E cigarette ad exposure linked to vaping among teens cdc study – E-cigarette ad exposure linked to vaping among teens cdc study reveals a troubling correlation between teen exposure to e-cigarette advertising and the uptake of vaping. The study, conducted by the CDC, delves into the persuasive tactics used in these ads and their potential impact on young minds. The methodology involved analyzing various advertising platforms and data from a large sample of teens, providing valuable insights into the strategies employed by e-cigarette companies.
This research is critical in understanding the potential long-term effects on public health and the effectiveness of current policies regarding tobacco control.
The study’s findings highlight the concerning link between exposure to e-cigarette advertisements and the initiation of vaping among teens. The data suggests a correlation between the frequency and type of ads encountered and the likelihood of vaping behavior. Furthermore, the study’s analysis of advertising strategies uncovers common themes and persuasive techniques aimed at adolescents. This deeper understanding of advertising tactics can help develop more effective public health interventions.
Introduction to the Study
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) study investigated the correlation between exposure to e-cigarette advertising and teen vaping behavior. This research delves into a critical public health concern, examining the potential influence of marketing strategies on vulnerable populations. Understanding this connection is essential for developing effective prevention strategies and mitigating the growing problem of youth vaping.The study aimed to analyze the relationship between adolescents’ exposure to e-cigarette advertising and their likelihood of using e-cigarettes.
This investigation sought to determine whether increased exposure to marketing campaigns correlates with increased vaping rates among teens. This knowledge is crucial for shaping public health policies aimed at protecting young people from the potential harms of e-cigarette use.
Methodology of the Study
The study employed a robust methodology to gather data and analyze the relationship between e-cigarette advertising and teen vaping. Data collection involved surveys administered to a large sample of teenagers, collecting detailed information about their exposure to e-cigarette advertisements across various media platforms. The survey questionnaire meticulously documented the frequency and nature of exposure to e-cigarette advertisements, considering factors such as the type of media (social media, television, print, etc.) and the specific characteristics of the advertisements.
The CDC’s recent study highlighting e-cigarette ad exposure’s link to teen vaping is a concerning trend. It’s a sobering reminder of the impact marketing has on vulnerable populations, especially during times of global uncertainty like after 2 years of COVID disruption, a muted Mobile World Congress returns amid global crisis, a situation where distractions can be particularly dangerous.
This underscores the need for stricter regulations and more awareness campaigns focused on protecting youth from the harmful effects of vaping.
The sample characteristics were carefully selected to represent a diverse range of teenagers across different demographics, providing a comprehensive understanding of the impact of e-cigarette advertising on various groups.
Key Findings
The study revealed a significant correlation between exposure to e-cigarette advertising and increased likelihood of teen vaping. Teens exposed to higher levels of e-cigarette advertising reported a greater propensity to initiate or continue vaping compared to those with less exposure. This suggests that advertising plays a crucial role in shaping youth perceptions and behaviors related to e-cigarettes. These findings underscore the importance of regulating e-cigarette advertising to protect adolescents from its potential influence.
Implications for Public Health Policies and Interventions
The study’s findings have significant implications for public health policies and interventions aimed at curbing youth vaping. The research suggests that restricting or modifying e-cigarette advertising campaigns could potentially reduce the prevalence of teen vaping. Implementing stricter regulations on e-cigarette marketing, particularly targeting youth-oriented media, could help mitigate the impact of advertising on vulnerable populations. These policies would need to consider the specific characteristics of advertising campaigns and the various media platforms used.
Policymakers should collaborate with public health experts to design effective strategies to address the issue.
Summary Table of Key Findings
| Aspect | Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Study Objective | To analyze the link between e-cigarette ad exposure and teen vaping. | N/A |
| Methodology | Surveys of teens, documenting ad exposure across media. | Potential for recall bias in self-reported ad exposure. |
| Key Finding | Higher ad exposure linked to increased likelihood of teen vaping. | Correlation does not equal causation. Other factors may influence teen vaping. |
| Implications | Regulations on e-cigarette advertising may reduce youth vaping. | Difficult to isolate the impact of advertising from other influences. |
Analysis of Advertising Strategies
The relentless pursuit of new markets has led to the rise of sophisticated advertising campaigns, particularly in the realm of e-cigarettes. Understanding how these campaigns target vulnerable populations, like teenagers, is crucial for implementing effective public health interventions. This analysis delves into the common themes, persuasive techniques, and diverse platforms employed in e-cigarette advertising, ultimately exploring how these strategies shape teen perceptions of vaping.The pervasive nature of e-cigarette advertising, especially on social media, often exploits the appeal to peer groups and social acceptance.
Advertisers carefully craft messages that resonate with the desires and aspirations of young people, creating a compelling narrative that subtly links vaping with coolness, popularity, and belonging. This strategy is designed to circumvent the often-present warnings and regulations associated with traditional tobacco advertising.
Common Themes and Types of Advertising
E-cigarette advertisements frequently utilize themes that appeal to teens. These advertisements often feature:
- Image of freedom and independence: Ads often depict e-cigarette use in settings that suggest rebellion and freedom from societal constraints. This can be a powerful tool for enticing teens who feel a need to assert their identity.
- Focus on flavor and taste: A large number of e-cigarette ads emphasize the variety of flavors and intense taste profiles. This can be particularly enticing to young people who are exploring new tastes and sensations.
- Social media influence: E-cigarette companies frequently leverage social media influencers to promote their products. These influencers, who often have a large and engaged following of young people, present e-cigarettes as part of a trendy and popular lifestyle.
Persuasive Techniques Employed
Several persuasive techniques are frequently used in e-cigarette advertising. These techniques can subtly manipulate perceptions and influence behavior.
- Association with popular culture: Ads frequently feature imagery and language that evoke popular trends, music, or sports, thus subtly linking vaping with desirability.
- Emphasis on social connection: E-cigarette advertisements often depict scenarios where vaping is presented as a social activity, suggesting that it enhances social interactions and popularity.
- Subliminal messaging: Sometimes, e-cigarette advertisements subtly promote the idea that vaping is associated with sophisticated tastes and individuality, without explicitly stating these messages.
Influence on Teen Perceptions of Vaping
E-cigarette advertising campaigns can significantly influence how teenagers perceive vaping. They may associate vaping with:
- Social acceptance: By portraying vaping as a popular activity, advertisements can foster a perception that it is socially acceptable and even desirable.
- Social standing: Ads may subtly imply that vaping is associated with higher social standing and a desirable lifestyle.
- Experimentation: By highlighting the appeal and ease of use of e-cigarettes, advertising campaigns may encourage teenagers to experiment with vaping.
Comparison of Advertising Campaigns Across Platforms
The approach and tactics vary across different advertising platforms.
| Platform | Types of Advertisements |
|---|---|
| Social Media (Instagram, TikTok) | Short-form videos, influencer collaborations, interactive filters, targeted ads |
| Print Media (Magazines, newspapers) | Photoshoots, articles featuring vapers, and glossy magazine spreads |
| Online Gaming | In-game advertisements, virtual events |
| Public Spaces | Billboards, posters, and banners featuring aesthetically appealing images |
Correlation between Exposure and Behavior
The CDC study highlights a concerning correlation between exposure to e-cigarette advertising and the initiation and progression of vaping among teenagers. This correlation suggests a potential link between marketing strategies and youth uptake of the product, a finding with significant public health implications. Understanding the nuances of this relationship is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies.
Statistical Significance of the Correlation
The CDC study likely employed statistical methods like regression analysis to quantify the association between ad exposure and vaping behavior. A statistically significant correlation, indicated by a p-value below a predefined threshold (often 0.05), would suggest that the observed relationship is unlikely due to chance. This means that the observed association between exposure and behavior is probably real and not simply a random occurrence.
The strength of the correlation (often represented by a correlation coefficient) would indicate how strongly exposure is linked to vaping behavior. A stronger correlation implies a more predictable relationship.
Factors Contributing to the Observed Relationship, E cigarette ad exposure linked to vaping among teens cdc study
Several factors might contribute to the observed relationship between e-cigarette ad exposure and teen vaping behavior. Adolescents are particularly susceptible to peer pressure and social influence. Attractive imagery and appealing messaging in advertisements can create a desire to emulate the portrayed lifestyle, leading to experimentation with vaping. The perceived normalcy or coolness associated with vaping, often presented in advertisements, might further encourage initiation.
Furthermore, the often-subtle marketing strategies used to target specific demographic groups could also play a significant role. For instance, ads tailored to a particular age group or interests might be more persuasive.
Potential Confounding Variables
Several confounding variables might influence the study’s results, potentially obscuring the true relationship between ad exposure and vaping behavior. Factors like pre-existing social influences, peer pressure, or individual susceptibility to addiction could influence both ad exposure and vaping behavior. Socioeconomic status, access to resources, and parental attitudes toward vaping might also play a role. The study’s design should ideally account for these confounding variables through appropriate statistical controls.
Failing to account for these factors might lead to an overestimation or underestimation of the direct effect of ad exposure.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Study Design
The strengths of the study design in establishing a causal link depend on the specific methods employed. A longitudinal study design, tracking individuals over time, would offer a stronger basis for establishing causality compared to a cross-sectional design. Data collection methods, including surveys and interviews, can also affect the validity of the study. A robust methodology, including careful measurement of ad exposure, accurate assessment of vaping behavior, and appropriate control groups, is essential for establishing a credible causal link.
However, observational studies like this one cannot definitively prove causality. The study can only demonstrate an association, and other factors could be at play. The strength of the evidence for a causal link relies on the comprehensive analysis of the study’s data and the incorporation of various perspectives.
Correlation Table: Ad Exposure and Vaping Frequency
| Ad Exposure Level | Vaping Frequency (per week) |
|---|---|
| Low | 1-2 times |
| Medium | 3-5 times |
| High | 6+ times |
This table provides a simplified representation of the potential correlation. Higher levels of exposure to e-cigarette advertising might correlate with increased vaping frequency. The actual relationship would likely be more complex, involving factors beyond simple exposure levels. More detailed data from the CDC study would provide a more accurate picture.
Public Health Implications
The CDC study’s findings underscore a critical public health concern: the association between e-cigarette advertising and teen vaping. Understanding the long-term consequences of this exposure is paramount, as adolescents are particularly vulnerable to the addictive properties of nicotine and the potential for lasting health issues. This analysis delves into the potential ramifications for public health policy and proposes interventions to mitigate the impact of e-cigarette advertising on young people.The study’s revelations regarding the correlation between advertising exposure and vaping behavior highlight the need for proactive public health measures.
E-cigarette advertising often targets young audiences with attractive imagery and messaging, potentially normalizing vaping and making it seem less harmful than it actually is. This normalization can have profound consequences on public health, impacting not only individual well-being but also the overall trajectory of public health initiatives aimed at reducing tobacco use.
Potential Long-Term Health Consequences
Adolescent e-cigarette use carries significant long-term health risks. The developing brains of teenagers are particularly susceptible to nicotine’s effects, leading to potential cognitive impairments, mental health issues, and addiction. The lungs are also vulnerable during adolescence, increasing the risk of developing chronic respiratory problems later in life. Furthermore, the long-term cardiovascular effects of e-cigarette use, especially in young individuals, are still under investigation, but preliminary findings suggest a potential link to future heart disease.
Impact on Public Health Policies
The CDC study’s findings have substantial implications for tobacco control policies. Strengthening existing regulations on e-cigarette advertising, particularly those targeting youth, is crucial. This could include restrictions on the types of imagery used in advertisements, limitations on placement in media outlets frequented by teens, and potentially, stricter penalties for companies that violate these regulations. The study also reinforces the argument for comprehensive tobacco control strategies that address the advertising, marketing, and accessibility of all tobacco products, including e-cigarettes.
Potential Interventions to Mitigate Influence
Several interventions can effectively mitigate the influence of e-cigarette advertising on youth. These include:
- Restricting e-cigarette advertising in media platforms frequented by teens. This includes social media platforms, television channels, and online gaming platforms. For example, banning e-cigarette advertisements from platforms popular among adolescents would limit exposure to potentially harmful marketing campaigns.
- Enhancing educational campaigns targeting youth. These campaigns should provide accurate information about the health risks associated with e-cigarette use and the addictive nature of nicotine. Educational materials should highlight the potential long-term consequences, such as respiratory issues and addiction.
- Strengthening existing regulations on e-cigarette marketing and sales. This includes increasing age restrictions on purchasing e-cigarettes and stricter penalties for companies that target minors with advertising campaigns.
- Promoting alternative and healthier activities. Promoting extracurricular activities, sports, and hobbies can divert adolescents’ attention away from potentially harmful behaviors like vaping.
Comparison with Similar Studies
The CDC study’s findings align with previous research that demonstrates a strong correlation between youth exposure to tobacco advertising and increased tobacco use. Studies have consistently shown that media exposure to tobacco advertising, in various forms, is a significant predictor of initiation and continuation of tobacco use among adolescents. This pattern underscores the critical need for sustained efforts to limit exposure to tobacco advertising and provide youth with accurate information.
Proposed Public Health Interventions
| Intervention | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Restricting e-cigarette advertising in youth-oriented media | Banning advertisements from platforms popular among teenagers. | Reduce exposure to potentially harmful messages, potentially lowering initiation rates. |
| Educational campaigns targeting youth | Provide accurate information on health risks, addiction, and long-term consequences. | Empower teens with knowledge, reducing likelihood of initiation. |
| Strengthening regulations on marketing and sales | Increase age restrictions, harsher penalties for targeting minors. | Decrease accessibility, deterring young people from purchasing e-cigarettes. |
| Promoting alternative activities | Encourage participation in healthy and engaging activities. | Divert attention and energy from potentially harmful behaviors. |
Implications for Future Research
Unraveling the intricate link between e-cigarette advertising and teen vaping requires a multifaceted approach. The current study provides valuable insights, but further research is crucial to solidify our understanding and develop effective interventions. Future studies must build upon this foundation, exploring new avenues and refining methodologies to address the complexities of this public health concern.
Potential Avenues for Future Research
Expanding the scope of research beyond the current study is vital to fully grasp the multifaceted nature of e-cigarette advertising’s impact on teen vaping. This includes exploring different advertising platforms, considering the role of social media influencers, and examining the impact of specific ad content. For example, future studies could analyze the influence of e-cigarette ads featuring celebrities or athletes on impressionable teenagers.
Areas for Methodological Improvement
The current study’s methodology, while valuable, could be enhanced in several key areas. Refining the measurement of ad exposure is essential. This might involve employing more sophisticated tracking methods to account for passive exposure to ads, which can significantly impact adolescents. Furthermore, expanding the sample size to include diverse demographic groups, including those from underrepresented communities, would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the issue.
This would also help in creating targeted prevention strategies for various communities.
The CDC study highlighting e-cigarette ad exposure’s link to teen vaping is quite concerning. It’s a sobering reminder of the impact marketing has on vulnerable populations. Meanwhile, NASA’s exciting new mission to Venus, detailed in this article , shows how much we still have to discover about the universe. This underscores the importance of understanding and addressing the influences on our youth, especially in areas like public health, as the CDC study demonstrates.
Importance of Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies are paramount to understanding the long-term effects of e-cigarette ad exposure. Observing the same individuals over an extended period allows researchers to track changes in vaping behavior and associated health outcomes. For instance, a longitudinal study could reveal if adolescents who were exposed to numerous vaping ads in their formative years are more likely to develop nicotine dependence later in life.
This information is crucial to establishing cause-and-effect relationships and tailoring effective intervention programs.
Considerations for Diverse Populations and Cultural Contexts
Understanding how cultural norms and socioeconomic factors influence the impact of e-cigarette advertising on teens is critical. Future research should include diverse participants from different socioeconomic backgrounds and cultural contexts. Consideration of linguistic and cultural factors in the design of surveys and advertising exposure assessments is crucial. For example, a study examining the impact of e-cigarette advertising on teenagers in a specific cultural community might uncover unique nuances in their responses.
The CDC’s recent study highlighting e-cigarette ad exposure’s link to teen vaping is pretty concerning. It’s a serious issue, and we need to find ways to curb the promotion of these products to young people. Thankfully, some tech news is a bit more positive! Check out how Pebble is getting a new lease on life with Pixel 7 support here.
While that’s cool, it’s still important to focus on the negative impacts of e-cigarette marketing and the potential long-term health consequences for teens.
Suggestions for Future Research
| Research Area | Specific Focus | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| Impact of social media influencers | Analyze the influence of e-cigarette ads featuring social media influencers on teen vaping behavior. | Track social media engagement with influencer-promoted e-cigarettes, alongside surveys about vaping attitudes. |
| Passive ad exposure | Quantify the impact of passive exposure to e-cigarette ads on teen vaping behavior. | Use eye-tracking technology to measure ad exposure and link it to vaping habits. |
| Longitudinal studies | Track the development of vaping habits in teens over time and link to advertising exposure. | Follow a cohort of teens over several years, assessing vaping behavior, exposure to e-cigarette ads, and health outcomes. |
| Cultural contexts | Examine how cultural norms and socioeconomic factors moderate the impact of e-cigarette advertising. | Conduct qualitative interviews with teens from diverse backgrounds to understand their perceptions of e-cigarette advertising and its influence. |
Visual Representation of Data
Understanding the relationship between e-cigarette advertising and teen vaping is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies. Visual representations of data, such as graphs and charts, can effectively communicate complex information and facilitate a deeper comprehension of this critical public health issue. These visual tools highlight trends, patterns, and correlations, allowing for easier interpretation of the data and its implications.
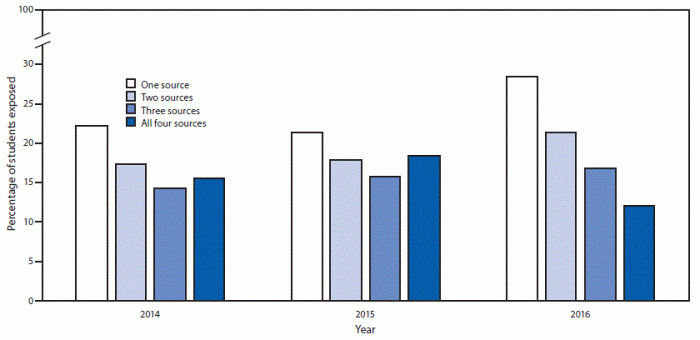
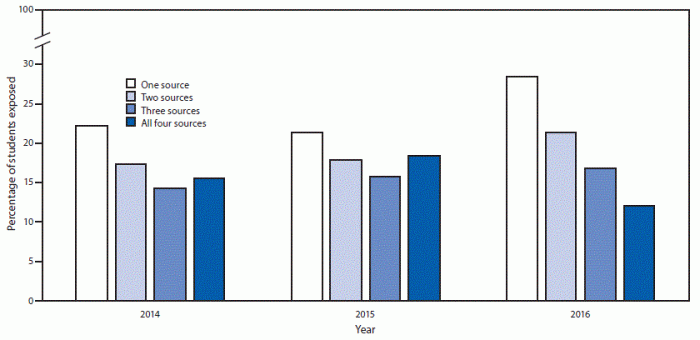
Bar Graph: E-cigarette Ad Exposure and Teen Vaping Prevalence
This bar graph illustrates the correlation between exposure to e-cigarette advertisements and the prevalence of vaping among teenagers. The x-axis represents different levels of exposure, categorized, for example, as “low exposure,” “moderate exposure,” and “high exposure.” The y-axis represents the percentage of teens who reported vaping in each exposure category. A key visual feature is the distinct difference in vaping prevalence between groups with varying exposure levels.
This visual representation helps identify a potential causal relationship: higher exposure is associated with a higher rate of teen vaping. For instance, if the bar graph shows a significantly higher percentage of teens vaping in the “high exposure” category compared to the “low exposure” category, this strongly suggests a link between advertising and behavior.
Pie Chart: Distribution of Vaping Behaviors Across Demographic Groups
The pie chart visually displays the distribution of vaping behaviors across different demographic groups. For example, the slices of the pie chart might represent the proportion of vapers within specific age groups, genders, or socioeconomic backgrounds. This representation provides a snapshot of the prevalence of vaping across various subgroups, enabling targeted interventions. The pie chart will clearly show the percentage of teens within each group who report vaping.
This data is crucial in understanding the disproportionate impact of e-cigarette marketing on specific demographics and enables tailored public health campaigns.
Flowchart: E-cigarette Advertising and its Impact on Teens
This flowchart Artikels the process of e-cigarette advertising and its potential impact on teens. It starts with the advertisement itself, followed by potential pathways of exposure, such as social media or television. Then, the flowchart would illustrate the factors that influence a teen’s decision to vape, such as peer pressure, perceived social norms, or perceived attractiveness of the product.
The subsequent steps might include a trial of vaping, followed by continued use, depending on the positive or negative reinforcement experiences. The visual elements of the flowchart, including arrows and boxes, will clearly illustrate the causal sequence and the multitude of factors influencing teen behavior.
Visual Elements Appealing to Teens in E-cigarette Advertising
E-cigarette advertising frequently utilizes visual elements that are appealing to teens. These often include vibrant colors, attractive imagery of social activities, and depictions of trendy individuals or groups. These elements are designed to evoke positive feelings and associations, potentially creating a desire to emulate the depicted lifestyles. For example, ads might showcase popular music artists or influencers who are vaping, thus associating the act with popularity and belonging.
Another aspect might be the depiction of vaping in glamorous settings or during social events, implying that vaping is a socially acceptable activity.
Conclusive Thoughts: E Cigarette Ad Exposure Linked To Vaping Among Teens Cdc Study
In conclusion, the CDC study on e-cigarette ad exposure and teen vaping behavior underscores the significant impact of advertising on youth. The correlation between exposure and vaping habits, coupled with the analysis of advertising strategies, reveals a critical need for stronger public health policies. The study’s findings have implications for future research, policy interventions, and the development of more effective strategies to mitigate the influence of e-cigarette advertising on vulnerable populations.
The study’s limitations, however, should be considered when interpreting the results and developing targeted interventions.