Apple privacy icon iOS macOS High Sierra personal information: Apple’s approach to user privacy is constantly evolving. This exploration delves into the history of Apple’s privacy policies, examining the visual cues, like the privacy icon, on iOS and macOS, specifically High Sierra. We’ll analyze how Apple collects, uses, and protects personal information, and discuss user control over their data.
Understanding these aspects is key to comprehending Apple’s commitment to user privacy.
From the subtle shifts in the privacy icon’s design across different operating systems to the nuanced ways users can manage their personal information, this comprehensive guide unpacks the intricate details of Apple’s privacy practices. We’ll compare Apple’s methods to those of competitors, highlighting the specific features and controls available in High Sierra, and tracing how they’ve evolved in later macOS versions.
This in-depth look aims to equip readers with a thorough understanding of Apple’s privacy policies and their implications.
Introduction to Apple Privacy on iOS and macOS
Apple has consistently prioritized user privacy, evolving its policies and practices to reflect changing technological landscapes and societal concerns. This evolution reflects a commitment to transparency and user control over personal data. From early iterations of iOS and macOS to the current suite of privacy features, Apple has consistently sought to empower users with tools and options to manage their digital footprint.Apple’s approach to privacy isn’t just about technical features; it’s deeply rooted in a philosophy that places the user’s well-being and digital security at the forefront.
This philosophy informs the design and implementation of privacy protections across its platforms.
Evolution of Apple’s Privacy Policies
Apple’s privacy policies have undergone significant transformations over the years. Early policies focused primarily on data security. Subsequent iterations have emphasized user control and transparency, allowing users to actively manage their data. Key changes include enhanced user consent mechanisms, detailed data usage disclosures, and a stronger emphasis on limiting data collection practices. These changes reflect Apple’s growing recognition of the importance of user privacy in the digital age.
Overview of Apple’s Privacy Features on iOS and macOS
Apple’s privacy features are deeply integrated into both iOS and macOS. These features are designed to provide users with control over their data and enhance their digital security. Examples include the ability to control location services, disable targeted advertising, and review app permissions. The design prioritizes user-friendliness, ensuring that these controls are readily accessible and easily understood.
Core Principles Behind Apple’s Approach to User Privacy
Apple’s approach to user privacy rests on several fundamental principles. Transparency is paramount, ensuring users understand how their data is being collected and used. Control is another key element, empowering users to make informed decisions about their data. Minimization is essential, limiting the collection of data to what is strictly necessary for the intended purpose. Security is prioritized, with robust measures to protect data from unauthorized access and misuse.
This approach aims to strike a balance between user privacy and the legitimate needs of developers and businesses.
Comparison of Apple’s Privacy Practices to Other Major Tech Companies
The table below provides a concise comparison of Apple’s privacy practices with those of other major tech companies. This comparison highlights the unique approach Apple takes, emphasizing user control and data minimization.
| Feature | Apple | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Limited to what’s necessary for functionality and specific user consent. | Extensive collection for targeted advertising and personalized services. | Extensive collection for targeted advertising and social networking. |
| User Control | Strong emphasis on user control and choice, including granular permissions. | Limited control over data collection and use, particularly for advertising. | Limited control, particularly regarding data sharing across services. |
| Transparency | Detailed data usage disclosures and clear consent mechanisms. | Less transparent regarding data collection and usage. | Limited transparency, particularly regarding data sharing across platforms. |
| Data Security | Robust security measures and encryption protocols. | Strong security measures but increasing scrutiny regarding data breaches. | Vulnerable to data breaches, especially concerning user privacy. |
Understanding the Apple Privacy Icon: Apple Privacy Icon Ios Macos High Sierra Personal Information
The Apple privacy icon, a subtle yet crucial element of the user interface, serves as a visual cue for users regarding the privacy implications of various actions and settings. Its consistent design across different Apple operating systems helps users quickly grasp the level of data protection offered. This guide delves into the visual aspects of this icon, its significance, and potential future evolutions.The icon, though simple, communicates a wealth of information about the privacy considerations surrounding a particular app or setting.
Understanding its subtle cues is essential for informed user choices.
Visual Elements of the Privacy Icon
The Apple privacy icon’s visual elements remain consistent across iOS and macOS, facilitating a unified user experience. The icon’s shape, color, and position within the interface are carefully considered to convey specific privacy implications.
Color Significance
The color of the Apple privacy icon is a key indicator of the level of privacy protection. A predominantly light-gray shade generally signifies minimal data collection or processing. A more pronounced or vibrant shade, such as a deep blue or green, might indicate more significant data usage, but the actual significance depends on the specific context. For instance, a light gray icon next to a photo-sharing app might indicate the app is only accessing basic metadata, whereas a deep blue icon alongside a location-tracking app implies more extensive data collection and sharing.
Shape and Positioning
The icon’s shape, often a stylized shield or a small closed eye, directly relates to its intended function. A shield shape, for example, emphasizes protection and security. The positioning of the icon within the app or settings window is equally important, as it guides users to the specific privacy considerations of the item in question. Placement beside an app icon, within a settings menu, or in a notification alert provides context.
For instance, an icon placed within a settings menu for location services directly signals that privacy settings are applicable to that function.
Potential Future Design Changes
As Apple’s privacy policies and user expectations evolve, the privacy icon’s design might adapt. The icon could incorporate additional elements to indicate specific privacy controls, such as the ability to disable data sharing or adjust the level of data protection. For instance, a small lock icon or an adjustable slider within the privacy icon could denote the level of customization available to the user.
This adaptation is expected to increase user awareness and transparency.
Possible Interpretations and Meanings
| Icon Element | Possible Interpretation | Example Context |
|---|---|---|
| Light Gray Shield | Minimal data collection or processing. | Basic app functionality that doesn’t require extensive data access. |
| Darker Blue Shield | More significant data usage. | Location services, financial transactions. |
| Closed Eye | Data privacy protection enabled. | Protecting sensitive data, preventing unwanted tracking. |
| Shield with Lock | Advanced data protection and control. | Secure app settings, encrypted data transfer. |
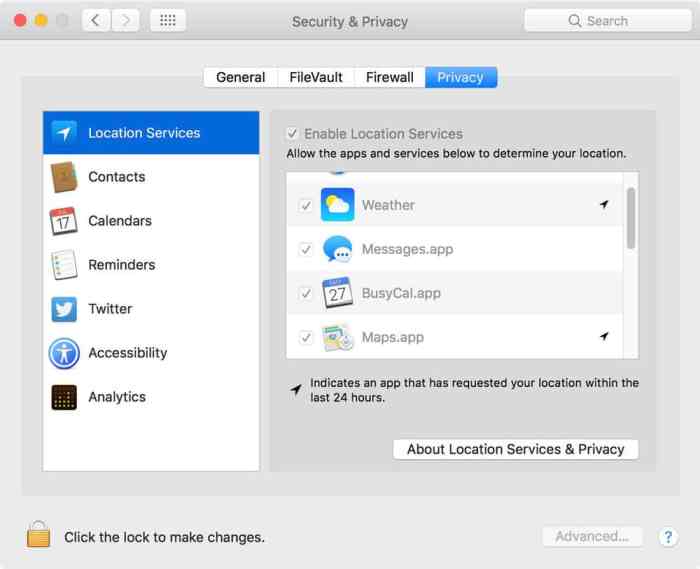
Privacy Considerations in High Sierra
macOS High Sierra, released in 2017, marked a significant step in Apple’s commitment to user privacy. This version introduced several key features designed to enhance user control over their personal information. It built upon the foundations of previous operating systems while introducing new, user-friendly ways to manage and protect data.
Privacy Features in High Sierra
High Sierra’s privacy enhancements focused on transparency and control. Users could now see how applications accessed their data and adjust permissions accordingly. This level of granular control empowered users to decide which apps could access their information, helping to address concerns about data collection and use.
Addressing User Concerns
High Sierra’s privacy features aimed to directly address user concerns regarding personal information. The introduction of detailed access controls allowed users to choose which applications could access sensitive data, such as location, contacts, and photos. This proactive approach ensured users felt empowered to safeguard their data, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or misuse.
Ever noticed that new Apple privacy icon on iOS and macOS High Sierra? It’s a subtle reminder of how our personal information is handled. While pondering those privacy concerns, I stumbled across an intriguing article about the future of rescue missions, specifically how shape-shifting drones could revolutionize disaster response. Shape shifting drone future rescue missions could potentially save lives and offer a new perspective on safety.
But, with the increasing use of technology, it’s important to remember that even advanced rescue drones still rely on the protection of our personal information. This brings us right back to the importance of understanding how Apple handles user data.
Practical Implications for Users
The practical implications of High Sierra’s privacy settings were substantial. Users could now selectively grant or deny access permissions to apps, thereby controlling what information was shared. This allowed users to carefully consider the trade-offs between app functionality and data protection. For example, a user could choose to allow an app to access their location data only when the app was actively running, rather than granting perpetual access.
Comparison with Later macOS Versions
| Feature | macOS High Sierra | Later macOS Versions |
|---|---|---|
| Location Services | Limited options for location access, often application-specific. | More granular control, including the ability to set precise location or to allow only when app is in use. |
| Contacts Access | Basic permissions for accessing contacts, often with a ‘full access’ option. | Enhanced control over which contact fields apps could access. |
| Photos Access | Generally broader access to photo libraries. | More nuanced control, allowing selective access to specific photo albums or categories. |
| Siri and Dictation | Limited data collection for Siri and Dictation features. | Continued improvement in data handling practices, and more options for managing personal data. |
| Application Permissions | Introduced a dedicated privacy settings pane for managing permissions. | Continued development and refinement of the privacy settings pane to improve user experience. |
This table highlights the progression in privacy controls from High Sierra to later versions of macOS. The evolution shows a continued effort to empower users with greater control and transparency.
Personal Information Handling on iOS and macOS
Apple takes user privacy seriously, and its approach to handling personal information on iOS and macOS is a core component of this commitment. This involves a transparent and multifaceted process, encompassing collection, use, sharing, and protection of data. Understanding these aspects empowers users to make informed choices about their data.Apple’s commitment to privacy extends to the way it collects, utilizes, and safeguards personal information, emphasizing user control and transparency.
This approach is vital for maintaining trust and upholding user expectations regarding data security.
Data Collection Practices
Apple collects various types of personal data to enhance user experience and provide tailored services. This data collection is not indiscriminate; it’s driven by the need to offer specific functionalities and features. These data points are essential for providing a personalized and efficient experience.
- Apple collects data like usage patterns, app interactions, and device settings. This includes information about the apps you use, how frequently you use them, and the features within those apps that you interact with.
- Location data, if enabled by the user, is collected to provide location-based services. For example, location data can be used to offer directions, find nearby businesses, and provide accurate weather information.
- Information about your device, such as its model, operating system version, and unique identifiers, is collected. This is used for troubleshooting purposes and to ensure optimal device performance.
Data Usage and Sharing
Apple utilizes the collected data for various purposes, including improving its products and services. This data is also crucial for addressing potential issues and enhancing overall functionality.
- The data is used to personalize your experience, offering customized suggestions, recommendations, and notifications. This might include suggestions for apps, music, or content based on your usage patterns.
- Apple shares data with third-party service providers for limited purposes, such as providing services you explicitly request. For example, if you use a payment service, Apple may share payment information with the payment provider.
- Apple uses data for system diagnostics and maintenance, aiming to improve the overall stability and functionality of its products. This includes identifying and fixing bugs and optimizing performance.
Data Protection Methods
Apple employs robust security measures to protect user data. These measures are designed to safeguard user information from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Apple utilizes end-to-end encryption to protect sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized parties can access it. This encryption technique is widely used to secure communications and transactions.
- Apple’s data centers are designed with advanced security protocols, protecting data from physical threats and unauthorized access. These protocols include physical security measures and sophisticated intrusion detection systems.
- Apple regularly updates its security practices to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps maintain a high level of data security.
User Rights
Understanding user rights regarding their personal data is essential. These rights are crucial for empowering users to control their data.
Apple’s privacy icon on iOS and macOS High Sierra, a visual cue for personal information handling, is pretty straightforward. However, checking out the new aluminum design refresh on the Acer Chromebook 15 acer chromebook 15 aluminum design refresh makes me wonder if the privacy icon needs a little visual update too. Ultimately, the core message about safeguarding personal data remains important regardless of the sleek new design choices.
| Right | Description |
|---|---|
| Access | Users can access and review the personal data Apple holds about them. |
| Correction | Users can request corrections or updates to their personal data if it is inaccurate or incomplete. |
| Deletion | Users can request the deletion of their personal data under certain circumstances. |
| Restriction | Users can restrict the use of their personal data. |
User Control over Personal Information
Apple places a strong emphasis on user control over personal information. This empowerment allows users to actively manage the data associated with their Apple devices, ensuring a high level of privacy and security. Users have numerous tools and options to safeguard their data and tailor their privacy settings to their specific needs.Understanding the various avenues for managing personal information empowers users to maintain control over their data.
This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about how their data is collected, used, and shared. Transparency in Apple’s data handling practices builds trust and allows users to make choices aligned with their privacy preferences.
Managing Personal Information on iOS and macOS
Apple provides a comprehensive suite of tools to manage personal information on both iOS and macOS. These tools allow users to easily access, modify, and delete their data. The core philosophy revolves around giving users the ability to control their personal information, a fundamental aspect of data privacy.
Accessing Personal Data
Users can access their personal data through dedicated settings on their Apple devices. Within the settings app on iOS, users can review and manage various data types, including contacts, calendar entries, and photos. macOS provides similar access points for controlling data within applications like Mail, Contacts, and Photos. Detailed descriptions of each data category are readily available within the settings menus.
Modifying Personal Data
Modifying personal data is straightforward. Users can edit contact information, update calendar events, or change preferences directly within the relevant applications. This flexibility allows users to maintain accurate and up-to-date records. Specific modification methods vary based on the type of data being altered.
Deleting Personal Data
Deleting personal data is equally simple. Users can select specific items or entire data categories for deletion within the respective applications or through the device settings. Carefully consider the implications of data deletion before proceeding. Detailed instructions are available within the device settings to guide users through the process.
Transparency in Data Collection Practices
Apple maintains a high level of transparency regarding its data collection practices. This transparency is evident in the detailed privacy policies available on Apple’s website. Users can access comprehensive information on how Apple collects, uses, and shares their data. This information is presented in a clear and understandable format. Apple’s privacy policy is regularly updated to reflect the latest advancements in technology and data protection standards.
Steps to Enhance Privacy on Apple Products
| Action | Steps |
|---|---|
| Review Privacy Settings | Navigate to the Settings app on your iOS device or System Preferences on macOS. Examine each privacy setting and adjust them to align with your privacy preferences. |
| Enable Two-Factor Authentication | Enable two-factor authentication for all accounts to add an extra layer of security to your personal information. |
| Use Strong Passwords | Create strong and unique passwords for all your accounts to protect your data from unauthorized access. |
| Limit Data Sharing | Carefully review the data sharing permissions for applications and services. Adjust settings to limit the amount of data that is shared. |
| Regularly Review Data | Periodically review the data associated with your Apple devices to ensure accuracy and identify any unnecessary information. |
Privacy Implications for Users
Apple’s approach to user privacy, while lauded by many, presents a nuanced picture for users. This section explores the potential benefits and drawbacks, highlighting how user behavior and choices impact personal data handling, and how users can actively leverage Apple’s features for enhanced digital security. It also examines the overall user experience implications of Apple’s privacy-centric design.Apple’s dedication to user privacy is a double-edged sword.
While it fosters trust and encourages responsible data handling, it also introduces complexities in the user experience, demanding a more active role from the user in managing their personal data.
Potential Benefits of Apple’s Privacy Approach
Apple’s privacy-focused design has several benefits for users. A key advantage is enhanced user trust. By prioritizing user data protection, Apple cultivates a sense of security, making users more comfortable sharing information with its services. This, in turn, encourages broader adoption and reliance on Apple’s ecosystem. Another significant benefit is the reduced risk of data breaches.
Apple’s stringent security measures and user-centric approach to privacy significantly minimize the likelihood of sensitive data falling into the wrong hands. This translates to a more secure digital environment for users.
Potential Drawbacks of Apple’s Privacy Approach
Despite the benefits, Apple’s privacy approach does present some drawbacks. A major consideration is the potential for a less seamless user experience. Certain features or services might require more explicit user input or settings adjustments, potentially leading to a more complex setup process. Another concern involves the potential for decreased functionality in certain applications or services. For example, features relying on extensive data collection, such as personalized recommendations, might be less effective or absent.
User Behavior and Data Collection, Apple privacy icon ios macos high sierra personal information
User behavior plays a critical role in shaping the collection and use of personal information. Users who are proactive in reviewing and adjusting their privacy settings can minimize the amount of data shared. Conversely, users who default to the default settings may inadvertently grant access to more data than they intend. Understanding how their actions affect data collection and use empowers users to take control of their digital footprint.
Apple’s privacy icon on iOS and macOS High Sierra, while seemingly innocuous, often raises questions about personal information. It’s a crucial element to consider when weighing your choices in smart home devices. For instance, if you’re considering an Amazon Echo Show 5 or 5, checking out 5 reasons buy Amazon Echo Show 5 and 5 not might help you understand the trade-offs.
Ultimately, how much personal data you’re willing to share with these devices is a key factor when considering your device choices. So, while the apple privacy icon may seem simple, it points to a larger conversation about data security.
Leveraging Apple’s Privacy Features for Enhanced Digital Security
Users can enhance their digital security by leveraging Apple’s privacy features. One key step is reviewing and adjusting privacy settings within applications and across the operating system. This proactive approach ensures that users grant access only to the necessary data. Actively using features like location services and advertising tracking controls can also limit the data shared with third parties.
Further, enabling two-factor authentication strengthens account security and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access.
User Experience Implications of Apple’s Privacy Settings
Apple’s privacy settings can impact the user experience in various ways. Some users may find the level of control over data sharing overwhelming or confusing. On the other hand, users who value privacy will appreciate the granular control provided. The complexity of these settings can potentially lead to a more involved setup process for new users. However, for experienced users, the control and security offered can significantly outweigh the complexity.
Furthermore, users might notice differences in the functionality of certain apps or services due to privacy restrictions.
Security and Privacy Features
Apple’s iOS and macOS operating systems are built with robust security and privacy features designed to safeguard user data from unauthorized access and misuse. These features are not isolated components but rather interconnected layers of protection, working together to create a comprehensive security architecture. This intricate system ensures that personal information remains confidential and accessible only to authorized users.
Data Encryption
Protecting sensitive data at rest and in transit is crucial. Apple employs robust encryption technologies to ensure that user information is unreadable to unauthorized parties. This encryption extends to various aspects of the operating systems, encompassing files, communications, and backups. Data is encrypted using industry-standard algorithms, making it extremely difficult to decipher without the proper decryption keys.
This is particularly important for sensitive data like financial information, passwords, and personal documents.
Access Control and Authentication
Multi-layered authentication mechanisms prevent unauthorized access to user accounts. These mechanisms include passwords, Touch ID, Face ID, and two-factor authentication. These features significantly limit the potential for unauthorized access, and the security of these systems is constantly being refined to account for emerging threats. The level of protection offered by these methods is constantly evolving to counter the sophistication of potential attackers.
Privacy-Preserving Technologies
Apple has developed innovative technologies that enhance user privacy without compromising functionality. For example, App Tracking Transparency (ATT) on iOS gives users more control over how apps collect and use their data. These features ensure that user data is collected and used in a manner that aligns with user expectations and privacy preferences. These tools empower users to make informed decisions about their data sharing practices.
Secure Communication Protocols
Apple utilizes secure communication protocols to protect user data during transmission. These protocols, like TLS (Transport Layer Security), encrypt data exchanged between devices and services. This ensures that sensitive information, such as passwords and financial details, remains confidential during transmission, and these standards are consistently updated to address emerging threats. The security of communication protocols is vital for protecting user data against eavesdropping and interception.
System Integrity Protection
System Integrity Protection (SIP) is a crucial feature designed to safeguard the operating system from malicious software. SIP prevents unauthorized modifications to core system files and processes, ensuring that the OS remains stable and secure. This system significantly reduces the risk of malware infections, which can compromise user data and potentially allow unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Summary Table of Security and Privacy Features
| Feature | iOS | macOS |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Yes (files, backups, communications) | Yes (files, backups, communications) |
| Access Control & Authentication | Touch ID, Face ID, Passwords, 2FA | Passwords, 2FA, strong password requirements |
| Privacy-Preserving Technologies | App Tracking Transparency (ATT) | Privacy-focused features in macOS versions |
| Secure Communication Protocols | TLS | TLS |
| System Integrity Protection | Yes | Yes |
Apple’s Approach to Data Sharing
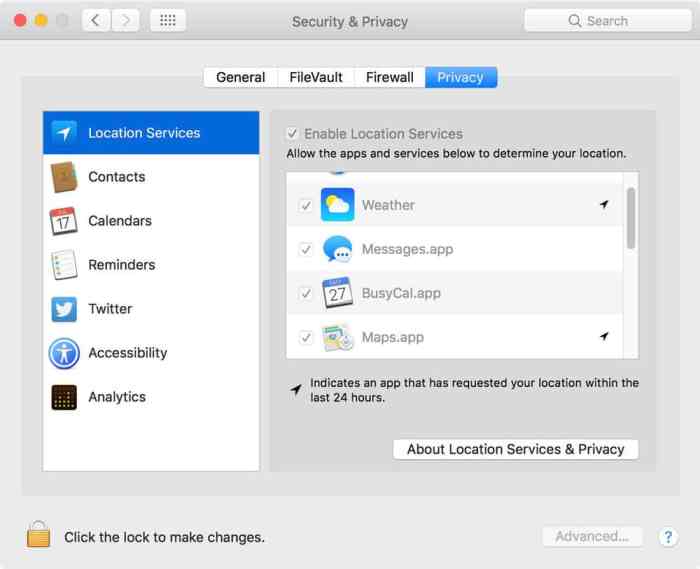
Apple prioritizes user privacy and takes a cautious approach to data sharing with third-party applications and services. This approach is designed to strike a balance between providing seamless app experiences and protecting user personal information. Transparency and user control are key components of this strategy.Apple’s policies on data sharing are carefully designed to minimize the amount of personal information shared with third parties, and to provide users with significant control over this sharing.
This is not a blanket permission to share all data; rather, specific permissions are required for each interaction.
Data Sharing Policies with Third-Party Apps
Apple’s stringent policies require explicit user consent for any data sharing with third-party applications. This is not a one-time permission, but a continuous review and adjustment process. Users retain the power to revoke these permissions at any time.
Types of Data Shared and Recipients
Apple shares only the minimum necessary data with third-party applications and services to enable functionality. This includes data like user preferences, device usage information, and location data in specific contexts. The specific recipients are determined by the app or service in question. Users can review and understand the data sharing requests within the app’s settings.
User Control over Data Sharing with Third Parties
Users have granular control over which data is shared with third parties. The ability to manage these settings is built directly into the iOS and macOS operating systems. This allows users to maintain a high level of privacy and security over their personal data. The settings are intuitive and easy to understand, with clear descriptions of the implications of each setting.
Reviewing and Adjusting Data Sharing Preferences
Users can review and adjust their data sharing preferences within the app settings. This table Artikels the process for various iOS and macOS platforms.
| Platform | Location of Settings | Process for Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
| iOS | App Settings -> Privacy -> [Specific App] | Users can toggle on or off the specific data sharing options for each app. |
| macOS | System Preferences -> Privacy & Security -> [Specific App] | Users can toggle on or off the specific data sharing options for each app. There is often a detailed explanation of what data is being shared. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Apple’s privacy initiatives, visualized by the privacy icon and deeply embedded in the iOS and macOS experience, are multifaceted. While the evolution of High Sierra’s privacy features showcases Apple’s commitment to user control, a nuanced understanding of data collection, use, and sharing is crucial. Ultimately, the benefits and drawbacks of Apple’s approach depend on individual user needs and priorities.
Understanding the various security and privacy features, and how users can effectively manage their data, empowers them to make informed choices about their digital footprint.