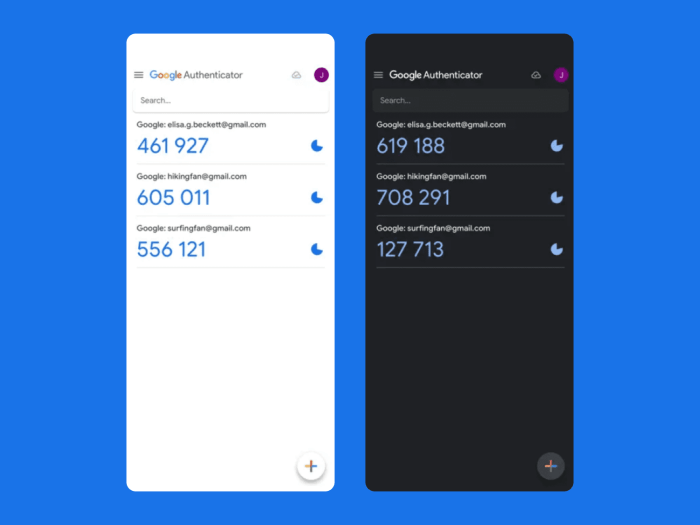
Google authenticator app update finally lets you transfer two factor codes between devices – Google Authenticator app update finally lets you transfer two-factor codes between devices, offering a significant boost to digital security and user convenience. This new feature simplifies the process of managing your two-factor authentication (2FA) across multiple devices, making it easier to switch phones or use different computers without losing access to your accounts. The update streamlines the whole process, reducing the potential for security lapses.
It’s a welcome enhancement for users who frequently switch between devices or want to secure their accounts in a more adaptable way.
The update simplifies the process of transferring codes between devices, ensuring seamless access to protected accounts. This improved functionality addresses a common pain point for users who frequently switch devices. With enhanced security protocols and a user-friendly interface, the updated Google Authenticator app offers a compelling solution for managing 2FA codes across multiple platforms.
Introduction to Google Authenticator App Update
The Google Authenticator app has received a significant update, introducing a game-changing feature: the ability to seamlessly transfer two-factor authentication (2FA) codes between devices. This update addresses a common pain point for users managing multiple devices and enhances overall digital security. This improved functionality simplifies the process of safeguarding accounts and maintaining access across various platforms.This update is crucial for users who frequently switch between personal and work devices, or who have multiple devices for different purposes.
The ability to quickly and securely transfer codes eliminates the need to manually reconfigure 2FA on each new device, which significantly improves user experience and reduces the risk of security breaches.
Transferring Two-Factor Codes Between Devices
The core enhancement in this update revolves around the streamlined transfer of 2FA codes. Users can now easily migrate their authentication codes from one device to another, maintaining access without compromising security. This functionality is particularly valuable for individuals who own multiple devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, and want to ensure consistent access to their accounts.
Benefits of the Updated Functionality
This new feature offers several key benefits for users:
- Simplified Account Access: Users can quickly switch between devices without needing to reconfigure 2FA settings, streamlining the login process and enhancing user experience.
- Enhanced Security: The seamless transfer of codes reduces the risk of losing access to accounts if a device is lost or damaged. This ensures users can still access their accounts from another device.
- Increased Convenience: Users no longer need to worry about manually re-entering codes or setting up new accounts on different devices, thereby making account management more convenient.
Comparison of Previous and Updated Functionality
The following table highlights the improvements introduced by the update:
| Feature | Previous Functionality | Updated Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Two-Factor Code Transfer | Not possible; required manual reconfiguration on each device. | Codes can be transferred seamlessly between devices. |
| Device Switching | Involved re-entering codes and configuring 2FA on each new device. | Effortless switching between devices without re-entering codes. |
| Security | Potential security risks associated with manual reconfiguration on new devices. | Improved security due to streamlined transfer process and elimination of manual entries. |
| User Experience | Inconvenient and time-consuming process of configuring 2FA on each new device. | Improved user experience by eliminating the need for repetitive configurations. |
Technical Aspects of Code Transfer

The Google Authenticator app update, allowing the transfer of two-factor authentication codes between devices, introduces a significant improvement in user experience and security. This feature streamlines the process of device changes, minimizing the disruption and inconvenience often associated with account recovery and setup. Understanding the technical mechanisms behind this transfer is crucial for appreciating the enhanced security protocols implemented.The core of the code transfer mechanism lies in securely transferring the cryptographic seed, or the initial data used to generate the time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs).
This seed, unique to each account, is encrypted and transmitted between devices, ensuring only authorized recipients can access it. The transfer process doesn’t involve transmitting the actual TOTPs themselves, thus preventing potential interception and misuse of active codes.
Security Protocols Employed
The transfer process employs robust encryption protocols to safeguard the cryptographic seed. Advanced cryptographic algorithms, such as AES-256, are used to encrypt the seed before transmission. Furthermore, the transfer is often authenticated using multi-factor authentication to verify the identity of the recipient device. This dual-layered approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access during the transfer.
Potential Vulnerabilities and Risks
While the transfer process is generally secure, potential vulnerabilities still exist. A major risk is compromised device access during the transfer. If a malicious actor gains control of the source device or the network during the transfer, they could potentially intercept the seed. This underscores the importance of maintaining secure network connections and protecting devices from unauthorized access.
Another risk is the possibility of flaws in the transfer protocol itself. A vulnerability in the algorithm or implementation could allow for unauthorized access or manipulation of the seed. Regular updates and security audits are crucial to mitigate such potential risks.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Transferring Codes
The exact steps for transferring codes between devices vary slightly depending on the specific implementation in the Google Authenticator app. However, the general procedure usually involves:
- Initiating the transfer on the source device. This usually involves selecting the account and confirming the action to initiate the transfer.
- Receiving the transfer request on the destination device. This will require a verification code or other security prompt to confirm the authenticity of the request.
- Confirming the transfer on the destination device. The recipient must verify the authenticity of the transfer on the receiving device.
- Successfully completing the transfer. Upon successful completion, the codes will be available on the destination device, ready for use.
It’s crucial to follow the on-screen instructions meticulously during the transfer process, and to ensure a secure network connection to avoid any security risks.
User Experience and Implementation
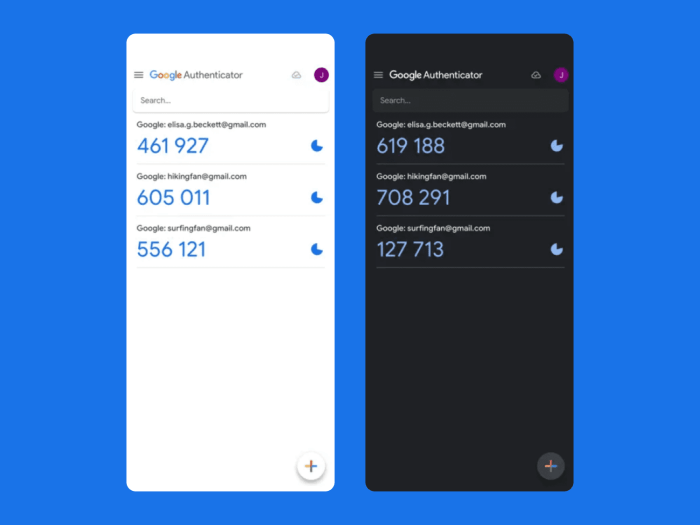
The updated Google Authenticator app introduces a significant improvement with the ability to transfer two-factor codes between devices. This feature enhances user convenience and security, enabling seamless transitions between phones, tablets, or other compatible devices. The new functionality streamlines the process of recovering access to accounts, even if a device is lost or damaged.The streamlined transfer process simplifies account recovery and improves the overall user experience.
So, the Google Authenticator app update finally lets you transfer two-factor codes between devices, which is awesome! This is a huge time-saver, especially if you’re juggling multiple phones or need to quickly switch between them. Speaking of switching, did you catch the news about Uncut Gems streaming on Netflix in the US? It’s a fantastic movie featuring Adam Sandler, the Safdie brothers, and even a cameo by Celtics legend Kevin Garnett, if you’re a fan of that kind of thing! uncut gems streaming netflix united states adam sandler safdie brothers kevin garnett celtics This new Authenticator feature is definitely a game-changer for anyone who values security and seamless access across their devices.
It eliminates the need for manual re-enrollment in security systems, saving users valuable time and effort. This robust functionality addresses a common pain point for users, making the transition to a new device smoother and more efficient.
User Interface Changes
The updated Google Authenticator app introduces intuitive changes to its user interface for code transfer. The “transfer” option is prominently displayed within the app’s settings menu, accessible with a few taps. This clear placement simplifies navigation for users, reducing the potential for confusion. Visual cues, such as a progress bar during the transfer, further enhance the user experience by providing clear feedback on the status of the transfer process.
User Guide for Code Transfer
To transfer two-factor codes, users first need to open the Google Authenticator app on their current device. Navigate to the settings menu, locate the “transfer” option, and select it. Follow the on-screen instructions to initiate the transfer process. This may involve scanning a QR code or entering a unique code on the new device. The new device will then automatically synchronize the codes.
The process is designed to be straightforward and user-friendly.
Ease of Use and Potential Challenges
The new code transfer feature is designed for ease of use. The intuitive interface and step-by-step instructions minimize potential challenges. However, users might encounter issues if they have complex network configurations or insufficient internet connectivity during the transfer process. Careful attention to network stability and device compatibility is essential for a smooth transfer. Troubleshooting steps, including checking network connectivity and ensuring the devices are updated to the latest app version, should be readily available to users.
Supported Device Types
The updated Google Authenticator app supports a wide range of devices for code transfer, encompassing smartphones, tablets, and potentially even computers running compatible operating systems. The flexibility of this feature allows users to seamlessly transition between devices without worrying about compatibility limitations.
| Device Type | Operating System Compatibility | Specific Models (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Android, iOS | Google Pixel, iPhone 13 |
| Tablets | Android, iOS | iPad Pro, Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 |
| Computers | Windows, macOS (with compatible software) | Windows 11, macOS Ventura |
The table above Artikels the different device types currently supported for seamless two-factor code transfer within the updated Google Authenticator app.
Security Implications and Best Practices
The Google Authenticator app’s new code transfer feature, while convenient, introduces potential security risks. Understanding these risks and implementing best practices is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your two-factor authentication (2FA). Users must be vigilant in protecting their accounts and adhering to the guidelines Artikeld here.
Potential Security Threats
The ability to transfer codes between devices opens the door to various security threats if not handled carefully. A compromised device or unauthorized access to a device where the codes are stored could lead to account takeover. Malicious actors could potentially gain access to the codes, circumventing the intended security measures. Moreover, if the transfer process isn’t secure, the transferred codes could be intercepted, further jeopardizing account safety.
Careless handling of devices where codes are stored can also compromise security.
Best Practices for Users
Implementing robust security measures is essential to mitigate risks associated with code transfer. Strong passwords, along with enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all accounts, significantly reduce the impact of compromised devices.
- Secure Device Management: Regularly update your devices’ operating systems and security software. Use strong passwords for all devices and enable device encryption whenever possible. Be cautious about public Wi-Fi networks and avoid connecting to them when handling sensitive information, including your 2FA codes.
- Account Security: Monitor your accounts for any unusual activity. Implement strong password policies and use a password manager to create and store complex passwords. Enable MFA on all accounts to add an extra layer of protection.
- Code Transfer Procedure: Carefully review the code transfer process within the Google Authenticator app. Verify the destination device’s authenticity before initiating the transfer. Avoid transferring codes if you suspect the device might be compromised.
Mitigating Potential Security Risks, Google authenticator app update finally lets you transfer two factor codes between devices
To minimize the impact of security breaches related to code transfer, proactive measures are vital. Implementing a layered approach to security can help significantly. This includes strong passwords, regularly updated software, and rigorous security protocols.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your data, including your 2FA codes. This ensures you have a copy in case of device loss or theft. Consider using cloud storage for backups.
- Secure Storage: Store your backup copies of codes securely, ideally in a password-protected vault. Avoid storing them in easily accessible locations. Avoid sharing backup information with others.
- Two-Factor Authentication Management: Regularly review your 2FA setup and ensure your recovery options are up-to-date. Be prepared to immediately disable or change 2FA if you suspect a breach.
Security Measures for Safeguarding Two-Factor Authentication Codes
A robust security posture requires a multi-layered approach. The table below Artikels crucial security measures for safeguarding your 2FA codes.
| Security Measure | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | Use complex passwords, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. | Essential for protecting your devices and accounts. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Enable MFA on all accounts to add an extra layer of security. | Adds significant protection against unauthorized access. |
| Device Security | Keep your devices updated with the latest security patches and software. | Minimizes vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit. |
| Secure Code Transfer | Verify the destination device before transferring codes. | Reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your codes. |
| Regular Monitoring | Monitor your accounts for any unusual activity. | Early detection of potential breaches. |
Comparison with Other Authenticator Apps
Google Authenticator’s new code transfer feature is a welcome addition, but how does it stack up against similar offerings from other authenticator apps? This section dives into a comparative analysis, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of Google Authenticator’s approach alongside competitors. We’ll examine the various methods for transferring codes and evaluate their efficacy and security implications.The proliferation of two-factor authentication (2FA) has spurred the development of numerous authenticator apps.
While Google Authenticator is a market leader, competitors have developed their own code transfer mechanisms. A direct comparison helps users understand the nuances of each system and choose the best solution for their needs.
Code Transfer Processes in Different Authenticator Apps
Understanding how different authenticator apps handle code transfer is crucial for informed decision-making. The processes vary significantly, affecting factors like security, ease of use, and compatibility with different platforms.
- Microsoft Authenticator: Microsoft Authenticator offers a straightforward transfer process, often leveraging cloud syncing. This makes it convenient for users who already use Microsoft’s ecosystem. However, the security reliance on cloud storage may be a concern for users prioritizing local control. It often seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft services, making it a valuable choice for those already deeply embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Authy: Authy’s code transfer process is generally efficient and reliable, but may vary depending on the specific service being transferred. Their system is known for its versatility across different platforms, including mobile and desktop applications. This adaptability is a significant advantage, allowing users to migrate codes between various devices without major complications.
- FreeOTP: FreeOTP is known for its robust security features. Code transfer is usually accomplished through manual copying and pasting, which might seem cumbersome compared to more automated systems. This approach, while not as user-friendly, prioritizes security by eliminating reliance on cloud storage or intermediary services.
Comparative Analysis Table
The following table provides a concise overview of the code transfer capabilities across various authenticator apps.
| Authenticator App | Transfer Method | Security | Ease of Use | Platform Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Authenticator | Cloud-based sync (new feature) | High (if secure cloud implementation) | High (generally intuitive) | Multi-platform |
| Microsoft Authenticator | Cloud-based sync | Moderate (dependent on cloud security) | High | Multi-platform (Microsoft ecosystem focused) |
| Authy | Various methods (app-specific) | High | Moderate to High | Multi-platform |
| FreeOTP | Manual copy-paste | Very High (no cloud dependency) | Low | Multi-platform |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Google Authenticator’s Approach
Google Authenticator’s new cloud-based code transfer method presents several advantages and disadvantages.
- Advantages: Streamlined process for transferring codes between devices. Improved user experience by eliminating manual steps. Enhanced compatibility with various platforms.
- Disadvantages: Potential security risks associated with cloud storage. Reliance on a third-party service (Google) for code transfer.
Future Implications and Potential Developments
The Google Authenticator update’s code transfer capability introduces exciting possibilities for enhanced mobile security. This feature opens doors to new strategies for safeguarding accounts and potentially streamlining the user experience, but it also presents challenges and considerations for the future. Its impact on overall security practices deserves careful consideration.
Potential Impact on Mobile Security Practices
The code transfer feature, when implemented correctly, can significantly enhance mobile security by enabling users to seamlessly migrate their authentication methods to new devices. This minimizes the risk of compromised accounts by ensuring users can quickly re-establish access should their primary device be lost or compromised. A well-implemented transfer process will mitigate the danger of stolen or lost devices.
So, the Google Authenticator app update finally lets you transfer those two-factor codes between devices, which is a huge plus. It’s a lifesaver, especially when you’re switching phones. However, if you’re currently battling connectivity issues with your Samsung Galaxy Android Auto on One UI 6 and Android 14, you might find yourself wishing you could transfer something else, like your car’s connection, to another device.
Check out this helpful article on samsung galaxy android auto connectivity problems one ui 6 android 14 for potential solutions. Regardless, this new Authenticator feature is a fantastic addition for securely managing your accounts across devices.
However, it’s crucial to recognize that user education and awareness are paramount to realizing the full potential of this security enhancement. Users need to be aware of potential risks and understand how to leverage this feature safely.
Future Developments and Enhancements to Code Transfer
The code transfer feature has the potential to be further enhanced to increase its utility. Future developments could include options for automated transfer upon device change, or the ability to restrict transfer to trusted devices. Implementing a feature that allows for multiple device backups could also bolster security. For example, a user could back up their codes to multiple trusted devices, ensuring they have access to authentication even if one device is lost or compromised.
Advanced security protocols could be incorporated, such as multi-factor authentication for initiating the transfer process.
Impact on the Overall Security Posture of Users
The code transfer feature, if used responsibly, can contribute to a stronger overall security posture for users. By enabling seamless account access on new devices, it can effectively mitigate the risk of account takeover in the event of a lost or compromised primary device. Furthermore, this feature can potentially reduce user friction in migrating to new devices, enhancing user satisfaction and adherence to security best practices.
This enhanced convenience can indirectly bolster security by encouraging users to maintain the use of two-factor authentication.
Anticipated Long-Term Effects on Two-Factor Authentication
The code transfer feature is poised to positively influence the future of two-factor authentication (2FA). Its potential for enhanced security, particularly in the context of device loss or compromise, could drive increased adoption of 2FA. This update, by streamlining the process of managing 2FA across devices, could contribute to greater security awareness and implementation across a wider user base.
The increased ease of use may also motivate users to employ 2FA across a broader range of accounts.
Finally, the Google Authenticator app update lets you transfer two-factor codes between devices! This is a huge security boost, especially if you’re constantly switching between phones or tablets. Speaking of transitions, have you heard about the upcoming Donkey Kong Bananza Nintendo Switch 2? donkey kong bananza nintendo switch 2 is shaping up to be a fun new game, but I’m just as excited about the improved security offered by the Authenticator app update.
It’s a small thing, but it makes a big difference in keeping your accounts safe.
Illustrative Examples of Code Transfer
The Google Authenticator app update’s ability to transfer two-factor codes between devices represents a significant advancement in user convenience and security. This feature streamlines the process of switching between devices, whether it’s a new phone, a work laptop, or a personal tablet. This section provides detailed examples of successful and problematic code transfers, helping users understand the process and potential pitfalls.This feature allows users to seamlessly transition their two-factor authentication (2FA) security to new devices.
This is particularly useful for users who frequently switch between devices or need to access accounts on different platforms.
Successful Code Transfer Scenarios
The successful transfer of two-factor codes depends on several factors. A user’s account must be configured to support code transfer. Additionally, the source and destination devices must meet specific technical requirements. The transfer process is initiated on the source device and completed on the destination device.
- Scenario 1: Switching Phones
– A user needs to replace their old phone. They initiate the transfer process on their old phone, ensuring all necessary security protocols are met, such as entering a PIN. The process guides them through the steps, including generating a QR code. They scan this QR code on their new phone using the Google Authenticator app, and the codes are successfully transferred.The user can now use their 2FA codes on the new phone for all linked accounts.
- Scenario 2: Accessing Work Account on a Laptop
-A user frequently accesses their work account on their personal phone. They now need to use their work laptop for accessing this account. They initiate the transfer on their phone, following the on-screen instructions to generate a QR code. The user then scans the QR code on their laptop’s Google Authenticator app. This transfers the necessary codes and configurations for their work account.The user can now access their work account without issues.
- Scenario 3: Using a New Tablet
– A user purchases a new tablet and wants to use it for accessing personal accounts. They initiate the code transfer on their primary phone. The transfer process guides them to scan a QR code generated on the phone and displayed on the tablet. Following the prompts on the tablet, the user successfully completes the transfer and now has access to their 2FA codes on the new tablet.
Unsuccessful Code Transfer Scenarios and Troubleshooting
The transfer process might encounter issues due to various reasons, including network connectivity problems, device compatibility issues, or security measures on the user’s account.
- Network Connectivity Issues
-If the user encounters network problems during the transfer process, the transfer might fail. Users should ensure a stable internet connection on both the source and destination devices. They should also try again after a few minutes to resolve any temporary connectivity issues. - Incompatible Devices
– In certain cases, the destination device might not be compatible with the transfer process. If this happens, users should verify the device meets the minimum requirements for the Google Authenticator app. They can check the app’s support documentation or contact Google support for assistance. - Account Security Measures
-Some accounts may have additional security measures that prevent the transfer process. Users should check their account’s security settings for any restrictions or limitations. If any restrictions are present, they might need to contact their account provider for guidance.
Resolving Transfer Issues
Troubleshooting code transfer issues requires a systematic approach. Users should first check their network connection. If the network is stable, they should verify the compatibility of their devices with the Google Authenticator app. If the problem persists, they should check their account’s security settings. Finally, they should contact Google support for further assistance.
Final Conclusion: Google Authenticator App Update Finally Lets You Transfer Two Factor Codes Between Devices
In conclusion, the Google Authenticator app update represents a significant leap forward in mobile security, providing a streamlined and secure method for transferring two-factor authentication codes between devices. The improved user experience and enhanced security protocols are valuable additions that improve the overall security posture of users leveraging this feature. The update offers a practical and reliable solution for managing 2FA codes in today’s digital landscape.