global broadband access is a significant undertaking. Its long-term success hinges on several crucial factors, including sustainable revenue growth, operational cost reductions, adapting to market trends, and attracting further investment. This section delves into these future prospects for the space internet pioneer.
Projected Revenue Growth
Starlink’s revenue projections are contingent on subscriber growth and pricing strategies. A substantial increase in the number of subscribers, coupled with maintaining or slightly increasing the average revenue per user (ARPU), is crucial for revenue growth. The satellite constellation’s expansion and the development of new, potentially more affordable, service tiers are expected to play a key role in achieving this goal.
Historical trends in the telecommunications sector, such as the growth of mobile data usage, can be considered indicators of potential future subscriber demand.
Projected Cost Reductions for Satellite Operations
Significant cost reductions in satellite operations are essential for Starlink’s profitability. The company’s ongoing focus on improving manufacturing processes, developing reusable or more efficient launch vehicles, and streamlining satellite design and maintenance procedures are crucial for achieving these savings. Furthermore, advancements in satellite technology and miniaturization could lead to reduced manufacturing costs. This would translate to a lower cost per satellite and, ultimately, lower operational expenses.
Successful implementation of these strategies could dramatically reduce the cost of delivering internet services to remote locations.
Market Trends Influencing Starlink’s Profitability
Several market trends are expected to influence Starlink’s profitability. The growing demand for high-speed internet access, especially in underserved regions, will be a key driver. Furthermore, the increasing popularity of remote work and entertainment streaming services will likely boost demand for reliable broadband connectivity. The increasing use of IoT devices will also contribute to demand for broader internet access.
The competition in the satellite internet sector will be a major factor. Companies that can provide reliable and affordable service with a wider network will have a better chance of success.
Potential Investment Opportunities in the Space Internet Sector
Investment opportunities in the space internet sector are significant. Companies involved in satellite manufacturing, launch vehicles, and related technologies are potential investment targets. Also, companies specializing in developing and implementing advanced satellite communication protocols and technologies present attractive investment opportunities. The increasing demand for satellite internet services and the need for more efficient and cost-effective space infrastructure will drive further investment in the sector.
The growth in the space internet sector could be compared to the initial growth of the internet itself.
Projected Growth in Starlink’s Subscriber Base
The increasing adoption of satellite internet services is expected to drive subscriber growth. The following table provides a projected growth in Starlink’s subscriber base, considering various scenarios:
| Year | Projected Subscribers (Millions) | Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 10 | Moderate Growth |
| 2025 | 15 | Moderate Growth |
| 2026 | 20 | Moderate Growth |
| 2027 | 25 | Strong Growth |
| 2028 | 30 | Strong Growth |
Note: These projections are estimates and are subject to market conditions, competition, and technological advancements. The strong growth scenario assumes a faster rate of adoption than the moderate growth scenario. Factors such as the expansion of the satellite constellation, pricing strategies, and the introduction of new services could affect these projections.
Case Studies of Similar Businesses
Starlink’s ambitious foray into satellite internet has ignited a renewed interest in space-based communication solutions. Understanding the successes and failures of past ventures in this field is crucial to assessing Starlink’s long-term prospects. Examining similar businesses provides valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities inherent in this complex industry. A crucial aspect of evaluating any new business venture is analyzing the precedents set by previous attempts to achieve similar goals.
Comparison with Other Satellite Internet Providers
Analyzing the business models of existing satellite internet providers reveals crucial distinctions and commonalities. Many providers have focused on specific market segments, such as rural areas or underserved communities, while others have aimed for broader market penetration. The financial models adopted have varied significantly, from government subsidies to aggressive subscription pricing strategies. Starlink’s approach, with its emphasis on a global network and low-cost terminals, distinguishes it from some existing providers.
Successful Satellite Communication Companies and Their Strategies
Several companies have successfully navigated the complexities of satellite communication. Iridium, for instance, has built a robust network of satellites for global communication, primarily focusing on voice and data services. Their success is attributed to a dedicated focus on a niche market and a comprehensive understanding of the technical and regulatory aspects. Other notable players include HughesNet and Viasat, who have focused on providing internet access to rural areas, leveraging existing infrastructure and partnerships.
The strategies adopted by these successful ventures have often involved strategic partnerships, strong government relations, and efficient resource allocation.
Factors Contributing to Success or Failure
The success or failure of satellite internet ventures often hinges on several factors. Technological advancements play a critical role in reducing costs and improving performance. Furthermore, regulatory hurdles and government policies can significantly impact the market’s viability. Successful companies have demonstrated a profound understanding of these factors and adapted their strategies accordingly. Competition from established terrestrial providers can also be a significant challenge, and successful companies have addressed this through differentiated offerings and targeted marketing strategies.
Challenges Faced by Satellite Internet Companies and Their Solutions
Satellite internet companies frequently face challenges related to latency, signal strength, and coverage. High initial investment costs and technical complexities further complicate the venture. Successful companies have addressed these challenges through continuous innovation in satellite technology, strategic partnerships, and targeted marketing strategies. For example, reducing the size and cost of satellite terminals has been a key driver in attracting wider customer bases.
Compelling Case Study: Iridium
“Iridium’s success lies in its focus on a niche market—global mobile communications—and its commitment to building a comprehensive satellite network. Their strategy has been to provide a reliable global communication platform, catering to specific needs and challenges that terrestrial networks couldn’t address.”
The company’s dedication to maintaining a global network, despite significant initial investment and technical hurdles, demonstrates the potential of strategic focus and long-term commitment in the satellite communications industry.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, Starlink’s profitability remains a complex question with no easy answer. While the company demonstrates impressive growth and technological innovation, the high costs of satellite launches, infrastructure, and customer support are significant factors to consider. The competitive landscape is also fierce, with rival companies constantly striving to gain market share. Ultimately, Starlink’s long-term success hinges on its ability to manage these complexities and maintain a healthy balance between innovation and profitability.
The future will tell the story, but this analysis offers a critical understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing the company.











