Google Magic Editor AI photos pixel fakery is rapidly changing how we perceive images. This powerful tool allows for intricate pixel manipulation, opening doors to both artistic expression and potentially malicious use. We’ll delve into the capabilities of this AI, examining how it alters photos, the ethical implications, and potential for misuse. The intricate processes behind the “magic” will be explored, alongside comparisons to traditional methods.
The basic functionalities of Google’s Magic Editor are impressive, allowing users to easily make subtle edits or significant transformations. However, this ease of use also presents a significant concern about the potential for fakery. The capability to realistically manipulate pixels raises questions about the authenticity of images, and the ethical implications are significant.
Introduction to AI Photo Editing
AI photo editing tools, like Google’s Magic Editor, are revolutionizing how we manipulate and enhance images. Leveraging artificial intelligence, these tools automate tasks previously requiring significant manual effort, offering a streamlined and often more sophisticated approach to image enhancement and manipulation. This shift towards AI-powered solutions is not just about convenience; it’s about unlocking new possibilities for creativity and precision.These tools use algorithms to analyze images, understand content, and apply edits automatically.
This intelligent approach allows for faster processing, more consistent results, and sometimes even more creative possibilities than traditional methods. The potential for these tools extends beyond simple adjustments, opening doors to advanced effects and creative explorations.
Basic Functionalities and Capabilities
AI photo editing tools, like Google’s Magic Editor, offer a wide array of functionalities. These include automatic enhancements like brightness, contrast, and color adjustments. They can also identify and remove objects, enhance facial features, and even change backgrounds. More advanced features allow users to stylize images with artistic effects or restore old photos. The tools learn from massive datasets of images, enabling them to make accurate and often impressive improvements with minimal user input.
Common Uses for AI Photo Editing
AI photo editing tools find diverse applications across various fields. In personal use, they allow users to quickly enhance snapshots, correct minor flaws, and apply creative effects, saving time and effort. Professionals in fields like photography, advertising, and design leverage these tools to streamline their workflow, improving output quality and efficiency. Furthermore, AI photo editing can be utilized for historical restoration, enabling preservation and accessibility of older images and documents.
Potential Impact on Industries
AI photo editing tools are expected to significantly impact various industries. For example, the speed and accuracy of image manipulation in advertising and marketing can lead to higher-quality campaigns. In the healthcare field, AI could automate the process of preparing medical images, improving diagnostic accuracy. In the art world, artists could use AI tools for generating novel visual effects and experimental creations.
Key Features and Functionalities of Google’s Magic Editor
This table Artikels some key features and functionalities of Google’s Magic Editor, highlighting its diverse capabilities.
| Feature | Functionality | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automatic Enhancement | Automatically adjusts brightness, contrast, and colors for improved image quality. | Improves the overall appearance of a poorly lit photo. | Saves time and effort for users. |
| Object Removal | Identifies and removes unwanted objects or elements from an image. | Removes a distracting background object from a portrait. | Allows for focused and clean compositions. |
| Facial Enhancement | Automatically adjusts facial features like skin tone, brightness, and expression. | Improves the appearance of wrinkles or blemishes on a portrait. | Improves portraits and self-portraits. |
| Background Replacement | Replaces the background of an image with a different one. | Changes the background of a product shot for a new backdrop. | Provides flexibility and creative possibilities. |
The Concept of “Magic” in AI Photo Editing: Google Magic Editor Ai Photos Pixel Fakery
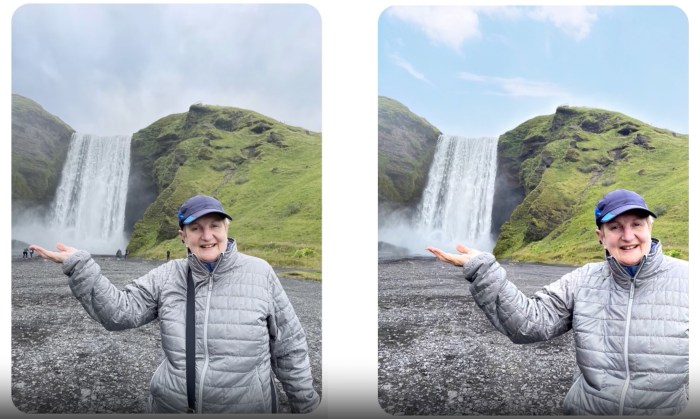

AI photo editing tools are rapidly changing the landscape of image manipulation. The ease and seemingly effortless transformations they offer evoke a sense of “magic.” This “magic” isn’t conjured by mystical forces but by sophisticated algorithms that learn from vast datasets of images. The underlying processes are complex, but the results can be stunning, allowing users to achieve effects previously requiring significant artistic skill and time.AI photo editing software leverages deep learning models, trained on millions of images, to identify patterns and relationships within the data.
These models then apply learned rules to input images, producing altered versions. For example, a model trained on portraits might automatically enhance facial features, smooth skin tones, and adjust lighting to achieve a “perfect” aesthetic. This automated process, though not a true act of magic, gives the impression of effortless transformation.
AI Algorithms and Photo Editing “Magic”
AI algorithms achieve photo editing “magic” through a combination of image recognition, feature extraction, and data manipulation. They identify objects, faces, and even subtle nuances in lighting and color. This identification allows the algorithm to make targeted changes, such as removing blemishes, adjusting color balance, or altering the perspective of a scene. The algorithms are continuously learning and improving their ability to understand and manipulate images.
Comparison with Traditional Photo Editing
Traditional photo editing techniques, often relying on manual adjustments and artistic judgment, differ significantly from AI-driven methods. Human editors meticulously control each aspect of the image, applying filters, adjustments, and corrections with precision. AI, on the other hand, operates on a broader, data-driven approach. While human editors retain creative control, AI algorithms automate many tedious tasks, allowing for faster and potentially more consistent results.
The human touch, however, remains essential in guiding the AI process and fine-tuning its output.
Limitations and Potential Biases in AI Photo Editing
AI photo editing tools, while powerful, have limitations. The algorithms can sometimes produce unrealistic or unnatural results, especially when dealing with complex scenes or highly detailed images. Furthermore, the training data used to develop these algorithms might reflect societal biases, leading to potentially skewed outputs. For instance, an algorithm trained predominantly on images of light-skinned individuals might not accurately represent skin tones of individuals from different ethnic backgrounds.
Careful consideration and human oversight are necessary to mitigate these issues.
Steps Involved in an AI Photo Editing Process (Focusing on “Magic”)
The process often begins with the user uploading an image. The AI software then analyzes the image, identifying key elements such as faces, objects, and lighting. Based on this analysis, the software applies learned transformations, such as enhancing details, removing imperfections, or adjusting color palettes. This process, although seemingly effortless, involves complex calculations and pattern recognition by the AI.
The user can then fine-tune the results to achieve the desired aesthetic. The “magic” lies in the software’s ability to perform these transformations automatically.
Comparison Table: AI Photo Editing vs. Human Photo Editing
| Feature | AI Photo Editing | Human Photo Editing | Key Differences | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster | Slower | AI automates many tasks. | AI can enhance a photo in seconds; a human editor might take minutes or hours. |
| Accuracy | High (consistent), potentially flawed | High (variable) | AI relies on learned patterns, humans use judgment. | AI might consistently over-sharpen an image; a human can adjust for detail. |
| Creativity | Limited | High | AI primarily follows learned patterns; humans have artistic control. | AI might not capture a unique artistic style; a human editor can implement specific artistic preferences. |
| Cost | Often affordable (software, cloud services) | Variable (skill, time, tools) | AI tools can be cost-effective, especially for routine tasks. | AI tools can be affordable for mass image processing; a professional human editor can command high fees. |
Pixel Manipulation and Fakery in AI Photo Editing
AI photo editing tools are rapidly evolving, blurring the lines between reality and fabrication. These tools, powered by sophisticated algorithms, allow for intricate manipulation of image pixels, opening up a new frontier in image creation and alteration. While this capability offers immense creative potential, it also raises significant ethical concerns regarding the authenticity and reliability of visual information.The power of AI lies in its ability to analyze and manipulate vast amounts of data within an image.
By identifying patterns and structures within the pixel data, AI can seamlessly blend, remove, or replace elements within an image, creating highly realistic but fabricated results. This ability to create convincing fakes poses challenges for verifying the authenticity of digital media in our increasingly interconnected world.
Methods of AI Pixel Manipulation
AI tools employ a variety of techniques to manipulate image pixels. These include deep learning models, specifically convolutional neural networks (CNNs), trained on massive datasets of images. These models learn to recognize and reproduce intricate patterns in pixel arrangements, enabling them to seamlessly blend objects or modify textures. The process often involves identifying edges, colors, and textures, then generating new pixel data that mimics the surrounding environment.
This ability to seamlessly integrate new elements into an image without obvious seams is a key factor in the realistic quality of AI-generated fakes.
Potential for Realistic Fakes
AI’s ability to create realistic fakes is undeniable. Imagine a photo of a celebrity in a location they never visited, or a historical event depicted with altered participants. AI can now produce such imagery with remarkable detail, making it extremely difficult to distinguish between genuine and fabricated images without specialized tools or knowledge. This capability has significant implications for areas like journalism, social media, and even legal proceedings, where visual evidence plays a critical role.
The potential for manipulation can erode trust in the very information we consume.
Ethical Implications of AI-Generated Pixel Fakery
The ethical implications of AI-generated pixel fakery are substantial. The ease with which realistic fakes can be produced raises concerns about the integrity of visual information. Misinformation and disinformation campaigns can become more sophisticated and convincing, impacting public opinion and potentially influencing important decisions. The potential for misuse in political campaigns, financial fraud, or even personal attacks is significant.
Establishing clear guidelines and ethical frameworks for the use of AI in image editing is crucial to mitigate these risks.
Examples of AI-Generated Fakes
Numerous examples showcase the capability of AI to create convincing fakes. A photo of a historical figure in a contemporary setting, or a celebrity in an unlikely environment, can be created with remarkably realistic results. Even the alteration of minor details, such as changing facial expressions or clothing, can be achieved with impressive precision. These examples underscore the importance of critical thinking and media literacy in discerning genuine content from AI-generated fakes.
Comparison of Pixel Manipulation Methods
| Feature | Traditional Methods (e.g., Photoshop) | AI-Based Methods | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Manual selection, cloning, masking, and adjustment layers | Deep learning models, image synthesis | AI automates processes; traditional methods require manual effort |
| Accuracy | Highly dependent on user skill | Generally more accurate in replicating details and blending elements | AI produces more seamless results |
| Time | Time-consuming, especially for complex edits | Faster, especially for repetitive tasks and large-scale edits | AI can complete tasks significantly faster |
| Control | High level of control over individual pixels, but limited by the user’s skill | Less direct control over the output, but highly accurate in creating realistic results | AI sacrifices some control for realism and speed |
Google Magic Editor and Photo Pixel Manipulation
Google’s Magic Editor, a facet of its broader AI image editing suite, offers sophisticated tools for manipulating photos at the pixel level. Leveraging advanced algorithms, the editor allows users to perform intricate transformations, enhancements, and even the creation of entirely new elements within images. This capability, while powerful, also presents potential for misuse, necessitating a critical understanding of the underlying mechanisms.This exploration delves into Google Magic Editor’s pixel manipulation techniques, highlighting its capabilities, potential pitfalls, and comparisons with other AI photo editing tools.
The analysis examines the algorithms at play, illustrating the complexities and nuances involved in such powerful technology.
Pixel Manipulation Capabilities of Google Magic Editor
Google Magic Editor boasts a range of capabilities related to pixel manipulation. These include but are not limited to, fine-grained adjustments to image detail, realistic object removal and replacement, and automated enhancement techniques. The tool offers features that allow users to modify textures, colors, and other visual attributes with precision. This degree of control over individual pixels is unprecedented in traditional photo editing software.
Techniques Used for Pixel Manipulation
Google Magic Editor employs various techniques to manipulate pixels. A key component is its advanced deep learning models. These models are trained on vast datasets of images, enabling them to identify and understand visual patterns, allowing for highly targeted modifications. Specific techniques may involve using generative adversarial networks (GANs) to create new details, or convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to recognize and modify objects.
Furthermore, algorithms that analyze image structure and content, and then refine pixel values accordingly, are employed. These algorithms often rely on sophisticated mathematical models to predict and adjust pixel values in a manner that preserves or enhances the overall image quality.
Potential for Misuse and Unintended Consequences
The ability to precisely manipulate pixels presents potential for misuse. Users could potentially fabricate or alter images with ease, leading to the creation of misleading or fraudulent content. The tools could also be employed for malicious purposes, like creating deepfakes or modifying evidence. Furthermore, unintended consequences of these manipulations may include distortions in the image’s overall aesthetic, inconsistencies in texture or color, or loss of image quality.
This necessitates a heightened awareness of the potential for both intentional and accidental errors.
Analysis of Google Magic Editor’s Algorithms
The algorithms powering Google Magic Editor are complex and proprietary. However, based on the available information and industry trends, the following aspects can be inferred. They rely heavily on deep learning models, often involving CNNs and GANs. These models learn from massive datasets, enabling them to identify and interpret visual patterns in images. The algorithms likely involve sophisticated techniques to blend and refine pixels, aiming to create seamless transitions between edited and original areas.
Further, the models likely incorporate feedback mechanisms to ensure the output image maintains a consistent level of quality and realism. These algorithms are likely highly optimized for efficiency and speed, making the process of pixel manipulation both powerful and practical.
Google’s Magic Editor AI is making some seriously impressive photo edits, but it’s also raising eyebrows about pixel fakery. It’s amazing how realistic the results can be, but you should also be aware of the potential for altering images beyond recognition. Speaking of impressive tech, you can get 25% off this Nespresso Vertuo Next Deluxe coffee and espresso machine, saving a cool $49! get 25 off this Nespresso Vertuo Next Deluxe coffee and espresso machine save 49 It’s worth considering the implications of this kind of AI-powered photo manipulation as we navigate a world where lines between reality and digital fabrication are getting increasingly blurred.
Comparison of Google Magic Editor with Other AI Photo Editing Tools (Regarding Pixel Manipulation)
| Feature | Google Magic Editor | Adobe Photoshop with AI Features | Photopea | Other AI Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pixel-Level Control | High, with focus on natural and seamless manipulation | Moderate, increasing with AI features | Low, more focused on basic adjustments | Varies greatly, some offering similar capabilities to Google’s |
| Object Removal/Replacement | High accuracy and realism, often maintaining context | Improving accuracy and realism | Limited | Varies by tool, some very advanced |
| Generative Capabilities | Potentially very strong | Growing, but often focused on style and enhancements | Limited | Highly variable, some focused on generating entire images |
| Ease of Use | Likely high due to user-friendly interface | High, but can have a steeper learning curve | High | Highly variable, depending on tool and features |
This table provides a general comparison, but the specific capabilities and ease of use can differ depending on the particular tools and features utilized.
AI Photo Editing and the Concept of “Truth”
AI photo editing tools, particularly those leveraging deep learning, are rapidly changing how we perceive and interact with images. Their ability to manipulate pixels with unprecedented precision raises significant questions about the authenticity and reliability of visual information. The blurring lines between reality and digital fabrication demand careful consideration of the implications for truth and trust in the digital age.The ease with which AI can alter images, from subtle adjustments to complete fabrications, challenges our fundamental understanding of visual truth.
We are increasingly exposed to images that may not accurately reflect the events or subjects they depict. This creates a fertile ground for misinformation and the erosion of public trust in visual media.
Challenges to Verifying Authenticity
The sophistication of AI-powered photo editing tools makes it exceptionally difficult to distinguish between genuine and manipulated images. Automated detection methods are often outpaced by the rapid evolution of these tools, and subtle alterations can easily evade human scrutiny. The complexity of algorithms used in AI editing can also create a lack of transparency, making it hard to understand the extent of modifications.
Examples of AI-Driven Image Alteration
AI photo editing has already been employed to alter historical photographs, changing facial features, adding or removing people, or even altering the background of a scene. These manipulations can subtly distort historical records, making it more difficult to understand and interpret the past. For example, an image of a historical event might be altered to include or exclude specific individuals, thus influencing our understanding of the event’s participants and outcomes.
Similarly, AI can manipulate images of public figures to create a false narrative or sentiment.
Google’s Magic Editor AI photo editing is fascinating, but the potential for pixel fakery is concerning. It’s a bit like the recent news about Apple’s App Store, where apps are apparently favoring their own competitors in search results. This raises serious questions about fairness and transparency , which also makes me wonder about the potential for bias in AI image manipulation.
Ultimately, we need more transparency and scrutiny in how AI tools like this are used to avoid misleading results.
AI Photo Editing and Misinformation
AI-powered photo editing plays a critical role in the spread of misinformation. Fabricated or altered images can be easily shared across social media platforms, amplifying false narratives and misleading the public. This can have far-reaching consequences, impacting political discourse, social movements, and even personal reputations. The speed and scale of image manipulation make it challenging to combat the spread of misinformation.
One example is the use of AI-generated deepfakes to create realistic but fabricated videos of public figures, often used to spread false information or manipulate public opinion.
Potential for Malicious Use
The potential for malicious use of AI photo editing tools is substantial. Manipulated images can be used to damage reputations, spread propaganda, or incite violence. The ease of creating convincing forgeries poses a serious threat to individual safety and public order. The tools used to manipulate images are becoming more accessible and user-friendly, which lowers the barrier for malicious actors to create convincing fakes.
Future Trends in AI Photo Editing

AI photo editing is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in machine learning and deep learning. The tools are becoming more sophisticated, offering users greater control and creative possibilities. This evolution is not just about enhancing existing capabilities; it’s about fundamentally changing how we interact with and manipulate images. The future promises even more seamless integration with other creative fields and applications, pushing the boundaries of visual storytelling.
Potential Future Developments in AI Photo Editing Tools
AI photo editing tools are poised for significant advancements. Expect tools that can automatically generate realistic variations of existing images, enhancing creativity by offering a multitude of stylistic options. More sophisticated algorithms will also enable the seamless merging of multiple images into a single, cohesive scene, opening doors for complex visual narratives. Furthermore, the ability to realistically restore damaged or degraded images will likely improve, benefiting historical preservation and archival efforts.
Emerging Technologies Influencing AI Photo Editing
Several emerging technologies will significantly influence AI photo editing. The advancements in generative adversarial networks (GANs) are crucial. These networks can create photorealistic images from text descriptions or other inputs, opening exciting possibilities for custom image generation. Another key technology is the rise of large language models (LLMs). LLMs can understand and respond to user prompts with more nuance and complexity, leading to more intuitive and effective image manipulation.
Additionally, advancements in 3D modeling and rendering will integrate seamlessly into photo editing, allowing for more sophisticated 3D objects and environments to be seamlessly incorporated into existing images.
Google’s Magic Editor AI photo editing is getting interesting, but is it just pixel fakery? The technology’s ability to manipulate images is quite impressive, but the ethical implications of such tools are certainly worth considering. Meanwhile, the recent advancements in self-driving trucking, like the uber freight aurora driverless truck deal , highlight a different kind of technological manipulation – this time, of the physical world.
Ultimately, both highlight how easily we can manipulate data, whether it’s a photo or a fleet of trucks, raising concerns about the authenticity of the outputs and the impact on society.
Analysis of Future Market Demand for AI Photo Editing Tools
The demand for AI photo editing tools is expected to surge in the coming years. Professionals in various fields, from photography and graphic design to marketing and journalism, will increasingly rely on these tools to enhance productivity and creativity. Furthermore, the growing popularity of social media and online content creation will fuel the demand for readily accessible and user-friendly AI tools that can quickly produce high-quality visuals.
The need for high-quality, quickly produced visual content is a key factor in this projected growth.
Potential Future Challenges and Opportunities for AI Photo Editing
| Challenge | Opportunity | Specific Example | Mitigating Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maintaining the authenticity of edited images | Development of transparency tools | Users need to distinguish between genuine and manipulated images, particularly in journalism and social media. | Implementing watermarks or metadata to indicate AI manipulation. |
| Addressing potential biases in AI algorithms | Creating diverse and inclusive datasets | AI models can inherit biases from training data, potentially leading to inaccurate or discriminatory results. | Using diverse and representative datasets to train AI models. |
| Ensuring user control over the editing process | Intuitive and user-friendly interfaces | Users may struggle to understand or control complex AI editing tools. | Developing intuitive interfaces and providing clear instructions. |
| Protecting intellectual property rights | Developing robust copyright protection mechanisms | Concerns exist over the ownership of images generated by AI tools. | Implementing clear copyright policies for AI-generated images and providing tools for attribution. |
User Experience and Accessibility in AI Photo Editing
AI photo editing tools are rapidly evolving, transforming how we manipulate images. A key aspect of their success lies in creating a seamless and accessible user experience for everyone, regardless of technical skills or physical limitations. Intuitive interfaces and robust accessibility features are paramount for widespread adoption and positive impact.A well-designed AI photo editing tool should prioritize ease of use, allowing users to achieve desired results with minimal effort.
Accessibility features ensure inclusivity, enabling individuals with disabilities to utilize the software effectively. This is not just a matter of good practice; it’s a fundamental requirement for a tool intended for widespread use.
Overview of User Experience with AI Photo Editing Tools, Google magic editor ai photos pixel fakery
AI photo editing tools are designed to streamline the process, automating many manual steps. Users can expect a fast and responsive interface, with intuitive controls and clear feedback mechanisms. The tools should empower users to achieve specific edits with minimal technical knowledge. A smooth workflow, allowing users to navigate easily between different editing options, is crucial for a positive experience.
For example, a tool with drag-and-drop functionalities, alongside clear visual representations of adjustments, can significantly improve user experience.
Accessibility Features for Users with Different Abilities
Accessibility in AI photo editing tools encompasses a range of features catering to diverse needs. This includes options for users with visual impairments, such as screen readers and high contrast modes. Keyboard navigation and alternative input methods are crucial for users with motor impairments. Clear, concise text descriptions of actions and options are vital for users with cognitive disabilities.
Providing alternative text for visual elements is critical for screen readers. For example, a photo editing tool with adjustable font sizes, color palettes, and customizable interface layouts caters to various visual needs. Users with dexterity issues might benefit from voice commands or gesture controls.
Examples of Intuitive Interfaces for AI Photo Editing
Intuitive interfaces prioritize simplicity and clarity. Examples include drag-and-drop tools for image adjustments, sliders for fine-tuning parameters, and visual previews to instantly see the impact of changes. A clean, uncluttered layout minimizes distractions and allows users to focus on the task at hand. The tools should provide clear feedback mechanisms, indicating the results of adjustments in real-time.
For instance, real-time previews of filters, effects, and other edits can significantly improve user engagement and satisfaction.
Design Principles Behind User-Friendly AI Photo Editing Tools
The design of user-friendly AI photo editing tools is based on several key principles. Prioritizing simplicity and ease of use is crucial, avoiding unnecessary complexity. Clear and concise instructions, tutorials, and help resources should be readily available. Visual aids, such as icons and tooltips, can greatly enhance understanding and usability. The interface should be adaptable to different user preferences, offering customizable options.
Consistency in design and terminology throughout the software is essential for a seamless experience. The tool should be highly responsive and avoid lag or performance issues.
Table: User Interfaces and Accessibility Options for AI Photo Editing
| User Interface Element | Description | Accessibility Options | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Adjustment Tools | Tools for modifying brightness, contrast, saturation, and other visual parameters. | Adjustable sliders with clear labels, real-time previews, keyboard shortcuts, high contrast options. | Slider to adjust brightness with real-time preview and keyboard navigation. |
| Filter and Effect Application | Tools for adding filters, artistic effects, and other image enhancements. | Visual previews of filters, keyboard shortcuts for filter selection, alternative text descriptions for screen readers. | Visual preview of a vignette filter, and a descriptive label in the screen reader for the filter. |
| Selection and Masking Tools | Tools for selecting and manipulating specific parts of an image. | Clear Artikels of selection tools, customizable brush sizes, keyboard shortcuts, alternative input methods (voice commands or gestures). | Selecting an area with a lasso tool and adjusting its opacity using keyboard controls. |
| Interface Navigation | Navigation through the software’s various components. | Clear labeling of buttons and menus, keyboard shortcuts for navigation, adjustable font sizes, high contrast modes. | Navigation through menus using keyboard arrows and enter key. |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, Google Magic Editor’s AI photo editing capabilities are undeniably powerful, but the potential for pixel fakery is a significant concern. The ease with which realistic alterations can be made demands careful consideration of the ethical implications and the need for tools to verify authenticity. As AI evolves, so too will our need to understand and mitigate the risks associated with its use in image manipulation.