SASE enterprise story the unity of security network and revenue explores how unified security and networking in Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) solutions drive revenue growth. This insightful journey delves into the core functionalities, highlighting the security enhancements, streamlined network infrastructure, and the crucial link between these aspects and increased revenue. We’ll explore different SASE implementations, their cost-saving potentials, and how they can boost business outcomes and customer experiences.
The key characteristics of SASE deployments, distinguishing them from traditional approaches, are central to this exploration. The role of cloud-based services in SASE and the impact on security and network performance will be examined in detail. We’ll analyze the revenue-generating capabilities of SASE, demonstrating how cost savings and efficiency gains translate into improved financial outcomes.
Defining SASE Enterprise
SASE, or Secure Access Service Edge, is revolutionizing enterprise networking. It’s more than just a new technology; it’s a paradigm shift, moving away from traditional, siloed approaches to a unified, cloud-centric model for security and access. This shift is driven by the increasing reliance on cloud applications and the need for secure access from anywhere, anytime. A SASE enterprise embraces this evolution, delivering a more agile and secure network architecture.SASE enterprises fundamentally differ from traditional networking by merging security and networking functions into a single, cloud-native platform.
This contrasts with the previous approach of having separate security appliances and networking equipment, often leading to fragmented security and complex management. This unification simplifies operations, reduces operational overhead, and improves overall security posture.
The SASE enterprise story hinges on the seamless integration of security and network, ultimately boosting revenue. Think about how a well-designed network security system, like those crucial to SASE, allows for the efficient flow of data and minimizes downtime. This directly impacts revenue generation. Interestingly, recent IIHS partial automated test results for Ford, GM, and Tesla, which you can check out here iihs partial automated test rank ford gm tesla , highlight the importance of robust systems in different contexts.
Ultimately, the story of SASE boils down to making sure security and network function as a cohesive unit to maximize profitability.
Key Characteristics of a SASE Enterprise
A SASE enterprise deployment exhibits several key characteristics that distinguish it from traditional networking approaches. These include: centralized policy management, cloud-delivered security services, and a flexible, scalable architecture.
Unifying Security and Networking in a SASE Environment
The core concept of SASE is the unification of security and networking. This unification occurs through a single platform that manages both aspects of the network. This integration streamlines operations, reduces complexity, and enhances security. It enables consistent security policies across all access points, regardless of whether users are accessing the network from the office, home, or on the go.
Types of SASE Solutions Available
The market offers various SASE solutions tailored to different needs and budgets. These solutions encompass a range of features and capabilities, providing a spectrum of options for organizations.
- Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) solutions are a fundamental part of SASE, enabling flexible, cost-effective connectivity across various locations. They provide a robust foundation for secure connectivity and streamline network management.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) are critical for securing access to cloud applications and data. They provide visibility and control over cloud usage, enforcing security policies and preventing unauthorized access.
- Secure Web Gateways (SWGs) are integral components, filtering and protecting internet traffic to prevent malicious content and ensure compliance with security policies.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a crucial element, enabling granular access control and restricting access to only necessary resources. This enhances security by implementing a strict least-privilege access model.
Role of Cloud-Based Services in SASE
Cloud-based services are integral to the SASE model. They enable the delivery of security and networking functionalities as software-as-a-service (SaaS) solutions. This approach reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure, lowering capital expenditures and operational costs. The cloud-based nature also facilitates scalability and agility, enabling organizations to easily adapt to changing needs. This allows for quick deployment and easy management of security updates and policy changes.
Cloud-based solutions also facilitate a higher level of security, as vendors are often responsible for maintaining the underlying infrastructure.
The Security Aspect of SASE
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) is rapidly reshaping the enterprise security landscape. Moving beyond traditional perimeter-based security, SASE leverages cloud-native security services to create a more dynamic and comprehensive defense against modern threats. This approach fosters greater agility and flexibility, allowing organizations to adapt to evolving security needs and business demands.SASE’s enhanced security capabilities extend beyond the traditional firewall, providing a holistic security posture that integrates various security controls.
This holistic approach is particularly crucial in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks and the rise of remote work. SASE is a strategic response to the challenges of protecting a distributed workforce and dynamic network environments.
Enhanced Security Capabilities
SASE provides a unified platform for security, encompassing various layers of protection. This consolidated approach streamlines security management and improves overall security posture. Crucially, SASE’s architecture enables the integration of multiple security tools and solutions, allowing organizations to enforce a consistent security policy across all users and devices, regardless of their location.
Improved Security Posture Against Threats
SASE significantly enhances an organization’s security posture against various threats. By centralizing security controls, SASE reduces attack surface, enabling organizations to identify and respond to threats more quickly. This proactive approach to security helps prevent breaches and minimizes potential damage. SASE architecture often includes advanced threat detection and prevention capabilities, including intrusion detection systems (IDS) and advanced malware protection, embedded directly into the SASE platform.
This embedded protection allows for real-time threat analysis and mitigation, significantly bolstering the organization’s security defenses.
Role of Zero-Trust Principles in SASE Deployments
Zero-trust is a fundamental principle in SASE deployments. Zero-trust assumes that no user or device should be implicitly trusted, regardless of their location or access credentials. SASE platforms are ideally suited to enforce zero-trust policies. This means that every access request is validated and authorized, enforcing strict access controls and preventing unauthorized access. By adhering to zero-trust principles, organizations can effectively limit the impact of a security breach by minimizing the attack surface.
Security Benefits of Centralized Management
Centralized management in a SASE architecture offers significant security benefits. The unified platform allows for consistent security policies and configurations across all users and devices. This consistency eliminates the inconsistencies that can arise in managing security across multiple, disparate systems. This streamlined management improves security operations and enhances the ability to respond to security events. Real-time monitoring and analysis of security events from various points in the network are often possible, which allows for quicker identification and resolution of security issues.
Examples of Enhanced Security Policies
SASE solutions allow for the creation and enforcement of more sophisticated security policies. For instance, a company could implement a policy that restricts access to sensitive data based on user location and device type. Another example could be implementing policies that require multi-factor authentication for all remote access attempts. By implementing such policies, organizations can significantly strengthen their security posture and mitigate risks.
Examples of these advanced security policies often include implementing granular access controls, enabling the enforcement of specific security protocols, and establishing security profiles for various devices.
The Network Aspect of SASE
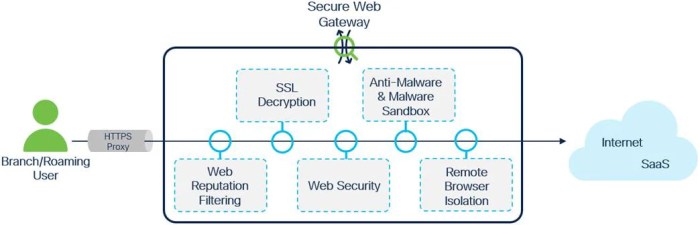
SASE, or Secure Access Service Edge, is revolutionizing network architectures by unifying security and networking functions into a single, cloud-native platform. This approach fundamentally alters how organizations manage their network infrastructure, offering significant advantages in terms of agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It’s a paradigm shift from traditional, siloed approaches, enabling a more streamlined and efficient network experience.The network aspect of SASE is deeply intertwined with its security counterpart.
SASE’s ability to simplify network infrastructure is predicated on its unified approach, enabling a single pane of glass for managing both security and networking aspects. This consolidation leads to improved visibility, control, and overall performance for the entire network.
Simplifying Network Infrastructure
SASE simplifies network infrastructure by consolidating multiple disparate systems into a single, integrated platform. This eliminates the need for complex, often overlapping, network devices and configurations. Instead of managing separate firewalls, VPNs, and WAN optimization tools, organizations can leverage a single SASE platform. This streamlined approach not only reduces operational overhead but also minimizes the potential for security vulnerabilities arising from misconfigurations or gaps in coverage across different systems.
Benefits of a Unified Network
A unified network offered by SASE provides substantial benefits in terms of scalability and flexibility. Scalability is achieved by the cloud-native nature of SASE. Resources can be dynamically provisioned and adjusted based on demand, allowing organizations to accommodate fluctuating user needs and traffic volumes without significant upfront investment or infrastructure changes. This agility also translates into greater flexibility, as organizations can adapt their network configurations to changing business requirements more quickly and efficiently.
Improved Network Performance and Reliability
SASE enhances network performance and reliability through optimized routing and traffic management. By leveraging advanced technologies like SD-WAN, SASE can dynamically route traffic across the most efficient paths, minimizing latency and maximizing throughput. This dynamic routing ensures consistent and high-quality connectivity for users, regardless of their location or the network conditions. Furthermore, the centralized management features of SASE contribute to increased network reliability by allowing for quicker identification and resolution of issues.
Speaking of streamlining operations, the SASE enterprise story, focusing on the unity of security and network revenue, is pretty interesting. It’s all about optimizing the whole system, and that’s where iOS 16.0.3 on your iPhone comes in handy – Apple fixes some annoying bugs, making things smoother for users, like this recent update. Ultimately, both the SASE approach and the iOS update highlight the importance of continuous improvement in tech, leading to a better user experience and more efficient operations, which directly impacts revenue streams.
The Role of SD-WAN in a SASE Environment
SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN) plays a crucial role in a SASE environment by providing a dynamic and automated way to manage network traffic. SD-WAN’s ability to intelligently select the best available connection path, regardless of whether it’s a traditional WAN link or a cloud-based connection, optimizes network performance and cost-effectiveness. In a SASE context, SD-WAN integrates seamlessly with the SASE platform, allowing for unified management and control of the entire network infrastructure.
Comparison Between SASE and Traditional Networking Architectures
Traditional networking architectures often involve a complex array of disparate devices and configurations. SASE, in contrast, presents a unified, cloud-native approach to network and security management. The following table illustrates the key differences:
| Feature | Traditional Networking | SASE |
|---|---|---|
| Network Design | Complex, multi-layered, often involving multiple vendors and technologies. | Unified, cloud-native, leveraging a single platform for both security and networking. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, requiring significant infrastructure upgrades for increased capacity. | Highly scalable, with dynamic resource provisioning based on demand. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility in adapting to changing business needs. | Highly flexible, allowing for quick adaptation to changing requirements. |
| Security | Security and networking are often managed separately, potentially creating gaps in coverage. | Integrated security and networking for comprehensive protection. |
This comparison highlights the significant advantages of SASE over traditional networking architectures in terms of simplifying infrastructure, improving scalability and flexibility, and enhancing network performance and reliability. SASE provides a more agile and cost-effective solution for modern businesses.
The SASE enterprise story is all about uniting security and network revenue streams. It’s a fascinating evolution, but the potential for misuse of data is always a concern. Take a look at how tools like Dataminr’s Twitter news tool, beacon lobbying, and foreign surveillance are used here. Ultimately, the key to successful SASE implementation is ensuring the security of data while maximizing the benefits for revenue generation.
Revenue Generation in SASE Enterprises
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) architectures are transforming how organizations approach network security and access. Beyond the enhanced security posture and streamlined network management, SASE offers significant opportunities for revenue generation and operational efficiency. This shift unlocks new possibilities for businesses to expand their services and reach new markets.SASE enables organizations to deliver secure and consistent experiences to their users, regardless of location or device.
This improved user experience translates directly into enhanced customer satisfaction and potentially increased customer lifetime value. Further, the optimized network and security infrastructure underpinned by SASE can free up IT resources to focus on more strategic initiatives, fostering innovation and potentially driving new revenue streams.
Revenue Streams Generated by SASE Deployments
SASE deployments create diverse revenue opportunities. A core aspect is the ability to offer more sophisticated and secure remote access services. This leads to new subscription-based revenue streams. Organizations can also leverage SASE to extend their existing business services to new geographical markets, further expanding revenue potential. Moreover, the streamlined network management often reduces operational costs, freeing up resources that can be redirected to revenue-generating activities.
Potential Cost Savings Associated with SASE
SASE architectures can deliver significant cost savings across various operational aspects. By consolidating security and networking functions, organizations can reduce the need for disparate hardware and software licenses. Furthermore, automated security and network management features reduce the need for manual intervention, lowering labor costs. Reduced latency and improved application performance also lead to increased productivity and efficiency, potentially lowering the cost of doing business.
Predictable network behavior allows for accurate resource allocation, further reducing unnecessary spending.
How SASE Increases Operational Efficiency
SASE’s centralized management and automation features drastically improve operational efficiency. Tasks previously requiring manual intervention are automated, reducing administrative overhead and freeing up IT personnel for strategic projects. Improved network performance and security reduce downtime and enhance overall application availability. Reduced troubleshooting time directly translates to faster resolution of issues and minimized operational disruptions. The predictive capabilities of SASE further allow for proactive network management, reducing the likelihood of issues occurring in the first place.
How SASE Supports the Expansion of Business Services
SASE enables businesses to securely extend their services to new geographical locations and customer segments. The consistent and secure access it provides allows businesses to serve clients globally with the same level of quality and reliability. This increased accessibility enables a wider customer base, potentially driving substantial revenue growth. Additionally, SASE simplifies the onboarding of new users and services, reducing the complexities associated with managing remote access.
This expanded reach translates to a broader market for existing services, fostering new revenue opportunities.
Revenue Impact of Different SASE Implementations
| Implementation Type | Cost Savings | Increased Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Example 1: Enhanced Remote Access for Sales Teams | $50,000 | $150,000 |
| Example 2: Global Expansion of Cloud Services | $100,000 | $300,000 |
Note: The figures in the table are illustrative examples and may vary depending on the specific organization, deployment scope, and SASE solution chosen.
The Unity of Security and Revenue
SASE, or Secure Access Service Edge, is rapidly reshaping the enterprise landscape. It’s not just about improving security; it’s about fundamentally altering how organizations operate and generate revenue. This shift is driven by the seamless integration of security and networking, creating a unified approach that unlocks significant business benefits. This unification is key to unlocking the true potential of SASE.The unified security and networking architecture of SASE directly impacts revenue streams by streamlining operations, reducing costs, and improving customer experiences.
By consolidating security and networking functions into a single, cloud-native platform, organizations can dramatically improve agility and efficiency. This, in turn, allows for better allocation of resources and a more focused approach to generating revenue.
Impact on Revenue Through Streamlined Operations
SASE’s unified approach enables a significant reduction in operational overhead. Organizations no longer need to maintain separate security and networking infrastructure, leading to lower maintenance costs and a more streamlined IT department. This freed-up capital can be redirected towards revenue-generating activities. For instance, a company might use these savings to invest in marketing campaigns or expand into new markets.
Positive Correlation Between Enhanced Security and Improved Business Outcomes
Robust security measures are not just a necessity; they are a powerful driver of business success. A secure network builds trust with customers and partners, fostering stronger relationships and ultimately driving revenue. When customers perceive a company as prioritizing their security, they are more likely to choose them over competitors. This positive reputation can lead to increased brand loyalty and market share.
How SASE Enables Better Customer Experiences
SASE enables organizations to deliver better customer experiences by providing secure and reliable access to applications and data. This enhanced accessibility translates into greater productivity and efficiency for employees and customers alike. For example, a remote workforce can access company resources securely from anywhere, leading to greater flexibility and a more productive work environment. Improved customer experiences often lead to higher customer satisfaction and increased loyalty, which directly impacts revenue.
SASE Deployment Case Studies
While specific revenue figures are often proprietary, numerous case studies highlight the positive impact of SASE implementations. For example, a financial services company that implemented SASE reported a significant reduction in security incidents, which in turn boosted customer confidence and led to an increase in new account openings. Another case study, from a retail company, highlighted reduced support tickets and faster application access, leading to increased customer satisfaction and ultimately, higher sales.
Framework for Evaluating SASE ROI
Evaluating the ROI of a SASE implementation requires a multi-faceted approach, considering both tangible and intangible benefits.
- Quantifiable Savings: Identify and quantify cost savings from reduced infrastructure, maintenance, and support. For example, a reduction in the number of security incidents can lead to a decrease in incident response costs.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Assess the impact of SASE on employee productivity and operational processes. A faster and more reliable access to resources, due to the implementation of SASE, may reduce the time required for certain tasks.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Measure improvements in customer satisfaction and loyalty metrics. This could involve tracking metrics like support ticket resolution time or customer retention rates.
- Increased Revenue: Evaluate the link between improved security, enhanced customer experience, and increased revenue. This may involve correlating sales figures with specific metrics, like a reduction in support tickets or increased customer engagement.
Illustrative Examples of SASE: Sase Enterprise Story The Unity Of Security Network And Revenue
SASE, or Secure Access Service Edge, is rapidly transforming network architectures and security strategies. Its unified approach to security and networking offers significant benefits, but understanding how it plays out in real-world scenarios is crucial. This section explores illustrative examples of SASE implementations, highlighting their key features, security implications, and impact on revenue.SASE implementation scenarios vary greatly depending on the specific needs and resources of an organization.
From small businesses transitioning to cloud-centric operations to large enterprises seeking to enhance remote worker security, the applications of SASE are diverse and impactful. These examples demonstrate the flexibility and adaptability of SASE in addressing different challenges and opportunities.
SASE Implementation Scenarios, Sase enterprise story the unity of security network and revenue
Understanding SASE implementations requires examining various scenarios. The following table Artikels key features, security implications, and revenue impacts across different situations.
SASE Implementation Strategies
Implementing a Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture requires a meticulous and strategic approach. It’s not a simple “turnkey” solution but rather a carefully planned transformation of your network infrastructure and security posture. Success hinges on understanding the specific needs of your organization and meticulously mapping out the implementation journey. This involves not just selecting the right vendor, but also integrating the SASE capabilities seamlessly into your existing IT environment.A well-defined SASE implementation strategy is critical for realizing the full potential of the platform.
This encompasses careful planning, vendor selection, risk mitigation, and ongoing management. A step-by-step process, coupled with a comprehensive migration plan, will ensure a smooth transition and avoid potential pitfalls.
Step-by-Step Guide to SASE Implementation
A phased approach is crucial for a successful SASE implementation. This methodology allows for controlled rollout, minimizes disruption, and facilitates continuous monitoring and refinement. Begin with a thorough assessment of current network and security infrastructure. Identify key use cases and prioritize the implementation of SASE capabilities accordingly. This methodical approach ensures the optimal utilization of SASE features, reducing operational complexities.
- Assessment and Planning: Conduct a comprehensive inventory of existing network infrastructure, security tools, and applications. Identify potential bottlenecks and pain points in your current setup. Define clear business objectives and use cases for SASE. Develop a detailed project plan with timelines, milestones, and budget allocation.
- Vendor Selection: Evaluate potential SASE vendors based on their capabilities, scalability, and support. Consider factors such as security features, integration with existing systems, and vendor reputation. Conduct thorough vendor demos and proof-of-concept (POC) implementations to ensure a seamless fit with your needs.
- Pilot Program: Deploy SASE in a limited, controlled environment (e.g., a specific department or branch). This pilot phase allows for testing, validation, and refinement of the implementation strategy before a full-scale rollout.
- Phased Rollout: Implement SASE functionalities in phases, gradually expanding its reach across the organization. This phased approach allows for a controlled transition and minimizes disruptions to existing operations.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor the performance of the SASE deployment. Identify areas for improvement and refine the configuration to optimize security and performance. Regularly update security policies and configurations to address emerging threats.
Key Considerations for Choosing a SASE Vendor
Selecting the right SASE vendor is critical for a successful implementation. The chosen vendor should align with your organization’s specific needs, scalability requirements, and long-term vision. Crucially, their ability to integrate with existing systems and support future growth is paramount.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Assess the vendor’s ability to handle future growth and accommodate evolving needs. A robust platform is essential to support increased user traffic and data volume without performance degradation.
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate the vendor’s ability to seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure and security tools. Minimize disruptions by choosing a vendor that integrates with your existing network and security tools, streamlining workflows.
- Security Features and Compliance: Verify the vendor’s adherence to relevant security standards and compliance regulations. Robust security features are crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Customer Support and Training: Evaluate the vendor’s customer support responsiveness and training programs. Comprehensive support and training materials are critical for ensuring a smooth implementation and ongoing management of the SASE platform.
Potential Challenges Associated with SASE Implementation
Implementing SASE presents certain challenges, including integration complexities, security concerns, and potential disruptions to existing workflows. Careful planning and risk mitigation strategies are crucial to address these challenges proactively.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating SASE with existing infrastructure and security tools can be complex. The diverse range of technologies involved necessitates careful planning and coordination.
- Security Concerns: Maintaining a strong security posture in a distributed SASE environment requires ongoing vigilance. Ensuring consistent security policies across the network is critical.
- Operational Disruptions: Transitioning to SASE can cause temporary disruptions to existing operations. A well-defined migration plan is essential to mitigate these disruptions.
Importance of a Comprehensive Migration Plan
A comprehensive migration plan is essential for a smooth and efficient SASE implementation. It Artikels the steps, timelines, and resources needed to transition from the existing infrastructure to the SASE platform. This meticulous approach reduces risks and ensures a seamless transition.A comprehensive migration plan details the steps, timelines, and resources needed to transition from the current infrastructure to the SASE platform.
This strategy mitigates risks and ensures a smooth transition, minimizing disruptions to business operations.
Potential SASE Vendors
| Vendor | Description |
|---|---|
| CloudGenix | A provider of SASE solutions that focus on cloud-based networking and security services. |
| Fortinet | A comprehensive security vendor offering a wide range of SASE capabilities integrated within their existing security portfolio. |
| Microsoft | A leading cloud provider with a robust SASE solution integrated with its Azure platform. |
| Palo Alto Networks | A prominent security vendor offering a full-featured SASE platform with robust security capabilities. |
| Zscaler | A prominent provider of cloud-based security solutions, including a comprehensive SASE platform. |
Future Trends in SASE
The SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by the ever-increasing complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments and the growing need for secure, flexible, and scalable network solutions. SASE is no longer a niche technology; it’s becoming a critical component of modern enterprise infrastructure. This evolution necessitates understanding the future trends shaping SASE solutions.The future of SASE hinges on its ability to adapt to the ever-changing technological landscape and evolving security threats.
Key to this adaptation is the integration of emerging technologies, such as AI and machine learning, to enhance security capabilities and optimize network performance. This evolution is not just about adding new features; it’s about redefining the core functionalities of SASE.
Evolving Landscape of SASE
The SASE market is expanding beyond its initial focus on security and network access. It is increasingly integrating with other cloud-based services, including collaboration platforms, data analytics tools, and application programming interfaces (APIs). This integration fosters a more comprehensive approach to enterprise networking, providing a unified platform for managing diverse digital resources. This interoperability will be a critical factor in the future of SASE.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in SASE
Several trends are reshaping the SASE landscape. These include:
- Enhanced Security Capabilities: SASE solutions are incorporating advanced threat detection and response mechanisms, such as AI-powered anomaly detection and automated threat mitigation. These enhancements improve the speed and effectiveness of security operations. Real-world examples include organizations deploying AI-powered solutions to proactively identify and block zero-day threats in real time.
- Improved Network Performance: SASE solutions are designed to optimize network performance through intelligent traffic routing and dynamic bandwidth allocation. This is crucial for maintaining a consistent user experience, particularly in hybrid cloud environments.
- Increased Automation and Orchestration: SASE is becoming increasingly automated, streamlining the deployment and management of security and network functions. This allows for faster implementation and reduced operational overhead, critical for organizations with complex deployments.
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Future SASE solutions will need to seamlessly integrate with existing enterprise infrastructure, including legacy systems and on-premises equipment. This interoperability is essential for a smooth transition to a SASE-based environment.
Key Factors Driving SASE Adoption
Several factors are driving the adoption of SASE solutions:
- The increasing complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments necessitates a unified approach to security and networking.
- The need for improved security posture in the face of evolving cyber threats compels organizations to adopt robust and scalable security solutions.
- The demand for greater agility and scalability in network infrastructure requires solutions that can adapt to dynamic business needs.
- The cost-effectiveness of SASE solutions compared to traditional approaches often proves to be a significant driver.
AI and ML Enhancement of SASE Capabilities
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing SASE capabilities by providing advanced threat detection, automated incident response, and intelligent traffic optimization.
- Threat Detection and Response: AI algorithms can analyze massive datasets to identify anomalies and predict potential threats, enabling proactive security measures. This leads to quicker response times and reduces the risk of breaches.
- Traffic Optimization: ML models can dynamically adjust network routing and bandwidth allocation based on real-time traffic patterns and user behavior, optimizing performance and minimizing latency.
- Zero-Trust Security Enhancements: AI and ML are critical to implementing a true zero-trust model by constantly assessing user and device risk profiles. This ensures only authorized users and devices have access to sensitive data and resources.
Future Directions for SASE Solutions
The future of SASE will likely involve a greater emphasis on:
- Context-aware security: Solutions that understand the context of user activity, device location, and application usage will be more effective in preventing and mitigating security risks.
- Zero trust security architecture: The move towards zero-trust will be further emphasized, with AI and ML playing a key role in constantly assessing and adapting to evolving threats and user behavior.
- Integration with cloud-native applications: Solutions will need to be more closely integrated with the rapidly evolving world of cloud-native applications.
Closure
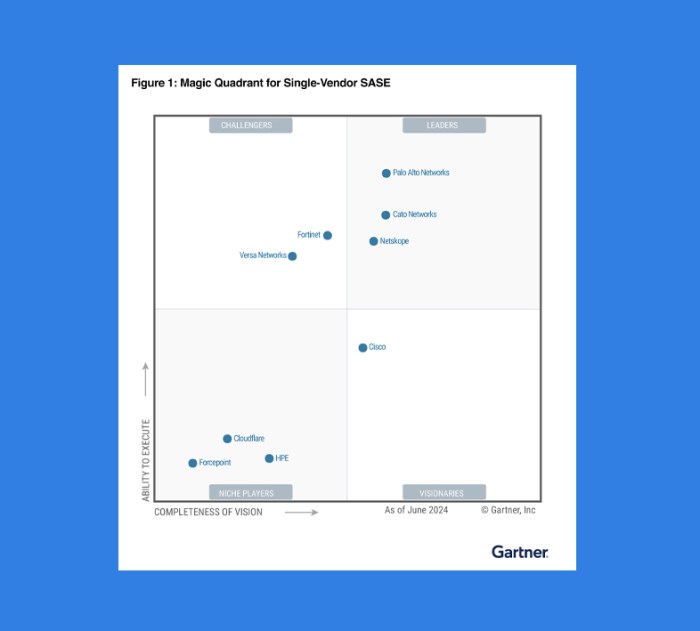
In conclusion, SASE enterprise story the unity of security network and revenue presents a compelling case for adopting SASE solutions. By unifying security and networking, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, improve network performance, and drive revenue growth. The various implementation strategies, potential challenges, and future trends offer a complete picture of the SASE landscape. Ultimately, the focus on improved customer experiences, cost savings, and increased operational efficiency through a unified SASE approach highlights the strategic value of this transformative technology.