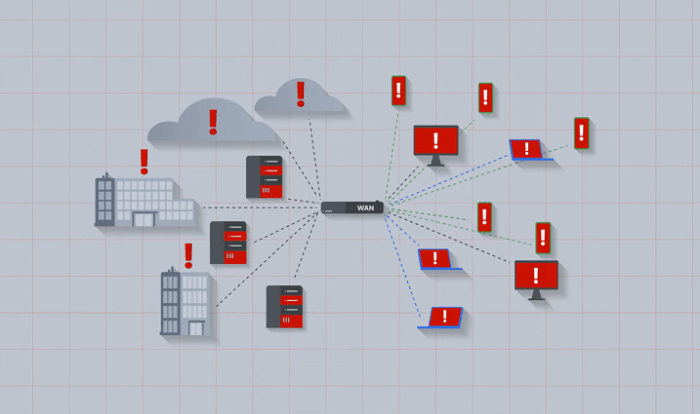
Gartner best security pracices for sd wan – Gartner best security practices for SD-WAN sets the stage for robust network security. This guide delves into the key recommendations, from design considerations to implementation strategies, monitoring, and future trends. We’ll explore how to secure your SD-WAN, mitigating risks and maximizing performance.
Gartner’s framework provides a structured approach to SD-WAN security, encompassing everything from initial design to ongoing maintenance. The document Artikels a comprehensive strategy, highlighting the crucial aspects for successful implementation.
Introduction to Gartner Best Practices for SD-WAN Security

Gartner’s best practices for SD-WAN security offer a crucial framework for organizations looking to protect their distributed networks. These recommendations address the unique challenges posed by the decentralized nature of SD-WAN deployments, focusing on securing the network edge, data in transit, and sensitive data at rest. The core principle is to integrate security measures seamlessly into the SD-WAN architecture, rather than treating security as an afterthought.Gartner’s recommendations are driven by the increasing reliance on SD-WAN for critical business operations and the rise of sophisticated cyber threats targeting these networks.
The growing attack surface presented by distributed SD-WAN deployments necessitates proactive security strategies to prevent breaches and maintain business continuity. Protecting sensitive data transmitted across these networks is paramount, as is the need to maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Gartner’s Approach to SD-WAN Security Best Practices
Gartner emphasizes a layered security approach that considers the entire SD-WAN lifecycle. This includes secure design, implementation, operation, and ongoing monitoring. Their recommendations cover various aspects, from network segmentation and access control to threat detection and response. Security isn’t viewed as an add-on, but rather an integral component of the SD-WAN strategy from the initial planning stages.
Key Motivations Behind Gartner’s Recommendations
The motivations behind Gartner’s recommendations stem from the evolving threat landscape and the increasing reliance on SD-WAN. Organizations are facing a complex mix of threats, including sophisticated malware, insider threats, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Securing SD-WAN is critical for protecting sensitive data and maintaining business operations. The rise of remote work further exacerbates the need for secure access and management of resources.
Structure and Organization of Gartner’s Best Practices
Gartner’s best practices are organized to provide a comprehensive guide. The documents likely cover a range of topics, including security considerations at each layer of the SD-WAN stack. This structure helps organizations tailor security measures to their specific needs and scale. Expected sections might include planning, implementation, and ongoing monitoring of security controls. The structure promotes a practical and actionable approach to securing SD-WAN deployments.
Key Areas of Focus in Gartner’s SD-WAN Security Recommendations
Gartner’s recommendations address various crucial areas to ensure robust security in SD-WAN deployments. A well-structured security framework is vital for mitigating potential vulnerabilities.
| Area | Description | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Segmentation | Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the impact of a breach. | Segmenting the network based on departments or locations. | Reduces the potential damage from a security incident by limiting the spread of malware or unauthorized access. |
| Access Control | Implementing policies to control user access to network resources. | Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) for remote access. | Reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. |
| Threat Detection and Response | Implementing mechanisms to detect and respond to security threats in real time. | Using intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools. | Enables quick identification and containment of security incidents, minimizing potential damage. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access or exfiltration. | Using DLP tools to monitor and control data movement across the network. | Maintains compliance with data protection regulations and prevents sensitive data breaches. |
Security Considerations for SD-WAN Design
SD-WAN deployments, while offering significant benefits in network flexibility and cost savings, introduce unique security challenges. Proper security design is crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data traversing the network. Gartner’s best practices provide a framework for addressing these challenges, focusing on a zero-trust approach and robust security controls.SD-WAN’s distributed nature and reliance on potentially less secure edge devices necessitates a proactive and layered security strategy.
This involves understanding and addressing the specific security vulnerabilities associated with different components of the SD-WAN architecture. A key element is incorporating zero-trust principles throughout the design to limit lateral movement and ensure granular access control.
Crucial Security Design Elements
Gartner emphasizes the importance of integrating security into every stage of the SD-WAN lifecycle, from design and implementation to ongoing monitoring and management. This includes comprehensive security assessments, strong access controls, and a robust incident response plan. Security should not be an afterthought but an integral part of the architecture.
Zero-Trust Principles in SD-WAN Security Architecture
Implementing zero-trust principles is paramount in SD-WAN security. This means verifying the identity and trustworthiness of every device and user, regardless of location, before granting access to network resources. Micro-segmentation, granular access controls, and multi-factor authentication are crucial components of a zero-trust SD-WAN. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface and isolates compromised devices.
Addressing Unique Security Challenges of SD-WAN
Gartner’s best practices address the unique challenges of SD-WAN by emphasizing the need for a holistic security strategy that considers the entire network perimeter. This involves using advanced threat detection and prevention technologies, implementing secure remote access solutions, and regularly updating security policies. Moreover, the inherent flexibility of SD-WAN necessitates constant monitoring and adaptation of security measures to address evolving threats.
Security Considerations for SD-WAN Design
A well-designed SD-WAN security strategy requires a thorough understanding of potential threats and vulnerabilities. The following table Artikels crucial security considerations, categorized by threat type, providing insights into effective mitigation strategies.
| Threat Type | Consideration | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | Vulnerabilities in edge devices, insecure remote access points, and insufficient authentication mechanisms. | Implementing strong authentication protocols (e.g., multi-factor authentication), securing edge devices with appropriate firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and enforcing strict access controls. |
| Data Breaches | Data exfiltration through compromised devices or insecure communication channels. | Employing encryption throughout the network, implementing data loss prevention (DLP) solutions, and conducting regular security audits. |
| Malware and Ransomware | Malware infections on edge devices, potentially compromising the entire network. | Implementing endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, regularly updating security software, and employing network security tools to detect and prevent malicious activity. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks | Attacks aimed at disrupting network availability by flooding it with malicious traffic. | Implementing DDoS mitigation solutions, utilizing load balancers, and monitoring network traffic for unusual patterns. |
Implementing Security Measures in SD-WAN
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for the success of any SD-WAN deployment. A well-secured SD-WAN protects sensitive data traversing the network, safeguards against threats, and ensures compliance with industry regulations. This involves a multi-layered approach, incorporating various tools and technologies to address diverse security vulnerabilities.Effective security in an SD-WAN environment necessitates a proactive and layered approach. This involves not just implementing security tools but also establishing policies and procedures that integrate security into the SD-WAN design and operational processes.
Understanding the nuances of various security technologies is vital to make informed decisions about selecting and deploying them within the SD-WAN framework.
Security Tools and Technologies Recommended by Gartner
Gartner often recommends a combination of security tools and technologies for SD-WAN, encompassing network access control, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and secure access service edge (SASE) solutions. These tools work in tandem to protect the network from various threats, from unauthorized access to malicious attacks. The choice of specific tools depends heavily on the unique security needs and risk profile of each organization.
Methods for Implementing Security Measures
Implementing security measures in an SD-WAN involves a systematic approach that addresses various aspects of the network, from access control to threat detection. This encompasses the use of security policies, firewalls, VPNs, and encryption to secure traffic flow and prevent unauthorized access.
Steps Involved in Securing an SD-WAN Network
Securing an SD-WAN network requires a phased approach, involving a series of steps to ensure comprehensive protection. This involves a phased approach, starting with initial assessments and culminating in continuous monitoring and updates. It is important to note that these steps are not necessarily sequential and can be implemented in parallel depending on the specific context and available resources.
| Step | Description | Tools/Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Network Segmentation and Access Control: Divide the SD-WAN network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the impact of a security breach. Implement strict access controls to regulate user and device access to specific resources. | Firewall, Network Access Control (NAC), VLANs, RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) |
| 2 | Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS): Deploy IDS/IPS systems to identify and block malicious activities. This proactive approach can detect anomalies and block potential threats before they cause significant damage. | IDS/IPS appliances, cloud-based security services |
| 3 | Secure VPN Tunnels and Encryption: Encapsulate traffic within secure VPN tunnels and employ strong encryption protocols to protect sensitive data in transit. | IPsec VPN, SSL VPN, TLS/SSL encryption |
| 4 | Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments: Periodically assess the security posture of the SD-WAN network, identifying vulnerabilities and patching them proactively. | Vulnerability scanners, penetration testing tools |
| 5 | Monitoring and Alerting: Implement comprehensive monitoring tools to track network activity, detect suspicious behavior, and generate alerts for immediate response. | Security information and event management (SIEM) tools, network monitoring tools |
| 6 | Security Policy Development and Enforcement: Create and enforce comprehensive security policies covering access, authentication, and data handling. | Security information and event management (SIEM) tools, policy management tools |
Monitoring and Maintaining Security Posture
Staying ahead of potential threats in an SD-WAN environment necessitates robust monitoring and proactive security posture maintenance. A comprehensive approach is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities, reacting quickly to incidents, and ensuring the continued operational integrity of the network. Regular assessments and diligent monitoring tools are essential to maintaining a secure SD-WAN infrastructure.
Gartner’s best security practices for SD-WAN are crucial for protecting sensitive data transmitted over a distributed network. However, the struggle to combat piracy, like the one Hollywood studios are facing with HBO, Netflix, and other content providers, hbo netflix hollywood ace fight piracy , highlights the need for robust security measures beyond the network itself. Ultimately, applying these Gartner-recommended practices will be key to a secure SD-WAN strategy.
Strategies for Monitoring Security Posture
Effective monitoring of an SD-WAN network’s security posture requires a multifaceted approach. This includes continuous analysis of network traffic, proactive detection of anomalies, and rapid response mechanisms. Key strategies involve utilizing a combination of security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and dedicated SD-WAN security tools. These tools provide real-time visibility into network activity, enabling prompt identification and mitigation of potential security breaches.
Identifying and Responding to Security Threats
A robust incident response plan is vital for effectively handling security threats within an SD-WAN environment. This plan should detail procedures for detecting, containing, and eradicating threats. Identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs) such as unusual network traffic patterns, unauthorized access attempts, and malicious code is critical. Prompt response to these threats minimizes damage and disruption. For example, rapid containment of a DDoS attack is critical to preventing widespread service outages.
A well-defined incident response process is paramount to minimizing the impact of security incidents.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security audits and assessments are not just recommended, but essential for maintaining a healthy security posture in an SD-WAN. These assessments help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network’s security infrastructure. They also provide a benchmark for measuring the effectiveness of security controls and identifying areas requiring improvement. A comprehensive audit should encompass all aspects of the SD-WAN, including network configurations, access controls, and security policies.
Monitoring Tools and Techniques
A variety of tools and techniques can be utilized for monitoring SD-WAN security. This comprehensive approach enhances visibility into the network, allowing for proactive identification of potential threats. The choice of tools depends on specific needs and the scale of the SD-WAN deployment.
| Tool/Technique | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Centralized system for collecting and analyzing security logs from various sources. | Provides a comprehensive view of security events, enabling early threat detection. | Can be complex to implement and manage, requires skilled personnel. |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | Detect and prevent malicious activity by monitoring network traffic. | Helps identify and block malicious traffic, protecting against various attacks. | May generate false positives, potentially impacting network performance. |
| SD-WAN Security Appliances | Dedicated devices designed to secure SD-WAN traffic. | Provide specialized security features tailored for SD-WAN environments. | May require specific expertise for deployment and management. |
| Network Traffic Analysis Tools | Monitor and analyze network traffic for anomalies. | Identify unusual patterns that might indicate malicious activity. | Requires significant expertise for proper interpretation of results. |
Case Studies and Real-World Examples: Gartner Best Security Pracices For Sd Wan
Putting Gartner’s SD-WAN security best practices into action requires understanding how other organizations have successfully implemented them. Real-world examples highlight the strategies, challenges, and lessons learned, providing valuable insights for organizations embarking on their SD-WAN security journey. This section delves into successful implementations, examining the key considerations and outcomes.Understanding the practical application of these best practices in diverse environments allows for a more nuanced understanding of their effectiveness and potential pitfalls.
Analyzing case studies provides a valuable framework for understanding the multifaceted nature of SD-WAN security and how different organizations have adapted the best practices to their specific needs.
Successful Implementations of Gartner’s SD-WAN Security Best Practices
Several organizations have successfully integrated Gartner’s SD-WAN security best practices into their infrastructure, leading to a significant improvement in their security posture. A common theme is the proactive approach to security, integrating it from the design phase onward. This proactive approach is crucial for preventing security vulnerabilities from arising in the first place.
Examples of Leveraging Best Practices to Enhance Security Posture, Gartner best security pracices for sd wan
One example involves a financial institution that implemented micro-segmentation within their SD-WAN. By segmenting their network traffic into smaller, isolated units, they significantly reduced the impact of potential breaches. This allowed them to isolate compromised segments, preventing the spread of malware and protecting sensitive data. Another example involves a healthcare organization that utilized zero-trust principles in their SD-WAN implementation.
They enforced strong authentication and authorization for all network access, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Challenges Encountered During Implementation
Organizations often face challenges in implementing Gartner’s SD-WAN security best practices. One common hurdle is the complexity of integrating security measures with existing infrastructure. This often requires significant investment in new technologies and personnel training. Another challenge is the need for ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure the security posture remains robust. The continuous evolution of cyber threats requires organizations to adapt and update their security protocols and tools regularly.
Lessons Learned from Real-World SD-WAN Security Implementations
Understanding the lessons learned from previous implementations is crucial for minimizing risks and maximizing effectiveness.
| Case Study | Key Lessons | Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Institution (Micro-segmentation) | Proactive security measures are crucial. Implementing micro-segmentation reduces the impact of breaches. | Complexity of integrating security measures with existing infrastructure. | Detailed planning and phased implementation of security solutions. |
| Healthcare Organization (Zero-Trust) | Zero-trust security principles are effective in reducing unauthorized access. | Requires significant investment in new technologies and personnel training. | Prioritizing security from the initial SD-WAN design phase. |
| Retail Company (Network Segmentation) | Effective network segmentation can contain the spread of threats. | Requires significant changes to existing network architecture. | Implementing a phased approach to network segmentation, addressing specific business needs. |
Future Trends in SD-WAN Security
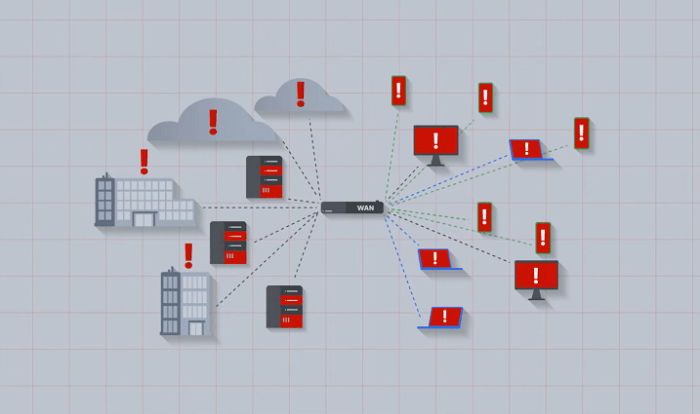
The SD-WAN landscape is constantly evolving, and security must keep pace. As organizations increasingly rely on SD-WAN for critical applications and data transfer, the threat landscape is also adapting. Protecting these networks requires a proactive approach that anticipates emerging vulnerabilities and adapts security measures accordingly.
Evolving Security Landscape
The security landscape for SD-WAN is characterized by a dynamic interplay of traditional threats and novel attacks. Traditional threats, such as malware and denial-of-service attacks, continue to pose risks, albeit with new vectors enabled by the distributed nature of SD-WAN. Moreover, the rise of sophisticated cybercriminals and nation-state actors targeting critical infrastructure, often leveraging SD-WAN as a pathway, necessitates a heightened focus on advanced persistent threats (APTs).
The growing use of SD-WAN in cloud-centric architectures further complicates security by introducing new attack surfaces and expanding the attack vectors.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
SD-WAN’s distributed nature, incorporating diverse network elements and third-party vendors, introduces novel vulnerabilities. The potential for misconfigurations in edge devices and remote access points, along with inadequate security protocols across the extended network, creates significant entry points for attackers. Insider threats, both intentional and unintentional, remain a critical concern. Additionally, the increased reliance on APIs and microservices in SD-WAN architectures presents new attack avenues.
The potential for supply chain attacks impacting SD-WAN vendors also merits attention. The rise of zero-day exploits, leveraging newly discovered vulnerabilities, further complicates security posture. This evolving landscape demands a proactive and multi-layered approach to security.
Gartner’s best security practices for SD-WAN are crucial for any modern network. While I’m diving deep into those, it got me thinking about the amazing Withings Steel HR Sport Hybrid Smartwatch Prime Day deal, a great value for a fitness tracker! withings steel hr sport hybrid smartwatch prime day deal Ultimately, strong security practices are still paramount for a robust SD-WAN solution.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as IoT devices and 5G networks, introduce new dimensions to SD-WAN security. IoT devices connected to the SD-WAN network could potentially be exploited as entry points, requiring robust device authentication and access controls. The increased bandwidth and lower latency offered by 5G networks can potentially lead to faster attacks, necessitating high-performance security tools. Cloud-native security solutions are increasingly crucial for managing the dynamic and distributed nature of SD-WAN.
Future Trends in SD-WAN Security
A proactive approach to SD-WAN security necessitates anticipating future trends. The following table Artikels potential future trends, including emerging technologies.
Gartner’s best security practices for SD-WAN are crucial for robust network protection. While exploring these, I was reminded of the recent Wear OS 3 Google IO announcements wear os 3 google io. The innovative features highlighted there, though seemingly unrelated, highlight the importance of continuous innovation in security protocols, which ultimately benefits SD-WAN strategies.
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Threat Protection | Enhanced security solutions capable of detecting and responding to sophisticated threats, such as APTs, will be critical. | Improved protection against advanced persistent threats and zero-day exploits. |
| Zero Trust Architecture | Implementing a zero-trust approach across the entire SD-WAN infrastructure, from edge devices to cloud applications, will become increasingly essential. | Reduced attack surface, enhanced security posture, and increased resilience to breaches. |
| AI-Powered Security Analytics | AI-driven tools will play a crucial role in detecting anomalies and identifying potential threats in real-time. | Improved threat detection and response capabilities, allowing for faster mitigation of security incidents. |
| Security-Focused SD-WAN Solutions | SD-WAN vendors will increasingly integrate security capabilities directly into their solutions, addressing security at the network level. | Streamlined security management, reduced attack surface, and easier deployment of security measures. |
| Integration with Cloud Security | SD-WAN security solutions will need to seamlessly integrate with cloud security platforms to provide comprehensive protection across the entire network. | Comprehensive protection across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, and improved threat visibility. |
Illustrative Scenarios
SD-WAN deployments, while offering significant benefits in terms of flexibility and cost-effectiveness, introduce new security vulnerabilities if not properly addressed. Understanding potential threats and how to mitigate them is crucial for maintaining a secure SD-WAN environment. This section details illustrative scenarios, focusing on practical applications of Gartner’s best practices for SD-WAN security.
Typical SD-WAN Security Threat Scenario
A malicious actor compromises a poorly secured branch office VPN gateway connected to the SD-WAN. This compromised gateway allows the attacker to gain unauthorized access to the internal network through the SD-WAN fabric, potentially leading to data breaches, disruption of services, and financial losses.
Response Steps Based on Gartner’s Best Practices
Implementing Gartner’s best practices can significantly reduce the risk of such an attack. These include:
- Robust Access Control: Implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms on all SD-WAN devices and gateways, limiting access to authorized users and enforcing least privilege principles. This involves multi-factor authentication and regular security audits to ensure these measures remain effective.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conduct periodic security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in the SD-WAN infrastructure. This includes vulnerability scanning of the entire network, including branch offices and cloud gateways, to ensure security measures remain effective.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integrate threat intelligence feeds into the security monitoring system. This allows for proactive identification and mitigation of emerging threats. Continuous monitoring and updating of the threat intelligence database is crucial for effectiveness.
- Segmentation and Isolation: Implement network segmentation to isolate critical systems and data. This limits the impact of a successful attack by preventing lateral movement within the network. Segmenting the network based on departments and their respective access requirements improves the security posture.
SD-WAN Security Measure Implementation Scenario
A company deploying a new SD-WAN solution decides to implement a zero-trust security model. They use a combination of micro-segmentation, dynamic access control, and secure access service edge (SASE) to restrict access to sensitive data and applications based on user and device attributes. Security policies are continuously updated and evaluated to reflect the evolving threat landscape. This approach limits the potential impact of a compromised device or user.
Security Monitoring Tool Use in SD-WAN
A large enterprise utilizes a specialized SD-WAN security monitoring tool that continuously tracks network traffic for suspicious patterns. The tool proactively identifies anomalies, such as unusual data transfers or access attempts, triggering alerts and enabling security personnel to investigate and mitigate potential threats. This real-time monitoring and response capability helps the company maintain a strong security posture. The tool’s reporting capabilities provide valuable insights into security events, enabling proactive adjustments to security measures and policies.
Last Point
In conclusion, implementing Gartner’s best security practices for SD-WAN is a crucial step towards a more secure and reliable network. By understanding the design considerations, implementation methods, and ongoing monitoring, organizations can effectively protect their SD-WAN deployments. This comprehensive guide provides a roadmap for achieving a robust security posture in the dynamic SD-WAN environment.