GDPR fines the biggest privacy penalties handed out so far, marking a significant escalation in the enforcement of data protection regulations. This isn’t just about fines; it’s a stark reminder of the critical importance of data privacy in today’s digital world. We’ll delve into the history of GDPR, its core principles, and the significant penalties levied on companies for violations.
The sheer scale of these fines is forcing a reevaluation of data protection strategies across industries.
This article will explore the top GDPR fines, analyzing the violations, penalties, and impact on businesses. We’ll also examine the future of GDPR enforcement, predicting potential changes in regulations and penalties, and how businesses can mitigate risk in this ever-evolving landscape. A case study of a significant fine will be presented to provide actionable steps for preventing similar issues.
The data reveals a clear trend: robust data protection strategies are no longer optional; they’re essential for survival.
Introduction to GDPR Fines
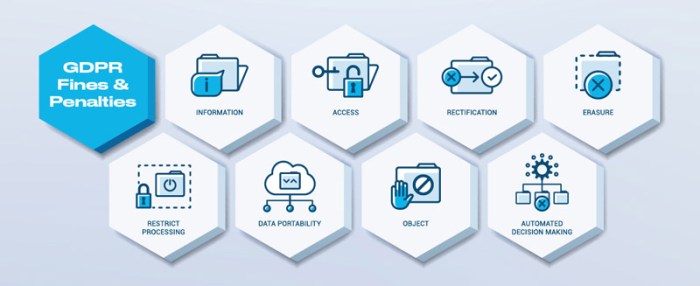
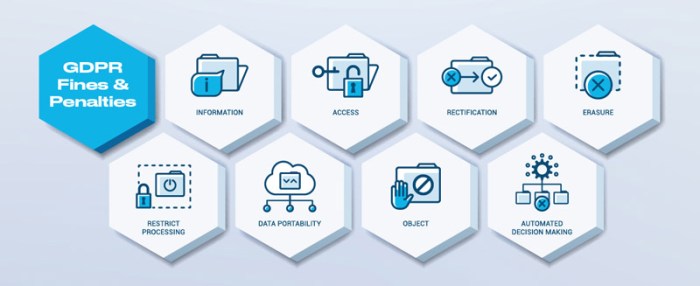
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was introduced in 2018, aiming to harmonize data protection laws across the European Union. Its evolution stems from a recognition of the increasing importance of data protection in the digital age and the need for a comprehensive framework to address the evolving risks associated with personal data processing. The regulation’s core principles reflect a commitment to empowering individuals and ensuring their control over their personal information.The core principles of GDPR revolve around the fundamental rights of individuals concerning their personal data.
These principles emphasize the need for data minimization, data security, and the transparency of data processing practices. Individuals are granted rights such as the right to access, rectify, erase, and restrict processing of their personal data.Key enforcement mechanisms within GDPR include investigations, audits, and sanctions by supervisory authorities. The authorities have the power to impose significant penalties for breaches of the regulation.
The aim is to ensure compliance with GDPR standards and deter any potential infringements.Examples of previous GDPR infringements and penalties include cases where companies failed to adequately protect user data leading to breaches. These breaches have resulted in substantial financial penalties, highlighting the seriousness with which the GDPR is enforced.
Key Areas Targeted by GDPR Fines
The table below Artikels the key areas of GDPR frequently targeted by fines, providing a concise description, an example of an infringement, and a typical penalty range. These examples demonstrate the importance of adhering to GDPR regulations for organizations handling personal data.
| Area of GDPR | Description | Example of Infringement | Typical Penalty Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Subject Rights | Ensuring individuals have control over their data, including access, rectification, erasure, and objection rights. | Failing to provide a clear and timely response to a data subject’s request to access their personal data or failing to correct inaccurate information. | €10 million or 2% of global annual turnover (whichever is higher). |
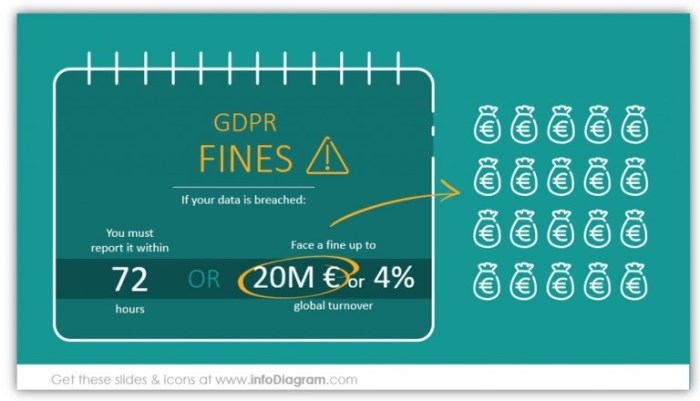
| Data Security | Protecting personal data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. | A significant data breach affecting a large number of users due to inadequate security measures, such as weak passwords or unpatched software. | €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover (whichever is higher). |
| Transparency and Consent | Clearly informing individuals about how their data is being collected and used, obtaining valid consent, and providing easily accessible information. | Using unclear or misleading privacy policies, collecting data without proper consent, or failing to provide individuals with sufficient information regarding data processing activities. | €10 million or 2% of global annual turnover (whichever is higher). |
| International Data Transfers | Ensuring appropriate safeguards for transferring personal data outside the EU. | Transferring personal data to a country without adequate protection mechanisms for data privacy, such as lack of an adequacy decision. | €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover (whichever is higher). |
Analyzing the Largest GDPR Fines
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has significantly impacted how organizations handle personal data. One key aspect of this impact is the substantial financial penalties for non-compliance. These fines act as a deterrent and underscore the importance of robust data protection measures. The largest fines illustrate the real-world consequences of violating GDPR principles.The GDPR’s emphasis on individual rights and data protection has spurred a new era of accountability for companies worldwide.
The magnitude of the largest fines reflects the regulatory bodies’ commitment to enforcing the regulation and safeguarding user privacy. This in turn, encourages businesses to adopt stringent data protection policies and practices.
Top GDPR Fines
The GDPR has established a framework for handling personal data, which is essential for maintaining trust between organizations and their users. Several prominent organizations have faced significant fines for violating this framework. These examples highlight the severity of the consequences for non-compliance.
- Google was fined €50 million in 2021 by the Irish Data Protection Commission for issues with the processing of personal data, including a failure to properly implement consent mechanisms for the use of cookies. This fine illustrates the importance of transparent consent procedures in handling user data. This case served as a strong reminder for organizations to diligently comply with the requirements for obtaining explicit and informed consent.
- The French data protection authority fined Facebook €500 million in 2021 for violations related to data protection and privacy issues. The violation was primarily due to insufficient data security measures that resulted in potential data breaches. This high-profile fine highlights the critical role of robust security measures in safeguarding personal data. The fine underscored the potential for massive financial penalties when companies fail to adequately protect user data.
-
Another notable case involves the €20 million fine levied against a large European retailer in 2021. The fine was imposed by the UK Information Commissioner’s Office for inadequacies in data security procedures, including a lack of robust measures for data encryption and access control. The fine reflects the significance of maintaining appropriate data security measures, emphasizing the importance of establishing and implementing stringent data protection practices.
The penalty demonstrates the critical need for comprehensive security protocols to prevent data breaches and safeguard sensitive information.
Comparison with Other Penalties
While the GDPR fines are substantial, they must be considered within the broader context of penalties in the digital world. Comparing GDPR fines to other penalties like those for antitrust violations or intellectual property infringements provides a more comprehensive understanding of the enforcement landscape. In some cases, GDPR fines might be relatively lower compared to penalties in other domains.
This suggests a focus on fostering compliance rather than solely punitive measures, especially in the digital sphere.
GDPR fines are definitely some of the biggest privacy penalties handed out so far, highlighting the importance of data protection. Meanwhile, a recent development, an HBO hacker charged with Game of Thrones related crimes, shows how serious these breaches can be. Ultimately, the hefty GDPR fines underscore the crucial need for companies to prioritize data security.
Timeline of Largest Fines
| Fine Number | Company/Organization | Violation | Penalty Amount | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Processing of personal data, cookie consent | €50 million | 2021 | |
| 2 | Data protection and privacy issues | €500 million | 2021 | |
| 3 | European Retailer | Data security procedures, encryption | €20 million | 2021 |
Impact of the Fines on Businesses
The substantial GDPR fines levied against organizations worldwide have significantly impacted business practices. These penalties have spurred a shift in corporate data protection strategies, highlighting the crucial need for robust compliance measures. The sheer size of these fines has demonstrated the potential repercussions of non-compliance, motivating companies to prioritize data protection and risk mitigation.The consequences of non-compliance extend beyond financial penalties.
Reputational damage, legal challenges, and loss of customer trust can be equally devastating. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the long-term value of proactive data protection measures as a crucial element of their overall business strategy.
Influence on Company Data Protection Practices
The immense financial burden of GDPR fines has forced many companies to reassess their data protection strategies. Organizations are now investing heavily in robust data governance frameworks, comprehensive data mapping, and employee training programs to ensure compliance. Implementing these measures is not just a reactive response but a proactive step towards establishing a culture of data protection within the organization.
This involves a clear understanding of the data being processed, the legal basis for processing it, and the rights of individuals with respect to their data.
Potential Repercussions of Non-Compliance
The potential repercussions of non-compliance with GDPR are substantial. Beyond the monetary fines, businesses face the risk of losing customer trust and damaging their reputation. Negative publicity, legal battles, and potential boycotts can significantly impact a company’s bottom line. Moreover, a lack of compliance can lead to regulatory investigations and further penalties, creating a vicious cycle of negative consequences.
The sheer scale of these potential repercussions underscores the importance of prioritizing data protection and compliance efforts.
Industries Most Affected by GDPR Fines
Several industries are particularly susceptible to GDPR fines. The most affected are those handling large volumes of personal data, such as those dealing with online advertising, e-commerce, and cloud services. These industries often deal with highly sensitive personal information, requiring rigorous data protection practices. For example, the e-commerce industry collects vast amounts of customer data for transactions and personalized experiences, making them vulnerable to breaches and penalties if not compliant.
Cloud services, by their nature, handle a significant volume of user data, making them a prime target for GDPR audits.
GDPR fines are undeniably the biggest privacy penalties handed out so far, highlighting the critical need for robust data protection regulations. However, the recent temporary halting of Xiaomi’s arbitrary and capricious US ban, as detailed in this article , offers a contrasting perspective on how international tech companies are navigating these complex legal landscapes. Ultimately, the ongoing debate around GDPR fines continues to shape the future of data privacy worldwide.
Measures Taken by Businesses to Mitigate Risk
To mitigate the risk of GDPR fines, businesses are taking various proactive measures. These include establishing robust data protection policies and procedures, conducting regular data protection audits, and investing in employee training to raise awareness of data protection principles. Implementing technical safeguards, such as encryption and access controls, to secure data is another crucial step. Further, companies are adopting a proactive approach to compliance, incorporating data protection principles into their overall business strategy and ensuring ongoing vigilance.
Contrast in Responses to GDPR Fines (Table)
| Industry | Typical Response to Fines | Examples of Specific Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Increased investment in data security measures, review and revision of privacy policies, and improved training for employees. | Implementation of stronger encryption protocols for customer data, enhancement of data breach response plans, and establishment of dedicated data protection teams. |
| Finance | Enhanced data security protocols, comprehensive privacy impact assessments, and rigorous compliance checks. | Upgraded data encryption technologies, implementation of stricter access controls, and more frequent security audits. |
| Technology | Focus on transparency, data minimization, and data subject rights, often through revisions to user agreements and privacy policies. | Developing user-friendly data access portals, implementing automated data deletion procedures, and enhanced data breach notification systems. |
Future Trends and Predictions
The escalating fines levied under GDPR highlight a growing emphasis on data protection. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the critical need for robust data protection strategies. This evolution is not merely a reaction to penalties; it’s a fundamental shift in how organizations approach customer data and privacy.The future of GDPR enforcement is likely to be characterized by greater scrutiny and a more proactive approach.
Expect more frequent audits and investigations, potentially targeting a wider range of data handling practices. This trend is driven by the evolving technological landscape and the increasing sophistication of data breaches.
Anticipated Developments in GDPR Enforcement
Enforcement agencies are expected to focus on a broader range of violations beyond the initial emphasis on large-scale breaches. This includes scrutinizing smaller, but potentially harmful, data processing errors and omissions. Furthermore, the emphasis is shifting towards preventative measures, requiring businesses to demonstrate proactive compliance efforts rather than merely reacting to incidents. This proactive approach necessitates a thorough understanding of data flows and the implementation of robust security protocols.
Potential Changes to the Penalty Structure
The current penalty structure, while substantial, may evolve to reflect the growing severity and sophistication of data breaches. The potential changes include:
- Increased Maximum Fines: As data breaches become more complex and costly, the maximum potential fines may increase, potentially impacting even the largest multinational corporations.
- Proportionality of Penalties: Future regulations might focus on a more proportional penalty structure, aligning fines with the severity of the violation and the potential harm to individuals.
- Repeated Offenses: A stricter approach to repeated offenses is also anticipated. This means that organizations with a history of non-compliance could face significantly higher penalties than those who commit violations for the first time.
Future Direction of Data Protection Regulations
The future direction of data protection regulations is likely to be influenced by the evolving technological landscape. Expect regulations to adapt to new technologies, like artificial intelligence and the internet of things (IoT). These technologies will bring new challenges in terms of data processing and security, necessitating adjustments to the existing frameworks. The need to protect personal data in these contexts will likely lead to more specific regulations for handling sensitive data collected through these innovative technologies.
For example, if AI systems use personal data to make decisions, the GDPR may include specific rules about the fairness and transparency of these decisions.
GDPR fines are definitely the biggest privacy penalties handed out so far, but talk about a distraction! Apparently, a new all electric very pink Jaguar concept leaked online ( the new all electric very pink Jaguar concept leaks online ). While that’s certainly eye-catching, the sheer scale of some of these GDPR fines is still pretty mind-boggling. It really highlights the importance of robust data protection practices.
Impact of Future Fines on Business Strategies
The increasing severity of GDPR fines will undoubtedly impact business strategies. Organizations will likely allocate more resources to ensure robust data protection measures. This includes investing in advanced security technologies, training employees on data privacy best practices, and establishing clear data governance policies. The need for proactive measures, rather than simply reactive measures, will become paramount. A potential scenario involves a business facing a substantial fine for a data breach.
This could result in reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and significant financial penalties.
Impact of Technological Advancements on GDPR Compliance
Technological advancements, while presenting challenges, also offer solutions for GDPR compliance. Advanced encryption technologies, data anonymization techniques, and enhanced security protocols can significantly bolster data protection efforts. Cloud computing, while raising concerns about data security, also provides opportunities for centralized data management and security. Organizations must carefully evaluate the potential risks and benefits of these technologies and implement appropriate safeguards.
For example, implementing robust access controls within a cloud environment can mitigate security risks and enhance GDPR compliance.
Case Study Analysis: Gdpr Fines The Biggest Privacy Penalties Handed Out So Far
Delving into the specifics of a significant GDPR fine reveals critical insights into the practical application of the regulation. Understanding the factors that led to a penalty allows businesses to identify vulnerabilities in their data protection practices and strengthen their compliance strategies. This case study will focus on the principles that apply to all organizations, regardless of size or industry.
The Google Ireland Case
The Google Ireland case, while not the highest fine, serves as a potent example of the importance of data subject rights and transparency. The European Data Protection Board found Google had insufficient transparency about data transfers, particularly to the US, violating the principle of lawful processing. This case highlighted the crucial role of demonstrating legitimate grounds for data transfers and the need for robust documentation.
Key Lessons Learned, Gdpr fines the biggest privacy penalties handed out so far
The Google Ireland case underscores several key lessons for businesses. Firstly, robust documentation and transparency regarding data transfers are paramount. Secondly, meticulous attention to the specific rights of data subjects, such as the right to access, rectification, and erasure, is critical. Finally, a proactive approach to compliance, rather than a reactive one, is essential for mitigating risks.
Actionable Steps to Prevent Similar Issues
Companies can take several proactive steps to avoid similar GDPR infringements. Establishing a clear data protection policy is crucial, outlining the organization’s data handling procedures and the specific rights of data subjects. Regularly reviewing and updating this policy is equally important, keeping pace with evolving regulations and best practices. Furthermore, companies should implement comprehensive training programs for all employees involved in data handling, ensuring they understand their responsibilities and the importance of compliance.
Visual Representation of GDPR Compliance Steps
The following flowchart illustrates the key steps in preventing a GDPR fine, focusing on proactive compliance:
+-----------------+
| Data Audit |
+-----------------+
| \
| \ Data Protection Policy
| \ Review and Update
v v
+-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Data Mapping |---->| Employee Training |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+
| \ |
| \ |
| \ v
v v
+-----------------+
| Data Transfers |
+-----------------+
|
| \ Documentation and Transparency
| \
v v
+-----------------+
|Regular Reviews |
+-----------------+
|
v
+-----------------+
|Compliance Checks|
+-----------------+
|
v
+-----------------+
| Incident Response|
+-----------------+
This flowchart illustrates a cyclical process, emphasizing continuous improvement and proactive measures.
Each step builds upon the previous one, fostering a culture of data protection compliance.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the escalating GDPR fines underscore the critical need for proactive data protection measures. Businesses must prioritize compliance and implement robust strategies to avoid costly penalties and reputational damage. The future of data protection hinges on the ability of businesses to adapt and anticipate evolving regulations. The lessons learned from these massive fines are invaluable for anyone working with data, ensuring that the protection of personal information is prioritized above all else.