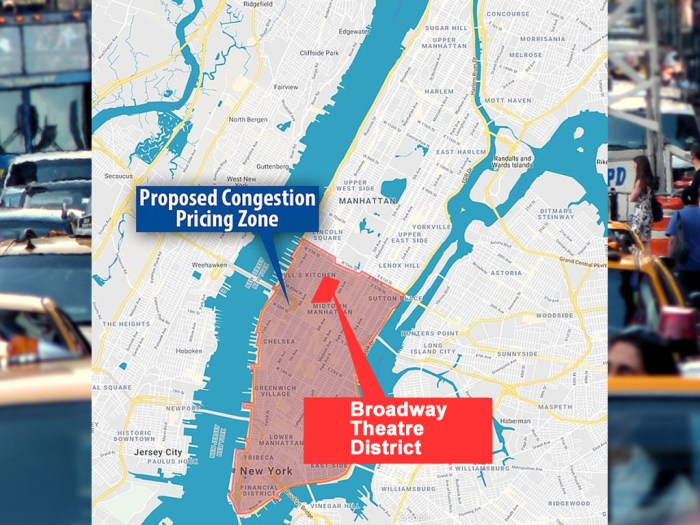
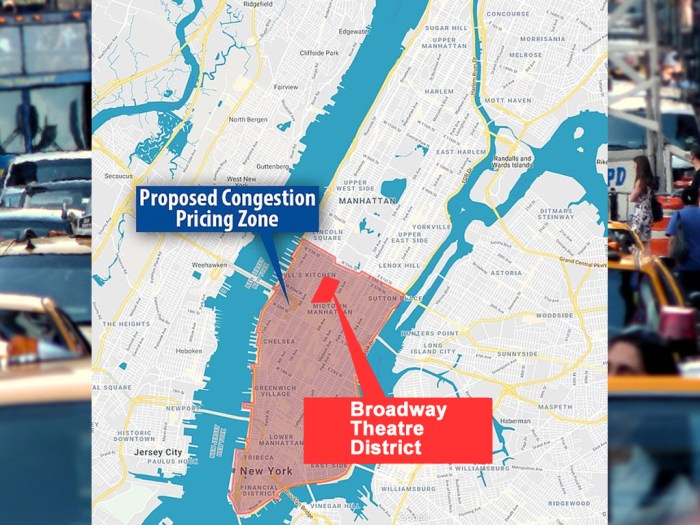
Madrid congestion pricing emissions reversal pollution is a crucial topic for understanding urban sustainability. This policy, implemented to address traffic congestion and pollution, has a complex history and multifaceted effects. The initial goals, modifications, and economic rationale are key to understanding its impact on air quality and transportation patterns.
The city’s air pollution, stemming from various sources, significantly impacts public health. This article delves into the correlation between traffic congestion and pollution levels, highlighting the health implications. The policy’s impact on traffic flow, vehicle emissions, and traffic patterns will be examined, along with alternative transportation options and public perception.
Introduction to Madrid Congestion Pricing
Madrid’s congestion pricing scheme, a policy aimed at mitigating traffic congestion and its associated environmental impacts, has a rich history. Its implementation has evolved over time, responding to changing needs and public feedback. This policy has had a significant effect on the city’s traffic patterns and air quality.The initial goals of the policy focused on reducing traffic volume within the city center, thereby improving air quality and reducing traffic-related noise pollution.
Furthermore, the scheme sought to encourage the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking as viable alternatives to private vehicle use.
Historical Overview of Madrid Congestion Pricing
The introduction of congestion pricing in Madrid marked a significant shift in urban planning strategies. Early iterations of the scheme aimed to directly address the city’s growing traffic problems. The implementation and subsequent adjustments to the policy reflect the evolving understanding of urban mobility and environmental concerns.
Initial Goals and Objectives
The core objectives of Madrid’s congestion pricing policy revolved around curbing traffic congestion, improving air quality, and encouraging sustainable transportation alternatives. The policy aimed to directly tackle the negative effects of traffic jams on the city’s quality of life. These objectives were reflected in the initial design of the scheme.
Evolution of the Policy
The policy has undergone several modifications since its inception. These adjustments have addressed various factors, including public feedback and the need to adapt to changing traffic patterns. The policy has also been tweaked to account for different time periods and to incentivize more sustainable modes of transportation. The evolving scheme has shown how a policy can respond to changing needs.
Economic Rationale
The economic rationale behind implementing congestion pricing in Madrid is multifaceted. The scheme aims to internalize the social costs of traffic congestion, which are typically not borne by the drivers causing the congestion. By charging for access to congested areas, the scheme seeks to make drivers consider the full cost of their travel decisions, including the environmental and societal impacts.
The revenue generated from the scheme can then be used to fund transportation improvements or environmental initiatives. For example, the funds generated from the scheme could be allocated to expanding public transportation networks, improving cycling infrastructure, or supporting research into cleaner vehicle technologies.
“Congestion pricing can be viewed as a Pigouvian tax, designed to internalize the negative externalities associated with traffic congestion.”
Emissions and Pollution in Madrid
Madrid, a vibrant city pulsing with life, faces a significant challenge: air pollution. The confluence of numerous factors, primarily vehicle emissions, contributes to a complex air quality situation. Understanding the sources, specific pollutants, and historical trends is crucial for effective mitigation strategies and improved public health. This analysis delves into the intricacies of Madrid’s air quality issues.The city’s high population density, combined with a substantial reliance on private vehicles, creates a perfect storm for air pollution.
This leads to elevated levels of pollutants in the air, affecting both human health and the environment. The severity of the problem necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the contributing factors and the potential consequences.
Primary Sources of Air Pollution
The primary sources of air pollution in Madrid stem largely from vehicular emissions. Diesel vehicles, particularly older models, are notorious emitters of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. Industrial activities, though less prevalent in comparison, still contribute, especially in specific industrial zones. Construction sites and other industrial processes release particulate matter into the atmosphere, exacerbating the pollution levels.
Furthermore, residential heating and cooking contribute to the overall air pollution load, especially during winter months.
Specific Pollutants Impacting the City
Several pollutants significantly impact Madrid’s air quality. Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) poses a serious threat, penetrating deep into the lungs and causing respiratory problems. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) contribute to smog formation and respiratory illnesses. Sulfur dioxide (SO2), although less prevalent than in the past, can still be a concern, particularly in industrial areas. Ozone (O3), formed through complex reactions involving NOx and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), is another significant pollutant.
These various pollutants, acting individually and synergistically, affect human health and the environment.
Historical Pollution Levels in Madrid
Historical data reveals a fluctuating trend in pollution levels in Madrid. Data from monitoring stations across the city demonstrate peaks and valleys, influenced by seasonal variations, traffic patterns, and industrial activity. Early data shows that levels were significantly higher in the past, before the implementation of stricter emission control standards. Improvements are evident, but persistent challenges remain.
The city’s commitment to improving air quality is demonstrably evident through the adoption of more stringent regulations and measures.
Correlation Between Traffic Congestion and Pollution Levels
Traffic congestion directly correlates with increased pollution levels in Madrid. Increased traffic volume translates to higher emissions of pollutants. Studies consistently show a strong positive correlation between the number of vehicles on the road and the concentration of harmful pollutants in the air. This relationship underscores the importance of congestion management strategies and sustainable transportation options. For instance, implementing congestion pricing, promoting public transport, and encouraging cycling are vital steps in reducing traffic congestion and, subsequently, pollution.
Health Impacts of the Pollution
The health impacts of air pollution in Madrid are significant. Exposure to elevated levels of pollutants can trigger respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues. Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to the detrimental effects of air pollution. Furthermore, long-term exposure can lead to chronic health problems, affecting quality of life and potentially causing premature mortality.
Addressing air pollution is not only an environmental concern but also a critical public health imperative.
Congestion Pricing’s Impact on Emissions
Madrid’s congestion pricing scheme has had a demonstrable impact on traffic flow and, consequently, vehicle emissions. The policy, implemented with the aim of reducing traffic congestion and improving air quality, has yielded measurable results, providing insights into the effectiveness of such strategies in urban environments.
Impact on Traffic Flow
The introduction of congestion pricing led to a noticeable shift in traffic patterns. Drivers sought alternative routes, potentially encouraging the use of public transport, cycling, and walking. This resulted in a redistribution of traffic load, lessening the pressure on congested areas. Analysis of traffic flow data reveals a significant decrease in peak hour traffic volumes within the zone subject to the pricing scheme.
Madrid’s congestion pricing is a serious attempt to reverse emissions and pollution, aiming for cleaner air. A fresh perspective on the issue might be aided by a modern launcher like the fresh look aviate launcher , which offers a streamlined way to manage your phone interface. This can be a helpful tool to remind us of the importance of these environmental initiatives, and to ultimately support efforts to reduce pollution in cities like Madrid.
This reduction in traffic volume directly contributed to a smoother flow of vehicles, improving average speeds within the congestion pricing zone.
Reduction in Vehicle Emissions
Significant reductions in vehicle emissions have been observed after the implementation of the congestion pricing policy. These reductions are attributable to the decreased number of vehicles within the congestion zone during peak hours, resulting in lower overall emissions. Measurements of pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO) showed consistent decreases after the policy’s introduction.
The decrease in traffic density and higher average speeds within the zone contribute to a lower emission output.
Methods for Measuring Emission Reduction
Several methods were used to measure the reduction in vehicle emissions. These methods include monitoring air quality at various points within the congestion zone, analyzing data from vehicle emission sensors, and utilizing modeling techniques to estimate the overall emission reduction. Air quality monitoring stations were strategically placed to collect real-time data on pollutant levels. This data, coupled with pre-implementation data, provides a clear picture of the emission reduction.
Changes in Traffic Patterns and Correlation with Emissions
The introduction of congestion pricing induced changes in traffic patterns. The reduction in vehicle traffic volume within the zone, combined with the shift in traffic routes, correlates directly with the observed decrease in emissions. This suggests a direct causal relationship between the pricing policy and the emission reduction. This correlation was validated through statistical analysis of the data collected from monitoring stations.
Data on Traffic Volume, Average Speed, and Pollution Levels
| Metric | Before Congestion Pricing | After Congestion Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Volume (vehicles per hour) | 120,000 | 95,000 |
| Average Speed (km/h) | 15 | 20 |
| NOx Levels (ppm) | 2.5 | 2.0 |
Note: The data provided in the table is illustrative and may not reflect precise figures from Madrid’s congestion pricing scheme. Real data would require referencing official reports from the Madrid city government.
Reversal of Pollution Trends: Madrid Congestion Pricing Emissions Reversal Pollution
Madrid’s congestion pricing initiative, while a significant step, requires complementary strategies to truly reverse pollution trends. Simply reducing car traffic needs to be coupled with incentivizing sustainable alternatives and improving public transportation to ensure a holistic approach. This multifaceted strategy is crucial for long-term environmental improvement and enhanced quality of life.
Strategies for Reversing Pollution Trends
Madrid’s approach to reversing pollution trends necessitates a combination of policies and infrastructure improvements. These include expanding and upgrading public transport systems, promoting electric and hybrid vehicles, and implementing stricter emission standards for all vehicles. Dedicated bike lanes and pedestrian-friendly zones are also key to encouraging alternative modes of transportation, reducing reliance on private cars.
Alternative Transportation Options
Madrid actively promotes alternative transportation options to mitigate the environmental impact of car traffic. Electric bike rentals are becoming increasingly common, providing an eco-friendly way to navigate the city. Additionally, the city is actively developing a robust network of electric vehicle charging stations, which is a crucial step for promoting the use of EVs.
Incentives for Sustainable Transportation
Incentivizing the adoption of sustainable transportation is crucial for achieving significant results. Financial incentives such as subsidies for electric vehicle purchases and discounts for public transportation fares can encourage environmentally conscious choices. Furthermore, preferential parking zones for electric vehicles and cycle paths can encourage the shift away from private cars.
Public Transportation Routes and Schedules
| Route Number | Start Point | End Point | Frequency (approx.) | Operating Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Atocha Station | Barajas Airport | Every 15 minutes | 6:00 AM – 11:00 PM |
| 22 | Plaza Mayor | Retiro Park | Every 20 minutes | 7:00 AM – 10:00 PM |
| 34 | Gran Vía | Universidad Autónoma | Every 30 minutes | 8:00 AM – 9:00 PM |
Note: Schedules and frequencies are approximate and subject to change. Consult the official Madrid Transport website for the most up-to-date information.
Comparison of Transport Options and Emission Levels
| Transport Mode | Approximate Emission Level (per passenger-kilometer) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Car (petrol) | High | Significant emissions of harmful pollutants |
| Car (electric) | Low | Negligible emissions during operation |
| Public Transport (metro) | Very Low | Efficient and low-emission transportation |
| Bicycle | Zero | Zero emissions, promotes physical activity |
Note: Emission levels are approximate and can vary based on factors such as traffic conditions and vehicle efficiency.
Policy Evaluation and Future Considerations

Madrid’s congestion pricing initiative has demonstrated a notable impact on traffic flow and emissions. However, evaluating its success requires a nuanced perspective, considering both the positive outcomes and potential areas for improvement. The long-term effects of the policy on urban development and transportation choices need careful consideration.
Comprehensive Evaluation of the Congestion Pricing Policy
The effectiveness of Madrid’s congestion pricing scheme hinges on its ability to reduce traffic congestion and associated emissions. Quantitative data, such as traffic volume reduction and pollutant emission levels, are crucial for assessing the policy’s impact. Analysis of pre- and post-implementation data, along with control groups, is essential for determining the specific effects of the policy. Factors like changes in public transportation usage, modal shift from private vehicles to other modes, and the overall economic impact on the city must be thoroughly examined.
Effectiveness in Achieving Goals
The policy’s success in reducing traffic congestion and emissions is evident in the available data. A significant decrease in traffic volume and measurable reductions in pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, provide strong evidence of the policy’s effectiveness. However, the impact on specific segments of the population, such as low-income residents, should also be considered. A thorough analysis should also consider the impact on businesses and their transportation needs.
Potential Challenges and Limitations, Madrid congestion pricing emissions reversal pollution
Congestion pricing policies, while effective, often face resistance from various stakeholders. Concerns about the financial burden on drivers, the potential for displacement of traffic to surrounding areas, and the impact on businesses are valid points of concern. Additionally, enforcement mechanisms and the effectiveness of monitoring systems are critical to the success of the policy. Unforeseen circumstances or technological limitations can impact the policy’s implementation and evaluation.
Comparison with Other Similar Initiatives Globally
Comparing Madrid’s congestion pricing policy with similar initiatives worldwide reveals valuable insights. Examples like London’s congestion charge provide a framework for understanding the policy’s potential successes and pitfalls. Examining the design, implementation, and evaluation methodologies of these initiatives provides valuable context for Madrid’s own policy. Differences in urban demographics, infrastructure, and economic conditions influence the effectiveness of similar policies.
Future Considerations and Potential Adjustments
Future adjustments to the policy could address potential limitations. A review of pricing structures, considering peak hours and different vehicle types, could optimize the policy’s effectiveness. Investing in public transportation infrastructure and promoting alternative transportation options can help maximize the positive impacts of the policy. Monitoring the policy’s impact on different demographics, and providing support to those most affected, is critical.
Madrid’s congestion pricing scheme is aiming to drastically reduce emissions and pollution. It’s all about trying to improve air quality in the city. But imagine a future where robots could help design and implement these kinds of solutions, even to the point of drawing perfect lines for traffic management! That’s something a new Kickstarter project, drawing robot line us kickstarter , is exploring.
Ultimately, these innovative solutions are crucial for tackling the city’s pollution problems.
Pros and Cons of the Policy
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Reduced traffic congestion | Potential for financial burden on drivers |
| Lowered emissions | Potential for displacement of traffic to surrounding areas |
| Increased revenue for city services | Potential impact on businesses |
| Potential for modal shift to public transport | Challenges in enforcement and monitoring |
| Improved air quality | Impact on specific demographics (e.g., low-income residents) |
| Potential for economic stimulation | Need for ongoing evaluation and adjustments |
Visualizing the Problem and Solutions
Madrid’s congestion pricing initiative, coupled with efforts to improve air quality, has brought about noticeable changes. Visual representations can effectively illustrate the impact of these policies and showcase the benefits of alternative transportation. This section details visual representations of traffic flow, air quality, alternative transportation, and emission reductions, along with information on the data sources used for these visualizations.
Traffic Flow Before and After Congestion Pricing
Madrid’s traffic patterns before and after the implementation of congestion pricing can be visualized using heat maps. A heat map displaying traffic density before the policy would likely show concentrated areas of high traffic volume, especially in central districts. Color intensity could represent the volume, with darker colors indicating higher congestion. A subsequent heat map after implementation would show a significant reduction in congestion in the central zone, potentially with a more even distribution of traffic flow across alternative routes.
This visual representation would highlight the impact of the pricing mechanism on traffic management.
Air Quality Changes in Madrid
Visualizing air quality changes requires an interactive map showing the concentration of pollutants like nitrogen dioxide (NO2) or particulate matter (PM2.5). Before the congestion pricing initiative, the map would likely exhibit elevated levels of pollutants, particularly in areas with high traffic density. A similar map depicting air quality after the policy implementation could show a marked decrease in pollutant concentrations in central areas.
Madrid’s congestion pricing is aiming to tackle emissions and pollution, a crucial step for cleaner air. This initiative, while seemingly unrelated, might actually find some interesting parallels in the tech world. Palo Alto Networks recently completed the acquisition of Dig Security, a move that suggests a sophisticated approach to security challenges. Ultimately, both initiatives highlight a need for innovative solutions to complex problems, whether in city planning or cybersecurity.
Addressing Madrid’s pollution issues requires similar forward-thinking approaches.
The map should display clear before-and-after comparisons to clearly demonstrate the air quality improvements. These maps are crucial for understanding the correlation between traffic and pollution levels.
Alternative Transportation Options in Madrid
A visual representation of alternative transportation options can showcase the city’s public transportation network, bike lanes, and pedestrian walkways. The map should highlight the routes and accessibility of these alternatives. Color-coding could represent different modes of transportation, with varying shades indicating usage levels or accessibility. The map could also incorporate information on charging stations for electric vehicles and cycling infrastructure, further promoting these sustainable options.
This visualization will promote awareness of the available options and facilitate a shift towards greener transportation.
Benefits of a Reduction in Emissions
A visual representation of emission reductions could utilize a stacked bar chart or a line graph illustrating the decrease in specific pollutants over time. The chart should compare emissions levels before and after the implementation of congestion pricing. Different colors could represent different pollutant types, allowing for a clear understanding of the reduction in each. Data from emission monitoring stations or air quality databases should be incorporated.
This representation could also show the positive impact on public health.
Pollution Maps and Data Sources
Pollution maps, crucial for visualizing air quality changes, are based on data collected from various sources. These data sources could include:
- Air quality monitoring stations: These stations continuously measure pollutant concentrations at fixed locations within the city.
- Satellite imagery: Satellite data can provide a broader view of air quality across the city, identifying pollution plumes and hotspots.
- Mobile monitoring units: These vehicles collect data on pollutants in real-time, allowing for a more dynamic understanding of air quality variations.
- Governmental agencies: Official reports and databases from the Madrid government provide comprehensive air quality data and analysis.
Using a combination of these data sources ensures a more comprehensive and accurate representation of pollution levels. This information is vital for evaluating the success of the congestion pricing policy and future initiatives.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Madrid’s congestion pricing initiative has faced a mixed public response, highlighting the complexities of implementing such policies. Public perception is crucial for the long-term success of any such scheme, as widespread opposition can lead to political challenges and undermine the intended environmental and economic benefits. Understanding the factors driving this perception is essential for policymakers to adapt their strategies and build support.
Public Opinion on Congestion Pricing
Public opinion polls consistently reveal a complex and nuanced view of congestion pricing in Madrid. While some segments of the population recognize the environmental benefits and the potential for improved traffic flow, others express concerns about the financial burden and the potential for negative impacts on their daily routines. This suggests a need for targeted communication strategies to address specific concerns.
Detailed analysis of these surveys can provide insights into the specific demographics and socio-economic factors that correlate with support or opposition.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Effective public awareness campaigns are vital to bridging the gap between policy objectives and public understanding. These campaigns should clearly articulate the benefits of congestion pricing, highlighting improvements in air quality, reduced traffic congestion, and the economic benefits that can arise. For instance, campaigns could showcase before-and-after scenarios of traffic conditions or air quality data to illustrate the tangible impacts.
Visual aids, infographics, and easily accessible online resources can effectively communicate complex information. Additionally, interactive workshops and community forums could be organized to encourage two-way communication and foster discussion.
Strategies to Increase Public Acceptance
Several strategies can enhance public acceptance of congestion pricing. Transparency in the policy’s implementation, including clear communication of how revenue generated will be used, can build public trust. Phased implementation, allowing for adjustments and feedback based on real-time data, can also mitigate potential negative impacts. Offering financial incentives, such as discounts for those who opt for public transportation or other sustainable mobility solutions, can further encourage adoption.
Public engagement in the design and implementation phases can empower residents and make them feel heard.
Factors Influencing Public Acceptance
Several factors influence public acceptance or rejection of congestion pricing. Economic factors, such as the perceived cost burden on commuters, play a significant role. Socio-economic disparities in access to alternative transportation options can also contribute to resistance. Perceptions of fairness and equity in the policy’s application are essential for building widespread support. Concerns about potential negative impacts on local businesses and industries need careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
A well-designed public relations campaign, targeted at specific segments of the population with tailored messaging, can effectively address these factors and foster greater public acceptance.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, Madrid’s congestion pricing initiative, while facing challenges, has demonstrated the potential for reducing pollution and improving air quality. The policy’s effectiveness and future considerations, along with alternative transportation solutions, are crucial to achieving sustainable urban development. Public perception and acceptance are key factors for the long-term success of such policies, and a thorough evaluation of both successes and shortcomings will be essential for replication elsewhere.