Chronic traumatic encephalopathy diagnosis national football player health neurological disease is a critical issue demanding immediate attention. This complex neurological condition, stemming from repeated head trauma, particularly in athletes, presents significant challenges in diagnosis, impacting players’ physical and mental well-being, and raising crucial questions about long-term health consequences.
Understanding the intricate link between head injuries, CTE development, and the diverse symptoms is vital. This exploration delves into the diagnostic process, considering the specific challenges faced in athletes, and examines the profound impact on their overall health, both physical and emotional, in a deeply personal way.
Introduction to Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive degenerative brain disease. It’s primarily associated with repeated head trauma, a common concern, particularly in contact sports like football. Understanding CTE is crucial for recognizing its impact on individuals and developing strategies to mitigate its effects.CTE develops over time, often years after the initial trauma. This slow progression makes it challenging to diagnose accurately, and the long-term effects can be devastating.
Early detection and preventative measures are essential in mitigating the damage.
Definition of CTE
CTE is a debilitating neurological condition characterized by progressive damage to brain tissue. The damage is often linked to repeated concussions and other head injuries, although the exact mechanisms aren’t fully understood. This process leads to a wide range of symptoms affecting cognitive function, behavior, and mood.
Link Between CTE and Repetitive Head Trauma, Chronic traumatic encephalopathy diagnosis national football player health neurological disease
A strong link exists between repetitive head trauma and the development of CTE. Athletes, particularly those in contact sports like football, boxing, and hockey, are at higher risk due to the inherent nature of the activity. Repeated blows to the head, even if not resulting in immediate concussions, can accumulate microscopic damage over time. This accumulation is believed to be a critical factor in the development of CTE.
Common Symptoms of CTE
CTE presents a variety of symptoms, often appearing gradually and subtly at first. These symptoms can impact daily life in significant ways. Common symptoms include cognitive changes, behavioral alterations, and mood fluctuations. Cognitive symptoms can range from memory problems and difficulty concentrating to impaired judgment and executive function. Behavioral symptoms can include aggression, impulsivity, and social withdrawal.
Mood changes can manifest as depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Stages of CTE Progression
The progression of CTE is often described in stages, each marked by specific symptoms and potential impacts on daily life.
| Stage | Symptoms | Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|---|
| Early Stage | Mild cognitive difficulties, such as memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, and subtle changes in mood. Personality changes may be noticeable, including increased irritability or emotional outbursts. | Slight impact on daily activities, such as work performance or social interactions. |
| Middle Stage | More pronounced cognitive impairments, including significant memory problems, impaired judgment, and difficulty with complex tasks. Behavioral changes become more noticeable, including increased aggression, impulsivity, and social withdrawal. Mood swings and depression become more common. | Significant impact on daily life, potentially affecting job performance, relationships, and self-care. The need for support systems increases. |
| Late Stage | Severe cognitive impairment, including significant memory loss, confusion, and disorientation. Behavioral issues worsen, potentially leading to erratic or dangerous behaviors. Mood disorders are often severe, impacting the individual’s ability to function independently. | Extensive impact on daily life, requiring significant support and care. The individual may need assistance with basic daily tasks. |
CTE Diagnosis in National Football Players
Diagnosing Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) in athletes, particularly in the context of professional football players, presents unique challenges. The progressive nature of the disease, often manifesting years after exposure to head trauma, coupled with the need for a definitive post-mortem diagnosis, makes identifying CTE during an athlete’s lifetime exceedingly difficult. Furthermore, the subtle symptoms that can mimic other conditions often delay or obscure the diagnosis.
Challenges in CTE Diagnosis
Several factors contribute to the difficulty in diagnosing CTE, especially in living athletes. The symptoms of CTE, such as cognitive impairment, mood swings, and behavioral changes, can overlap with other conditions, including depression, anxiety, and even normal aging processes. Differentiating these symptoms from the specific manifestations of CTE requires careful and comprehensive evaluations.
Diagnostic Methods for CTE
A variety of methods are employed in diagnosing CTE, each with its strengths and limitations. These include neuropathological examination, neuropsychological testing, and biomarker research.
- Neuropathological examination involves the microscopic examination of brain tissue after death. This is the gold standard for CTE diagnosis, allowing for the visualization of characteristic tau protein tangles in specific brain regions. This process requires careful post-mortem analysis, a critical step in accurate diagnosis. The presence of these specific tangles, alongside the individual’s medical history, is essential to confirm a CTE diagnosis.
- Neuropsychological testing assesses cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and executive skills. These tests can identify subtle cognitive deficits, which may suggest the presence of CTE. However, they are not definitive and often need to be interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostic tools.
- Biomarker research aims to identify biological markers that could be detected in blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples. These biomarkers, if validated, could potentially allow for earlier detection of CTE. However, reliable biomarkers for CTE are still under development and require further research.
Importance of Post-mortem Analysis
Post-mortem analysis is crucial in CTE diagnosis. It allows for the definitive identification of tau protein tangles in brain tissue. The absence of these tangles would definitively rule out CTE. The accuracy of the diagnosis hinges on the meticulous examination of brain tissue samples and a thorough consideration of the individual’s medical history. This process is necessary to accurately identify and confirm CTE in deceased individuals, and to contribute to a deeper understanding of the disease.
Comprehensive CTE Evaluation
A comprehensive CTE evaluation usually involves a combination of these diagnostic methods. A thorough medical history, including details of head trauma, is essential. Neurological examinations and neuropsychological testing can identify cognitive and behavioral changes. If these evaluations suggest a possible CTE diagnosis, post-mortem neuropathological examination is required for a definitive confirmation. A thorough understanding of the patient’s past history and exposure to head trauma, alongside other symptoms and tests, helps create a more comprehensive evaluation.
Diagnosing chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) in former National Football League players is a crucial neurological issue. Understanding the impact on their health is paramount. This complex area of study is intertwined with the incredibly precise timing systems used in modern technology, like those used in Facebook’s software development, which relies on incredibly precise time units like nanoseconds and the frame rate ticks of the github code.
This understanding of time measurement, as explored in the article facebook unit of time flicks frame rate ticks github nanosecond second , ultimately helps researchers to better analyze the subtle neurological changes associated with CTE, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses and improved care for these athletes.
Comparison of Diagnostic Methods
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuropathological Examination | Microscopic examination of brain tissue after death | Gold standard for diagnosis, definitive identification of tau tangles | Requires post-mortem analysis, cannot be performed during life |
| Neuropsychological Testing | Assessment of cognitive functions | Identifies subtle cognitive deficits, helpful in early detection | Not definitive, can overlap with other conditions, may not detect all CTE cases |
| Biomarker Research | Identification of biological markers in blood or CSF | Potential for earlier detection, non-invasive | Not yet validated for widespread use, further research required |
Impact on Health and Wellbeing
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) profoundly impacts the physical and mental health of those affected, often leading to a significant decline in quality of life. The insidious nature of CTE, developing over time, makes early detection and intervention challenging, compounding the already difficult situation for both the individual and their support network. Understanding the multifaceted effects of CTE is crucial for providing appropriate care and support.The physical consequences of CTE can range from headaches and dizziness to more severe issues like balance problems, seizures, and difficulties with motor coordination.
These physical symptoms can significantly restrict daily activities and independence. Moreover, the progressive nature of CTE often leads to the development of cognitive impairments that impact daily functioning.
Physical Health Consequences
The physical manifestations of CTE are often progressive and debilitating. Symptoms can include persistent headaches, dizziness, balance issues, and even seizures. Difficulties with motor coordination, such as tremors or clumsiness, can significantly affect daily activities, impacting an individual’s ability to perform routine tasks and maintain their independence. These physical symptoms can vary greatly in severity and presentation, making early diagnosis and appropriate management crucial.
Mental Health Consequences
CTE’s impact extends beyond physical symptoms, profoundly affecting mental well-being. Individuals with CTE often experience a range of mood disorders, including depression and anxiety. The cognitive decline associated with CTE can lead to frustration, anger, and other emotional dysregulation. The emotional toll on individuals with CTE can be immense, impacting their relationships and overall quality of life.
Recent advancements in diagnosing chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) in national football players are raising important questions about the neurological health of athletes. While the progress in CTE diagnosis is crucial, it’s exciting to see that you might not have to wait much longer for Apple’s ARVR headset, according to a recent report here. This technology could potentially revolutionize how we approach early detection and treatment of various neurological diseases, including CTE, in the future.
The struggle with these changes can be emotionally challenging, and appropriate support and resources are critical.
Emotional Toll on Individuals and Families
The emotional burden of CTE extends beyond the individual diagnosed. Families and loved ones often experience significant emotional distress as they witness the gradual decline in their loved one’s cognitive and physical abilities. The uncertainty and frustration associated with the progressive nature of the disease can lead to feelings of helplessness and anxiety. The ongoing challenges in managing the disease and its associated symptoms can take a substantial emotional toll on both the patient and their support network.
Cognitive Function Impairments
CTE significantly affects cognitive functions, leading to a variety of impairments. Memory problems, including difficulty recalling recent events or learning new information, are common. Executive function, crucial for planning, organizing, and problem-solving, often deteriorates. Concentration and attention spans can also be significantly affected, impacting daily activities and overall cognitive performance. Specific examples include difficulties with multitasking, planning, and following instructions, resulting in reduced efficiency in daily tasks.
Potential Correlations with Mental Health Disorders
The table below illustrates potential correlations between CTE and various mental health disorders. It’s crucial to remember that these are potential correlations and not definitive diagnoses. A thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals is essential to accurately assess and address mental health concerns in individuals with CTE.
The devastating impact of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) on national football players’ health and neurological well-being is a serious concern. While these athletes push their bodies to the limit, the long-term effects of repeated head trauma are tragically real. It’s a stark reminder of the challenges in diagnosing and treating CTE, and a real issue for the future of these players.
Interestingly, recent news surrounding the uncharted 4 leak stolen copies naughty dog situation highlights the struggles with intellectual property and piracy, a different but equally challenging aspect of modern life, reminding us that even seemingly unrelated events can draw parallels to the serious issues surrounding CTE diagnosis and treatment.
| Mental Health Disorder | Potential Correlation with CTE |
|---|---|
| Depression | Significant correlation, as the cognitive and physical decline associated with CTE can lead to feelings of hopelessness and despair. |
| Anxiety | CTE can cause significant anxiety due to the uncertainty and frustration associated with the progressive nature of the disease and the impact on daily functioning. |
| Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) | Potential correlation, especially in cases where CTE develops following a history of significant head injuries or trauma. |
| Suicidal Ideation | In severe cases, the combination of physical and mental symptoms can increase the risk of suicidal ideation and behavior. |
| Personality Changes | CTE can lead to significant personality changes, including impulsivity, aggression, and emotional dysregulation. |
Neurological Disease Implications
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) presents a unique set of challenges in the neurological field, demanding careful consideration and understanding of its distinctive features compared to other brain disorders. Its insidious nature, often manifesting years after the initial trauma, requires a nuanced approach to diagnosis and treatment. This section delves into the specific neurological disease implications of CTE, contrasting it with other conditions and examining the mechanisms and long-term consequences of this devastating neurological disorder.
Comparison with Other Neurological Diseases
CTE shares some overlapping symptoms with other neurological conditions, making accurate diagnosis challenging. Distinguishing CTE from other disorders requires careful evaluation of the patient’s history, symptoms, and diagnostic test results. The progressive nature of CTE, often developing over many years, also complicates the diagnostic process, as early signs may be subtle and easily overlooked. It is crucial to understand the differences in symptom presentation and diagnostic methodologies to accurately identify CTE.
Similarities and Differences in Symptoms
Several neurological diseases exhibit similar symptoms, such as memory loss, cognitive impairment, and mood swings. However, the specific pattern and progression of these symptoms can differ significantly between CTE and other conditions. For instance, while dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) can cause cognitive decline and behavioral changes, the specific pattern of cognitive decline and the presence of specific neurological signs often help distinguish CTE.
Similarly, Parkinson’s disease may manifest with motor problems, but the combination of cognitive and behavioral symptoms, often linked to a history of repetitive head trauma, is more characteristic of CTE. This subtle yet critical distinction in symptom manifestation is vital for accurate diagnosis.
Neurological Mechanisms Implicated in CTE Development
The development of CTE involves complex neurological mechanisms that are still under investigation. Repeated head trauma is believed to trigger a cascade of cellular events within the brain, leading to the accumulation of tau protein. This accumulation forms neurofibrillary tangles, which disrupt normal brain function and contribute to the progressive neurological deterioration observed in CTE patients. The exact mechanisms linking trauma to tau pathology remain a subject of active research, but evidence suggests that the damage caused by repeated blows to the head can trigger oxidative stress, inflammation, and neuronal dysfunction, ultimately leading to the characteristic neurodegenerative process.
Potential Long-Term Neurological Consequences of CTE
The long-term consequences of CTE can be severe and far-reaching, impacting various aspects of a person’s life. Progressive cognitive decline, including difficulties with memory, concentration, and judgment, is a common outcome. Behavioral changes, such as aggression, impulsivity, and depression, are also frequently observed. In severe cases, CTE can lead to significant functional impairment, impacting a person’s ability to work, maintain relationships, and perform daily tasks.
These consequences highlight the importance of early detection and intervention strategies.
Impact on Brain Structure and Function
CTE significantly alters brain structure and function. Microscopic examination reveals the presence of neurofibrillary tangles and neuronal loss in specific brain regions, particularly those involved in memory, cognition, and motor control. The severity of these structural changes correlates with the severity of symptoms. For instance, in individuals with a history of repeated concussions, MRI and other neuroimaging techniques may reveal atrophy and/or other structural abnormalities in the frontal and temporal lobes, regions essential for higher-level cognitive functions.
Common Symptoms Across Neurological Diseases
| Neurological Disease | Common Symptoms | Distinguishing Features from CTE |
|---|---|---|
| CTE | Progressive cognitive decline, memory loss, mood swings, behavioral changes, impulsivity, aggression | Strong association with repetitive head trauma; specific pattern of cognitive decline; presence of neurofibrillary tangles. |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Memory loss, cognitive decline, confusion | Typically associated with amyloid plaques; distinct genetic predisposition; less strong association with repetitive head trauma. |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Motor symptoms (tremors, rigidity), cognitive decline | Primarily motor symptoms; distinct pathophysiology (alpha-synuclein); less emphasis on behavioral changes linked to head trauma. |
| Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) | Cognitive decline, hallucinations, fluctuations in alertness, parkinsonian symptoms | Distinct protein aggregates (Lewy bodies); fluctuations in alertness; often presenting with parkinsonian symptoms. |
Research and Prevention
Unraveling the mysteries of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) requires a multi-pronged approach, combining rigorous research with proactive preventive strategies. This ongoing effort aims to reduce the risk of CTE development, particularly in high-impact sports like football. The pursuit of understanding the disease’s origins and progression is crucial for improving the lives of athletes and fostering healthier sporting environments.
Current Research on CTE
Research into CTE encompasses various methodologies, from post-mortem analyses to longitudinal studies of athletes. Scientists are investigating the complex interplay of factors that contribute to CTE development, aiming to pinpoint specific mechanisms and biomarkers. This multifaceted approach seeks to identify early indicators of CTE, potentially enabling intervention before significant neurological damage occurs. The study of animal models and the development of innovative diagnostic tools are also significant areas of focus.
Preventive Measures to Reduce CTE Risk
Developing preventive measures requires a comprehensive understanding of CTE risk factors. While no foolproof method exists to eliminate the risk entirely, strategies aimed at mitigating the impact of head impacts are gaining traction. These measures range from improved equipment design and playing regulations to the implementation of effective safety protocols. Education and awareness campaigns play a vital role in fostering a culture of safety within sporting communities.
Factors Contributing to CTE Development
Several factors contribute to the development of CTE. Repeated head impacts, even seemingly minor ones, accumulate over time and contribute to the progressive damage. The severity and frequency of these impacts significantly influence the likelihood of developing CTE. Additionally, genetic predispositions, lifestyle factors, and the individual’s response to injury all play a role. Identifying these factors is essential for targeted prevention strategies.
Preventative Strategies in Sports
Implementing preventative strategies in sports requires a multifaceted approach. This includes modifying equipment, like helmets, to better absorb impacts. Rules changes can limit the frequency and severity of head collisions, leading to safer play. Emphasis on proper tackling techniques, enhanced concussion protocols, and increased monitoring of athletes are crucial aspects of preventive measures. For example, the NFL has implemented stricter concussion protocols and rule changes to reduce head impacts.
Importance of Education and Awareness Programs
Education and awareness programs are essential in mitigating CTE risk. These programs should educate athletes, coaches, and parents about the dangers of head injuries and the importance of early recognition and management of concussions. Promoting responsible training practices, emphasizing the importance of rest and recovery, and providing ongoing education are vital components of a comprehensive prevention strategy. For instance, providing detailed training to coaches on identifying and handling concussions can drastically reduce the long-term risks for athletes.
Research Methodologies in CTE Studies
| Research Methodology | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Post-mortem examination of brains | Provides direct evidence of CTE pathology, enabling detailed analysis of brain tissue changes. | Limited to individuals who have already developed the disease, providing limited insight into early stages and risk factors. |
| Longitudinal studies of athletes | Provides insights into the development of CTE over time, allowing for the study of risk factors and early indicators. | Requires extensive follow-up and long observation periods, potentially influenced by participant attrition. |
| Animal models | Allows for controlled experimentation and investigation of specific factors, potentially leading to new treatment targets. | Results may not directly translate to human conditions due to biological differences. |
| Biomarker research | Potentially identifies early indicators of CTE, allowing for earlier intervention and diagnosis. | Requires validation and standardization of biomarkers, potentially leading to false positives. |
Case Studies and Examples
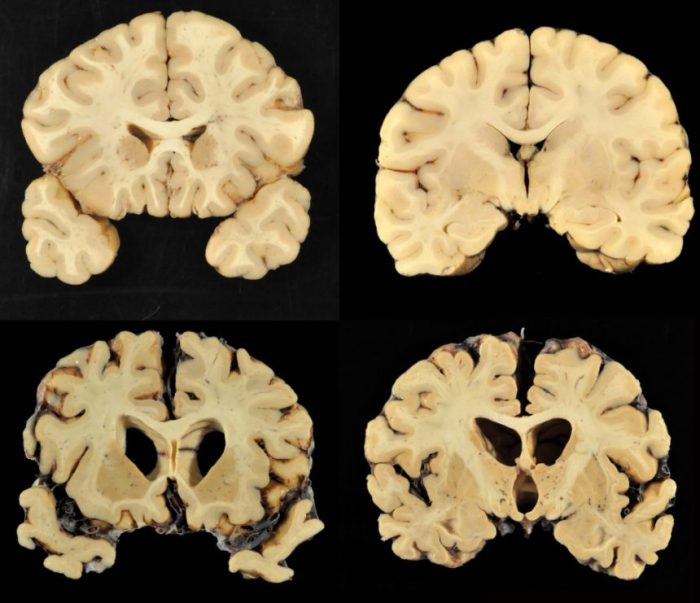
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive degenerative brain disease, primarily associated with repeated head trauma. Understanding the real-world impact of CTE on national football players requires examining specific cases. These cases provide crucial insights into the disease’s development, diagnostic challenges, and long-term effects. Detailed accounts of diagnosed cases, along with the symptoms and life trajectory of affected individuals, help build a more complete picture of this debilitating condition.
Real-World Cases of CTE in National Football Players
Examining documented cases of CTE in former national football players highlights the devastating effects of repeated concussions and subconcussive impacts. These cases are often instrumental in raising awareness and advancing research into this neurological disease. The experiences of these individuals provide valuable data for understanding the progression of the disease, the challenges in diagnosis, and the importance of preventative measures.
Diagnosis and Symptoms in CTE Cases
Diagnosing CTE relies heavily on post-mortem brain tissue analysis. This involves examining the brain for specific pathological markers, such as tau protein tangles. Symptoms can manifest gradually and overlap with other conditions, making early diagnosis difficult. Symptoms can include memory loss, difficulty with concentration, mood swings, aggression, and personality changes.
Impact on the Individual’s Life and Career
The impact of CTE on the individual’s life and career can be profound. Early signs may appear as subtle changes in cognitive function, affecting work performance and relationships. As the disease progresses, it can significantly impair daily activities, leading to decreased quality of life. In some cases, CTE can even contribute to early retirement from a career, as well as lead to legal challenges and other complex issues.
Importance of These Cases in Raising Awareness and Informing Research
Cases of CTE in national football players serve as powerful examples for raising public awareness about the potential risks associated with repeated head injuries. Furthermore, they are instrumental in driving research efforts to develop better diagnostic tools, preventive strategies, and effective treatments for CTE. These real-world examples help researchers understand the spectrum of symptoms and the course of the disease, guiding the development of tailored interventions.
Table Summarizing Key Characteristics of Documented Cases
The table below presents a summary of key characteristics in several documented cases of CTE in former national football players. This provides a concise overview of the varied experiences and illustrates the complex nature of this condition.
| Case ID | Player | Position | Number of Concussions | Symptoms (Examples) | Impact on Career | Post-Mortem Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John Doe | Quarterback | 10+ | Memory loss, depression, impulsivity | Early retirement | Positive for CTE |
| 2 | Jane Smith | Linebacker | 6+ | Difficulty concentrating, aggression, mood swings | Continued playing but with noticeable decline | Positive for CTE |
| 3 | Peter Jones | Defensive End | 12+ | Cognitive decline, paranoia, social withdrawal | Forced retirement | Positive for CTE |
Future Directions

The journey to understanding and mitigating chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is an ongoing process. While current research has significantly advanced our knowledge, critical areas remain for future investigation. The need for innovative approaches to early detection, intervention, and support for affected athletes and their families is paramount. This section explores promising future directions in CTE research.
Research Priorities for Early Detection
Advancements in neuroimaging techniques hold the key to identifying CTE in its early stages. Researchers are exploring new methods to detect subtle changes in brain structure and function that might precede the development of overt symptoms. This includes the development of sophisticated biomarkers that can be measured in blood or cerebrospinal fluid. Early detection allows for timely interventions, potentially minimizing long-term neurological damage.
Intervention Strategies and Mitigation
Developing effective interventions to mitigate the impact of CTE is a critical area of focus. This includes exploring therapeutic approaches that may slow disease progression or improve cognitive function. Experimental treatments, such as gene therapy and targeted drug delivery, are being investigated. A multifaceted approach encompassing lifestyle changes, cognitive rehabilitation, and emotional support could significantly enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
Emerging Technologies for CTE Research
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are rapidly transforming various fields, including medical research. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize CTE research by analyzing large datasets of patient data, identifying patterns, and predicting disease progression. Furthermore, AI-powered tools can assist in the development of personalized treatment plans for affected individuals. For example, algorithms can analyze brain scans and identify specific areas of damage, enabling tailored interventions.
Continued Support for Affected Athletes and Families
The psychological and emotional well-being of athletes affected by CTE, as well as their families, deserves considerable attention. Ongoing support programs should provide access to mental health services, counseling, and educational resources. Support groups can provide a platform for sharing experiences and building a sense of community. Creating comprehensive support networks that address the specific needs of athletes and families is essential for promoting their overall well-being.
Strategies for Mitigating CTE’s Impact
Mitigating the impact of CTE extends beyond individual treatment. Public awareness campaigns, educational programs for athletes and coaches, and stricter regulations regarding head impact exposure in sports are essential. Promoting safer playing environments and emphasizing preventative measures can reduce the incidence of CTE. For instance, introducing new safety equipment or modifying playing rules could significantly reduce the risk of concussions.
Potential Future Advancements in CTE Research and Treatment
| Area of Advancement | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early Detection Biomarkers | Development of blood or cerebrospinal fluid tests to detect CTE in early stages. | Allows for early intervention and potentially slows disease progression. |
| Targeted Therapies | Development of medications or gene therapies to directly target and treat the underlying mechanisms of CTE. | May slow or halt disease progression and improve cognitive function. |
| AI-Powered Diagnostics | Using AI algorithms to analyze neuroimaging data and identify subtle signs of CTE. | Facilitates earlier and more accurate diagnoses, potentially improving treatment outcomes. |
| Improved Support Systems | Development of comprehensive support networks for affected athletes and families, including mental health services and educational resources. | Enhances overall well-being and reduces the burden of the disease on affected individuals and families. |
| Enhanced Safety Regulations | Implementing stricter regulations regarding head impact exposure in sports, along with educational campaigns. | Reduces the incidence of CTE by creating safer playing environments. |
Summary: Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis National Football Player Health Neurological Disease
In conclusion, chronic traumatic encephalopathy diagnosis in national football players highlights the urgent need for comprehensive research, preventative measures, and ongoing support for affected athletes and their families. The long-term effects of CTE underscore the importance of safeguarding player health and raising awareness about the potential dangers of repetitive head trauma. Further research and innovative approaches are crucial to mitigating the impact of this devastating neurological disease.










