Strava beacon live location tracking map data privacy is a critical concern for users. This in-depth exploration delves into how Strava beacons function, examining the data collected, transmitted, and the potential privacy implications of this live location tracking. We’ll also analyze the security measures in place, user control options, and the legal frameworks surrounding this sensitive information.
The detailed analysis will cover various aspects, from the technical specifics of beacon technology to the potential risks of misuse. We’ll also explore user feedback, compare Strava’s practices with competitors, and present alternative methods for fitness tracking while prioritizing privacy.
Strava Beacon Functionality
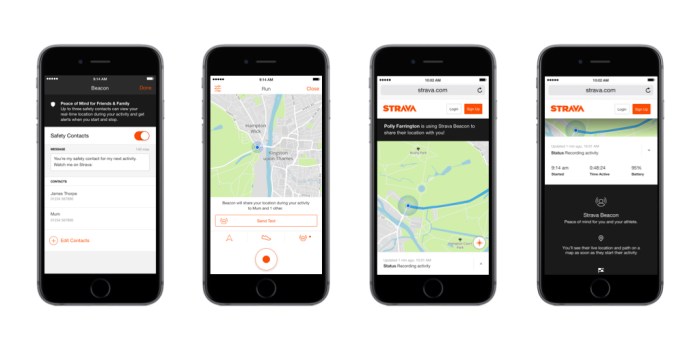
Strava beacons are a key component of the Strava platform, providing real-time location tracking for users engaging in various activities. They offer a convenient way to share your location with friends, family, and the wider Strava community. This feature empowers users with increased safety and social connectivity while participating in outdoor activities.Strava beacons leverage advanced technology to pinpoint your location with accuracy, providing valuable data for athletes and outdoor enthusiasts.
The core functionality hinges on the continuous collection of position data, combined with other relevant information. This data is then transmitted wirelessly, enabling real-time updates on the user’s activity.
Strava Beacon’s live location tracking map data privacy is a hot topic, and it’s important to consider how that data is used. While the technology can be incredibly useful for tracking your runs and rides, concerns about the security and potential misuse of this information are valid. This is a similar concern to how YouTube’s redirect method for anti-terrorist videos search ( youtube redirect method anti terrorist videos search ) raises questions about transparency and control.
Ultimately, understanding these potential implications is crucial for maintaining trust and responsible data handling, especially with location-based services like Strava.
Beacon Tracking Technology
Strava beacons utilize a combination of technologies to provide precise and reliable location tracking. They commonly employ GPS (Global Positioning System) for determining latitude and longitude coordinates. In conjunction with GPS, other technologies may be integrated to enhance accuracy and provide additional data points. These technologies can include cellular data networks for rapid updates, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for shorter-range communication.
Data Collection
Strava beacons gather a range of data points that enhance the user experience and provide valuable insights into the activity. The collected data typically includes speed, distance traveled, elevation gain or loss, and time spent performing the activity. This comprehensive data set provides a detailed record of the user’s performance and progress. For example, a user hiking a mountain trail will receive data such as the time spent climbing, the elevation gained, and the total distance covered.
Data Transmission Methods, Strava beacon live location tracking map data privacy
The chosen data transmission method plays a crucial role in determining the frequency and reliability of location updates. Different methods have varying degrees of accuracy and power consumption. Strava beacons often utilize Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for short-range, low-power communication, which is ideal for quick updates and sharing with nearby devices. For longer-range and more frequent updates, cellular data networks are often employed.
The method selected balances the need for real-time updates with the need for conserving battery power.
Beacon Technology Comparison
| Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| GPS | High accuracy in open areas, widely available, global coverage. | Accuracy can be reduced in urban areas or dense foliage, requires clear line of sight to satellites. |
| Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) | Low power consumption, suitable for short-range tracking, good for sharing with nearby devices. | Limited range, updates might be less frequent than cellular, prone to interference in crowded environments. |
| Cellular | Long range, frequent updates, good for long-distance tracking, no line of sight limitations. | Higher power consumption, data costs may apply, cellular signal availability is not universal. |
This table Artikels the comparative advantages and disadvantages of different beacon technologies, highlighting the trade-offs in terms of accuracy, power consumption, and range. Choosing the appropriate technology depends on the specific use case and desired level of functionality. For instance, a runner might opt for cellular for real-time updates, while a hiker might prioritize BLE for sharing location with a companion nearby.
Live Location Tracking Data
Strava’s live location tracking feature provides a dynamic view of a user’s movement, capturing real-time data as they exercise. This feature, while popular for its interactive nature, raises important considerations about the data being collected and its potential implications. Understanding the specifics of this data and its privacy implications is crucial for informed use.Live location tracking records the user’s precise location at regular intervals, usually marked by GPS coordinates.
This data stream includes the user’s latitude and longitude, speed, elevation, and often, timestamps. These points, when combined, create a detailed map of the user’s activity, offering a comprehensive record of their journey.
Data Points in Live Location Tracking
The data points collected in live location tracking extend beyond basic location coordinates. This data often includes timestamps, altitude, and speed. The frequency of data points is typically high, enabling a real-time representation of the user’s movement. This granular level of detail, while providing an immersive experience, also means more data is being transmitted and stored.
Potential Implications on User Safety and Privacy
Live location tracking, while offering a compelling experience, presents potential implications for user safety and privacy. The precise location data shared can be a valuable asset for emergency responders in the event of an accident or incident. However, this same data could also be vulnerable to misuse if not protected appropriately.The data’s accessibility to third parties, even with privacy protocols in place, is a critical concern.
Strava Beacon live location tracking map data privacy is a hot topic, and it’s easy to see why. But, while we’re on the topic of privacy concerns, have you heard about OnePlus’s decision to deviate from the stock Android design? OnePlus explains why it moved away from stock Android design in a way that, ironically, also raises some questions about their own user data handling.
Ultimately, the focus needs to remain on the implications of live location tracking, and how Strava handles user data.
Users should be aware that sharing their real-time location exposes them to potential risks, and this information could be used for stalking or harassment.
Comparison of Data Privacy Policies Across Fitness Tracking Apps
Different fitness tracking apps employ varying approaches to handling location data. Some apps prioritize detailed location tracking, while others may focus on less precise location data, or only capture it when a user initiates a particular activity. This difference stems from the various levels of data collection needed for the features of each app.
Data Collection Practices: Strava vs. Other Fitness Apps
| Feature | Strava | Other Fitness Apps (e.g., Nike Run Club, MapMyFitness) |
|---|---|---|
| Location Data Collection Frequency | High-frequency, typically at regular intervals during activity. | Varying frequency, often lower than Strava’s, depending on the activity and app settings. |
| Location Data Precision | Generally high precision, utilizing GPS signals. | Precision may vary depending on the app’s configuration and device’s GPS capabilities. |
| Data Retention | Data retention policies vary, with options for users to delete their data. | Data retention policies vary. Some apps retain data indefinitely, others for a set period. |
| Data Sharing | Data sharing options exist for certain features and integrations. | Data sharing options vary based on the app’s features and user settings. |
The table above highlights the differences in data collection practices among popular fitness apps. Users should carefully review the privacy policies of each app to understand how their location data is handled.
Privacy Implications of Map Data
Strava’s live location tracking feature, while offering a compelling way to share athletic achievements and connect with fellow enthusiasts, presents significant privacy concerns. Understanding these risks and how Strava addresses them is crucial for responsible use of the platform. This discussion delves into the potential vulnerabilities of public live location data, Strava’s data protection measures, and potential misuse scenarios.Strava, as a platform relying heavily on user-submitted location data, must prioritize data security and user privacy.
The platform’s privacy policies and technical safeguards are designed to mitigate risks associated with public location tracking, but users need to be aware of the inherent vulnerabilities. Careful consideration of potential risks is necessary to maintain personal safety and trust in the platform.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Public live location tracking on Strava exposes users to various risks. A primary concern is the potential for stalking and harassment. Knowing an individual’s precise location in real-time can enable malicious actors to track movements, potentially leading to unwanted attention or dangerous situations. Furthermore, the data could be used for identity theft or other malicious purposes. The possibility of accidents or unforeseen circumstances during an activity, combined with the public nature of the data, creates an additional risk layer.
Moreover, data breaches, even with strong security measures, are a potential threat.
Strava’s Data Handling and Protection
Strava employs various measures to protect user data. These include robust encryption protocols to secure data transmission and storage. The platform also provides a range of privacy settings that allow users to control who can see their location data and for how long. Regular security audits and updates are implemented to address vulnerabilities. User authentication and access control measures help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Furthermore, user reports and feedback mechanisms are in place to quickly address potential security breaches or misuse of the platform.
Potential Misuse Cases
Location data from Strava can be misused in various ways. One significant concern is stalking and harassment. Malicious individuals could exploit public live location tracking to monitor and potentially endanger users. Furthermore, the data could be used for targeted advertising or for purposes of data aggregation and analysis. This can include situations where competitors or others attempt to gain insights into an individual’s routines or habits.
Comparison of Privacy Settings
| Feature | Strava | Competitor 1 (e.g., Runkeeper) | Competitor 2 (e.g., MapMyRun) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Live Tracking | Enabled by default, customizable | Option to disable public live tracking | Option to disable public live tracking |
| Privacy Settings | Comprehensive settings for controlling who can view location data | Good range of privacy options | Good range of privacy options |
| Data Retention | Data retention policies are stated in terms of compliance | Data retention policies are stated in terms of compliance | Data retention policies are stated in terms of compliance |
| Data Security Measures | Robust encryption and security protocols | Robust encryption and security protocols | Robust encryption and security protocols |
This table provides a comparative overview of privacy features across platforms. Differences in privacy settings and handling procedures might exist between platforms, affecting how users can control their data. It’s essential for users to carefully review and understand these features on different platforms.
Strava’s beacon live location tracking map data privacy is a hot topic, especially when considering the broader issue of how companies handle user location data. It’s a similar concern to the recent Facebook whistleblower allegations, detailed in the facebook new whistleblower allegations sec report, which highlight the potential risks of unchecked data collection. Ultimately, the public needs to be aware of how companies like Strava are using and protecting this information.
Transparency and clear data usage policies are crucial in maintaining trust.
User Control and Data Management
Strava’s live location tracking feature offers a wealth of information about your activities, but it’s crucial to understand how to manage your privacy settings. This control ensures you’re comfortable sharing your location data while maintaining your desired level of privacy.Users have significant control over what location data is shared and with whom. This allows for customization and adaptation to changing privacy needs.
Levels of User Control
Strava provides multiple levels of control to manage the sharing of live location data. These settings allow you to tailor the visibility of your activity to different groups of people.
Modifying Privacy Settings
Strava’s privacy settings are designed to be easily accessible and navigable. Modifying these settings ensures your comfort with the sharing of your location data.
- Access and Modify Your Profile Settings: You can adjust your privacy settings directly within your Strava profile. This often involves accessing a specific privacy settings section within the app or website. Detailed instructions for adjusting these settings are available on Strava’s support pages.
- Controlling Visibility to Specific Groups: Strava allows you to control who can view your live location data. This may include specific friends, followers, or the general public. For instance, you might want your training partners to see your location in real-time, but not the general public.
- Customizing Data Sharing: You can specify if you want to share your live location data with your followers on Strava or with friends only. You can also decide whether your live location will be visible only to the groups that you select.
Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Privacy Settings
This guide Artikels the steps to modify your privacy settings for live location tracking on Strava.
- Log in to your Strava account: Access your Strava account either through the app or the website.
- Navigate to your profile settings: Look for a profile icon or settings option within the platform.
- Locate privacy settings: Identify the section dedicated to privacy settings or location sharing.
- Choose your desired level of privacy: Select the privacy settings that align with your needs and preferences. This often includes selecting which groups can see your location in real-time.
- Save your changes: After making your selections, save the changes to your profile.
Deleting or Accessing Location Tracking Data
Strava provides options for deleting or accessing your location tracking data.
- Data Deletion: Strava allows users to delete their location tracking data. This may include individual activities or all historical location data. Instructions on how to delete location data are often found within the privacy settings section.
- Data Access: Users can access their location tracking data to download it or review it for personal use. Specific methods for downloading or reviewing location data are usually Artikeld within the app or website’s support documentation.
Data Security and Protection
Strava’s commitment to user data security is paramount, especially concerning sensitive location tracking data. They understand the importance of protecting user privacy and have implemented various measures to safeguard this information. This section will delve into Strava’s security protocols, focusing on encryption techniques and their preventative measures against unauthorized access.
Strava’s Security Measures
Strava employs a multi-layered approach to protect user data, recognizing that no single method is foolproof. Their security measures are designed to deter potential threats and maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of user information.
Encryption Methods
Strava utilizes robust encryption techniques to protect location tracking data during transmission and storage. Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, meaning it’s protected while moving between servers and while stored on their systems. This process ensures that even if a hacker gains unauthorized access to the data, they won’t be able to decrypt the information without the proper keys.
Specific encryption algorithms are not publicly disclosed, but the general principle is that industry-standard, strong encryption methods are in place.
Preventing Unauthorized Access
Strava implements various measures to prevent unauthorized access to user data. These include strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular security audits, and rigorous incident response plans. Access to user data is strictly controlled, and only authorized personnel have access to specific information. Data breaches are mitigated by having well-defined protocols for identifying and responding to potential threats.
This is a crucial element in protecting user data.
Summary of Security Protocols
| Security Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| Strong Password Policies | Users are required to create strong, unique passwords to access their accounts. This discourages the use of easily guessable passwords. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide more than one form of verification to log in, such as a code sent to their phone. |
| Regular Security Audits | Strava conducts periodic security audits to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their systems. |
| Incident Response Plans | Comprehensive plans are in place to respond to and mitigate potential security incidents. |
| Access Control | Access to user data is strictly controlled, with only authorized personnel having access to specific information. |
| Data Encryption | Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest using industry-standard methods to protect against unauthorized access. |
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Strava Beacon Live Location Tracking Map Data Privacy
Navigating the digital world of location-based services requires a deep understanding of the legal and regulatory landscape. Strava, as a platform collecting and utilizing user location data, must be acutely aware of the relevant frameworks to ensure compliance and protect user privacy. This section will delve into the specifics of these frameworks, including the relevant laws, potential challenges, and the implications for Strava.The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding user location data is complex and multifaceted, varying significantly across jurisdictions.
Different countries have different laws and regulations governing data privacy, data security, and the use of personal information. This complexity necessitates a meticulous approach to ensure compliance.
Data Privacy Laws and Regulations
Numerous data privacy laws and regulations govern the collection, use, and storage of user location data. These regulations aim to protect user privacy rights and ensure that data controllers handle user information responsibly. Key examples include the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and various national laws in other countries. These regulations typically Artikel principles such as data minimization, purpose limitation, and data security.
Understanding these regulations and their specific requirements is crucial for companies handling user location data.
Examples of Data Privacy Challenges for Other Companies
Several companies have faced legal challenges regarding location data privacy. For instance, Google has faced lawsuits related to the collection and use of location data for advertising purposes. Similarly, companies offering location-based services have been challenged regarding the accuracy and transparency of their data collection practices. These examples highlight the potential legal ramifications of mishandling user location data.
Analyzing these precedents can provide valuable insights into potential issues for Strava.
Potential Legal Ramifications for Strava
Strava’s handling of user location data is subject to legal scrutiny, and potential breaches or issues could have significant ramifications. Breaches of data security could lead to fines, legal action, and reputational damage. Issues related to user consent, data accuracy, or transparency could also result in legal challenges. Moreover, if Strava fails to comply with applicable data privacy laws, it could face penalties and restrictions on its operations.
For example, non-compliance with GDPR could lead to substantial fines.
Data Security and Protection Measures
Strava should prioritize robust data security measures to protect user location data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. These measures should include encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Furthermore, Strava should ensure that its data handling procedures are compliant with the applicable regulations. Implementing such measures can mitigate potential risks and protect user privacy.
Public Perception and User Feedback
Public perception of live location tracking on platforms like Strava is a complex mix of enthusiasm and apprehension. Users appreciate the social aspect and the ability to share their activities, but privacy concerns are a significant counterpoint. The visibility of real-time location data, especially in potentially vulnerable areas, raises legitimate concerns about safety and security.The public perception of live location tracking is often influenced by the perceived benefits and risks associated with the feature.
While many find the feature engaging and motivating, others are wary of the potential implications for their personal safety and the potential for misuse of their data. User feedback reflects this duality, with passionate advocates and concerned critics alike.
User Concerns Regarding Privacy
Understanding user concerns about privacy is critical to evaluating the effectiveness of data protection measures. Users often express concerns about the potential for their location data to be misused or shared without their explicit consent. They are particularly concerned about the visibility of their data to unauthorized parties, potentially putting them at risk in real-world situations.
- Data breaches: Users express apprehension about the possibility of data breaches, which could expose their sensitive location data to malicious actors. They highlight the importance of robust security measures to protect this data.
- Accidental sharing: Some users are concerned about the potential for accidental sharing of their location data with unintended parties, such as through improper settings or social media interactions. This emphasizes the need for clear and user-friendly privacy controls.
- Potential for stalking: Users express concerns about the potential for their live location data to be used for stalking or harassment. This underscores the need for stringent measures to prevent misuse and ensure user safety.
- Unintended consequences: Users worry about the broader implications of live location data sharing, including potential impacts on their personal safety and the safety of others. This emphasizes the importance of user awareness and education about the potential risks.
- Lack of transparency: Users often express a desire for greater transparency in how their data is collected, used, and protected. This underscores the need for clear and concise privacy policies that are easily understandable and accessible.
Examples of User Comments
User feedback on Strava’s live location tracking feature frequently surfaces on online forums, social media, and support channels. These comments often highlight the importance of privacy and data security.
- “I love tracking my runs, but I’m worried about my data being accessible to people who shouldn’t have access to it.”
- “The feature is cool, but I’m concerned about potential safety risks if my live location is visible to anyone.”
- “Strava needs to be more transparent about how it handles user data and ensure that my information is secure.”
- “I’m worried about the potential for stalking or harassment if my live location is tracked and visible.”
- “Strava should offer more control over who can see my live location and provide clear explanations of how data is used.”
Summary of Common Concerns
“A significant portion of user feedback highlights concerns about the potential misuse of live location data, emphasizing the need for stronger privacy controls, transparency, and robust data security measures to protect users from potential risks.”
Alternatives and Best Practices
Fitness tracking apps have become ubiquitous, but the privacy implications of location data collection are a growing concern. This section explores alternative methods for tracking fitness activities without sacrificing user privacy, and Artikels best practices for handling location data responsibly in the fitness tracking industry. We’ll also examine strategies for anonymizing location data while preserving valuable fitness tracking information.Understanding the importance of user privacy in fitness tracking is paramount.
Transparency and user control over data are essential to building trust and maintaining a positive user experience. Users should be empowered to choose how their data is collected, used, and shared.
Alternative Methods for Privacy-Focused Fitness Tracking
Different methods exist for tracking fitness activities without relying on constant GPS location data. These methods can provide similar insights while minimizing the exposure of precise location information. Heart rate monitors, pedometers, and activity trackers can accurately capture steps, distance, and calorie expenditure without requiring constant location data.
Best Practices for Collecting and Handling Location Data
Best practices in the fitness tracking industry prioritize user privacy. Collecting only the necessary location data, using robust encryption methods, and providing clear data usage policies are crucial steps. Employing techniques that minimize the granularity of location data, while still allowing for meaningful fitness tracking, is vital.
Anonymizing Location Data While Maintaining Fitness Tracking
Anonymizing location data is possible without losing valuable fitness tracking information. Techniques like aggregating data points over time, using pseudonyms, or employing differential privacy can obscure precise locations while preserving the overall trends in activity. A good example is a service that tracks aggregate user activity in a given park or neighborhood without identifying individual users.
Comparison of Privacy-Focused Fitness Tracking Options
| Feature | Strava | Privacy-Focused Alternative 1 (e.g., Activity Tracker) | Privacy-Focused Alternative 2 (e.g., Aggregated Data Service) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location Data Collection | Continuous GPS tracking | No continuous GPS tracking | Aggregated location data |
| Data Sharing | Publicly viewable activities | Data kept on device; optional sharing | Data aggregated and summarized |
| Data Anonymization | Limited anonymization options | Data is not shared beyond the user | Data anonymized through aggregation |
| User Control | User settings to control visibility | User controls data storage and sharing | User controls whether data is shared |
| Privacy Policy | Publicly available | Clear privacy policy | Transparent aggregation policy |
Last Point
In conclusion, Strava beacon live location tracking map data privacy is a complex issue demanding careful consideration. Understanding how the system works, the potential risks, and the user’s rights to control their data is crucial. This comprehensive overview provides insights into the practicalities of location tracking, the legal and regulatory context, and user concerns, ultimately helping users make informed decisions about their data sharing on Strava.











