Accessibility Mac Apple macOS features how to navigate the world of assistive technology on Apple’s macOS platform. This comprehensive guide explores various accessibility features, from visual aids to motor control options, offering practical steps and insights for users with diverse needs. We’ll delve into the core principles behind macOS accessibility, examining specific features like VoiceOver and Zoom, and demonstrating how to use them effectively.
Unlocking the full potential of your Mac involves understanding and utilizing its accessibility tools. We’ll also cover third-party solutions, troubleshooting common problems, and providing real-world examples to show how these features enhance the user experience. This is your complete guide to mastering macOS accessibility.
Overview of Accessibility Features on macOS
macOS boasts a robust suite of accessibility features designed to empower users with diverse needs. These features cater to a wide range of disabilities, ensuring a more inclusive and user-friendly experience for everyone. From visual impairments to motor difficulties, macOS provides tools and adjustments to help users navigate and interact with their devices effectively.The core principle behind macOS accessibility design is to provide equal access to technology for all users.
This philosophy is reflected in the wide array of features available, from simple adjustments to complex assistive technologies. By enabling users to customize their experience, macOS promotes independence and empowers them to participate fully in the digital world.
Accessibility Feature Categories
macOS accessibility features are categorized to streamline understanding and navigation. These categories reflect the different ways users may interact with and experience technology. Categorizing features helps users quickly locate relevant tools and customizations.
Figuring out accessibility features on macOS can be a bit tricky, but there are tons of helpful resources online. While you’re exploring those, you might also want to check out the latest phone releases, like the Nothing Phone 2 preorder in India, nothing phone 2 preorder india. Once you’ve got your new phone sorted, you can dive back into those macOS accessibility guides and fine-tune your setup for ultimate comfort and ease of use.
- Visual: These features are designed for users with visual impairments, including low vision or blindness. Features often include screen readers, high contrast modes, and magnification tools. Screen readers provide auditory feedback of on-screen text and other content, allowing users to navigate and interact with their computers by hearing the information instead of seeing it.
- Auditory: These features cater to users with hearing impairments or those needing alternative auditory feedback. Features may include volume adjustments, captions, and alternative audio descriptions for video content. Alternative audio descriptions for video content provide auditory information that complements visual elements, providing context for users who may be unable to see or interpret visual information.
- Motor: These features are designed for users with motor impairments, such as tremors, limited dexterity, or paralysis. Features often include keyboard navigation enhancements, alternative input methods (such as eye-tracking), and assistive devices integration. These features allow users with limited motor control to effectively use their computer, enhancing their independence.
Comprehensive List of Accessibility Features
The following table provides a concise overview of some key accessibility features available in macOS.
Figuring out how to make macOS more accessible for everyone is crucial. Learning about the built-in features is a great place to start. However, before we dive into all that, it’s worth considering the broader implications of companies like Uber on the labor market. For example, before Uber revolutionizes labor, it’s going to have to explain these fundamental questions about worker rights and compensation.
Ultimately, understanding these larger societal issues can help inform our choices when seeking out accessible macOS features.
| Feature Name | Category | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| VoiceOver | Visual | A screen reader that provides auditory feedback of on-screen elements, enabling users with visual impairments to navigate and interact with the computer. |
| Magnifier | Visual | Magnifies portions of the screen for users with low vision. |
| High Contrast | Visual | Adjusts the color scheme of the interface for improved readability and visibility. |
| Dictation | Motor | Allows users to input text by speaking. |
| Keyboard Navigation | Motor | Enables users to navigate and interact with applications using only the keyboard. |
| Zoom | Visual | Provides various options for zooming in on content. |
| Closed Captions | Auditory | Displays captions for audio content. |
Specific Accessibility Features: Accessibility Mac Apple Macos Features How To
macOS offers a wide array of accessibility features designed to empower users with diverse needs. These features enhance usability and inclusivity, allowing individuals with visual, auditory, and motor impairments to fully participate in digital experiences. This section delves into the specific features catering to these needs.
Visual Impairments
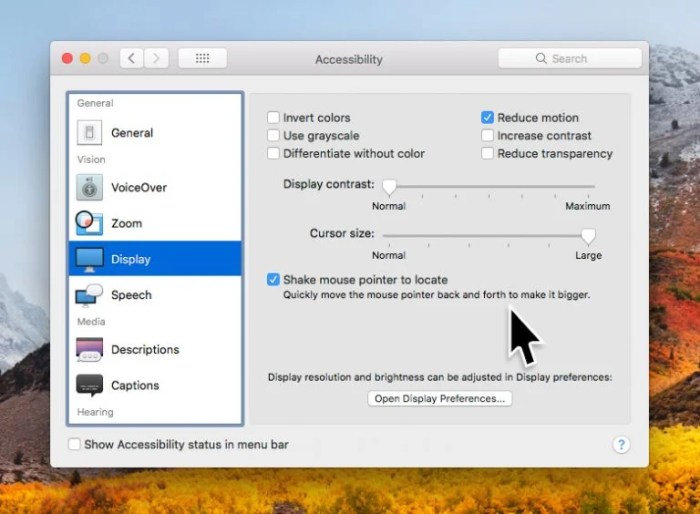
macOS provides powerful tools for users with visual impairments. These tools enhance screen readability, navigation, and interaction. Key features include VoiceOver, a screen reader, and Zoom, which magnifies the display.
- VoiceOver: VoiceOver is a screen reader that provides auditory feedback for visually impaired users. It describes the content of the screen, allowing users to navigate and interact with applications without seeing the display. It announces active windows, controls, and selected items. Users can customize the voice, speed, and volume.
- Zoom: The Zoom feature enlarges the content on the screen. This is particularly helpful for users with low vision, allowing them to see details more clearly. Users can customize the magnification level and choose whether to zoom in on the entire screen or a specific area.
Hearing Impairments
macOS features support for users with hearing impairments. These features aim to provide alternative ways to perceive audio information.
- Sound Recognition: Sound Recognition allows users to identify the source and type of sounds in their environment. This is useful for users with hearing impairments, particularly in situations where audio cues may be critical, like identifying a doorbell or fire alarm.
Motor Impairments
macOS features support for users with motor impairments. These features aim to make interactions with the computer easier and more accessible.
- Trackpad Alternatives: Users with motor impairments may find trackpads challenging to use. macOS offers alternative input methods such as the Magic Mouse, trackpad features for assistive users and third-party keyboards with special features. These provide users with various ways to navigate and interact with the computer, including switch control and other accessibility features.
Summary Table of Accessibility Features
| Feature | Description | Example Usage Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| VoiceOver | A screen reader that provides auditory feedback for visual information. | Navigating web pages, using applications, and reading documents. |
| Zoom | Magnifies the screen content. | Reading small text, reviewing images, and viewing details. |
| Sound Recognition | Identifies sounds in the environment. | Identifying fire alarms, doorbells, and other critical sounds. |
| Trackpad Alternatives | Provides alternative input methods for users with motor impairments. | Using a Magic Mouse or other assistive input devices, using switch control. |
How to Use Accessibility Features
Embracing accessibility features on macOS empowers users with diverse needs to fully utilize their devices. This section provides practical, step-by-step instructions for activating and customizing key accessibility tools, ensuring a more inclusive and user-friendly experience. From adjusting display settings to navigating with alternative input methods, these techniques can transform the way you interact with your Mac.Effective utilization of accessibility features requires understanding their functionalities and how they can be tailored to individual preferences.
This section provides a detailed guide, enabling users to personalize their macOS experience for maximum usability and comfort.
Activating and Customizing VoiceOver
VoiceOver is a screen reader that provides auditory feedback for on-screen elements, enabling users with visual impairments to navigate and interact with their Mac. To activate VoiceOver, you need to go to System Preferences > Accessibility > VoiceOver and click the checkbox.
- Click the VoiceOver button in the menu bar to toggle it on and off.
- Customize VoiceOver settings by clicking the VoiceOver button in the menu bar, then selecting “VoiceOver Options” to configure various aspects, such as the voice, speed, and volume.
- To learn more about navigating with VoiceOver, refer to the VoiceOver user guide within macOS System Preferences.
Adjusting Display Settings for Better Readability
Improving display settings can significantly enhance readability for users with visual challenges.
- Open System Preferences > Accessibility > Display.
- Adjust the text size by dragging the slider to your preferred size.
- Enable features like increased contrast to make text and backgrounds stand out more clearly.
- Explore other display options, such as color filters, to optimize visibility and readability.
Using the Magnifier Tool
The Magnifier tool enlarges portions of the screen, aiding users with low vision or visual impairments.
- Open System Preferences > Accessibility > Magnifier.
- Activate the Magnifier by clicking the Magnifier button in the menu bar.
- Adjust magnification levels and settings for your preferred viewing experience.
- Move the magnifier window around the screen using the mouse or trackpad, as needed.
Setting Up Alternative Input Methods
Alternative input methods cater to users with motor impairments, offering varied ways to interact with the Mac.
- Open System Preferences > Accessibility > Keyboard.
- Explore various keyboard alternatives, such as the on-screen keyboard, which can be particularly helpful for users with limited dexterity.
- Configure other input methods, like assistive devices, to match individual needs.
- Familiarize yourself with specific instructions provided for each alternative input method to ensure optimal use.
Summary Table of Accessibility Features
| Feature | Step-by-step Instructions | Screen Capture Example (Conceptual) |
|---|---|---|
| VoiceOver | 1. Open System Preferences > Accessibility > VoiceOver. 2. Click the VoiceOver checkbox. 3. Customize settings in VoiceOver Options. |
A screenshot showcasing the VoiceOver menu bar icon and the option to adjust voice settings. |
| Display Settings | 1. Open System Preferences > Accessibility > Display. 2. Adjust text size and contrast. 3. Enable color filters (if needed). |
A screenshot of the Display settings panel, highlighting adjustable text size and contrast options. |
| Magnifier | 1. Open System Preferences > Accessibility > Magnifier. 2. Activate the Magnifier. 3. Adjust magnification level and position. |
A screenshot of a portion of the screen magnified using the Magnifier tool. |
| Alternative Input | 1. Open System Preferences > Accessibility > Keyboard. 2. Choose alternative input options (e.g., on-screen keyboard). 3. Configure assistive devices. |
A screenshot showing an on-screen keyboard interface or a picture of a physical assistive device connected to the Mac. |
Customization and Configuration
Taking control of your macOS accessibility settings allows you to tailor the system to your specific needs and preferences. This is crucial for optimizing usability and comfort. This section delves into the various customization options available, empowering you to personalize your experience.Personalization is key to making macOS accessible for everyone. Whether you need to adjust text size, configure keyboard shortcuts, or select alternative input methods, these options offer a high degree of adaptability.
Customizing Text Size, Color, and Contrast
macOS provides robust tools for adjusting the visual presentation of text. This ensures that text remains legible and comfortable to read, catering to varying visual needs. Adjusting these elements can significantly improve readability for users with visual impairments.
- Text Size: You can increase or decrease the size of text throughout the system, making it easier to read on displays of different sizes. This is particularly useful for users with low vision or those who prefer larger fonts.
- Text Color and Contrast: macOS offers options to modify the colors of text and backgrounds. This can enhance readability by increasing the contrast between text and its background. Adjusting these settings is essential for users with color blindness or other visual sensitivities.
- Color and Contrast Settings: macOS provides a dedicated section for adjusting color schemes and contrast levels. This allows users to modify the overall visual presentation of the operating system, optimizing it for their individual needs.
Personalizing Keyboard Shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts provide an efficient way to perform specific tasks without using a mouse or trackpad. This is extremely beneficial for users who prefer or need to use keyboard navigation.
Learning how to access features on a Mac can be tricky, but thankfully, Apple has built-in accessibility tools. There’s a wealth of information out there on how to navigate those options, from adjusting text size to using voiceover. While delving into the world of accessibility features, it’s interesting to note that the parent company of Pornhub, MindGeek, recently rebranded to Aylo, as detailed in this article pornhub parent company mindgeek rebrand aylo.
This rebranding certainly isn’t related to the technical aspects of Mac accessibility, but it does highlight the diverse world of online content and its corporate structure. Regardless, mastering Mac accessibility tools remains a useful skill for many.
- Customization Options: macOS allows users to customize keyboard shortcuts for various accessibility features. These customizations can be tailored to specific needs and preferences.
- Modifying Existing Shortcuts: The system allows modification of existing keyboard shortcuts for common tasks. This can be used to reassign shortcuts to specific actions that align with individual user preferences.
- Creating New Shortcuts: Users can create custom keyboard shortcuts for specific tasks, further streamlining their workflow.
Configuring Alternative Input Methods
Alternative input methods are designed to assist users with physical limitations in controlling their computer. These methods include voice recognition and on-screen keyboards.
- Voice Control: Voice Control lets users control their computer using voice commands. This is particularly helpful for individuals with limited motor skills.
- On-Screen Keyboard: An on-screen keyboard provides a visual representation of the keyboard, enabling users to input text with a pointing device. This is helpful for users with limited dexterity.
- Other Input Options: macOS offers other input methods such as switch control and eye-tracking. These options cater to different physical needs and provide varied input mechanisms.
Personalizing Accessibility Feature Settings
This table illustrates how to personalize settings for a specific accessibility feature, such as VoiceOver.
| Setting | Options | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| VoiceOver Voice | Male, Female, Neutral | Choose the voice you want VoiceOver to use for reading text and providing feedback. |
| VoiceOver Rate | Slow, Medium, Fast | Adjust the speed at which VoiceOver reads text. |
| VoiceOver Volume | Low, Medium, High | Adjust the volume of the VoiceOver feedback. |
Third-Party Accessibility Tools
Beyond the robust built-in accessibility features of macOS, a wealth of third-party tools further enhance usability for diverse needs. These supplementary applications often provide specialized functionalities or alternative methods for interacting with the system, complementing rather than replacing the core macOS accessibility tools. They can be particularly valuable for users with specific requirements or for those seeking tailored solutions.
Identifying Third-Party Tools
Many third-party applications are designed to extend the capabilities of macOS accessibility features. These tools frequently focus on specific needs, such as improved text-to-speech functionality, advanced screen reader integration, or customized keyboard navigation. The availability of such tools demonstrates a broader commitment to accessibility solutions beyond the core operating system.
Integration with macOS Accessibility Features
These third-party tools often integrate seamlessly with macOS accessibility features. This integration allows for a cohesive user experience, enabling users to leverage the strengths of both the built-in and external applications. For instance, a third-party screen reader might work in conjunction with VoiceOver, providing additional options and customizations. The combined effect often results in a more refined and adaptable accessibility experience.
Installation and Configuration
The installation and configuration process for third-party accessibility tools generally follow a similar pattern to other applications. Users typically download the application from a reputable source, such as the developer’s website or a trusted app store. The installation process usually involves a straightforward series of prompts, and configuration options allow users to personalize the tool’s settings to match their preferences.
Examples of Complementary Tools
Many third-party tools effectively complement the macOS accessibility features. For instance, some applications provide alternative input methods, making interactions more intuitive for users with motor impairments. Others focus on enhancing screen reader functionality, offering additional customization and integration options. These applications can also provide features that the core macOS tools lack.
Comparative Overview of Third-Party Tools
| Tool Name | Primary Feature | Integration with macOS | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaturalReader | Advanced text-to-speech engine | Integrates with macOS accessibility settings | Improved speech clarity and customization options |
| ZoomText | Magnification software | Works seamlessly with screen magnifiers | Increased visibility for users with low vision |
| Dragon NaturallySpeaking | Speech recognition software | Provides alternative input method | Enhanced dictation and voice-controlled interaction |
| NVDA (Non-Visual Desktop Access) | Powerful screen reader | Compatible with macOS accessibility | Comprehensive screen reading support and customization |
This table provides a concise overview of some popular third-party tools, highlighting their core functionality, macOS integration, and key benefits. Note that the specific features and functionalities of these tools may vary depending on the version and configuration.
Troubleshooting Accessibility Issues
Navigating macOS with accessibility features can sometimes present challenges. This section dives into common problems users might encounter and provides practical solutions, along with guidance on reporting issues to Apple. Understanding these troubleshooting steps empowers users to effectively utilize macOS accessibility features.
Common Accessibility Issues
Troubleshooting accessibility issues often begins with identifying the specific problem. Users might experience various difficulties, from minor display adjustments to more complex interactions with assistive technologies. Recognizing these common problems is crucial for finding effective solutions.
- Display Issues: Problems with text size, color contrast, or font selection can hinder readability. Users might struggle to see elements on the screen, leading to frustration and reduced usability.
- Keyboard Navigation Difficulties: Complex navigation patterns or inconsistent keyboard shortcuts can impede tasks. Users relying on keyboard input might find certain functions inaccessible or require excessive effort.
- Assistive Technology Conflicts: Software conflicts or incompatibility with third-party accessibility tools can lead to unexpected behaviors. Certain combinations of accessibility features might not work as intended.
- Software or Operating System Updates: Newly installed updates or system changes can introduce unforeseen issues, impacting accessibility features and requiring adaptation.
- Hardware Compatibility Problems: Certain hardware devices, like external displays, might not function correctly with accessibility features, leading to unexpected behaviors.
Solutions for Common Issues
Effective solutions depend on the specific problem encountered. Troubleshooting should involve systematically checking various aspects of the accessibility settings.
- Display Issues: Users should review the system’s display settings, adjusting text size, color contrast, and font preferences. They can also utilize accessibility features to optimize the screen for improved readability. Adjusting brightness and contrast levels can enhance the visibility of the screen. For example, if text is too small, increasing the font size in System Preferences can resolve the issue.
- Keyboard Navigation Difficulties: Users can verify the keyboard shortcuts for specific actions. Adjusting the keyboard settings and using the accessibility features’ keyboard navigation controls might resolve the issue. For example, using the VoiceOver feature’s navigation options can improve keyboard interactions.
- Assistive Technology Conflicts: Rebooting the system can often resolve software conflicts. Disabling or uninstalling potentially conflicting third-party tools can also help. Checking for updates to both the operating system and assistive technology applications is essential.
- Software or Operating System Updates: Users should check for software updates and apply any necessary updates to the operating system and assistive technologies. This often resolves issues introduced by new releases.
- Hardware Compatibility Problems: Users should ensure that their hardware devices are properly connected and configured. Consult the manufacturer’s documentation for compatibility information, as certain hardware might not be compatible with specific accessibility features.
Reporting Accessibility Problems to Apple, Accessibility mac apple macos features how to
Apple values user feedback and actively seeks to improve its accessibility features. Providing feedback on accessibility issues can contribute to improvements for future users.
- Online Feedback Mechanisms: Apple provides online channels for reporting accessibility issues and submitting feedback. Visiting the Apple Support website or using dedicated forums can provide the appropriate avenues for feedback.
- Support Communities: Joining online support communities or forums for macOS users can allow users to interact with other users and potentially discover solutions to their issues.
- Submitting Feedback about Accessibility Features: Apple provides a dedicated feedback mechanism within the operating system for reporting accessibility issues. Users can provide specific details, including steps to reproduce the issue and relevant error messages.
Troubleshooting Table
This table summarizes common accessibility issues, their potential causes, and recommended solutions.
| Issue | Potential Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Difficulty reading text | Low text size, poor color contrast | Adjust text size and color contrast in System Preferences |
| Inability to navigate using the keyboard | Inconsistent keyboard shortcuts, software conflicts | Verify keyboard shortcuts, disable conflicting software |
| Assistive technology not working as expected | Software conflicts, outdated drivers | Reboot the system, update software and drivers |
| Unexpected behavior after an update | Compatibility issues with new software versions | Check for and apply updates for affected software |
| External display not functioning correctly | Incompatible hardware, incorrect settings | Verify connections, check device compatibility, adjust settings |
Illustrative Examples of Accessibility in Action
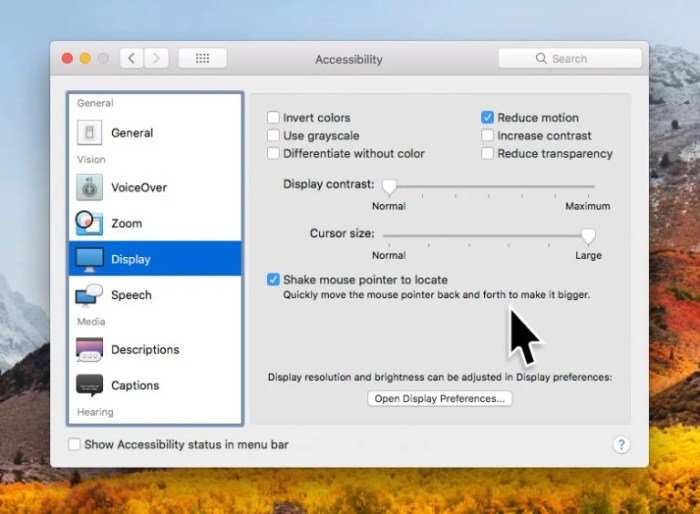
macOS’s accessibility features empower users with diverse needs to seamlessly interact with the operating system and applications. These features range from simple adjustments to complex tools, all designed to enhance inclusivity and remove barriers to participation. This section provides concrete examples of how various accessibility tools work in practice.
VoiceOver for Visual Impairment
VoiceOver is a powerful screen reader that transforms the visual interface into spoken words, providing users with visual impairments with a fully auditory representation of the screen. Imagine a user, Sarah, navigating her macOS desktop. With VoiceOver activated, each element on the screen, from menu items to file names, is announced in a clear and concise voice. She can use keyboard shortcuts to move through the system, and VoiceOver provides feedback on her location and selected items.
This allows Sarah to perform tasks such as opening files, creating new documents, and managing applications without visual cues. VoiceOver’s ability to describe elements in real-time is critical for navigating menus, forms, and interactive elements.
Alternative Input Methods for Motor Impairment
Users with motor impairments often benefit from alternative input methods that bypass the traditional keyboard and mouse. These methods allow them to control the computer using a variety of tools. For example, a user, David, with limited hand movement can utilize a head-tracking device. By simply moving his head, he can select items on the screen, navigate menus, and control applications.
Other options include eye-tracking software, allowing users to select items by looking at them, or specialized keyboards with adapted keys for greater control. Such devices ensure that users with motor impairments have the same level of access and functionality as other users.
Sound Recognition Features for Hearing Impairment
For users with hearing impairments, macOS offers sound recognition features that translate auditory information into text. This can be particularly useful for understanding spoken content. Consider a user, Emily, who uses a sound recognition feature to caption videos. By activating the feature, Emily can now access a transcript of the audio content in real-time, making it possible to follow conversations, presentations, or any audio-based material.
This is a significant improvement in access to information and allows users to interact with the content in a meaningful way.
VoiceOver Navigation of a Website
VoiceOver isn’t limited to macOS’s built-in applications; it extends to web browsing as well. When a user, Michael, navigates a website using VoiceOver, he experiences a different but equally effective browsing experience. VoiceOver reads out the website’s content, including headings, links, and images, providing a comprehensive description of the page’s structure and content. This is invaluable for users who rely on audio feedback to comprehend web pages.
VoiceOver’s support for websites helps to bridge the gap between visual and auditory access, allowing users with visual impairments to fully engage with online information.
Final Review
In conclusion, macOS offers a robust suite of accessibility features to cater to diverse needs. From customizing settings to leveraging third-party tools, this guide provides a clear pathway to maximizing your Mac’s usability. We’ve covered a wide range of topics, from the basics to advanced configurations. Remember to explore the options and find what works best for you.