Iceberg South Georgia melt fresh water climate is a critical issue, highlighting the dramatic changes occurring in the Antarctic region. Glacial systems on South Georgia are shedding icebergs at an accelerating pace, and this meltwater is significantly altering the surrounding marine environment. The influx of freshwater is impacting salinity, density, and nutrient levels, potentially disrupting the delicate balance of local ecosystems, from phytoplankton to fish populations.
This blog post delves into the mechanisms of iceberg melt, the effects of freshwater on oceanography, and the profound connection to global climate change.
The accelerated melting of icebergs in South Georgia has profound implications for local marine life. Ocean currents and water temperatures play a significant role in how quickly icebergs melt, as does the salinity of the water. Atmospheric conditions, like wind and precipitation, can also influence the melt process. Understanding these interacting factors is key to comprehending the broader consequences for the region’s environment.
South Georgia Iceberg Melt: A Closer Look
South Georgia, a remote island in the Southern Ocean, is a vital habitat for diverse marine life, and its glacial systems play a critical role in shaping the surrounding ecosystem. Over recent decades, the rate of iceberg calving and melt has increased, raising concerns about the potential consequences for the delicate balance of the region’s marine environment. The observed trends in iceberg melt are linked to broader climate change patterns, and understanding these processes is crucial for predicting future impacts and developing appropriate conservation strategies.The increased frequency and size of icebergs calving from glaciers on South Georgia reflect the impact of warming ocean temperatures.
The melting icebergs around South Georgia are impacting freshwater levels, and that’s causing some serious climate concerns. It’s a fascinating, yet concerning, natural phenomenon. Meanwhile, the recent news about the Mattel Aristotle AI child monitor being canceled is a bit of a bummer, especially for parents looking for innovative tech solutions. Hopefully, this setback won’t delay the development of safer and more reliable child monitoring systems, which will ultimately help with the safety of families.
This whole iceberg melt situation highlights the interconnectedness of our world, and how one environmental issue can affect everything else, including the tech we rely on. It really makes you think about the importance of finding sustainable solutions for future generations.
Warmer water erodes the base of glaciers, accelerating their retreat and the detachment of icebergs. This process, while natural, is being amplified by human-induced climate change, leading to faster melt rates than historically observed. The consequences of this accelerated melt extend beyond the immediate vicinity of the island, affecting marine ecosystems across a wider area.
Observed Trends in Iceberg Calving and Melt Rates
The observation of a clear upward trend in iceberg calving and melt rates in recent decades is directly linked to rising ocean temperatures. Studies show a significant increase in the frequency and volume of icebergs breaking away from glaciers on South Georgia. Satellite imagery and field observations have documented these changes, providing crucial data for understanding the dynamics of this process.
For instance, the increased melt rates correlate with the observed warming of the Southern Ocean surrounding the island.
Potential Impacts on Surrounding Marine Ecosystems
The influx of freshwater from melting icebergs can have a profound impact on the marine environment. The freshwater, being less dense than seawater, creates a layer on the surface that can alter the salinity and temperature gradients in the water column. This stratification can affect the distribution and abundance of phytoplankton, the base of the marine food web.
Changes in salinity and temperature can impact the species composition and distribution of marine organisms, potentially causing disruptions in the entire food web. Furthermore, the presence of large amounts of icebergs can physically obstruct the movement of marine life.
Impact on Phytoplankton
Changes in water column stratification, influenced by the increased input of freshwater from melting icebergs, can significantly alter the availability of nutrients and light for phytoplankton growth. This disruption in the balance of nutrients and light availability could lead to a decline in phytoplankton populations, which in turn affects the entire marine food web. For example, a reduced phytoplankton bloom could negatively impact krill populations, a critical food source for numerous marine animals.
Impact on Krill
The reduction in phytoplankton populations, caused by changes in water column stratification due to freshwater input from melting icebergs, can negatively impact krill populations. Krill are a crucial component of the Southern Ocean food web, serving as a primary food source for many marine species, including whales, penguins, and seals. A decline in krill populations could have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, potentially impacting the survival and reproduction of many dependent species.
Impact on Fish Populations
The changes in water column stratification due to freshwater input from melting icebergs can also impact fish populations. Different species of fish have specific temperature and salinity requirements for survival and reproduction. Alterations in these parameters can disrupt the habitats of various fish species, potentially leading to shifts in their distribution and abundance. For instance, the change in water conditions may force some fish species to migrate to different locations, impacting the overall structure and diversity of the ecosystem.
Mechanisms of Iceberg Melt: Iceberg South Georgia Melt Fresh Water Climate
Icebergs, magnificent but fragile, are constantly interacting with their surrounding environment. Their fate, ultimately, is intertwined with the processes of melting, a complex interplay of physical forces. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial to predicting the behavior of icebergs and assessing their impact on the surrounding ecosystem.Iceberg melt is a dynamic process driven by a combination of factors. The primary mechanism involves the transfer of heat from the surrounding water to the iceberg.
This transfer can occur through various pathways, including conduction, convection, and radiation. The rate at which this transfer occurs, and hence the melt rate, is influenced by several key factors.
Physical Processes Driving Iceberg Melt
The melting of icebergs is a fundamental physical process governed by thermodynamics. Heat transfer from the warmer surrounding water to the colder iceberg surface is the primary driver. This heat transfer is a consequence of the temperature difference between the two. The rate of this heat transfer depends on the surface area of the iceberg exposed to the water, the difference in temperature between the iceberg and the water, and the properties of the water itself, such as its conductivity and flow patterns.
As the iceberg melts, the resulting meltwater further influences the surrounding environment.
The melting icebergs off South Georgia are dumping fresh water into the surrounding ocean, significantly impacting the local climate. It’s a fascinating study in how these shifts affect the ecosystem, but honestly, the way kids use memes is melting my brain sometimes. the way kids use memes is melting my brain It’s a whole other kind of glacial melt, and I’m not sure which one is more concerning for the future.
This fresh water influx is likely altering ocean currents and potentially impacting marine life in the region, just like the ever-changing digital landscape.
Factors Influencing Melt Rates
Several factors interact to determine the rate at which an iceberg melts. Ocean currents play a significant role, transporting warmer water against the iceberg, increasing the heat transfer rate. The temperature of the surrounding water is a critical factor, with warmer water leading to faster melt rates. Salinity also plays a role; warmer, less saline water typically has a higher heat capacity, accelerating the melting process.
These factors often work in concert, making precise predictions about melt rates challenging.
Role of Atmospheric Conditions, Iceberg south georgia melt fresh water climate
Atmospheric conditions also exert an influence on iceberg melt. Strong winds can enhance the contact between the iceberg and the water, leading to increased heat transfer. Precipitation, particularly rain, can also contribute to melt by providing additional heat and by diluting the salinity of the water around the iceberg. The interplay between atmospheric and oceanic factors often creates complex patterns of melt that are difficult to predict.
Impact of Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification, driven by increased carbon dioxide absorption, presents a less direct but still significant impact on iceberg melt. While not directly affecting the heat transfer mechanisms, acidification can alter the properties of the surrounding water. This change might indirectly influence melt rates, although more research is needed to quantify the magnitude of this effect. The effect of acidification on the overall ecosystem of the surrounding area should be considered as a secondary impact on the iceberg melt.
Freshwater Impacts
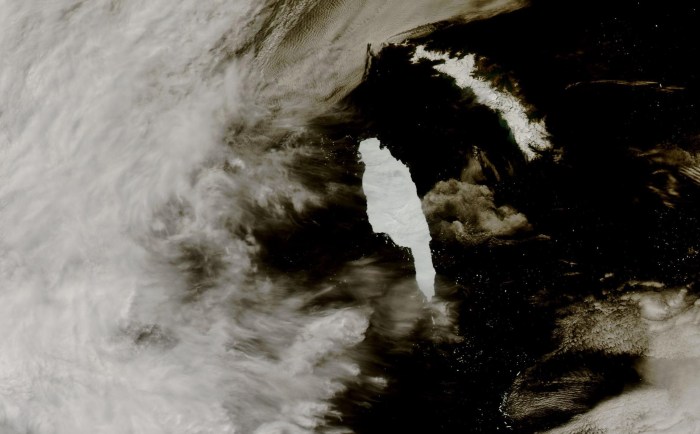
The influx of freshwater from melting icebergs significantly alters the local oceanographic conditions around South Georgia. This influx, while seemingly benign, can have cascading effects on the delicate ecosystem of the surrounding waters. Understanding these impacts is crucial for predicting and mitigating potential future consequences.The freshwater, being less dense than seawater, tends to float on top. This creates a layer of relatively low-salinity water that can disrupt the natural stratification of the ocean.
This stratification is vital for the distribution of nutrients and oxygen, as well as the survival of marine organisms. The alteration of this natural order has a domino effect on the marine ecosystem.
Effects on Salinity and Density Gradients
The influx of freshwater from melting icebergs directly reduces the salinity of the surrounding seawater. This decrease in salinity leads to a corresponding reduction in the density of the water. The reduced density gradient affects the vertical mixing processes in the water column, potentially impacting the distribution of nutrients and oxygen, which are essential for marine life. This phenomenon has been observed in other regions experiencing similar glacial melt events.
The changes in salinity and density can alter the stratification of the water column, impacting the movement of nutrients and the overall health of the ecosystem.
Effects on Marine Life
The alteration of salinity and density gradients can have profound effects on marine organisms. Phytoplankton, the base of the marine food web, require specific salinity conditions for optimal growth. Changes in salinity can hinder their growth and reproduction, which, in turn, affects the entire food chain. Zooplankton, the primary consumers, rely on phytoplankton for sustenance. A reduction in phytoplankton abundance directly impacts zooplankton populations.
Similarly, fish populations, particularly those with specific salinity requirements for spawning or growth, could be negatively affected. Reduced salinity can impact their survival and reproduction rates. It’s important to note that some species are more resilient to these changes than others. However, the overall impact on the diversity and abundance of marine life can be significant.
Predicted Changes in Oceanographic Parameters
The table below summarizes the predicted changes in oceanographic parameters due to iceberg melt, along with their potential impacts on marine life.
| Parameter | Expected Change | Impact on Marine Life |
|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Decrease | Reduced osmoregulation ability for some species. Organisms adapted to specific salinity ranges may struggle to maintain internal balance. |
| Density | Decrease | Alteration of water column stratification. This can impact the vertical distribution of nutrients and oxygen, potentially affecting primary producers and the entire food web. |
| Nutrient levels | Potential increase | Altered phytoplankton growth. Increased nutrient availability can lead to algal blooms, but can also disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem. |
Climate Change Connection

The accelerated melt of icebergs around South Georgia is inextricably linked to global climate change. Warming ocean temperatures, a direct consequence of rising global temperatures, are the primary drivers behind this phenomenon. The increased heat energy in the surrounding waters directly impacts the stability and longevity of the ice shelves and glaciers that contribute to the iceberg calving process.
Global Warming’s Impact
Global warming, driven largely by increased greenhouse gas emissions, is causing a significant rise in global temperatures. This warming trend is not uniform across the planet, but it is demonstrably impacting the Antarctic region. The warming ocean acts as a heat sink, absorbing vast amounts of heat energy from the atmosphere, which in turn accelerates the melting process of icebergs.
This process is further compounded by the thinning of ice shelves, making them more susceptible to fracturing and calving.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from human activities like burning fossil fuels, are the primary culprits behind global warming. These gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to a gradual but significant increase in global temperatures. The emission of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide contributes directly to the greenhouse effect, leading to the warming trend that is causing the accelerated melting of icebergs in the South Georgia region.
Reducing these emissions is crucial to mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Feedback Loops
A crucial aspect of this issue is the existence of feedback loops. As icebergs melt, they release fresh water into the surrounding ocean. This influx of fresh water can alter the ocean’s salinity and density, potentially impacting ocean currents and weather patterns. Additionally, the melting ice reduces the reflectivity of the Earth’s surface, leading to increased absorption of solar radiation and further warming.
The melting icebergs around South Georgia are significantly impacting the freshwater climate. This influx of meltwater is altering the delicate balance of the ecosystem, and scientists are actively monitoring these changes. To stay on top of these developments, checking out the latest smartwatch apps like those available on google pixel watch apple watch smartwatch apps could be helpful for tracking weather patterns and other crucial data.
Ultimately, understanding these environmental shifts is key to protecting this fragile region.
These feedback loops amplify the effects of global warming, creating a self-reinforcing cycle that makes the situation more complex and difficult to manage.
Historical and Projected Climate Data
The following table presents a hypothetical comparison of historical and projected climate data for South Georgia. Please note that actual data would require specific, reliable meteorological records from the region. These figures are for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered definitive.
| Year | Temperature (°C) | Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | -2.5 | 150 |
| 2000 | -2.2 | 165 |
| 2050 (projection) | -1.8 | 180 |
Potential Effects on Climate
The melting of icebergs from South Georgia, a seemingly isolated event, can have far-reaching consequences on regional and global climate patterns. This meltwater, released into the surrounding ocean, alters the heat exchange between the ocean and atmosphere, potentially impacting weather systems and overall climate stability. Understanding these effects is crucial for predicting and adapting to the potential consequences of ongoing glacial melt worldwide.The influx of fresh water from melting icebergs significantly alters the ocean’s density and salinity gradients.
This alteration can disrupt existing ocean currents, impacting heat transport and atmospheric circulation patterns. These changes can have cascading effects, potentially affecting regional and global weather patterns.
Impact on Atmospheric Circulation
The modified salinity and temperature profiles of the surrounding waters directly influence the formation and movement of atmospheric pressure systems. Changes in these patterns can lead to shifts in prevailing winds, affecting precipitation patterns across various regions. For example, alterations in the jet stream’s path can lead to prolonged droughts in some areas and increased rainfall in others.
The precise mechanisms and magnitudes of these shifts remain a subject of ongoing research and modeling.
Impact on Precipitation Patterns
Changes in atmospheric circulation, driven by altered ocean currents, directly influence precipitation patterns. Increased freshwater input can affect the formation and movement of weather systems, leading to shifts in rainfall distribution. These shifts can manifest as increased or decreased rainfall in specific geographical areas, potentially leading to more frequent and intense droughts or floods, with significant implications for water resources and agriculture.
Examples include the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events, where changes in ocean temperatures significantly affect global weather patterns.
Role of Albedo Changes
The process of iceberg melt directly impacts the Earth’s albedo, or reflectivity. The high albedo of ice reflects a significant portion of incoming solar radiation back into space. As ice melts, the darker ocean water absorbs more solar radiation, leading to increased heat absorption in the system. This, in turn, can accelerate the melting process through a positive feedback loop.
This albedo effect is a critical factor in understanding the potential for rapid and cascading changes in the region and its surrounding areas. A simplified representation of this effect can be seen in comparing the reflectivity of a snow-covered field to a bare field on a sunny day.
Potential Chain Reactions
The melting of icebergs from South Georgia can trigger a series of interconnected changes, forming a complex chain reaction. The release of freshwater into the ocean modifies ocean currents, altering atmospheric circulation. These changes in circulation patterns, in turn, affect precipitation patterns and potentially intensify extreme weather events. This intricate interplay highlights the importance of understanding these interconnected systems.
- Initial trigger: Iceberg melt from South Georgia.
- Oceanographic response: Freshwater influx alters ocean currents and salinity gradients.
- Atmospheric response: Changes in ocean temperatures and salinity impact atmospheric circulation and pressure systems.
- Regional climate shifts: Altered precipitation patterns and potentially more extreme weather events.
- Global climate feedback: The altered heat absorption and redistribution can influence larger-scale global climate patterns.
Monitoring and Research
Unraveling the intricate dance between melting icebergs and the surrounding environment requires meticulous monitoring and sustained research. Understanding the dynamics of iceberg melt and freshwater discharge is crucial for predicting potential impacts on the climate and ecosystems of South Georgia. This necessitates a multifaceted approach encompassing various technologies and long-term data collection strategies.
Current Monitoring Methods
Various methods are employed to track iceberg melt and freshwater discharge, ranging from traditional observations to cutting-edge technologies. Direct measurements of melt rates are often taken by deploying instruments directly on or near the icebergs. These instruments collect data on temperature, salinity, and flow rate of the meltwater, providing a precise snapshot of the current situation. Buoys equipped with sensors provide real-time data on water temperature and salinity changes in the surrounding waters.
These buoy networks offer a crucial overview of the broader impact of iceberg melt on the marine environment.
Satellite Imagery and Data Collection
Satellite imagery plays a critical role in monitoring iceberg extent and behavior. High-resolution satellite images allow scientists to track the movement of icebergs, identify calving events, and estimate the total ice volume affected by melt. These images can be used to develop accurate models of iceberg trajectories and predict their potential impact on the surrounding environment. Furthermore, the imagery enables researchers to monitor changes in the overall ice sheet, providing valuable context for the iceberg melt.
Importance of Long-Term Monitoring Programs
Long-term monitoring programs are essential to establish baselines and detect long-term trends in iceberg melt and freshwater discharge. By tracking data over extended periods, scientists can identify patterns and establish correlations between factors like climate variations and changes in the melt rate. This longitudinal data collection allows for a deeper understanding of the complex processes at play and helps predict future changes.
Such programs are vital to assess the potential impacts of climate change on South Georgia’s unique ecosystem.
Oceanographic Measurements
Oceanographic measurements, including temperature, salinity, and current profiles, provide critical information about the physical characteristics of the water masses affected by iceberg melt. The interaction between freshwater from melting icebergs and the surrounding seawater can have a profound effect on the marine environment. Analyzing this interaction can provide valuable insight into how the meltwater is distributed and how it influences the local ecosystem.
Visual Representation of Data Collection Methods
| Data Collection Method | Description | Technology/Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Measurement | Measurements of temperature, salinity, and flow rate are taken directly on or near the iceberg. | Sensors, buoys, and specialized instruments |
| Satellite Imagery | Tracking iceberg movement, calving events, and ice volume estimation. | High-resolution satellite sensors |
| Oceanographic Measurements | Assessing temperature, salinity, and current profiles in the water masses affected by melt. | Conductivity-Temperature-Depth (CTD) probes, current meters |
Future Projections
The relentless march of climate change is casting a long shadow over South Georgia, a remote island paradise in the Southern Ocean. Continued iceberg melt, driven by warming ocean temperatures and atmospheric conditions, presents a significant threat to the delicate ecosystem and the livelihoods of those who depend on it. Understanding the potential impacts and developing proactive strategies are crucial for ensuring a sustainable future for this unique region.The escalating rate of iceberg calving and subsequent melt will reshape South Georgia’s environment in profound ways.
Sea level rise, while not a primary concern for the island itself, could still impact surrounding waters, altering currents and potentially impacting the intricate food web that supports the region’s biodiversity. The ramifications extend beyond the natural world, affecting the economic activities reliant on South Georgia’s resources.
Potential Impacts on the Environment and Ecosystem
The increased influx of freshwater from melting icebergs will alter the salinity and temperature profiles of the surrounding waters. This disruption will likely affect the distribution and abundance of marine life, potentially leading to the displacement of species adapted to specific salinity ranges. For example, the sensitive krill population, a cornerstone of the ecosystem, could experience reduced feeding grounds and reproduction rates due to changing water conditions.
The delicate balance of the marine food web will be challenged, impacting predators such as penguins and seals.
Potential Consequences for Human Activities
South Georgia’s economy is heavily reliant on fishing, tourism, and research. The shift in water conditions caused by iceberg melt could impact fishing grounds, potentially reducing catches and impacting the livelihoods of local fishermen. The changing environment could also affect the viability of existing tourism activities, such as penguin viewing and wildlife expeditions. For instance, if key penguin colonies are negatively affected, it could impact tourism revenue and local employment.
Changes in sea ice extent and the frequency of icebergs could also affect research operations, potentially altering the types of studies conducted and the duration of field work.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the challenges posed by iceberg melt requires a multifaceted approach. International cooperation is essential to develop and implement effective mitigation strategies. Monitoring and research play a critical role in understanding the complex dynamics of the changing environment and the cascading effects of iceberg melt. Developing adaptable infrastructure and alternative economic activities are vital for minimizing the negative impacts on human livelihoods.
Adaptation Strategies for Local Communities
A proactive approach to adaptation is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of South Georgia’s communities.
| Sector | Potential Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Fisheries | Shifting fishing grounds, exploring alternative fishing methods, and diversifying the fishing fleet. |
| Tourism | Developing new attractions, such as educational programs focusing on the effects of climate change, or offering opportunities to observe the impact of iceberg melt on the ecosystem, or developing eco-tourism packages emphasizing sustainable practices. |
| Infrastructure | Strengthening coastal defenses to protect against rising sea levels and potential storm surges, or improving the resilience of existing infrastructure to accommodate changing conditions, and investing in early warning systems for potential hazards like iceberg calving events. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the melting icebergs of South Georgia are a clear indicator of global climate change, with cascading effects on the local environment. Freshwater influx alters oceanographic conditions, impacting marine life and potentially influencing regional climate patterns. Ongoing monitoring and research are essential to understand these complex interactions and develop effective adaptation strategies for the future. The fate of South Georgia’s ecosystem, and potentially much of the Antarctic region, hinges on our collective ability to address climate change.











