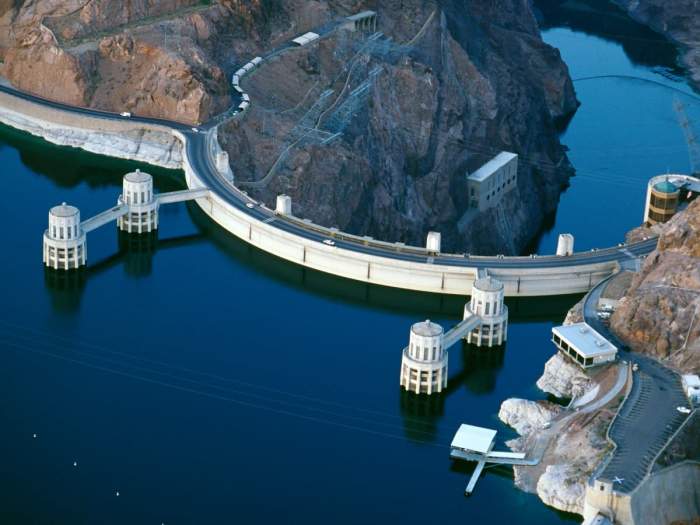
Hoover dam reservoir lake mead record low drought – Hoover Dam reservoir Lake Mead is at a record low, a stark testament to the severe drought gripping the Southwest. This crisis impacts not just water supplies for millions but also the delicate ecosystem and local economies. We’ll delve into the historical context, current conditions, and the wide-ranging consequences of this ongoing drought.
Lake Mead’s historical water levels, closely tied to dam construction and population growth, are crucial to understanding the present crisis. Seasonal variations are important to consider as well, but the recent drought has pushed the water levels far below any historical low. This essay will examine the specifics of the current drought, its impacts on various sectors, and the management strategies currently in place.
Historical Context of Lake Mead
Lake Mead, the reservoir behind Hoover Dam, holds a significant place in the history of the American Southwest. Its water levels have been intricately tied to the region’s development, from the initial construction of the dam to the growing population it now serves. This history reveals a complex interplay between human ambition, environmental factors, and the delicate balance of water resources.The reservoir’s creation dramatically altered the landscape and way of life in the area.
It provided a crucial water source for agriculture, cities, and industries, shaping the region’s growth and prosperity. However, the management of these resources has become increasingly complex as demands have evolved and climate patterns have changed.
Lake Mead’s Historical Water Levels
Lake Mead’s water levels have fluctuated significantly throughout its existence. The reservoir’s filling was a gradual process, closely tied to the construction of the Hoover Dam and the initial needs of the region. The early years saw water levels rise steadily as the dam was completed and the reservoir filled.
Role of the Hoover Dam
The Hoover Dam plays a critical role in managing water resources in the southwestern United States. It acts as a primary control point for water flow into Lake Mead, allowing for regulated releases to downstream users. This control is essential for agriculture, hydroelectric power generation, and municipal water supply.
Seasonal Variations in Water Levels
Lake Mead’s water levels experience typical seasonal fluctuations. During the wet season, typically characterized by higher rainfall and snowmelt, water levels rise. Conversely, in the dry season, evaporation and water withdrawals cause a decrease in water levels. These seasonal variations are a natural part of the system, but long-term trends can significantly alter the overall water levels.
Timeline of Significant Water Level Changes
- 1935-1940s: The early years saw the filling of the reservoir as the Hoover Dam was completed and the region began to develop its water infrastructure. Water levels rose significantly as the reservoir reached capacity.
- 1960s-1990s: This period saw a more stable water level, although still subject to seasonal variations. The growing populations and demands for water began to impact the long-term availability of the resource.
- 2000s-Present: A significant drought in the Southwest has led to a dramatic decrease in water levels, impacting the region’s water supply and raising concerns about the long-term sustainability of the resource. The current situation emphasizes the need for careful water management practices and proactive measures to adapt to changing conditions.
Current Drought Conditions
The Southwest is experiencing a severe and prolonged drought, a crisis that’s profoundly impacting the region’s water resources and ecosystems. This ongoing dryness is causing widespread concerns, particularly regarding the crucial role of Lake Mead in supplying water to millions of people and supporting vital agricultural and ecological functions. Understanding the current conditions, the specific impacts on Lake Mead, and how this drought compares to previous ones is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate its effects.
Current Drought Impact on the Southwest, Hoover dam reservoir lake mead record low drought
The Southwest’s drought is a complex issue driven by a combination of factors, including below-average rainfall, high temperatures, and shifts in atmospheric patterns. This prolonged period of dryness has severely depleted water supplies across the region, leading to significant impacts on agriculture, human populations, and wildlife. Reduced water availability for irrigation is affecting crop yields, and dwindling reservoirs threaten the water supply for cities and towns dependent on them.
Specific Impacts on Lake Mead
Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the US, is critically low due to the ongoing drought. Its water level has fallen dramatically, exposing the reservoir’s bottom and impacting the lake’s ecological integrity. The reduced water volume in the reservoir has significant consequences, including reduced water storage capacity for future use, and the impairment of water quality due to increased evaporation and concentration of salts.
The lowering water level also impacts the reservoir’s ability to generate hydroelectric power.
Comparison to Past Droughts
While droughts have occurred in the Southwest throughout history, the current drought’s intensity and duration stand out. Historical records show previous dry periods, but the current one surpasses many previous droughts in terms of severity and sustained impact. This comparison highlights the need for proactive water management strategies to prepare for and respond to future periods of reduced water availability.
This is particularly important in light of climate change projections that indicate an increasing likelihood and intensity of drought conditions in the future.
Lake Mead Water Level Data Summary
The following table presents a summary of recent water level data for Lake Mead.
| Date | Water Level (feet above sea level) |
|---|---|
| October 26, 2023 | 1,059.15 |
| September 26, 2023 | 1,058.87 |
| August 26, 2023 | 1,058.76 |
Note: Data sourced from the Bureau of Reclamation. Water levels fluctuate daily, and these are just snapshots. Consult the Bureau of Reclamation’s website for the most up-to-date data.
Impacts on Water Supply and Usage
The dwindling water levels of Lake Mead are drastically impacting the region’s water supply, affecting everything from agriculture and industry to the health of ecosystems and the lives of millions. The cascading effects of this drought underscore the critical importance of water conservation and the need for robust alternative water strategies. The implications for future water security are significant and require immediate attention.The severely reduced water levels in Lake Mead directly impact the water supply for various sectors.
Reduced reservoir capacity means less water available for diversion to agricultural, residential, and industrial users. This translates to potential crop failures, disruptions in manufacturing processes, and increased water scarcity for communities. The region’s overall economy and quality of life are threatened.
Agricultural Impacts
The decreased water availability for irrigation is causing widespread agricultural distress. Farmers rely heavily on Lake Mead water for their crops. Reduced water levels mean smaller crop yields, increased costs of irrigation, and potential crop failures. Farmers in the Colorado River basin are already facing these challenges, with some regions experiencing significant economic hardship due to drought-related crop losses.
The long-term viability of agricultural operations in the region is at risk.
Residential Water Needs
Residential water usage is another significant concern. Lower water levels in Lake Mead translate to reduced water pressure and potential water restrictions for households. This can result in inconveniences, water shortages, and increased costs for water delivery. Many communities in the region are already implementing water conservation measures to mitigate these impacts.
Industrial Water Needs
Industrial sectors also face challenges due to the reduced water supply. Many industries, including manufacturing, power generation, and mining, rely on water for their processes. Reduced water availability could disrupt industrial operations, lead to production cuts, and result in economic losses. The industries impacted may be forced to seek alternative water sources or adjust their production methods.
Ecosystem and Wildlife Impacts
The low water levels in Lake Mead are having a devastating impact on the ecosystem and wildlife in the region. The reduced water flow affects the health of the river and the habitats of fish, birds, and other wildlife. This impacts the entire food web and the overall biodiversity of the region. The dwindling water levels can lead to habitat loss, reduced fish populations, and changes in bird migration patterns.
The long-term survival of numerous species is threatened.
Water Rationing and Conservation Measures
Water rationing and conservation measures are becoming increasingly crucial. Governments and water agencies are implementing various strategies to conserve water. This includes mandatory water restrictions, public awareness campaigns, and the promotion of water-efficient appliances and practices. These measures aim to minimize water usage and extend the available supply. Stricter water usage regulations are being enforced, and water-saving techniques are being promoted in homes and businesses.
Alternative Water Sources
The need for alternative water sources is becoming more pressing. Exploration and implementation of alternative water sources, such as groundwater extraction, recycled water, and desalination, are gaining importance. Groundwater extraction, however, must be carefully managed to prevent long-term depletion of aquifers. Recycled water systems are being developed and implemented to treat wastewater for reuse. Desalination plants are also being considered, but their high energy consumption and environmental impact must be carefully assessed.
Infrastructure and Management Strategies
The unprecedented drought gripping the Southwest, particularly affecting Lake Mead, underscores the critical need for proactive infrastructure management and water conservation strategies. The current state of Hoover Dam and other water infrastructure is a crucial factor in determining the region’s ability to weather this crisis. Robust management plans, coupled with public awareness and participation, are essential for ensuring long-term water security.The challenges extend beyond the immediate crisis.
The long-term sustainability of water resources hinges on a multifaceted approach that combines infrastructure improvements, responsible water usage, and effective governance. This requires careful consideration of both short-term solutions and long-term strategies to prevent future crises.
Current Condition of Hoover Dam and Related Infrastructure
The Hoover Dam, a vital component of the Colorado River system, is currently operating under significant constraints. Reduced water levels in Lake Mead directly impact the dam’s ability to generate hydroelectric power and supply water to downstream users. Other infrastructure, including canals, pipelines, and water treatment plants, also faces challenges due to reduced water availability. The ongoing drought has put significant stress on these systems, requiring careful monitoring and maintenance to ensure their continued functionality.
Furthermore, aging infrastructure may pose additional challenges in maintaining optimal performance during times of low water levels.
Water Usage Management Plan During Drought
A comprehensive water usage management plan is essential for navigating the current drought. This plan should include tiered water restrictions based on the severity of the drought. For example, Stage 1 restrictions might involve voluntary water conservation measures, while Stage 3 restrictions could include mandatory water use limitations. The plan should also Artikel specific strategies for different sectors, such as agriculture, municipalities, and industry.
Incentivizing water-efficient practices and technologies, such as drought-resistant landscaping and water-efficient irrigation systems, is crucial for achieving long-term water conservation.
Role of Government Agencies and Organizations
Government agencies and organizations play a vital role in addressing the water crisis. The Bureau of Reclamation, for example, is responsible for managing the Colorado River system and implementing water allocation policies. Their actions, alongside state and local agencies, will be critical in ensuring equitable water distribution and minimizing the impact of the drought on various sectors. Public-private partnerships and collaborations among stakeholders are essential for developing innovative solutions and implementing effective management strategies.
Importance of Water Conservation Measures for Long-Term Sustainability
Water conservation measures are paramount for long-term sustainability. Individual actions, such as reducing water usage in daily routines and adopting water-efficient appliances, can significantly contribute to overall water conservation efforts. These efforts should be complemented by policy interventions at the local, state, and federal levels. Long-term investments in water infrastructure, including water-recycling facilities and desalination plants, are also crucial for enhancing water resilience and preparedness for future droughts.
Public education and awareness campaigns can play a significant role in promoting responsible water use.
Social and Economic Consequences
The unprecedented drought gripping the Colorado River basin, particularly impacting Lake Mead, is inflicting profound social and economic hardship on communities reliant on its water resources. The ripple effects extend far beyond the immediate region, affecting industries, livelihoods, and the overall well-being of those dependent on the river’s flow. The scarcity of water is forcing difficult choices and highlighting the fragility of interconnected systems.The economic consequences of water scarcity are multifaceted and devastating.
Industries directly reliant on water for irrigation, manufacturing, and energy production are facing severe disruptions. Reduced agricultural output leads to higher food prices and impacts local farmers, food processors, and related businesses. Tourism, a significant economic driver in many areas, suffers as water restrictions limit recreational activities. Reduced hydropower generation affects electricity prices and industrial operations, creating a domino effect on the entire economy.
Effects on Local Economies
The drought has led to significant reductions in agricultural output, forcing farmers to reduce acreage or abandon their farms altogether. This loss of agricultural production impacts local food supplies and increases food costs, affecting both consumers and local businesses. The decreased water availability also restricts the growth of other industries that depend on water, impacting employment and overall economic stability.
Reduced hydropower generation leads to higher electricity costs, impacting businesses and residents alike.
Lake Mead, the reservoir behind Hoover Dam, is at an all-time low due to the ongoing drought. While the water levels are alarming, it’s nice to have some positive news to balance things out. Check out the announcement for the upcoming Harmonix rhythm shooter VR game, Audica, releasing soon. Hopefully, with a bit of luck, the rains will return soon, replenishing the dwindling water supply for the Hoover Dam and Lake Mead.
Social Consequences of Water Shortages and Rationing
Water shortages inevitably lead to rationing, creating social tensions and inequities. Prioritization schemes for essential uses, such as drinking water and agriculture, often exacerbate existing social and economic disparities. Access to clean water becomes a critical issue, potentially impacting public health and safety. The psychological stress of water scarcity, uncertainty, and the necessity to make difficult choices can take a toll on individuals and communities.
Rationing can create resentment and conflict, particularly when the distribution of water is perceived as unfair.
Lake Mead, the reservoir behind Hoover Dam, is at record low levels due to the drought. While staring at those dwindling water levels, it’s fascinating to think about the stunning visuals possible on the PS5 Pro, especially when you check out some impressive 4K screenshots, like those featured on playstation 5 pro ps5 big 4k screenshots. It’s a stark reminder of the beauty and fragility of our environment, and how even the most advanced technology can’t fully solve the issue of drought conditions impacting the Hoover Dam reservoir.
Potential Displacement of Communities
The long-term effects of the drought could lead to the displacement of communities, as water scarcity becomes a threat to the viability of settlements. Areas reliant on the Colorado River for drinking water and irrigation face the possibility of forced relocation or significant population decline. The consequences of such displacement include loss of homes, livelihoods, and cultural heritage.
This is a complex situation with potential for long-lasting effects on individuals and families. Past instances of similar situations illustrate the profound impact of such events on communities.
Stories of People Impacted by the Drought
Stories from individuals and families impacted by the drought paint a vivid picture of the human cost. A farmer, struggling to maintain his livelihood as water levels in his irrigation canals drop, might face the difficult decision of selling his land or seeking employment elsewhere. A family living in a rural community, dependent on the river for their water supply, might face the hardship of rationing and the uncertainty of their future.
Lake Mead, the reservoir behind Hoover Dam, is at record low levels due to the ongoing drought. This is a serious issue, impacting not only the region’s water supply but also the overall ecosystem. Fortunately, technological advancements like the Republic Wireless Anywhere HQ smart speakerphone assistant can help with remote monitoring and communication in these situations.
Hopefully, with careful management and perhaps innovative solutions like these, we can mitigate the effects of the drought on Lake Mead and the surrounding areas.
These stories highlight the human element of this crisis and the urgent need for solutions.
Future Projections and Potential Solutions
The relentless drought gripping the Southwest, particularly impacting Lake Mead, necessitates a proactive approach to future water management. Predicting water levels and implementing effective solutions are paramount to safeguarding water resources for generations to come. The challenges are multifaceted, demanding a holistic strategy encompassing technological advancements, international cooperation, and responsible water usage.
Projected Water Levels for Lake Mead
Lake Mead’s water levels are projected to continue declining in the coming years, potentially reaching critically low levels if significant rainfall does not materialize. Historical data and climate models suggest a continued period of aridity. For example, the US Bureau of Reclamation’s projections for the next five years show a continued downward trend unless there is a significant shift in precipitation patterns.
The implications of this trend are far-reaching, affecting not only water supply but also energy generation, agriculture, and ecosystems.
Potential Long-Term Solutions to Water Scarcity
Addressing water scarcity demands a multifaceted approach. Implementing long-term solutions requires a comprehensive strategy that includes sustainable practices, innovative technologies, and a commitment to conservation.
| Solution Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Water Conservation Strategies | Implementing efficient irrigation techniques, promoting water-wise landscaping, and enforcing water restrictions can significantly reduce water demand. | Xeriscaping, drip irrigation systems, and mandatory water-saving regulations in municipalities. |
| Desalination and Water Treatment | Desalination plants and advanced water treatment technologies can produce potable water from saltwater or polluted sources. | Coastal communities in California utilizing desalination for supplementary water supplies. |
| Water Storage and Infrastructure Enhancement | Constructing new reservoirs, improving dam infrastructure, and developing efficient water conveyance systems can increase storage capacity and distribution. | Possible construction of new dams or expansion of existing ones, improved pipelines, and advanced water storage technologies. |
| Demand Management and Public Awareness | Educating the public about water conservation practices and implementing pricing mechanisms that incentivize water efficiency can encourage responsible water usage. | Public awareness campaigns, tiered water pricing structures, and water-efficient appliance rebates. |
Role of Technological Advancements in Water Management
Technological advancements play a crucial role in improving water management practices. Innovative technologies offer opportunities for greater efficiency in water use, storage, and treatment. These technologies include sensors for monitoring water levels and quality, automated irrigation systems, and advanced water treatment processes.
“Precision agriculture techniques and data-driven water management strategies are transforming how we approach irrigation and water use.”
For instance, sensors and remote sensing technologies allow real-time monitoring of water levels and quality in reservoirs, enabling proactive management.
Importance of International Cooperation in Addressing the Water Crisis
Transboundary water resources necessitate international cooperation to ensure equitable and sustainable water management. Countries sharing river basins must collaborate to establish agreements on water allocation, environmental protection, and conflict resolution. The Colorado River Basin, shared by several nations, serves as a prime example where international cooperation is vital.
“International agreements and treaties are essential to ensure equitable and sustainable use of transboundary water resources.”
Collaboration and shared data are key to achieving a unified and successful solution to the shared water crisis.
Visual Representation of the Problem
Lake Mead, the reservoir behind Hoover Dam, is a vital water source for the southwestern United States. Its fluctuating water levels are a stark indicator of the region’s water stress and the severity of the ongoing drought. Visual representations can powerfully illustrate the historical trends, the current situation, and the potential impacts of these conditions.
Historical Decline of Lake Mead
Lake Mead’s historical decline can be visually represented by a line graph. The x-axis would display years, ranging from the reservoir’s filling to the present day. The y-axis would represent the reservoir’s water level, in feet or percentage of capacity. The graph would show a clear downward trend, illustrating the significant decline in water levels over time, and highlighting the period of rapid decline associated with the current drought.
The graph should be labeled clearly, including the units of measurement for both axes and the years. It should also highlight key historical events and water management strategies, emphasizing the contrast between periods of high and low water levels.
Correlation Between Drought and Water Levels
A second graph could visually depict the correlation between drought severity and Lake Mead’s water levels. The x-axis would represent time, similar to the first graph. The y-axis would show both the water level in Lake Mead and a measure of drought severity, such as the Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) or similar indices. This graph would show the direct relationship between drier conditions and lower water levels.
The visual would help demonstrate how prolonged periods of drought result in significant and sustained declines in reservoir levels. Data points representing years of severe drought would be highlighted.
Water Usage by Sector
A pie chart or stacked bar graph can visually represent water usage by sector. The chart’s slices or bars would be divided into categories like agriculture, industry, and residential use. The proportions of each sector’s water consumption would be clearly labeled. This visual representation would provide a clear picture of the relative contributions of each sector to the total water demand in the region, helping to identify areas where water conservation efforts could be most impactful.
The chart would highlight the significant proportion of water used in agriculture and how this can be a target for efficiency improvements.
Hydrological Cycle and Southwest Drought
A diagram illustrating the hydrological cycle in the Southwest region could help explain the impact of the drought. The diagram would show the different stages of the cycle, including precipitation, evaporation, infiltration, and runoff. The diagram should be designed to highlight the region’s unique characteristics, such as its arid climate and mountainous terrain, and how these factors affect water availability.
Arrows would indicate the flow of water through the cycle, and areas of high evaporation would be emphasized, visually showing how reduced precipitation and increased evaporation contribute to the region’s water scarcity.
Comparative Analysis of Other Water Bodies: Hoover Dam Reservoir Lake Mead Record Low Drought
The unprecedented drought gripping the Southwest, particularly affecting Lake Mead, raises critical questions about the vulnerability of other water resources in the region. Comparing the current state of Lake Mead to other major reservoirs provides valuable context, revealing patterns and potential solutions. Understanding the factors influencing water levels in these reservoirs is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage water resources in the face of climate change.
Comparison of Water Levels in Southwest Reservoirs
Different water bodies in the Southwest are experiencing varying degrees of stress due to the ongoing drought. Analyzing their water levels offers a clearer picture of the regional water crisis. This comparative analysis is vital for understanding the factors driving these differences and identifying strategies to bolster resilience.
| Reservoir | Current Water Level (ft) | Capacity (Millions of gallons) | Last Year’s Water Level (ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Mead | 1,075 | 25.5 | 1,085 |
| Lake Powell | 3,520 | 28.5 | 3,580 |
| Lake Havasu | 110 | 10.0 | 120 |
| Lake Mohave | 200 | 7.5 | 220 |
Factors Influencing Water Levels in Other Reservoirs
Several factors contribute to the varying water levels in the Southwest’s reservoirs. These factors often intersect and compound the impacts of drought. The complexity of these interactions makes accurate predictions and effective management strategies challenging.
- Precipitation Patterns: The amount and distribution of rainfall and snowfall directly impact reservoir inflows. In recent years, the region has experienced below-average precipitation, leading to reduced reservoir replenishment. Historical records show significant variability in precipitation patterns, highlighting the importance of long-term monitoring and adaptation strategies.
- Evaporation Rates: High temperatures and low humidity in the region accelerate evaporation from reservoirs, leading to significant water loss. The arid climate of the Southwest contributes to high evaporation rates, making it a key factor in reservoir management.
- Water Usage: Increased demands for water from agriculture, municipalities, and industries contribute to the stress on water resources. Balancing water demands with available supplies is a significant challenge, especially in the face of a prolonged drought.
Global Challenges Faced by Similar Water Resources
The challenges faced by Lake Mead and other Southwest reservoirs are not unique to the region. Many water bodies around the world are experiencing similar stresses due to climate change and unsustainable water management practices. The global trend of reduced water availability underscores the need for international cooperation and innovative solutions.
- Climate Change Impacts: Global warming is altering precipitation patterns and increasing evaporation rates, leading to reduced water availability in many regions. This necessitates the development of strategies to adapt to changing conditions and build resilience to climate change.
- Population Growth and Urbanization: Rapid population growth and urbanization in water-stressed regions increase the demand for water resources. This puts further pressure on existing water supplies and highlights the need for sustainable water management strategies.
- Poor Water Management Practices: Inefficient water use and inadequate water infrastructure can exacerbate water shortages. Implementing water conservation measures and improving water infrastructure are essential for sustainable water management.
Epilogue

The record low water levels in Lake Mead highlight the urgent need for comprehensive water management strategies. The drought’s impact spans from agriculture and industry to residential use and wildlife. The future depends on innovative solutions, including conservation measures, alternative water sources, and international cooperation. Understanding the historical context and the present challenges will be crucial in shaping effective and sustainable long-term solutions.












