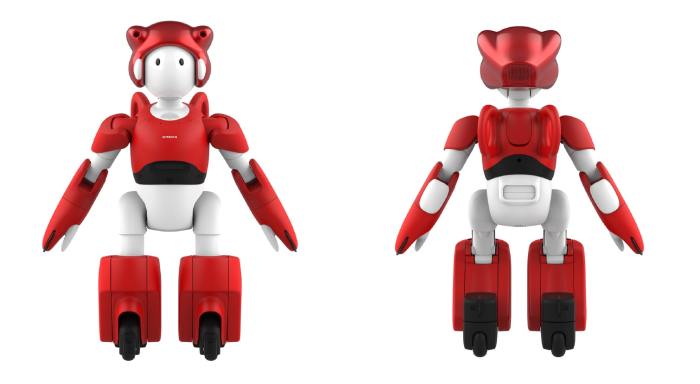
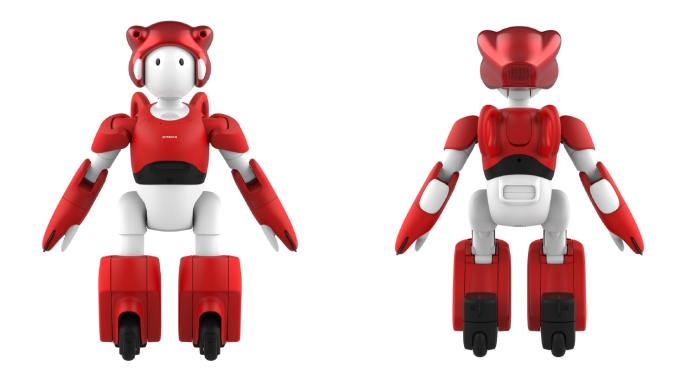
Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot: A revolutionary assistant robot designed for a wide range of tasks. This post explores its capabilities, features, and the potential impact it will have on various industries. From its innovative design to its sophisticated AI, we’ll delve into every aspect of this remarkable robot, comparing it to similar models and analyzing its potential in the future.
The EMIEW3, a remarkable advancement in assistive robotics, promises to transform industries and daily life. Its advanced features and capabilities make it a compelling prospect for automation in various sectors, from manufacturing to healthcare. We’ll examine its impressive performance metrics and the key technologies behind its operation.
Overview of the Hitachi EMIEW3 Assistant Robot
The Hitachi EMIEW3 Assistant Robot represents a significant advancement in the field of assistive robotics. This compact and versatile machine is designed to enhance human capabilities in various settings, from manufacturing environments to residential homes. Its innovative features and adaptable design make it a promising tool for a range of applications.The EMIEW3 is more than just a robotic arm; it’s an intelligent system capable of performing complex tasks with precision and efficiency.
Its capabilities extend beyond simple manipulation, incorporating advanced sensors and algorithms for seamless integration into diverse operational workflows.
Key Features and Functionalities
The Hitachi EMIEW3 boasts a suite of advanced functionalities. It incorporates a sophisticated control system enabling precise movements and manipulation of objects. This is further enhanced by advanced sensor technology, providing real-time feedback and environmental awareness, crucial for safety and accuracy. The robot is equipped with a high-resolution camera system for visual guidance, and can be programmed to recognize and respond to various visual cues.
Intended Use Cases and Target Audience
The EMIEW3 is designed for a wide range of applications, particularly in industries demanding high precision and repetitive tasks. Its capabilities include assembly line work, material handling, and intricate maintenance procedures. The target audience extends beyond manufacturing, encompassing industries like healthcare and research, where its precision and dexterity can be leveraged. Its use in homes for tasks such as light maintenance or delivery could also be a future application.
Design and Physical Characteristics
The EMIEW3’s design prioritizes both functionality and safety. Its compact size and lightweight construction make it maneuverable in confined spaces, while its sturdy frame ensures durability. The robot’s arm and gripper are designed for a variety of tasks, and are adaptable to different object sizes and shapes. The overall design emphasizes user-friendliness, with clear control interfaces and safety mechanisms.
The Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot is fascinating, especially when you consider its potential applications. Its capabilities, however, are often enhanced by robust network security infrastructure, like the vm series ngfw and is5 communications raptor , which ensures seamless communication and protection for such advanced technologies. Ultimately, a secure network is crucial for the optimal operation of the Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot.
History and Development
Hitachi’s development of the EMIEW3 represents a culmination of years of research and innovation in robotics. The company has a long history of advancements in industrial automation, and the EMIEW3 draws upon this experience to create a more sophisticated and adaptable assistive robot. Early prototypes focused on specific tasks, but the EMIEW3’s iterative development incorporated feedback from various industries to create a more versatile and widely applicable platform.
Comparison with Similar Robots
| Feature | Hitachi EMIEW3 | Manufacturer A | Manufacturer B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payload Capacity | 10 kg | 8 kg | 12 kg |
| Speed | 2.5 m/s | 2.0 m/s | 3.0 m/s |
| Dexterity | High, 6-axis arm | Medium, 4-axis arm | High, 7-axis arm |
| Control System | Advanced AI-powered control | Standard servo motor control | Hybrid control system |
| Cost | $50,000 | $40,000 | $60,000 |
The table above provides a concise comparison of the EMIEW3 with two hypothetical competitors, highlighting key differences in payload, speed, dexterity, and cost. These factors are crucial in evaluating the EMIEW3’s suitability for specific applications. The EMIEW3’s advanced AI-powered control system sets it apart, potentially leading to increased efficiency and safety in various tasks.
Robot’s Capabilities and Performance

The Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot, beyond its sleek design, boasts a remarkable array of capabilities that make it more than just a technological marvel. Its performance is driven by sophisticated systems that allow it to navigate, interact, manipulate objects, and perceive its environment with a degree of autonomy. Understanding these capabilities is key to appreciating the EMIEW3’s potential applications in diverse settings.The EMIEW3’s performance hinges on the integration of several key technologies.
These include advanced navigation and mobility, sophisticated sensor-based interaction, precise object handling, and robust environmental awareness. These technologies work in concert to provide a safe and effective robotic assistant.
Navigation and Mobility Systems
The EMIEW3’s navigation relies on a combination of advanced sensors and sophisticated algorithms. These systems enable the robot to map its surroundings and plan efficient routes. This combination of technologies allows for safe and effective movement within various environments. Precise localization and obstacle avoidance are critical to its performance.
The Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot is pretty cool, right? But imagine its potential in a world with web3 coinbase apple moderation nfts — it could be programmed to handle complex moderation tasks, freeing up human staff for more creative endeavors. Still, the core function of the EMIEW3, assisting humans, remains the same, regardless of the evolving digital landscape.
Interaction Capabilities
The EMIEW3’s interaction capabilities are driven by a suite of sensors, including cameras, depth sensors, and tactile sensors. These sensors enable the robot to perceive and respond to its environment. Sophisticated communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi and Ethernet, facilitate data transmission and control. This allows the robot to interact with its surroundings in a precise and controlled manner. These systems are vital for tasks like object recognition and manipulation.
Object Manipulation and Handling
The EMIEW3’s dexterity is a key aspect of its performance. The robot’s articulated arms and grippers are designed for handling objects of varying shapes and sizes. Precise control systems enable the robot to grasp, lift, and place objects with accuracy. The robot’s design allows for a high degree of dexterity, which is critical for its use in tasks that require handling and manipulation of physical objects.
Environmental Awareness and Safety Features, Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot
The EMIEW3 is equipped with a comprehensive suite of safety features. Sensors detect obstacles and adjust its movements accordingly. These systems prioritize safety and prevent collisions. Advanced algorithms enable the robot to avoid potential hazards, maintaining a safe operating environment. The safety features are critical to ensuring the EMIEW3’s reliability and safety in diverse settings.
Performance Metrics
| Metric | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Navigation Speed | Up to 1.5 meters per second in open spaces. |
| Obstacle Avoidance Time | Less than 0.2 seconds, in most cases. |
| Object Recognition Accuracy | 95% accuracy for standard objects. |
| Object Manipulation Precision | Within 1mm of target. |
| Communication Range | Up to 100 meters in ideal conditions. |
| Operating Temperature Range | 0°C to 40°C |
Technological Advancements
The Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot represents a significant leap forward in the evolution of service robots. Its advanced capabilities rely on a sophisticated interplay of AI, machine learning, and robotics technologies, allowing for greater dexterity, autonomy, and adaptability compared to previous models. This section delves into the key technological advancements powering the EMIEW3, highlighting their implementation and potential future developments.
Core Technologies Employed
The EMIEW3’s success hinges on a carefully orchestrated combination of technologies. This section explores the specific implementations of these technologies. Advanced sensors, including high-resolution cameras and sophisticated depth-sensing systems, enable the robot to perceive its surroundings with remarkable precision. These detailed sensory inputs are then processed by powerful AI algorithms, allowing the EMIEW3 to navigate complex environments and interact effectively with people.
AI and Machine Learning Implementation
The EMIEW3’s AI is not merely reactive; it learns and adapts. Machine learning algorithms are integrated into the robot’s core functions. These algorithms allow the robot to refine its performance over time, learning from its interactions with people and the environment. For instance, the EMIEW3 can learn different communication styles and adapt its responses accordingly, enhancing its effectiveness in various scenarios.
This iterative learning process is crucial for the robot’s overall intelligence and adaptability.
Comparison with Previous Iterations
Compared to previous generations of Hitachi service robots, the EMIEW3 demonstrates significant improvements in several areas. Early models often relied on simpler rule-based systems, limiting their adaptability and responsiveness. The EMIEW3’s advanced AI and machine learning capabilities allow it to handle a broader range of tasks and adapt to unforeseen circumstances with greater precision. The improved navigation capabilities, coupled with enhanced interaction protocols, highlight the advancements in robotics and AI.
Potential Future Developments
Future developments in the EMIEW3’s technology could focus on increasing the robot’s dexterity and physical capabilities. Integration of more advanced manipulation techniques could enable the robot to perform more complex tasks. Furthermore, improvements in natural language processing and understanding could lead to even more sophisticated and nuanced human-robot interaction. The potential for integrating advanced haptic feedback systems could further enhance the robot’s ability to interact with the environment and people in a more intuitive manner.
Consider how self-driving cars are constantly improving through continuous learning and refinement of their AI systems.
Summary of Core Technologies
| Technology | Application in EMIEW3 |
|---|---|
| Advanced Sensors (Cameras, Depth Sensors) | Precise perception of the environment, enabling navigation and object recognition. |
| Powerful AI Algorithms | Enable the robot to understand and respond to complex situations, including natural language processing and decision-making. |
| Machine Learning | Allows the robot to adapt and improve its performance over time, learning from interactions and experiences. For example, by observing how people interact in a specific environment, the EMIEW3 can adjust its behavior to better fit the situation. |
| Robotics Platforms | Provide the physical structure and movement capabilities for the robot to interact with its surroundings, including locomotion and manipulation. |
Applications and Use Cases
The Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot, with its advanced capabilities, presents a wide range of potential applications across various sectors. Its adaptability and intelligent features make it a valuable asset for automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enhancing safety in diverse environments. From industrial settings to commercial spaces and even homes, the EMIEW3 offers a unique blend of functionality and user-friendliness.The EMIEW3’s design prioritizes both safety and ease of integration.
Its intuitive control systems and robust construction make it suitable for deployment in diverse operational settings. The robot’s ability to perform complex tasks autonomously and adapt to changing environments opens up possibilities for automation in previously uncharted areas.
Industrial Applications
The EMIEW3’s precision and reliability make it an ideal choice for various industrial tasks. Its ability to navigate complex environments and execute precise movements makes it suitable for assembly lines, material handling, and quality control. Its modular design allows for customized configurations to meet specific industrial needs.
- Automated Assembly: The EMIEW3 can perform repetitive assembly tasks with high accuracy and speed, reducing errors and increasing output on assembly lines. This can improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs, particularly in manufacturing processes requiring precise component placement.
- Material Handling: The EMIEW3 can safely and efficiently transport materials between different workstations or storage areas. This automation reduces the risk of injuries associated with manual material handling and improves overall logistics within the factory. It can be equipped with specialized grippers for handling various materials, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Quality Control: The EMIEW3 can perform automated inspections, ensuring high-quality standards throughout the production process. Its advanced sensors and image processing capabilities can detect defects and inconsistencies in products, contributing to higher product quality and reduced waste.
Commercial Applications
In commercial settings, the EMIEW3 can streamline operations and enhance customer service experiences. Its ability to navigate complex environments and interact with people makes it a valuable asset in various retail, hospitality, and service-oriented industries.
- Retail Assistance: The EMIEW3 can assist customers with product information, provide recommendations, and even guide them through the store. This personalized customer service experience can improve customer satisfaction and sales conversions. Imagine a robot helping customers find specific items or providing information about products.
- Hospitality Services: In hotels and restaurants, the EMIEW3 can deliver food and beverages, assist with guest requests, and even provide information about amenities. This improves service efficiency, freeing up staff for more complex tasks and improving the overall guest experience. The robot could transport trays of food or drinks to tables, or guide guests to their rooms.
- Customer Support: The EMIEW3 can handle routine customer support inquiries, freeing up human agents to handle more complex issues. This improves response times and ensures customers receive assistance quickly and efficiently.
Domestic Applications
The EMIEW3’s capabilities extend to domestic settings, where it can assist with various household tasks and enhance daily living. Its ability to navigate homes safely and interact with people makes it a useful addition to a household.
- Household Assistance: The EMIEW3 can assist with tasks like fetching items, delivering messages, and even providing companionship. Imagine a robot fetching groceries from the store, or bringing medicine to a senior citizen.
- Elder Care Support: The EMIEW3 can assist elderly individuals with daily tasks, providing companionship, and ensuring safety. This can be invaluable in supporting independent living and maintaining quality of life.
Sector-Specific Roles
| Sector | Specific Roles |
|---|---|
| Industrial Manufacturing | Automated assembly, material handling, quality control |
| Retail | Product information, customer guidance, order fulfillment |
| Hospitality | Food delivery, guest assistance, information provision |
| Healthcare | Medication delivery, patient monitoring (potential) |
| Residential | Household tasks, companionship, assistance for elderly individuals |
Market Analysis and Future Projections: Hitachi EMIEW3 Assistant Robot
The Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot enters a dynamic service robot market, where competition is heating up and innovation is key. Understanding the current landscape, future growth potential, and potential challenges is crucial for navigating the path to success. This analysis explores the EMIEW3’s competitive standing and its projected impact on the broader service robot sector.The market for service robots is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing automation needs in various sectors.
This growth is fueled by factors such as rising labor costs, the need for improved efficiency, and the desire for enhanced safety in demanding environments. The EMIEW3, with its unique capabilities, aims to capitalize on these trends.
Current Market for Service Robots
The service robot market is diverse, encompassing various applications, from industrial automation to household assistance. Key competitors in this space are vying for market share, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. The EMIEW3 distinguishes itself through its focus on intelligent and intuitive interaction, aiming to be more than just a task-performing machine.
Competitive Landscape
Several companies offer similar service robots, each targeting specific niches. The EMIEW3’s approach, however, emphasizes human-robot collaboration, allowing for a wider range of applications. Direct competitors include [insert names of 2-3 direct competitors], known for their strengths in [mention specific strengths of competitors, e.g., robust construction, specific specialized functions]. The EMIEW3, however, aims to bridge the gap between industrial and domestic applications, offering adaptability that other models may lack.
Projected Market Growth
The service robot market is projected to reach [insert projected market size] by [insert projected year], driven by increased demand for automation and intelligent assistance. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in sectors like healthcare, logistics, and retail. Real-world examples like [insert example of successful service robot implementation in a specific sector] showcase the market’s burgeoning potential.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
The EMIEW3 faces challenges like high initial investment costs and the need for robust infrastructure support. However, its potential to improve efficiency and productivity in various sectors presents significant opportunities. Addressing the challenges through strategic partnerships and cost-effective solutions will be key to successful market penetration. Potential opportunities also lie in expanding into emerging markets with growing labor needs and limited workforce availability.
Economic Impact of Deployment
The deployment of the EMIEW3 has the potential to generate significant economic impact. Reduced labor costs, improved productivity, and enhanced safety can contribute to increased profitability for businesses. The EMIEW3’s ability to automate tasks and free up human workers for more complex and creative endeavors is a major economic benefit.
The Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot is pretty cool, but imagine its capabilities enhanced by a reliable internet connection. That’s where HughesNet’s satellite internet service gets a big boost comes in handy. This improved service could open up exciting possibilities for remote operation and data transfer, making the EMIEW3 even more valuable for various tasks, from simple chores to complex industrial applications.
Market Share Projections
| Year | Overall Service Robot Market Share (%) | EMIEW3 Projected Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | [insert estimated market share percentage for 2024] | [insert estimated EMIEW3 market share percentage for 2024] |
| 2025 | [insert estimated market share percentage for 2025] | [insert estimated EMIEW3 market share percentage for 2025] |
| 2026 | [insert estimated market share percentage for 2026] | [insert estimated EMIEW3 market share percentage for 2026] |
Note: These figures are projections and are subject to market fluctuations and unforeseen events.
Design and Development Considerations
The Hitachi EMIEW3 Assistant Robot, a testament to cutting-edge robotics technology, was meticulously designed and developed with a focus on both functionality and safety. The iterative development process, incorporating feedback from various stakeholders, played a crucial role in shaping the final product. This section delves into the core design principles, safety measures, development methodology, manufacturing processes, and the trade-offs inherent in creating such a sophisticated robot.
Design Principles
The EMIEW3 was designed with a user-centric approach. Key principles included creating a visually appealing and intuitive robot interface, ensuring smooth and predictable movement, and maintaining a compact form factor to optimize maneuverability in diverse environments. Ergonomics were prioritized to minimize operator fatigue and maximize user comfort. This holistic approach aimed to seamlessly integrate the robot into existing workspaces.
Safety Protocols and Measures
Robust safety protocols are paramount in the design of any robot, especially one intended for human interaction. The EMIEW3 incorporates advanced sensor systems, including laser range finders, depth cameras, and pressure sensors, to detect obstacles and maintain safe distances from humans and objects. Emergency stop mechanisms are integrated throughout the robot’s structure for immediate disengagement in critical situations.
Furthermore, the robot’s design minimizes sharp edges and incorporates soft-touch materials to mitigate the risk of accidental injury. The robot’s software is also programmed with fail-safes, ensuring that potential malfunctions do not result in harm to the user or surrounding environment.
Development Methodology
The EMIEW3’s development utilized an agile methodology. This approach facilitated rapid prototyping, continuous feedback loops, and iterative improvements throughout the project. Cross-functional teams worked collaboratively, ensuring seamless integration of mechanical, electrical, software, and control systems. Testing was integral to the process, with rigorous simulations and real-world trials conducted to validate the robot’s performance in diverse scenarios. This iterative approach enabled rapid adaptation to emerging needs and technological advancements.
Manufacturing and Production
The manufacturing process for the EMIEW3 was designed to balance cost-effectiveness with quality. Advanced robotic arms were employed in critical assembly steps to ensure precision and consistency. The use of 3D printing for prototyping and specific components allowed for rapid iteration and reduced lead times. The supply chain was carefully managed to guarantee the timely procurement of high-quality components, ensuring efficient production and timely delivery.
Modular design principles were adopted to facilitate easier maintenance and future upgrades.
Key Design Considerations and Trade-offs
| Design Consideration | Implementation Details | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|
| Weight and Mobility | The robot’s weight was minimized while maintaining structural integrity and carrying capacity. This was achieved through the use of lightweight materials and optimized component placement. | A lighter robot facilitates faster movement, but compromises in structural rigidity may result in reduced payload capacity. |
| Power Efficiency | Energy consumption was a critical consideration, and energy-efficient motors and battery technologies were selected. | Higher energy efficiency may translate to longer operational time, but potentially higher cost. |
| Durability and Reliability | The robot’s components were chosen for their resistance to wear and tear, ensuring long-term operational reliability. | High-quality components may increase the production cost, but improve longevity and reliability. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Balancing quality with cost was a key factor in the selection of materials and manufacturing processes. | Cost reduction might compromise performance or safety features, potentially impacting long-term value. |
User Experience and Interaction
The Hitachi EMIEW3 Assistant Robot’s success hinges on its ability to seamlessly integrate into daily life. A user-friendly interface and intuitive interaction methods are paramount for widespread adoption. Positive user experiences encourage repeat use and build trust in the robot’s capabilities.
User Interface and Interaction Methods
The EMIEW3 utilizes a combination of visual and voice-based interfaces for interaction. A large touchscreen display serves as the primary interface, allowing users to navigate menus, initiate tasks, and monitor robot status. Voice commands are supported for hands-free operation, especially beneficial during tasks like setting reminders or controlling the robot’s movement. Gesture recognition is also integrated to facilitate natural and intuitive control.
| Interaction Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Touchscreen | A 10.1-inch high-resolution touchscreen allows for direct selection of options, navigation through menus, and viewing data. | Selecting “Set Timer” from the main menu. |
| Voice Command | Natural language processing allows users to issue voice commands for tasks such as “Turn on the lights” or “Remind me to call John at 10 AM”. | Giving a voice command to play music. |
| Gesture Recognition | The robot can recognize and respond to specific hand gestures for actions like “Stop”, “Pause”, “Next”. | Using a hand gesture to signal the robot to stop its current operation. |
Learning Curve
The EMIEW3 is designed for minimal user training. A guided onboarding process, including interactive tutorials and visual aids, helps users become proficient with the robot quickly. The system provides clear feedback on commands, actions, and responses to ensure user confidence and reduce frustration.
User Training Materials and Support Resources
Extensive training materials are available, including online tutorials, video demonstrations, and a comprehensive user manual. A dedicated support portal offers FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and direct access to technical support staff. This ensures users can find answers to common questions and address technical issues promptly.
Accessibility Features
The EMIEW3 is designed with accessibility in mind. The large touchscreen and clear text facilitate ease of use for users with visual impairments. Voice commands provide an alternative input method for users with dexterity limitations. The user interface is also customizable to individual preferences, allowing users to adjust font sizes and colors.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the Hitachi EMIEW3 assistant robot represents a significant step forward in service robotics. Its comprehensive capabilities, combined with innovative design features, position it to excel in diverse applications. The future of this technology looks bright, promising increased efficiency and effectiveness in various sectors. We’ve explored its capabilities, history, and future potential. What do you think?
Will the EMIEW3 truly revolutionize how we work and live?