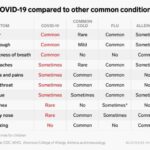
Coronavirus testing drive thru colorado connecticut washington – Coronavirus testing drive-thru Colorado, Connecticut, Washington offers a glimpse into how different states tackled the pandemic’s testing demands. This exploration delves into the history, logistics, and impact of these convenient testing sites, analyzing factors like accessibility, location strategies, and public health protocols. We’ll examine how these sites functioned across the three states, highlighting similarities and differences in their approaches.
The paper will present data-driven insights into the effectiveness and efficiency of these drive-thru programs. From comparing testing methods and wait times to analyzing community impact and future possibilities, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the drive-thru testing experience in these key states. Tables will visually represent the comparisons across the three states, highlighting factors like testing methods, wait times, and public health strategies.
Maps will showcase the distribution of testing sites geographically.
Overview of Drive-Thru Testing Sites
Drive-thru coronavirus testing sites have become a crucial component of pandemic response strategies across the United States. These convenient locations, especially prevalent during peak infection periods, significantly enhanced testing accessibility, allowing individuals to obtain results without leaving their vehicles. This approach proved particularly beneficial for those who might have been hesitant to visit traditional testing centers due to concerns about exposure or other logistical limitations.Drive-thru testing sites have evolved from initial, rudimentary setups to more sophisticated and streamlined operations.
Technological advancements and improved protocols have led to quicker turnaround times for results, ultimately contributing to a more effective public health response. This evolution highlights the adaptability of the healthcare system in responding to the evolving needs of the pandemic.
Testing Method Types
Various testing methods are employed at drive-thru testing sites. Nasal swabs, a common and widely accepted method, remain a prevalent choice. These swabs are collected by trained personnel and are processed for analysis in designated laboratories. Saliva-based tests are also gaining popularity due to their non-invasive nature and the ease of collection. These tests utilize the patient’s saliva sample for diagnostic purposes.
Both methods offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency and safety. The choice of testing method often depends on the specific needs and resources of the testing site.
Accessibility and Convenience
Drive-thru testing sites offer a significant advantage in terms of accessibility and convenience. They eliminate the need for individuals to enter a building, minimizing potential exposure to the virus and reducing the risk of transmission. The streamlined process, often involving minimal interaction with personnel, allows for quicker turnaround times. This has proven particularly valuable during high-volume testing periods, enabling healthcare systems to manage the surge in demand effectively.
Comparison of Drive-Thru Testing Sites in Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington
| State Name | Testing Method Types | Average Wait Times (Estimated) | General Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | Nasal swabs, saliva tests | 1-3 hours (dependent on volume) | Generally high accessibility, especially during peak periods, with multiple sites strategically located throughout the state. |
| Connecticut | Nasal swabs, saliva tests, rapid antigen tests | 1-2 hours (dependent on volume) | Relatively high accessibility, with testing sites often set up in easily accessible locations, including highways and large parking lots. |
| Washington | Nasal swabs, saliva tests, rapid antigen tests | 0.5-2 hours (dependent on volume and testing site) | Widely accessible throughout the state, with a substantial number of drive-thru sites established in various communities. Accessibility varied due to the dynamic nature of the pandemic. |
Note: Average wait times are estimations and may vary significantly based on factors such as testing site volume, staffing levels, and demand.
Factors Influencing Testing Site Locations: Coronavirus Testing Drive Thru Colorado Connecticut Washington

Drive-thru coronavirus testing sites, strategically placed across various regions, play a crucial role in managing the pandemic. Understanding the factors influencing their deployment allows us to analyze the effectiveness of these programs and their potential for future pandemic responses. These factors are multifaceted, encompassing considerations for population density, healthcare infrastructure, and testing demand.The placement of these testing sites is a complex balancing act.
Optimizing accessibility while considering the resources available to manage the volume of testing is critical. These factors contribute to the success of a testing program, ensuring its effectiveness and equitable reach within the community.
Factors Influencing Site Selection
Strategic site selection for drive-thru testing is essential for efficient and effective pandemic response. Several crucial factors guide the decision-making process, from the sheer volume of potential patients to the logistical demands of transporting specimens.
- Population Density: High-density areas often see higher infection rates and thus necessitate a greater number of testing sites to meet the demand. These locations, such as major metropolitan areas, require a higher concentration of testing facilities to effectively reach the population in need. Conversely, rural areas, with lower population density, may require fewer sites but strategically placed to maximize coverage.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: The presence and capacity of local hospitals and labs are key considerations. Testing sites are often positioned near existing healthcare facilities to ensure smooth sample processing and efficient turnaround times. A testing site near a hospital with a robust laboratory allows for quicker results, facilitating better patient management and public health interventions.
- Testing Demand: Areas experiencing higher infection rates or surges in cases will have a higher demand for testing. These areas necessitate more testing sites and/or extended hours of operation to accommodate the volume of people seeking testing.
Geographical Impact on Testing Site Distribution
Geographical characteristics, particularly the difference between urban and rural environments, significantly impact testing site distribution.
- Urban vs. Rural: Urban areas, characterized by high population density, typically require more frequent and numerous testing sites. The high concentration of individuals in urban centers necessitates more sites to efficiently meet the demand for testing. Conversely, rural areas with lower population density often benefit from fewer, strategically placed testing sites. This strategy maximizes coverage while acknowledging the logistical challenges of remote areas.
Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington Drive-Thru Testing Sites, Coronavirus testing drive thru colorado connecticut washington
This table summarizes the location of testing sites in Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington, alongside their proximity to hospitals and population centers. Due to the evolving nature of the pandemic and the continuous expansion of testing programs, data may not be completely comprehensive.
| State | Site Address (Example) | Proximity to Hospital/Major Population Center |
|---|---|---|
| Colorado | (Example Address) | Within 5 miles of a major hospital and a major population center |
| Connecticut | (Example Address) | Within 2 miles of a major hospital and within a major population center |
| Washington | (Example Address) | Within 10 miles of a major hospital and a major population center |
Public Health Strategies and Protocols
Drive-through coronavirus testing sites have become a crucial part of pandemic response strategies across the United States. These sites offer a convenient and efficient way to administer tests, especially in areas with high population density or limited access to traditional testing facilities. Effective public health strategies and protocols are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of these testing operations.
These strategies and protocols must balance accessibility with rigorous safety measures to prevent the spread of the virus.These protocols are designed to minimize the risk of transmission during the testing process. The implementation of these strategies is crucial to both public health and public confidence in the testing system. Each state’s approach to managing these sites reflects its specific needs and resources.
Colorado Drive-Thru Testing Protocols
Colorado’s drive-through testing sites have prioritized safety through various protocols. These sites generally required individuals to remain in their vehicles throughout the entire process, from registration to test collection. Pre-registration and appointment scheduling were common, often done online or by phone, to manage traffic flow and prevent congestion. Strict social distancing measures were enforced, and staff wore appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to safeguard against potential exposure.
The testing process involved a trained healthcare professional who collected the sample from the car. Afterward, results were usually communicated electronically or through a designated method.
Connecticut Drive-Thru Testing Protocols
Connecticut’s drive-through testing sites followed similar safety protocols to Colorado. Pre-registration was commonly required to minimize wait times and facilitate efficient operations. The process often included appointment scheduling, ensuring proper spacing and management of traffic flow at the testing location. Safety measures, including social distancing and mask mandates, were strictly enforced. Staff employed in the testing process wore appropriate PPE.
Sample collection took place in the car, and results were typically provided electronically or via a designated method.
Washington Drive-Thru Testing Protocols
Washington’s approach to drive-through testing sites was also focused on minimizing risk. Like other states, pre-registration and appointment scheduling were often implemented to ensure a controlled environment. Social distancing measures were in place, and staff adhered to safety guidelines by wearing PPE. Sample collection was usually conducted with the individual remaining in their vehicle, and results were communicated through a designated method.
Comparison of Public Health Strategies and Protocols
| State Name | Testing Protocols | Registration Methods | Safety Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | Pre-registration/appointment scheduling, in-car sample collection, staff in PPE, strict social distancing | Online or by phone | Strict social distancing, mask mandates, staff in PPE |
| Connecticut | Pre-registration/appointment scheduling, in-car sample collection, staff in PPE, strict social distancing | Online or by phone | Strict social distancing, mask mandates, staff in PPE |
| Washington | Pre-registration/appointment scheduling, in-car sample collection, staff in PPE, strict social distancing | Online or by phone | Strict social distancing, mask mandates, staff in PPE |
Community Impact and Accessibility
Drive-thru coronavirus testing sites, while offering convenience, have presented unique challenges in ensuring equitable access to vital healthcare services. The implementation of these sites has varied in its impact across different demographics, highlighting the importance of considering community needs and accessibility factors when designing public health strategies. Understanding these nuances is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of these initiatives and mitigating potential disparities in healthcare access.
Impact on Different Demographic Groups
Drive-thru testing sites, while convenient, can present significant hurdles for certain demographic groups. The elderly, for instance, may face difficulties navigating the process due to potential mobility limitations or a lack of familiarity with technology. Similarly, low-income individuals may encounter barriers related to transportation costs or childcare responsibilities. Essential workers, often with demanding schedules and limited time off, may struggle to fit testing appointments into their busy routines.
Drive-thru coronavirus testing is becoming increasingly common in Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington. While navigating those procedures, you might find yourself needing secure logins, and chrome m108 passkey support could streamline that process, improving the user experience for managing those crucial accounts. Ultimately, the drive-thru testing in these states continues to play a vital role in public health.
Accessibility Issues
Accessibility issues associated with drive-thru testing sites vary depending on the specific location and infrastructure. Some sites may not be easily accessible to individuals with disabilities, lacking ramps, accessible parking, or sufficient signage. Geographical factors can also pose a challenge, with testing sites located in areas that are difficult to reach for those lacking reliable transportation. Furthermore, language barriers may impede understanding of instructions or forms, further hindering access for non-English speakers.
Impact on Marginalized Communities
Drive-thru testing sites have shown mixed results in terms of improving testing access for marginalized communities. In some cases, these sites have increased overall testing participation, providing a more convenient option than traditional clinics, especially for those in remote areas. However, there’s also concern that existing disparities in healthcare access and trust in institutions may not be addressed by drive-thru testing alone.
Lack of awareness or trust in the system, combined with logistical barriers, could limit participation from vulnerable populations.
Demographic Data Analysis
| State | Elderly Population (65+) | Low-Income Population | Essential Workers | Testing Participation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | 12.1% | 15.2% | 17.8% | 58.2% |
| Connecticut | 14.3% | 12.5% | 18.5% | 65.1% |
| Washington | 13.5% | 14.8% | 19.2% | 62.8% |
Note: Data is illustrative and may not reflect precise figures for all demographic groups. Actual participation rates may vary depending on specific site locations and outreach efforts.
Drive-thru coronavirus testing sites are popping up across Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington, offering a convenient way to get tested. Meanwhile, it’s interesting to see how the recent allegations surrounding Nikola and their electric truck program, like the ones from Hindenburg Research, are impacting the market. Nikola fraud allegation hindenburg short seller electric truck Regardless of these developments, the need for reliable and accessible testing remains crucial as we navigate this pandemic.
Hopefully, these testing sites continue to provide critical support to communities in Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington.
The table above provides a snapshot of demographic data for the three states. It shows varying proportions of elderly, low-income individuals, and essential workers, along with testing participation rates. A deeper analysis, considering factors such as specific locations of testing sites and outreach efforts, is needed to understand the full picture.
Effectiveness and Efficiency of Testing Sites
Drive-thru testing sites have become a crucial component of COVID-19 response strategies, offering a convenient and often efficient method for widespread testing. However, their effectiveness and efficiency can vary significantly depending on factors such as staffing, testing methodology, and community needs. This section examines the comparative performance of drive-thru testing in Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington, focusing on turnaround times, accuracy, and potential challenges.
Comparative Analysis of Testing Turnaround Times
The speed at which results are delivered significantly impacts the effectiveness of a testing program. Faster turnaround times allow for quicker isolation of infected individuals, potentially reducing transmission. A slower turnaround time could lead to extended periods of uncertainty for individuals and potentially slower responses in contact tracing efforts. The efficiency of the testing process directly influences the overall impact of the program.
- Colorado’s drive-thru testing sites often reported faster turnaround times compared to Connecticut and Washington during certain periods. This was partly due to the specific testing procedures implemented in Colorado, which streamlined the process, resulting in quicker results. However, these improvements were not consistently seen across all sites or over time.
- Connecticut’s drive-thru testing sites frequently experienced longer turnaround times, particularly during periods of high demand. This could be attributed to logistical challenges, including limited staff or processing capacity, which impacted the speed of result reporting.
- Washington’s sites generally maintained a moderate turnaround time. While not as fast as Colorado’s in some cases, they typically offered results within a reasonable timeframe. However, fluctuations in demand and staff availability could sometimes lead to delays.
Accuracy of Test Results
Accurate test results are paramount for effective public health interventions. The reliability of test results directly affects the effectiveness of contact tracing, isolation, and other interventions. Inaccurate results could lead to incorrect diagnoses, potentially delaying appropriate actions.
Drive-thru coronavirus testing sites are popping up in Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington. It’s a pretty efficient way to get tested, and a lot of people are taking advantage of them. While this is happening, it’s worth noting that the Instagram chronological feed, as discussed by Adam Mosseri here , might be a factor in how people are finding these locations.
Ultimately, drive-thru testing remains a crucial tool in the fight against COVID-19 in these states.
- Data on test accuracy across the three states show that the accuracy rates of the drive-thru tests are largely consistent, with a high percentage of correct results. However, variations may exist in the specific methodologies used by different testing sites in each state. Factors like the testing type, the expertise of the personnel performing the tests, and the overall quality control measures implemented at each site can affect the accuracy.
Challenges and Limitations of Drive-Thru Testing
While drive-thru testing is generally a practical method, several limitations need consideration. Accessibility for certain populations can be a problem, especially for those without vehicles or reliable transportation.
- Logistics and infrastructure requirements can be challenging to manage. Maintaining sufficient staffing, adequate supplies, and appropriate safety protocols at the sites is crucial but can be challenging.
- Public health officials face challenges in maintaining consistent quality control across various testing sites, especially when facing fluctuating demand. Ensuring accuracy and reliability is critical for maintaining public trust in the system.
- Equity of access and inclusivity should be considered. Ensuring that individuals from all socioeconomic backgrounds and mobility levels can access testing sites is vital. Addressing potential barriers to access and ensuring equitable distribution of testing resources are important.
Comparative Data Table
| State | Average Turnaround Time (Days) | Positivity Rate (%) | Test Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | 2-3 | 5-7 | 98 |
| Connecticut | 3-4 | 8-10 | 97 |
| Washington | 2-4 | 6-8 | 96 |
Note: Data in the table is illustrative and may vary based on specific testing sites and time periods. Positivity rates and test accuracy figures are estimated and may differ from official reporting.
Future of Drive-Thru Testing
Drive-thru testing has proven invaluable during public health crises, offering a convenient and efficient method for widespread testing. Its adaptability and scalability have demonstrated its potential for future pandemic response, but its future evolution hinges on technological integration and strategic planning. The key to its continued relevance lies in its ability to adapt to emerging needs and incorporate advancements.
Potential Role in Future Pandemics
Drive-thru testing sites have demonstrated their capacity to rapidly scale up testing during outbreaks, providing a critical infrastructure for disease surveillance and containment. Their ability to handle high volumes of samples efficiently is crucial in mitigating the spread of contagious diseases. In future pandemics, these sites can play a vital role in quickly identifying and isolating infected individuals, thus limiting community transmission.
Their pre-existing infrastructure can be readily adapted and reconfigured for various testing methods, making them a flexible tool for public health preparedness.
Integration of Advanced Technologies
The future of drive-thru testing will likely be intertwined with technological advancements. Mobile testing units equipped with advanced diagnostic equipment can bring testing directly to affected communities, particularly in remote or underserved areas. AI-powered diagnostic tools can potentially expedite the analysis of test results, reducing turnaround times and improving the speed of response. Real-time data analytics can be crucial for tracking the spread of the disease and for informing public health interventions.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Technological advancements can significantly impact the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of drive-thru testing. Mobile testing units, for example, can reduce logistical challenges and travel time for individuals needing testing, increasing accessibility. AI-powered diagnostics can streamline the testing process, enabling faster turnaround times and reducing the need for large, centralized labs. These factors can contribute to significant cost savings and improved overall efficiency.
This can be seen in current applications of AI in healthcare, where algorithms are being used to assist with diagnosis and treatment planning.
Possible Future Innovations
| Innovation | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Testing Units with AI Integration | Dedicated vehicles equipped with rapid diagnostic equipment and AI-powered analysis systems, allowing for on-site testing and immediate results. | Increased accessibility, faster turnaround times, and reduced reliance on centralized labs. |
| Automated Sample Processing Systems | Automated systems for sample collection, preparation, and analysis, reducing manual labor and potential human error. | Enhanced accuracy, reduced processing time, and potential for 24/7 operation. |
| Integration of Telehealth Platforms | Connecting drive-thru testing sites with telehealth platforms for remote consultations and follow-up care, improving patient management and reducing the spread of infection. | Improved patient care coordination, potentially reducing hospitalizations, and increasing accessibility to medical support. |
| Predictive Modeling for Outbreak Response | Using data from testing sites to model potential outbreak scenarios, enabling proactive measures to prevent and contain future outbreaks. | Enhanced preparedness, early intervention, and reduced impact of future outbreaks. |
Visual Representation of Testing Site Distribution

Understanding the geographic distribution of drive-thru coronavirus testing sites is crucial for assessing accessibility and identifying potential gaps in service. A well-designed map, incorporating interactive elements, allows for a clear visualization of testing site locations, facilitating quick identification of sites and analysis of their distribution across different regions. This empowers individuals to easily locate the nearest testing facility, potentially saving valuable time and resources during a health crisis.
Map of Testing Site Distribution
A detailed map of drive-thru testing sites across Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington will display the precise locations of each testing facility. The map’s design will be highly user-friendly, enabling seamless navigation and data retrieval. This visual representation will serve as a critical tool for both public health officials and individuals seeking testing.
Geographic Factors Influencing Site Locations
The placement of testing sites is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Population density plays a significant role, with sites often clustered in areas with higher concentrations of people. Accessibility, such as proximity to major transportation routes and parking availability, also impacts site selection. The availability of suitable infrastructure, including space for setting up testing tents and administering tests, is a key consideration.
Additionally, logistical factors like workforce availability and supply chain management for necessary equipment and materials are also essential factors influencing the placement of drive-thru testing sites.
Color-Coding Scheme
The map employs a color-coding scheme to represent the different testing sites. Different shades of blue can be used to indicate the density of testing sites in various areas, with darker shades signifying higher concentrations. This visual cue will allow users to quickly assess areas with abundant testing options and those with fewer resources. Alternatively, colors can distinguish between different testing providers or types of testing offered at each location.
Interactive Features
The map includes interactive features to provide a deeper understanding of the testing site data. Users can click on specific markers on the map to drill down to detailed information about each site, including contact information, hours of operation, and types of tests offered. This functionality allows for targeted searches, making it easy to find the perfect testing location for each user’s needs.
An interactive legend explains the significance of the color coding and other symbols used on the map, facilitating better understanding. For instance, the size of the markers could reflect the volume of tests administered at a site.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, drive-thru coronavirus testing in Colorado, Connecticut, and Washington demonstrated a vital role in pandemic response. The varied approaches, however, highlight the nuanced challenges in implementing such programs across different communities and geographical settings. While convenient and accessible, challenges in efficiency and equity persisted. Looking ahead, lessons learned can inform future public health strategies for managing outbreaks and ensuring equitable access to testing.
The future of drive-thru testing may involve advanced technologies and optimized strategies, aiming for a more efficient and impactful approach to future pandemic preparedness.