Electricity bill tariff Canada is a complex landscape, varying significantly across provinces. Understanding these differences is crucial for Canadians, as electricity costs can impact household budgets. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of electricity pricing structures, examining factors like energy production, government regulations, and even the effects of climate change. We’ll analyze how these elements contribute to the variability in electricity bills across the country, highlighting the impact on consumers and exploring strategies for saving money.
The article will provide a detailed overview of electricity bill tariffs in Canada, examining the different types of pricing structures employed in various provinces. It will delve into the key factors influencing these tariffs, including energy production methods, government regulations, and seasonal demands. The impact of climate change on electricity prices will also be discussed, along with potential future trends and consumer implications.
Overview of Electricity Bill Tariffs in Canada
Electricity bills in Canada vary significantly from province to province, reflecting diverse energy sources and regulatory frameworks. Understanding these variations is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions about energy consumption and potentially reduce their bills. This overview explores the commonalities and differences in electricity pricing structures across the country.
Electricity Pricing Structures in Canadian Provinces
Electricity pricing in Canada isn’t a one-size-fits-all model. Instead, each province employs its own unique structure, which typically includes a base rate, energy charges, and potentially other surcharges or taxes. These variations stem from factors like the prevalence of hydroelectric power, the availability of natural gas, and provincial regulations.
Components of Electricity Bills
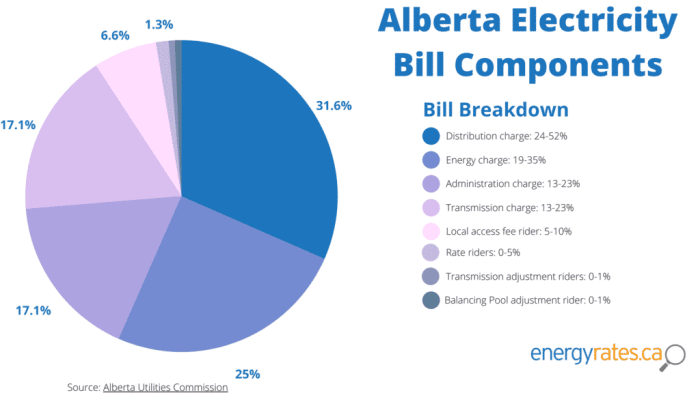
Different provinces have different components in their electricity bills. A standardized structure is beneficial for comparison. Here’s a breakdown of common components, illustrated with examples from different provinces:
| Province | Pricing Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alberta | Base Rate | A fixed monthly charge, regardless of energy consumption. | $15 per month |
| Alberta | Energy Charge | A rate per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity consumed. | $0.12/kWh |
| British Columbia | Base Rate | A fixed monthly charge, regardless of energy consumption. | $10 per month |
| British Columbia | Energy Charge | A rate per kWh of electricity consumed, often tiered for higher consumption levels. | $0.15/kWh (first 500 kWh); $0.18/kWh (over 500 kWh) |
| Ontario | Base Rate | A fixed monthly charge, often based on service class and meter size. | $20 per month |
| Ontario | Energy Charge | A rate per kWh of electricity consumed, potentially with different rates for off-peak and peak hours. | $0.18/kWh |
| Quebec | Base Rate | A fixed monthly charge, potentially varying based on the customer’s usage class. | $25 per month |
| Quebec | Energy Charge | A rate per kWh of electricity consumed, often with different rates for different time periods. | $0.16/kWh (day); $0.12/kWh (night) |
The table illustrates the common elements in electricity pricing structures, demonstrating how each province can adjust the components to fit its unique energy landscape and regulatory framework. The examples given are illustrative and may not reflect current pricing in all areas.
Variations in Electricity Pricing Structures
Beyond the fundamental components, there are considerable variations in electricity pricing structures. Some provinces incorporate time-of-use (TOU) pricing, where energy rates fluctuate depending on the time of day. Others may include demand charges, reflecting the maximum power drawn by the customer at any given time. Further, some provinces might have specific pricing for large industrial consumers, tailored to their specific needs and usage patterns.
Figuring out electricity bill tariffs in Canada can be a real headache. With so many different providers and plans, it’s easy to get lost in the details. Fortunately, the competition in the smart home tech market, like the samsung bixby app store alexa google home competition , is keeping things interesting and potentially influencing energy efficiency in the long run.
Ultimately, understanding the various Canadian electricity bill tariff options is crucial for budget-conscious consumers.
Factors Influencing Electricity Tariffs
Electricity bills in Canada, like anywhere else, are complex and influenced by various interconnected factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions and potentially manage their energy costs. These factors range from the methods used to generate electricity to government regulations and even seasonal demands.Electricity prices in Canada aren’t a one-size-fits-all situation. Different provinces have varying electricity generation sources, regulatory environments, and consumer demands.
This diverse landscape results in unique tariff structures across the country. This article delves into the key factors shaping electricity tariffs, focusing on how these factors differ across major Canadian provinces.
Energy Production Methods and Pricing
Electricity generation methods directly impact electricity costs. Hydropower, a renewable source, typically has lower operating costs compared to fossil fuel-based power plants. However, the initial investment for hydroelectric dams can be substantial. Nuclear power, while also having low operating costs, faces regulatory hurdles and public concerns about waste disposal. Fossil fuel plants, like coal and natural gas, have fluctuating costs depending on fuel prices, creating price volatility.
The mix of these sources significantly impacts provincial electricity rates. Provinces heavily reliant on renewables may have lower overall costs, while those dependent on fossil fuels might experience more price fluctuations.
Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies play a critical role in shaping electricity tariffs. Regulations on emissions, renewable energy mandates, and energy efficiency standards all influence the cost of electricity production. For instance, policies encouraging the use of renewable energy sources might lead to higher upfront costs for utilities, which could be reflected in consumer bills. Conversely, regulations that incentivize energy efficiency measures could lower overall demand and potentially reduce long-term costs.
Provincial governments have varying approaches to these policies, resulting in different electricity rate structures.
Seasonal Demands and Peak Hours
Electricity demand fluctuates throughout the year and across different hours of the day. During peak summer months, air conditioning use increases demand, while winter months experience higher heating demands. Similarly, peak hours, such as evenings and weekends, often see increased consumption. Utilities typically implement time-of-use (TOU) tariffs to reflect these variations. Higher rates during peak hours encourage consumers to shift consumption to off-peak periods, thereby reducing strain on the grid and potentially lowering overall costs.
Canada’s electricity bill tariffs are a real pain, right? It’s interesting to see how global trade ripples through our daily costs. For example, General Motors (GM) is apparently thankful for the $5 billion tariff hit they’re expecting to absorb, according to this recent article. While that’s a hefty price to pay, it’s a reminder of how interconnected our economies are, and how these kinds of decisions ultimately impact our electricity bills, which is something I’ve been tracking lately.
Hopefully, the resulting price changes are manageable for everyone.
These factors can also affect electricity prices in different provinces.
Comparison of Factors Across Provinces
| Factor | Alberta | British Columbia | Ontario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Predominantly natural gas and coal-fired power plants, with some renewables. | Significant reliance on hydropower and renewables, with some natural gas plants. | Diverse mix, including nuclear power, natural gas, and renewables. |
| Government Regulations | Historically less stringent environmental regulations compared to other provinces. | Stronger focus on renewable energy sources and emissions reduction. | Combination of nuclear power and environmental policies. |
| Seasonal Demands | High demand during the summer for air conditioning and the winter for heating. | Similar to other provinces, with higher demand in winter for heating. | High demand in winter due to heating and in summer for cooling. |
| Peak Hours | Significant peak demand in the evenings and on weekends. | Peak demand varies depending on seasonal needs and specific regions. | High peak demand in the evenings and on weekends, particularly during winter. |
Note: This table provides a general overview. Specific details and nuances may vary across different regions and time periods within each province.
Impact of Climate Change on Electricity Tariffs
Canada’s electricity sector is facing significant pressure from the escalating effects of climate change. Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, along with shifting energy demands, are impacting electricity prices across the country. Understanding these impacts is crucial for consumers and policymakers alike to prepare for the future of energy costs.The changing climate is directly affecting electricity pricing in Canada.
More frequent and severe weather events, such as heat waves, blizzards, and floods, strain the electricity grid. The increased demand for cooling during heat waves and the need for emergency power during storms drives up electricity generation costs and ultimately leads to higher tariffs. This is a critical factor in understanding the connection between climate change and electricity prices.
Extreme Weather Events and Tariff Fluctuations
Extreme weather events are becoming more unpredictable and intense, leading to significant fluctuations in electricity tariffs. Heat waves, for example, place immense strain on the power grid as demand for air conditioning surges. This surge in demand necessitates increased generation, often from more expensive sources like peaking power plants. Similarly, severe winter storms can disrupt transmission lines and necessitate costly repairs and replacements, adding to the overall cost of electricity.
The recent increase in the frequency of these events is directly reflected in the fluctuations seen in electricity prices, demonstrating the connection between weather patterns and energy costs.
Changing Energy Demand Patterns and Pricing Structures
Climate change is altering energy demand patterns, directly impacting pricing structures. Warmer winters, for example, reduce the demand for heating, but this reduction is often offset by higher summer cooling demands. This mismatch in seasonal demand requires utilities to maintain sufficient generation capacity to meet peak demands, which adds to the overall cost of electricity. Additionally, the shift towards electric vehicles and other energy-intensive technologies will place further pressure on the electricity grid, and the price of electricity will likely reflect this increased demand.
Canada’s electricity bill tariffs are a real pain, right? They’re constantly fluctuating, and trying to figure out the best plan can be a headache. While I’m trying to decipher the latest adjustments to my bill, it got me thinking about the implications of google fcc wireless device 60ghz radar leak on future energy consumption patterns.
Hopefully, the new tech won’t drastically increase my electricity bill tariff in the future.
Projected Changes in Electricity Prices Due to Climate Change
The following table Artikels projected changes in electricity prices across different Canadian regions due to climate change. These projections highlight the anticipated impact of extreme weather events and shifting energy demands. These figures are estimates and may vary depending on specific regional conditions and policy responses.
| Region | Impact of Extreme Weather | Projected Price Change | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southern Ontario | Increased frequency of heat waves, leading to higher peak demand for air conditioning. More frequent and intense storms impacting transmission lines. | Potential 10-15% increase in electricity prices over the next 10 years. | Investment in smart grid technologies, development of energy storage solutions, and promotion of energy efficiency measures. |
| Western Canada | Increased frequency of wildfires impacting transmission lines, potential for prolonged droughts reducing hydroelectric generation. | Potential 5-10% increase in electricity prices over the next 5 years. | Investment in renewable energy sources, improving forest management practices, and implementing drought-resistant irrigation systems. |
| Atlantic Provinces | Increased intensity of winter storms disrupting power grids, potential for more frequent and intense flooding. | Potential 15-20% increase in electricity prices over the next 10 years. | Investing in more resilient power infrastructure, implementing early warning systems for extreme weather, and promoting energy efficiency programs. |
Consumer Implications and Savings Strategies
Electricity bills in Canada can vary significantly depending on factors like usage, location, and the chosen tariff plan. Understanding these tariffs and implementing smart energy-saving strategies is crucial for Canadian consumers to manage their expenses effectively. This section delves into the implications of these tariffs and provides actionable steps to reduce electricity costs.
Implications of Electricity Bill Tariffs for Canadian Consumers
Electricity bill tariffs in Canada often incorporate time-of-use rates, where electricity costs fluctuate based on demand. This means that consumers might pay more during peak hours, typically when many people use electricity simultaneously. Higher electricity costs can have a direct impact on household budgets, potentially affecting other essential expenses. Understanding the structure of tariffs in your region is vital to making informed choices about energy consumption.
Consumers in areas with higher electricity rates may need to be more mindful of their energy usage to avoid unnecessary costs.
Strategies for Saving on Electricity Bills in Canada
Implementing energy-saving strategies can substantially reduce electricity bills. These strategies can range from simple lifestyle adjustments to investing in energy-efficient technologies. Consistent application of these strategies over time can lead to significant savings. By adopting these strategies, consumers can effectively manage their electricity consumption and lower their monthly bills.
Energy-Efficient Practices and Technologies
Numerous energy-efficient practices and technologies are readily available to Canadian consumers. These include upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, using smart power strips to manage standby power consumption, and implementing better insulation in homes. By integrating these practices into daily routines, households can significantly lower their energy consumption and associated costs. Examples include replacing incandescent bulbs with LED lighting, which consume considerably less energy.
Government Incentives and Programs for Consumers, Electricity bill tariff canada
Canadian governments offer various incentives and programs to encourage energy efficiency. These programs can provide financial support for energy audits, insulation upgrades, and the purchase of energy-efficient appliances. Government incentives can help offset the upfront costs associated with adopting energy-efficient technologies, making them more accessible to consumers. These programs play a significant role in reducing overall energy consumption and supporting sustainable practices.
Table of Common Energy-Efficient Practices and Potential Savings
| Practice | Estimated Savings (monthly) | Implementation Details |
|---|---|---|
| Switching to LED lighting | $5-$20 | Replace incandescent or CFL bulbs with LED bulbs throughout the home. |
| Using energy-efficient appliances | $10-$50 | Choose appliances with Energy Star ratings. Consider refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines. |
| Improving home insulation | $15-$40 | Insulate walls, attics, and basements to reduce heat loss or gain. |
| Unplug electronics when not in use | $3-$10 | Use power strips with on/off switches to easily turn off multiple devices. |
| Adjust thermostat settings | $5-$15 | Lower thermostat in winter and raise it in summer when not at home. |
Comparing Electricity Tariffs Across Provinces: Electricity Bill Tariff Canada
Electricity costs vary significantly across Canada’s provinces, impacting household budgets and industrial operations. Understanding these discrepancies is crucial for informed decision-making and potentially identifying cost-saving opportunities. Factors like energy source mix, regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure investments play a major role in shaping these diverse pricing structures.
Provincial Electricity Cost Variations
Electricity tariffs are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. The differences in electricity costs across provinces are substantial, impacting residents and businesses alike. Analyzing these variations reveals important insights into the energy landscape of each province.
Average Electricity Costs by Province
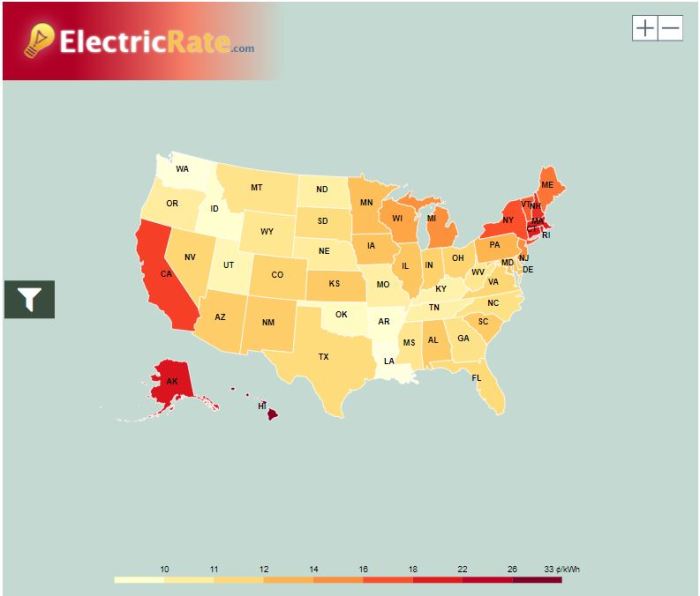
Provincial electricity costs are influenced by a multitude of factors, including the abundance of hydroelectric resources in certain regions, the presence of nuclear power plants, and the reliance on fossil fuels. The following table presents an illustrative overview of average electricity costs per province, reflecting a snapshot of the current energy market. Note that these are approximate averages and actual costs can fluctuate based on usage patterns and specific plans.
| Province | Approximate Average Electricity Cost (per kWh) |
|---|---|
| Alberta | $0.12 – $0.15 |
| British Columbia | $0.13 – $0.18 |
| Manitoba | $0.08 – $0.11 |
| New Brunswick | $0.10 – $0.14 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | $0.12 – $0.16 |
| Nova Scotia | $0.11 – $0.15 |
| Ontario | $0.14 – $0.17 |
| Prince Edward Island | $0.12 – $0.16 |
| Quebec | $0.09 – $0.12 |
| Saskatchewan | $0.11 – $0.14 |
Illustrative Representation of Provincial Tariffs
Visualizing the variations in electricity prices across provinces helps to grasp the magnitude of the differences. Imagine a bar graph, where each bar represents a province. The height of each bar corresponds to the average electricity cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Alberta’s bar would be noticeably higher than Manitoba’s, highlighting the substantial differences. This graphical representation effectively communicates the price variations between provinces, providing a quick overview.
Reasons for Different Pricing Structures
The variations in electricity tariffs stem from a combination of factors, including the province’s energy mix. Provinces heavily reliant on hydroelectricity, like Quebec, often enjoy lower costs due to the relatively low operating expenses of hydroelectric dams. Conversely, provinces that rely more on fossil fuels, like Alberta, typically face higher costs. Government regulations and incentives also play a significant role.
Provincial regulations regarding renewable energy sources and energy efficiency standards also influence the cost of electricity.
Impact of Regulatory Environments
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence electricity prices. Provinces with strict environmental regulations might incentivize renewable energy sources, which can impact the overall cost structure. For example, Ontario’s move towards renewable energy sources has had an impact on electricity prices, although the effects can be complex and multifaceted. Conversely, provinces with fewer regulatory requirements may see higher reliance on fossil fuels and associated costs.
Differences in electricity generation capacity, distribution networks, and the degree of competition within the electricity market further contribute to these variations.
Future Trends in Electricity Bill Tariffs
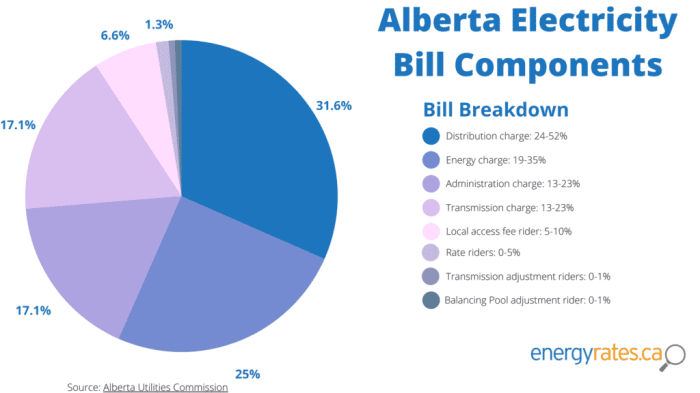
Canada’s electricity bill tariffs are poised for significant changes in the coming years. The shift towards renewable energy sources, technological advancements, and evolving government policies will all play crucial roles in shaping these future rates. Understanding these trends is vital for consumers to anticipate potential impacts and strategize for savings.
Role of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are rapidly gaining prominence in Canada’s energy mix. As these sources become more prevalent, electricity tariffs are expected to experience a multifaceted transformation. The initial costs of setting up infrastructure for renewable energy are substantial, which can initially increase electricity prices. However, as production scales and technology improves, the cost of renewable energy is anticipated to decrease.
This will likely lead to lower electricity prices for consumers in the long run, especially in areas with abundant renewable resources. Furthermore, policies supporting the development and integration of renewable energy can further impact the cost of electricity.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the electricity sector. Smart grids, for instance, can optimize energy distribution, potentially reducing transmission losses and leading to lower overall costs. Smart meters enable real-time monitoring of energy consumption, providing consumers with valuable insights to make informed decisions about their energy use. These advancements will lead to more efficient energy management and lower costs for consumers and utilities.
Influence of Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in shaping electricity tariffs. Policies that encourage the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, such as rebates or tax credits, can drive down overall electricity consumption and reduce costs. Conversely, policies that mandate the use of renewable energy or place limitations on carbon emissions will influence electricity pricing. Government subsidies for renewable energy projects can lead to lower prices for consumers, but the long-term impacts on electricity tariffs depend on the specific nature of the policies and incentives.
Potential Future Trends in Electricity Tariffs
| Trend | Description | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|
| Increased reliance on renewable energy | The growing use of solar, wind, and other renewable sources will influence pricing structures. Initial costs might be higher, but long-term costs are expected to decrease. | Potential for lower long-term electricity costs, especially in regions with abundant renewable resources. |
| Technological advancements (e.g., smart grids, smart meters) | Improved grid efficiency and real-time consumer feedback will reduce losses and encourage more efficient consumption. | Potential for lower electricity bills through improved energy management and reduced transmission losses. |
| Government policies and incentives | Policies encouraging energy efficiency or mandating renewable energy adoption will impact rates. Subsidies for renewable energy projects could lead to lower prices. | Variable impacts depending on the specific policy. Incentives for efficiency could lead to savings, while mandates could lead to temporary increases. |
| Time-of-use pricing | Increased integration of variable renewable energy sources might necessitate time-of-use pricing to balance supply and demand. | Consumers could face higher electricity costs during peak demand periods. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, navigating Canada’s electricity bill tariffs requires a deep understanding of provincial variations, influencing factors, and the ongoing impact of climate change. Consumers can significantly reduce their energy costs by adopting energy-efficient practices and exploring available government incentives. As Canada continues to transition to cleaner energy sources and faces evolving climate conditions, electricity prices will likely continue to evolve.
Staying informed about these trends is key to managing household budgets and making informed decisions about energy consumption.