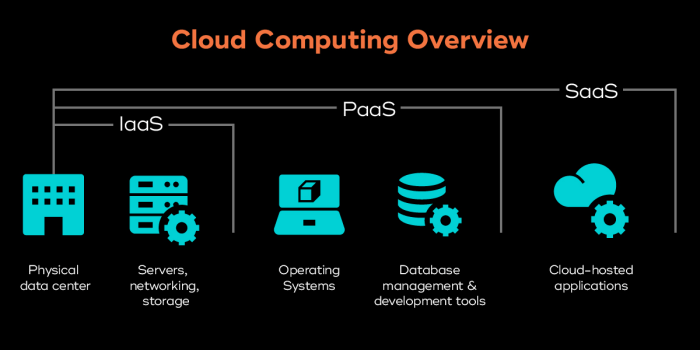
What is SaaS security definition and explanation? SaaS, or Software as a Service, is rapidly changing how businesses operate. Understanding its unique security landscape is crucial for both providers and users. This deep dive explores the multifaceted nature of SaaS security, from fundamental principles to real-world scenarios and best practices.
This comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of securing SaaS applications, outlining common threats, robust security measures, and compliance considerations. It provides a detailed comparison of traditional on-premises security with the nuances of cloud-based protection, highlighting the distinct challenges and solutions within this evolving technological space.
Defining SaaS Security
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) security is a multifaceted approach to protecting data and applications hosted in the cloud. It encompasses a range of measures to safeguard sensitive information and ensure the integrity and availability of cloud-based services. This differs significantly from traditional on-premises security, which often relies on physical security and dedicated IT staff. SaaS security focuses on cloud-specific vulnerabilities and the shared responsibility model between the SaaS provider and the user.SaaS security’s core principles revolve around robust access controls, data encryption, and regular security audits.
These principles aim to mitigate risks associated with cloud environments, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and service disruptions. The shared responsibility model is a critical element of SaaS security. It Artikels the responsibilities of both the SaaS provider and the user, ensuring a proactive approach to maintaining security.
SaaS Security vs. Traditional On-premises Security
Traditional on-premises security typically involves physical security measures, like locked server rooms, and dedicated IT staff responsible for patching and monitoring systems. SaaS security, in contrast, leverages cloud-specific security controls, such as multi-factor authentication and data loss prevention tools. The shared responsibility model is a key differentiator, with the SaaS provider handling infrastructure security and the user managing data access and application-level security.
A significant difference lies in the inherent reliance on third-party providers in SaaS, demanding a focus on vendor risk management.
Security Considerations in Cloud-Based Applications
Several security considerations are specific to cloud-based applications. These include ensuring compliance with industry regulations, like HIPAA or PCI DSS, implementing robust access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, and continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is crucial for protecting sensitive information. The shared responsibility model necessitates a clear understanding of the provider’s and user’s roles and responsibilities to minimize risk.
The ever-evolving threat landscape demands continuous vigilance and adaptation in cloud security practices.
Different SaaS Security Models
Various security models exist for SaaS applications. These models vary based on the level of security features offered and the degree of control provided to users. Some models prioritize enhanced security with dedicated security teams, while others rely on the inherent security of the platform. The choice of model depends on the specific security requirements of the organization.
A robust security model should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization, factoring in sensitivity of data and regulatory requirements.
Key Elements of SaaS Security
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Control | Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, and granular access permissions to control who can access data and applications. |
| Data Encryption | Protecting sensitive data both in transit and at rest using robust encryption methods. This includes encrypting data stored in the cloud and encrypting data transmitted between the user and the cloud. |
| Regular Security Audits | Conducting periodic security assessments and vulnerability scans to identify and address potential security weaknesses. Regular reviews and patching of applications are critical for maintaining security. |
| Compliance with Regulations | Adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR, to ensure data protection and privacy. Understanding and adapting to the specific regulations is paramount. |
| Vulnerability Management | Proactively identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities in the SaaS application. Staying up-to-date on the latest security threats is essential for a comprehensive approach. |
Threats and Vulnerabilities in SaaS
SaaS applications, while offering convenience and scalability, introduce unique security challenges. Understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities inherent in these cloud-based services is crucial for organizations leveraging them. These risks extend beyond the traditional perimeter security concerns and demand a holistic approach to security management. Multi-tenancy, a core aspect of SaaS, presents specific challenges requiring careful consideration.The shared nature of SaaS environments, where multiple clients’ data resides on the same platform, presents a significant security concern.
This shared infrastructure can expose data to various threats, including malicious actors targeting vulnerabilities in the platform or inadvertently exploiting shared resources. Understanding these threats and vulnerabilities empowers organizations to implement robust security strategies to mitigate potential risks.
Common Security Threats Targeting SaaS Applications
SaaS applications face a diverse array of threats, including malicious actors attempting to exploit vulnerabilities in the platform itself or in the applications used by the users. Phishing attacks, social engineering tactics, and compromised credentials are frequent threats targeting SaaS users, often leading to data breaches. These attacks can exploit vulnerabilities in user authentication, authorization, and data access mechanisms.
So, SaaS security boils down to protecting software applications and data hosted in the cloud. This is crucial, especially now, with companies relying more heavily on cloud services. For example, T-Mobile is expanding LTE speeds for millions of Americans during the pandemic, a move that highlights the importance of reliable internet access. Ultimately, strong SaaS security measures ensure data safety and prevent unauthorized access, which is essential for maintaining a smooth operation and user trust.
Risks Associated with Data Breaches in SaaS Environments
Data breaches in SaaS environments have significant consequences for organizations. Compromised data can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and legal liabilities. The sensitive nature of data stored in SaaS applications, such as customer information, financial records, and intellectual property, makes data breaches especially damaging. Breaches can result in significant operational disruptions, impacting business processes and customer trust.
Vulnerabilities Inherent in Multi-Tenant SaaS Architectures
Multi-tenancy, a core feature of SaaS, presents vulnerabilities that single-tenant systems typically do not face. Shared infrastructure, while increasing efficiency and cost-effectiveness, can inadvertently expose one tenant’s data to security risks from another tenant. Cross-contamination of data or code, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and exploitation of vulnerabilities in the shared platform are potential issues. Security isolation between tenants is a crucial concern in mitigating these vulnerabilities.
Impact of Insider Threats on SaaS Security
Insider threats, both malicious and unintentional, pose a significant risk to SaaS security. Malicious insiders, motivated by financial gain, revenge, or other factors, can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or disrupt services. Unintentional insiders, through negligence or lack of awareness, can also contribute to security breaches. Training and awareness programs are essential to mitigating the risk of insider threats.
Threat Vectors and Their Impact
| Threat Vector | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing Attacks | Deceptive emails or messages attempting to gain sensitive information like login credentials. | Unauthorized access to accounts, data breaches, and financial losses. |
| Malware Infections | Malicious software that compromises systems, often used to steal data or disrupt operations. | Data breaches, system disruptions, and financial losses. |
| SQL Injection Attacks | Exploiting vulnerabilities in database queries to gain unauthorized access to data. | Data breaches, data modification, and system compromise. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks | Injecting malicious scripts into websites to compromise user accounts and steal data. | Data breaches, account takeovers, and reputational damage. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks | Overwhelming a system with traffic to prevent legitimate users from accessing services. | Service disruptions, loss of revenue, and damage to reputation. |
Security Measures and Controls
SaaS security is a multifaceted approach that extends beyond just the software itself. It encompasses a range of measures to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of the service. Effective SaaS security relies on a layered defense strategy, encompassing technical controls, user awareness training, and robust governance frameworks. These strategies must adapt to the evolving threat landscape and the specific needs of the organization using the SaaS application.
Essential Security Measures in SaaS Environments
Security measures in SaaS environments are designed to mitigate various threats and vulnerabilities. These measures include strong authentication mechanisms, secure data encryption, and regular security audits. The effectiveness of these measures depends on their implementation and the continuous monitoring of the security posture.
Access Controls and Authentication
Access controls are fundamental to SaaS security. They dictate who can access specific data and resources within the SaaS platform. Effective authentication mechanisms verify the identity of users attempting to access sensitive information. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access the data and functionality. Strong authentication methods are crucial for preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementing Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Robust password policies and the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) are vital for securing user accounts. A strong password policy mandates the use of complex passwords, employing a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. This approach makes passwords difficult to crack by automated tools. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification (e.g., a code sent to a mobile device) beyond just a password.
Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit
Data encryption is a critical security measure for protecting sensitive data both at rest (stored in the SaaS provider’s systems) and in transit (being transmitted between users and the SaaS application). Data encryption converts readable data into an unreadable format, making it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. Strong encryption algorithms are essential for protecting sensitive information from potential breaches.
The use of industry-standard encryption protocols, such as TLS/SSL, is recommended for securing data transmission.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the SaaS security posture. Security audits provide a comprehensive assessment of the security controls in place. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss. This proactive approach allows organizations to address potential security risks before they can be exploited.
This process ensures the SaaS application remains resilient to evolving threats.
Summary of Security Controls and Their Effectiveness
| Security Control | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Password Policies | Enforce complex password requirements | High – Reduces vulnerability to brute-force attacks |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple verification steps | High – Adds an extra layer of security |
| Data Encryption (at rest & in transit) | Transforms data into an unreadable format | High – Prevents unauthorized access during storage and transmission |
| Regular Security Audits | Comprehensive assessment of security controls | Medium – Identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses |
| Penetration Testing | Simulates real-world attacks | High – Reveals vulnerabilities that automated tools may miss |
Compliance and Regulations
SaaS providers operate in a complex regulatory landscape. Navigating these requirements is crucial for maintaining user trust and avoiding costly penalties. Compliance ensures data security, privacy, and adherence to industry standards, ultimately safeguarding both the provider and its clients. Understanding and adhering to relevant regulations is paramount for a successful SaaS business.
Compliance Requirements for SaaS Providers
SaaS providers face a multitude of compliance requirements, varying by region and industry. These regulations dictate how data is handled, stored, and secured. Compliance ensures data privacy and security, minimizing the risk of data breaches and legal action. Key areas of compliance include data protection, security, and financial reporting.
Industry Regulations Impacting SaaS Security
Numerous industry regulations impact SaaS security. These regulations address data privacy, security, and handling across different sectors. For example, GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and HIPAA in healthcare are prominent examples, each with specific requirements for data handling and security. These regulations often impose stringent requirements on how sensitive data is managed and protected. Organizations operating in regulated industries need to understand and implement controls that meet these standards.
Examples of Compliance Standards Relevant to SaaS
Several compliance standards directly apply to SaaS. ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for information security management systems, offering a framework for building robust security controls. SOC 2, a suite of standards, evaluates the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of data. These standards provide a structured approach to security implementation, ensuring data protection and privacy.
Other standards, like PCI DSS for credit card processing, may also apply based on the type of data processed.
Best Practices for Ensuring SaaS Solutions Meet Regulatory Demands
Best practices for compliance include implementing robust security measures, conducting regular security assessments, and establishing clear data handling policies. Regular audits and penetration testing help ensure the effectiveness of security controls. A detailed data handling policy, outlining data storage, access, and usage protocols, is vital for compliance. Proactive risk assessments and regular updates to security controls help in maintaining compliance.
Transparent communication with users about data handling practices is also a crucial aspect.
Implications of Non-Compliance for SaaS Providers and Users
Non-compliance can lead to significant consequences for SaaS providers and users. Penalties can range from hefty fines to reputational damage. User trust is eroded when a provider fails to meet regulatory requirements. In some cases, legal action or service disruptions may occur. Compliance violations can be costly in terms of financial penalties and reputational harm.
Table of Compliance Standards and Associated Requirements
| Compliance Standard | Associated Requirements |
|---|---|
| ISO 27001 | Implementing a documented information security management system (ISMS), establishing security policies, conducting risk assessments, and regularly reviewing and updating the ISMS. |
| SOC 2 | Demonstrating compliance with security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy controls. |
| GDPR | Ensuring data subject rights, obtaining explicit consent, implementing data minimization principles, and ensuring data security measures are in place. |
| CCPA | Providing consumers with clear information about data collection practices, enabling consumers to access, delete, and correct their data, and implementing procedures to comply with opt-out requests. |
Security Best Practices for SaaS Users
Securing your SaaS accounts is crucial in today’s digital landscape. A strong security posture minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, protecting sensitive information and maintaining business continuity. These best practices provide a comprehensive framework for users to implement robust security measures within their SaaS environments.Effective security strategies in SaaS extend beyond just technical controls. User awareness and proactive measures play a vital role in preventing security incidents.
This includes understanding the potential threats, following established security protocols, and reporting suspicious activities promptly.
So, SaaS security? It’s basically protecting software and data hosted online. This often involves strong access controls, encryption, and regular security audits. Speaking of security, did you know that the canary person detection feature is now available? canary person detection feature now available This innovative technology enhances overall security by automatically identifying and responding to unusual activities.
Ultimately, robust SaaS security is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining user trust.
Securing SaaS Accounts
Establishing strong passwords is paramount. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid easily guessable passwords like birthdates or names. Consider using a password manager to securely store and generate complex passwords for multiple accounts. Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible.
This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a code sent to your phone, to log in. Regularly review and update your security settings within the SaaS platform to ensure that they align with your current security needs.
Managing User Access, What is saas security definition and explanation
Properly managing user access is essential for maintaining control over sensitive data. Grant users only the access they need to perform their job functions, adhering to the principle of least privilege. Regularly review and revoke unnecessary access permissions to minimize the potential impact of compromised accounts. Implement a robust account lockout policy to prevent brute-force attacks. This policy should automatically lock accounts after a certain number of failed login attempts.
Keeping Software Updated
Keeping software updated is critical for patching vulnerabilities. SaaS providers regularly release updates that address security flaws and enhance overall platform stability. Ensure that your operating system, applications, and any related software are updated promptly to the latest versions. Enable automatic updates whenever possible to minimize manual effort and ensure you always have the latest security protections.
Proactive Security Awareness Training
Proactive security awareness training empowers users to recognize and avoid security threats. Training programs should cover topics like phishing attacks, social engineering tactics, and safe password practices. Regularly update and refresh training materials to keep pace with evolving threats and security best practices. Encourage employees to report any suspicious activity or phishing attempts immediately.
Handling Security Incidents in a SaaS Environment
Establishing clear procedures for handling security incidents is crucial. Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that Artikels steps to follow in case of a suspected breach or security incident. This plan should include procedures for containing the incident, investigating the cause, and implementing preventative measures. Document all incidents, including the date, time, affected systems, and actions taken.
This documentation serves as a valuable record for future analysis and improvement.
Summary of Security Best Practices for Users
| Best Practice | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | Use complex, unique passwords and enable MFA. |
| Access Management | Grant users only necessary access; regularly review and revoke permissions. |
| Software Updates | Keep software and applications up-to-date. |
| Security Awareness Training | Regular training on phishing, social engineering, and safe practices. |
| Incident Response Plan | Develop a documented plan for handling security incidents. |
Security Considerations for Specific SaaS Applications
SaaS applications, while offering convenience and scalability, introduce unique security challenges. Understanding the specific security implications for different types of SaaS applications, such as CRM and ERP, is crucial for organizations adopting these services. Choosing the right provider and implementing robust security measures are vital for protecting sensitive data and maintaining operational continuity.
Security Implications for CRM Software
CRM software, managing customer interactions and data, faces specific security threats. Unauthorized access to customer information, data breaches, and manipulation of customer records are significant risks. Data breaches in CRM systems can lead to reputational damage, financial losses, and regulatory penalties. Implementing strong access controls, encryption, and regular security audits is essential for safeguarding customer data. Furthermore, maintaining compliance with industry regulations like GDPR is paramount.
Security Implications for ERP Software
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, handling critical business processes and data, requires stringent security measures. Disruptions to core business operations, financial losses, and compliance violations are potential consequences of inadequate security. Compromised ERP systems can result in the theft of intellectual property, financial records, and sensitive employee information. Data integrity, availability, and confidentiality are paramount.
Security Features Offered by Different SaaS Providers
Different SaaS providers offer varying security features. Some providers prioritize robust access controls, while others excel in data encryption and compliance certifications. Comparing and contrasting the security features offered by different vendors is essential for selecting a provider that aligns with organizational needs. Thorough research and evaluation are critical.
Assessing the Security Posture of a SaaS Application Before Deployment
Before deploying a SaaS application, organizations must assess its security posture. This involves evaluating the provider’s security policies, procedures, and technical controls. Organizations should examine the provider’s security certifications, data encryption practices, and incident response plans. Security audits and penetration testing should be considered for evaluating the application’s vulnerability to potential threats.
Table Contrasting Security Features of Various SaaS Application Types
| Application Type | Access Controls | Data Encryption | Compliance Certifications | Incident Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRM | Role-based access, multi-factor authentication | End-to-end encryption, data at rest encryption | GDPR, CCPA | Dedicated incident response team, clear communication channels |
| ERP | Fine-grained access control, audit trails | Data encryption at rest and in transit, data masking | HIPAA, SOX | Business continuity plan, disaster recovery procedures |
| Collaboration Tools | User permissions, access restrictions | Data encryption, secure file sharing | ISO 27001 | Security awareness training, vulnerability management |
Illustrative Scenarios: What Is Saas Security Definition And Explanation
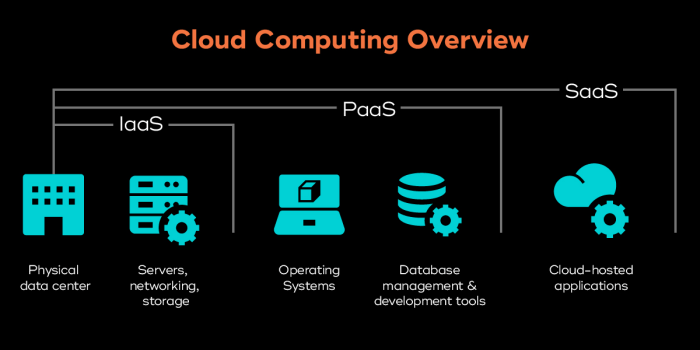
SaaS security is a multifaceted challenge, requiring a comprehensive understanding of potential threats and vulnerabilities. Real-world scenarios offer valuable insights into the practical application of security measures and the potential consequences of neglecting them. These examples highlight the importance of proactive security strategies and effective incident response protocols.
Successful SaaS Security Breach
A marketing firm utilizes a popular SaaS CRM for client management. A sophisticated phishing campaign targets the firm’s employees, successfully tricking several into revealing their login credentials. The attackers gain access to the CRM, modify client data, and extract sensitive financial information. The breach remains undetected for several weeks, allowing the attackers to manipulate client interactions and siphon off substantial funds.
This underscores the importance of multi-factor authentication and robust email filtering systems.
Impact of Compromised SaaS Account
A small business owner uses a cloud-based accounting software for their financial transactions. Their account is compromised due to a weak password and social engineering tactics. The attacker gains access to sensitive financial data, including customer information and transaction records. The compromised account allows the attacker to manipulate transactions, potentially leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage for the business.
This scenario emphasizes the need for strong passwords, regular account reviews, and robust security protocols within the SaaS application.
So, SaaS security? Basically, it’s about protecting software-as-a-service applications from threats. This is crucial, especially given recent high-profile cases like Harold Arlen, the composer, suing Apple, Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Pandora for music piracy. This case highlights the critical need for robust security measures in online platforms, a concept directly applicable to SaaS. Strong authentication, data encryption, and regular security audits are all part of a good SaaS security strategy.
Security Incident Response Protocol
A large e-commerce company uses a SaaS platform for customer support. A security breach is detected, where unauthorized access to customer data is identified. The company immediately activates its incident response protocol, which involves isolating the affected systems, containing the breach, and notifying affected customers. The company conducts a forensic investigation to determine the extent of the breach and the root cause.
This illustrates the critical need for pre-defined incident response plans and the importance of communication throughout the process.
Importance of User Training
A non-profit organization utilizes a SaaS platform for fundraising. A significant number of employees are unaware of the organization’s security policies and procedures regarding SaaS usage. This lack of awareness results in vulnerabilities, such as employees clicking on malicious links or sharing sensitive information inadvertently. Implementing regular security awareness training and phishing simulations helps educate employees about potential threats and appropriate security behaviors.
This illustrates the crucial role of employee education in preventing security breaches.
Breach Prevention Strategy
A healthcare provider uses a SaaS platform for patient records. They implement a layered security approach, including strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and intrusion detection systems. They also establish clear guidelines for data access and usage. This comprehensive strategy significantly reduces the risk of a security breach, protecting sensitive patient information. This demonstrates the effectiveness of a multi-faceted security strategy in mitigating potential risks.
Summary Table of Scenarios
| Scenario | Description | Impact | Key Lessons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Successful SaaS Breach | Sophisticated phishing attack compromises a CRM system. | Data modification, financial loss, reputational damage. | Strong authentication, email filtering. |
| Compromised Account | Weak password and social engineering compromise an accounting software account. | Financial loss, customer data exposure, reputational damage. | Strong passwords, regular account reviews. |
| Incident Response | E-commerce company detects a security breach and activates its protocol. | Limited data exposure, minimal financial loss, customer notification. | Pre-defined incident response plan, clear communication. |
| User Training | Non-profit employees lack awareness of security policies. | Increased vulnerability to phishing attacks and data breaches. | Regular security awareness training, phishing simulations. |
| Breach Prevention | Healthcare provider employs a layered security approach. | Significant reduction in breach risk, protection of sensitive data. | Multi-faceted security strategy, strong passwords, regular audits. |
Illustrative Security Examples
SaaS applications are increasingly critical for businesses, requiring robust security measures to protect sensitive data. This section provides illustrative examples of security features, controls, and protocols employed within SaaS environments. Understanding these examples helps appreciate the complexity and importance of SaaS security.
Robust Security Feature in a SaaS Application
A strong example of a robust security feature is multi-factor authentication (MFA). Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of verification beyond a username and password. This often involves requiring a code from a mobile device or a security token. By requiring multiple forms of identification, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
Strong Security Control in Action
A strong security control is a well-defined incident response plan. This plan Artikels procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from security breaches. A well-executed incident response plan can minimize damage and expedite recovery, which is crucial for maintaining business continuity. For example, a plan might involve isolating affected systems, notifying relevant parties, and implementing preventative measures to prevent future incidents.
Security Protocol Implementation in SaaS
Implementing secure communication protocols is paramount. Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a crucial protocol. It ensures that data transmitted between a user’s device and the SaaS application is encrypted. TLS protects data from eavesdropping and tampering, maintaining confidentiality and integrity. This is crucial for sensitive data like financial information.
Encryption Technologies in SaaS
Encryption technologies are essential for protecting data at rest and in transit. Data encryption, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), protects sensitive data stored within the SaaS application. This ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable without the correct decryption key. Furthermore, encryption can protect data during transmission, preventing interception and manipulation.
Well-Designed Access Control System
A well-designed access control system is fundamental to SaaS security. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common approach. RBAC assigns specific permissions to different roles within the organization. This granular control limits access to sensitive data only to those authorized users. For example, only specific employees with the appropriate roles may access financial records.
Comparison of Security Examples
| Security Feature/Control | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password, code from device). | Increased security, reduces risk of unauthorized access. | Requires user effort, potential for device issues. |
| Incident Response Plan | Procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from security breaches. | Minimizes damage, expedites recovery, maintains business continuity. | Requires planning, training, and regular testing. |
| Transport Layer Security (TLS) | Encrypts data transmitted between user and application. | Protects data confidentiality and integrity, prevents eavesdropping. | Requires implementation and configuration. |
| Data Encryption (AES) | Protects data at rest with strong encryption algorithms. | Maintains data confidentiality even in case of unauthorized access. | Requires key management, potential for key compromise. |
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Assigns specific permissions to different roles. | Limits access to authorized users, improves security posture. | Requires careful role definition and maintenance. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, securing SaaS applications requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing robust security measures, user awareness, and adherence to compliance regulations. This guide has explored the intricacies of SaaS security, offering practical insights into protecting data, mitigating threats, and ensuring a secure environment for both providers and users. By understanding the key elements discussed, businesses can confidently leverage the benefits of SaaS while safeguarding their valuable assets.