Trump china tariffs dhl shipment import duty fees – Trump China tariffs, DHL shipment import duty fees – this complex issue profoundly impacted global trade. The escalating trade war between the US and China, particularly the tariffs imposed by the Trump administration, significantly affected DHL’s operations, shipping costs, and procedures. This article delves into the historical context of the trade disputes, the Trump administration’s rationale behind the tariffs, their effects on DHL shipments, import duty fees, and the broader global impact.
We also examine alternative trade strategies and the impact on businesses, both US and Chinese.
Understanding the intricacies of these tariffs requires exploring the different types of tariffs imposed, the specific goods targeted, and the regulations governing imports. Analyzing the data and the impact on various sectors is key to grasping the full scope of this issue. The narrative follows the timeline of significant events and offers insightful comparisons of the impact across different industries and countries.
Historical Context of Tariffs
The ongoing trade tensions between the US and China, marked by tariffs and trade disputes, have a rich and complex history. Understanding this history provides crucial context for analyzing the current situation and potential future developments. This exploration examines the evolution of trade policies between the two nations, highlighting past trade wars, their impacts, and the diverse economic consequences.The US-China trade relationship has been characterized by periods of both cooperation and conflict.
Initially, economic engagement fostered significant growth in both countries, but this relationship has been punctuated by disagreements over trade practices, intellectual property rights, and market access. The application of tariffs has often been a central element in these disputes, impacting various sectors of the economy and global trade dynamics.
Evolution of Tariffs and Trade Policies
The application of tariffs and trade policies between the US and China has evolved over time, reflecting changing economic landscapes and geopolitical realities. Early trade interactions were characterized by lower tariffs and increasing interdependence. However, disputes arose as China’s economic power grew, leading to concerns about unfair trade practices and intellectual property theft. These concerns, coupled with broader geopolitical factors, led to escalating trade tensions.
Examples of Previous Trade Wars
Several historical trade disputes offer valuable insights into the potential outcomes and impacts of trade wars. The 1980s saw trade disputes between the US and Japan, involving similar issues of market access and unfair trade practices. These conflicts demonstrated the complexities of international trade negotiations and the potential for retaliatory actions. While the specific details differ, the underlying themes of protectionism, economic competitiveness, and geopolitical considerations resonate across historical trade disputes.
Impact on Various Sectors of the Economy
Tariffs can have significant ripple effects across various sectors of the economy. Industries reliant on imported components or raw materials can experience increased costs, potentially impacting their competitiveness and profitability. For example, manufacturers heavily dependent on Chinese imports may face higher production costs, potentially leading to reduced profits and job losses. Conversely, domestic industries that benefit from protectionist policies may see increased demand and market share.
Timeline of Significant Events
A timeline of key events provides a structured overview of the escalation of US-China trade tensions:
- 2018: Imposition of tariffs by the US on Chinese goods, leading to retaliatory measures by China. This marked a significant escalation of trade tensions, impacting global trade and market confidence. The tariffs targeted various sectors, including technology, agriculture, and consumer goods.
- 2019: Negotiations between the US and China aimed at resolving trade disputes. These negotiations, while initially successful in achieving some agreements, ultimately faced challenges and delays.
- 2020: Further escalation of trade tensions, with additional tariffs and trade restrictions imposed. The pandemic and broader geopolitical issues contributed to the complex interplay of factors influencing trade relations.
These examples illustrate the complex and multifaceted nature of trade disputes, the wide-ranging impacts on various economic sectors, and the long-term consequences of trade wars.
Trump Administration Tariffs
The Trump administration’s trade policies, particularly the imposition of tariffs on Chinese goods, were a significant aspect of its economic strategy. This approach aimed to address perceived trade imbalances and unfair practices, but its impact on the US economy and global trade relationships was multifaceted and far-reaching. The administration’s rationale, the specific goods targeted, and the ensuing consequences for consumers, businesses, and the global supply chain are detailed below.
Rationale Behind the Tariffs
The Trump administration argued that China engaged in unfair trade practices, including intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. These practices, according to the administration, resulted in a substantial trade deficit with China and hindered American businesses’ competitiveness. The tariffs were intended to level the playing field and protect American industries and jobs. The administration also cited national security concerns, believing that some Chinese goods posed a risk to US technological sovereignty.
Specific Goods Targeted
The tariffs encompassed a wide range of Chinese goods, including consumer products, industrial machinery, and agricultural products. Notable examples included smartphones, electronics, clothing, and steel. The initial tariffs were often imposed on broad categories of products, which could lead to uncertainty for businesses involved in international trade. Subsequent rounds of tariffs and exclusions were often announced with limited notice, adding complexity to the situation.
Impact on US Consumers and Businesses
Tariffs imposed on Chinese goods increased the prices of imported products for US consumers. This resulted in higher costs for everyday goods, potentially impacting consumer purchasing power. Businesses faced increased costs for materials and components, which could lead to reduced profits or price increases for their products. Some businesses shifted their supply chains to other countries to mitigate the tariff impact, while others faced significant disruptions.
Impact on the Global Supply Chain
The tariffs significantly disrupted the global supply chain, leading to delays, increased costs, and uncertainty for businesses involved in international trade. The interconnectedness of global supply chains meant that tariffs imposed on one country often had ripple effects throughout the world. Businesses that relied on components sourced from China were particularly affected. Examples of companies facing disruptions include major automotive manufacturers.
Different Types of Tariffs Imposed, Trump china tariffs dhl shipment import duty fees
The Trump administration imposed various types of tariffs, including ad valorem tariffs (a percentage of the value of the imported good) and specific tariffs (a fixed amount per unit). The combination of different tariffs added to the complexity of the trade landscape. Furthermore, the use of tariffs as a negotiating tool in trade disputes often creates uncertainty and unpredictability in international trade relations.
Effects on DHL Shipments
The Trump administration’s tariffs on Chinese goods significantly impacted global supply chains, and DHL, a major international shipping company, was directly affected. These tariffs introduced complexities and uncertainties, forcing companies to adapt and re-evaluate their logistics strategies. The following sections detail the effects on DHL’s operations.DHL’s operations experienced substantial shifts in the wake of the tariffs. Shipping costs rose as import duties and associated administrative fees increased, impacting profitability for both DHL and its customers.
Customs clearance procedures became more intricate, leading to delays in delivery times. Companies needed to adjust their strategies to navigate these challenges.
Changes in Shipping Costs and Procedures
The tariffs introduced substantial increases in the costs of shipping goods between the US and China. These increases were not uniform and varied based on the specific product and the amount imported. Companies were required to factor these additional costs into their pricing models. Customs clearance procedures also became more complex, with increased paperwork and inspections. This led to longer processing times and greater administrative burdens for DHL.
The additional costs and complexity prompted companies to seek alternative shipping routes, if possible.
Company Adjustments to Supply Chains
Companies adjusted their supply chains in response to the tariffs in various ways. Some companies sought to diversify their sourcing from countries outside of China. Others established inventory buffers to mitigate the risk of disruptions. Some firms implemented more sophisticated logistics strategies, potentially using different ports or routes to optimize their shipping strategies. Ultimately, companies sought to reduce their vulnerability to the tariff impacts and minimize delays and extra costs.
Impact on Volume of DHL Shipments
The tariffs had a noticeable impact on the volume of DHL shipments between the US and China. Some sectors experienced declines in shipments due to the higher costs and complexities. Other sectors may have shifted their sourcing or production strategies. Accurate figures on the overall volume change are difficult to pinpoint without sector-specific data.
Challenges Faced by DHL Related to the Tariffs
DHL faced several challenges due to the tariffs. The increased complexity of customs procedures led to delays and added administrative burdens for the company. Managing the varying tariff rates for different goods and maintaining compliance with constantly changing regulations required significant resources. DHL needed to adapt its internal processes to handle the increased paperwork and administrative requirements.
Companies also had to understand the complexities of the new tariffs, which included calculating the tariffs for specific goods and complying with the rules. This complexity added to the overall challenges faced by DHL.
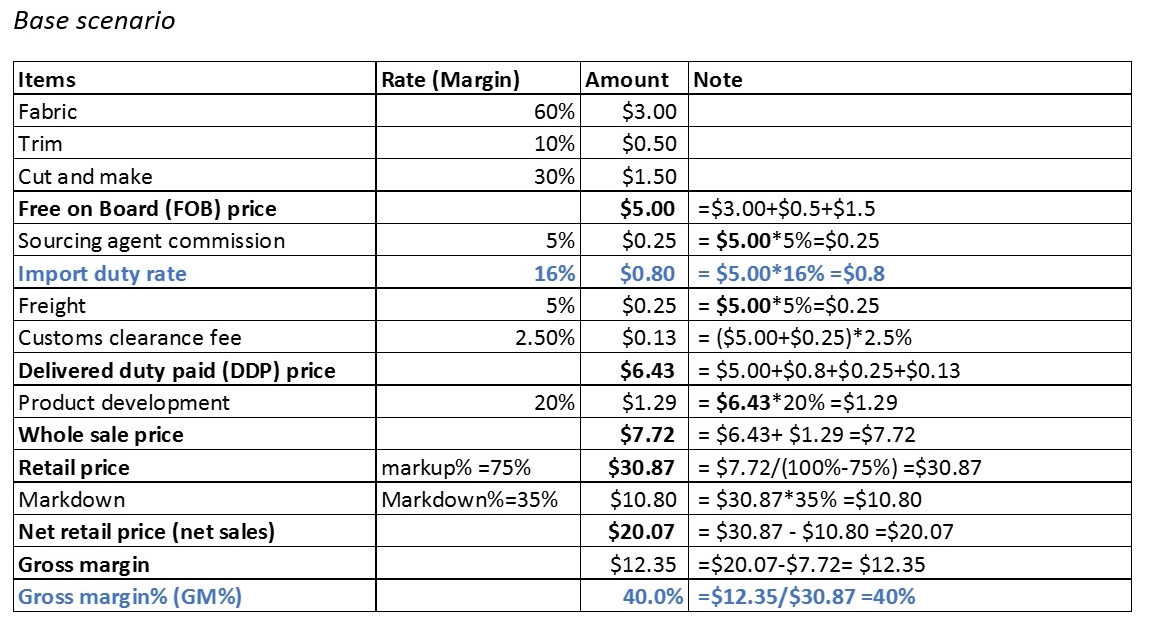
Import Duty Fees and Regulations
Navigating the intricate world of international trade often involves complex import duty fees and regulations. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses engaging in cross-border transactions, especially those impacted by trade disputes like the US-China tariffs. These regulations can significantly influence pricing, logistics, and overall profitability.The Trump administration’s tariffs on Chinese goods introduced a new layer of complexity to existing import procedures.
Companies now had to factor in not only traditional import duties but also the added costs associated with these tariffs. This inevitably led to a greater need for businesses to carefully analyze the specific import regulations for each product category.
Import Duty Fee Structure for Various Goods
Import duty fees are not uniform across all product categories. They vary based on the specific goods being imported and the applicable tariff codes. These codes, often found in the Harmonized System (HS) codes, define the characteristics of the product and thus determine the rate of duty. For instance, electronics typically attract higher tariffs than agricultural products.
- Raw Materials: Duties on raw materials, like metals or lumber, are generally lower than those on finished goods. This reflects the principle of adding value through processing.
- Consumer Goods: Import duties on consumer goods like clothing or electronics are often substantial, and rates are usually based on the level of sophistication and processing involved in the product.
- Capital Goods: These are goods used in the production of other goods, and their import duties are typically calculated considering the specific industry and technology level involved.
Regulations and Procedures for Importing Goods Subject to Tariffs
Precise adherence to import regulations is essential to avoid penalties and delays. Clear documentation and compliance with customs procedures are paramount. The process usually involves obtaining necessary licenses, declarations, and providing detailed information about the imported goods.
- Documentation: Accurate and complete documentation is critical. This includes customs declarations, invoices, and bills of lading. Failure to comply with documentation requirements can lead to delays and penalties.
- Tariff Classification: Proper classification of goods according to the Harmonized System (HS) codes is essential for accurate duty calculations.
- Origin Verification: Proof of origin, particularly relevant in cases of tariffs based on country of origin, is needed to ensure the proper application of import duties.
Comparison of Import Duty Fees Across US-China Trade Sectors
The impact of tariffs varied across different US-China trade sectors. A table illustrating the potential difference in duty fees is presented below. This demonstrates the need for a nuanced understanding of tariff impacts based on specific product categories.
| Trade Sector | Typical Import Duty Rate (pre-tariff) | Tariff Rate Applied (e.g., Trump era) |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | 5-10% | 25% |
| Machinery | 2-8% | 10-25% |
| Textiles | 3-7% | 15-20% |
| Agricultural Products | 1-5% | 10-25% |
Categories of Import Duties
Import duties can be categorized in several ways. Understanding these classifications helps in grasping the overall structure of import regulations.
- Ad Valorem Duties: These duties are calculated as a percentage of the value of the imported goods. This is the most common type.
- Specific Duties: These duties are based on the physical quantity of the imported goods (e.g., per kilogram).
- Compound Duties: These combine both ad valorem and specific duties, applying both methods to the import.
Factors Determining Import Duty Fees
Several factors influence the calculation of import duty fees. A deeper understanding of these factors is vital for businesses to prepare effectively.
- Tariff Codes: The specific HS code assigned to the imported goods is crucial as it determines the applicable duty rate.
- Country of Origin: Country-specific tariffs, particularly in cases of trade disputes, can significantly affect the final duty.
- Product Characteristics: The level of processing, sophistication, and material composition of the product directly impacts the duty rate.
Global Impact of the Tariffs
The Trump administration’s tariffs on Chinese goods had far-reaching consequences, impacting not only the US and China but also the global economy. These measures significantly altered international trade patterns, leading to supply chain disruptions and price fluctuations across various sectors. The ripple effects were felt by businesses, consumers, and governments worldwide.The tariffs imposed by the United States on Chinese goods, particularly during the 2018-2020 period, aimed to reduce the US trade deficit and protect American industries.
However, the consequences extended beyond the direct participants, affecting the global economy in complex and often unforeseen ways. Understanding these broader effects requires examining the impact on different countries and industries, as well as the overall long-term implications for international trade.
Trump’s China tariffs and the resulting import duty fees on DHL shipments are definitely impacting businesses. Navigating these complexities is crucial, but so is protecting your online privacy. A good way to do that is by using a browser like Samsung Internet’s Android mobile tracking blocker, which offers excellent privacy features. samsung internet android mobile tracking blocker privacy Ultimately, these import fees are still a headache, but understanding digital privacy tools can help balance the economic challenges.
Ripple Effects on Other Countries
The tariffs’ impact wasn’t confined to the US and China. Other countries experienced various consequences, often indirectly. For example, companies in Southeast Asian countries that relied on the Chinese supply chain for components saw reduced exports to the US, and a decrease in overall business. This highlights the interconnectedness of global trade, and how a single action can have widespread effects on the world economy.
Responses from Other Countries
Several countries responded to the US tariffs in various ways. Some retaliated with tariffs on US goods, aiming to protect their own industries and maintain favorable trade balances. Others sought alternative trading partners and diversified their supply chains. These reactions demonstrate the complex interplay of global economic interests and the challenges of navigating international trade disputes.
Impact on Different Industries
The tariffs’ effects varied across industries. Industries heavily reliant on imported Chinese components, such as electronics and manufacturing, experienced increased production costs and reduced competitiveness. The automotive industry, for example, saw significant disruptions in the supply of parts, impacting production schedules and potentially leading to higher prices for consumers. The agricultural sector was also affected, with farmers facing decreased demand for their products in certain markets.
Long-Term Effects on the Global Economy
The long-term effects of the tariffs are still being assessed. The disruptions to global supply chains and the uncertainty surrounding trade relationships could potentially lead to reduced economic growth and increased trade barriers. Furthermore, the tariffs’ impact on consumer prices remains a critical area of analysis, as higher costs can impact purchasing power and overall economic activity. The tariffs’ impact on the global economy, while complex and multi-faceted, could lead to significant changes in global trade patterns and market dynamics.
The ultimate impact will depend on future trade policies and global economic conditions.
Impact on Businesses
The Trump administration’s tariffs on Chinese goods significantly impacted businesses across the US and China. These tariffs, intended to protect American industries and jobs, had a ripple effect, altering supply chains, pricing strategies, and market dynamics. Understanding the nuanced impacts on businesses of varying sizes, and the strategies they employed to navigate these changes, is crucial for evaluating the long-term effects of such trade policies.
Impact on US Businesses Importing from China
US businesses reliant on Chinese imports faced increased costs due to tariffs. These added expenses were often passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. Companies experienced disruptions in their supply chains as they sought alternative sourcing or negotiated contracts with Chinese suppliers. The search for alternative suppliers introduced new complexities and logistical challenges. For smaller businesses, these challenges could be particularly daunting.
Impact on Chinese Businesses Exporting to the US
Chinese businesses exporting to the US faced a reduction in demand as tariffs increased the cost of their products for American consumers. This led to a decline in sales and profitability for many Chinese companies. Some Chinese exporters adapted by seeking alternative markets, which involved significant effort in establishing new distribution networks and adapting their products to meet differing regulatory standards.
Impact on Businesses of Different Sizes
The impact of tariffs varied significantly based on business size. Larger corporations often had greater financial resources to absorb increased costs and diversify their supply chains. They could potentially negotiate better terms with suppliers and explore alternative markets. Smaller businesses, lacking the same financial resources, often struggled to adapt to the changes. They faced a higher risk of closure due to increased costs and reduced sales.
Strategies Businesses Used to Mitigate the Effects of Tariffs
Businesses employed several strategies to mitigate the impact of tariffs. These included diversifying their supply chains, finding alternative sources for imported goods, and exploring new markets beyond the US and China. Negotiating lower prices with existing suppliers, or shifting production locations to reduce costs were also common strategies. In some cases, businesses even shifted product lines to better match market demands and to avoid tariffs.
Examples of How Businesses Adapted to the Changing Trade Environment
Numerous businesses adapted to the changing trade environment. Some companies shifted production to countries with lower tariffs or no tariffs, while others adjusted their product offerings to avoid tariffs or to capitalize on lower-cost sourcing options. For instance, some electronics manufacturers moved production to Southeast Asian countries, while others modified their product designs to avoid tariffs on certain components.
These adaptations demonstrate the resilience and adaptability of businesses in the face of changing trade policies.
Alternative Trade Strategies
The escalating trade tensions between the US and China, fueled by tariffs and import duties, highlight the need for alternative trade strategies. These strategies must address the underlying issues causing friction while fostering mutually beneficial relationships. Finding common ground and establishing fair trade practices are crucial for long-term economic prosperity for both nations and the global economy.
Alternative Trade Strategies for the US
The US can diversify its supply chains to reduce reliance on specific countries, particularly China. This diversification could involve exploring new trading partners and fostering stronger economic ties with nations in Southeast Asia, South America, and other regions. Strengthening domestic manufacturing capabilities through investments in infrastructure and research and development is another vital step. This will not only create jobs but also increase resilience in the face of global economic shifts.
Negotiating new trade agreements that address intellectual property rights, labor standards, and environmental protection is also crucial for ensuring a level playing field.
Alternative Trade Strategies for China
China can explore opportunities to further integrate its economy into global value chains while ensuring fair competition and adherence to international trade norms. This might involve greater transparency in its trade practices, along with further opening up its markets to foreign investment and goods. Focusing on technological advancements and innovation, while maintaining a commitment to sustainable development, will allow China to further its global standing and competitiveness.
China can also seek to resolve trade disputes through constructive dialogue and negotiations, emphasizing mutual respect and understanding.
Resolving Trade Disputes
Resolving trade disputes requires a commitment to dialogue and diplomacy. Negotiation and mediation can facilitate the identification of common ground and the development of mutually acceptable solutions. International arbitration can provide a neutral platform for resolving disagreements and enforcing agreements. International organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), play a vital role in facilitating the process, providing a framework for rules and dispute resolution.
Role of International Organizations in Addressing Trade Issues
International organizations, such as the WTO, offer a platform for nations to discuss and resolve trade disputes through established rules and regulations. The WTO provides a forum for negotiations, dispute settlement, and monitoring of trade policies. The organization acts as a neutral arbiter, aiming to ensure fair and equitable trade practices among its members. It also fosters cooperation and understanding among nations through dialogue and the sharing of best practices.
Examples of Alternative Trade Agreements
Numerous examples of alternative trade agreements exist, each with its own focus and structure. Regional trade agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), aim to reduce trade barriers among participating countries. These agreements can create a more integrated and efficient trading environment, fostering economic growth and stability. Bilateral trade agreements, focusing on specific trade issues between two nations, also play a significant role in promoting trade relations and addressing concerns.
Such agreements can address specific areas of concern and potentially lead to broader cooperation.
Methods for Promoting Fair and Stable Trade Relations
Promoting fair and stable trade relations requires a commitment to transparency, accountability, and mutual respect. This includes clearly defined rules and regulations, along with transparent dispute resolution mechanisms. Encouraging open communication and dialogue between trading partners is essential. Implementing effective enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance with trade agreements and fostering a culture of trust and cooperation are also crucial steps.
Furthermore, supporting international institutions that promote fair trade practices, such as the WTO, is essential.
Illustrative Examples
The Trump administration’s tariffs on Chinese goods had a profound impact on various sectors, from individual consumers to multinational corporations. Understanding the tangible effects requires examining specific examples that demonstrate the ripple effect through the supply chain and the resulting economic shifts. These examples highlight the complexities and unintended consequences of trade policies.
Ugh, those Trump-era China tariffs are still impacting DHL shipment import duty fees, aren’t they? It’s a real headache trying to figure out the new costs. Luckily, Amazon just had their big event, announcing some exciting new products and updates on their Alexa Echo line, which might have some surprisingly helpful tools for navigating global trade complications.
Hopefully, some of these new innovations will help streamline the whole process and make international shipping more predictable for everyone, including those pesky import duty fees.
Cost Increases for Specific Products
Tariffs added a significant layer of expense to imported goods, impacting consumer prices. This section illustrates the price hikes on specific products due to the tariffs.
| Product | Pre-Tariff Price (USD) | Post-Tariff Price (USD) | Tariff Increase (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | 800 | 950 | 150 |
| Clothing | 50 | 65 | 15 |
| Electronics | 200 | 250 | 50 |
| Toys | 15 | 20 | 5 |
Note that these are illustrative examples and actual price changes varied depending on specific product models, import channels, and other factors. The tariffs added a substantial cost burden to consumers, which was often passed on through higher retail prices.
Case Study: Company Supply Chain Adjustment
One example of a company adapting to the tariff environment was a major retailer that sourced electronics from China. Facing increased import costs, the company had to evaluate different sourcing options, including shifting some manufacturing to other countries, such as Vietnam or India. This led to increased logistics and transportation costs. Moreover, the retailer had to absorb a portion of the tariff costs, potentially affecting its profit margins and pricing strategies.
Those pesky Trump-era China tariffs sure threw a wrench in things, didn’t they? DHL shipments were getting hit hard with import duty fees, and it all felt like a real headache. But hey, at least I could find some pretty cool Sony PlayStation VR photos online to distract me from the financial woes sony playstation vr photos – and maybe even inspire some creative VR gaming ideas.
Still, those tariffs were a major pain point for international shipping, and it seems like we’re still dealing with the ripple effects today.
Impact on Consumer Prices
Tariffs led to increased prices for a broad range of consumer goods. Consumers directly felt the impact through higher prices at retail stores. This was particularly evident in sectors heavily reliant on imported components or raw materials. For example, the price of certain types of furniture increased due to the tariffs on the wood and metal components imported from China.
Similarly, the cost of electronics and apparel also rose significantly.
Effects on the Global Supply Chain
The tariffs disrupted the global supply chain by creating uncertainty and volatility. A key example was the automotive industry, which saw a decrease in the supply of certain components. This led to production delays and shortages in some models, highlighting the interconnected nature of global trade. Further, manufacturers had to consider the tariffs in their production and distribution strategies, which could result in a shifting of manufacturing operations from one country to another.
Case Study: Company Negatively Impacted by Tariffs
A large US-based consumer goods manufacturer relied heavily on Chinese suppliers for its key components. The tariffs significantly increased their production costs. As a result, they were forced to raise prices for their products, potentially losing market share to competitors with more affordable alternatives. This company also considered relocating part of its manufacturing to other countries to mitigate the impact of the tariffs.
This example demonstrates the substantial financial pressure tariffs could impose on companies.
Data Representation: Trump China Tariffs Dhl Shipment Import Duty Fees

The intricacies of the Trump administration’s tariffs on Chinese goods and their ripple effects on global trade demand a clear and concise visual representation. Understanding the shifts in import volumes, the distribution of tariffs across different product categories, and the impact on shipping costs is crucial for grasping the full extent of this economic policy. This section utilizes graphs, charts, and other visualizations to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of these complex dynamics.
Import Volume Changes Over Time
Visualizing the change in import volumes over time helps to understand the direct impact of the tariffs. A line graph would be ideal. The x-axis would represent time, spanning the period before, during, and after the implementation of the tariffs. The y-axis would depict the volume of imports in a specific unit (e.g., millions of USD). The graph would clearly show any significant fluctuations in import volumes correlating with the introduction and adjustments of tariffs.
This visual representation would highlight periods of sharp declines or increases, providing insights into the responsiveness of the market to these trade policies.
Tariff Distribution Across Product Categories
A pie chart or a bar graph effectively displays the distribution of tariffs across various product categories. The size of each slice or bar would represent the percentage of tariffs applied to that specific product category. This visualization would reveal which sectors were most affected by the tariffs, allowing for an analysis of the impact on specific industries.
For example, a large slice corresponding to consumer electronics would indicate a substantial impact on that sector. The chart would be highly informative for understanding the overall impact on different segments of the global economy.
Impact on DHL Shipping Costs
A scatter plot would effectively illustrate the impact of tariffs on DHL shipping costs. The x-axis would represent the value of shipments, while the y-axis would depict the corresponding shipping costs. Different colored markers could be used to represent shipments before, during, and after the implementation of the tariffs. The scatter plot would visually show any noticeable increases in shipping costs that might correlate with the imposition of tariffs.
This visualization would highlight the indirect consequences of trade policies on logistics and supply chains.
Comparative Analysis of Tariffs Across Different Years
A table comparing tariff rates across different years would allow for a detailed comparison. Columns would represent specific years, while rows would list the relevant tariff rates for different product categories or overall import volumes. This table format would make it easy to spot trends and changes in tariff rates over time. This analysis would help to determine whether tariff rates increased, decreased, or remained constant during different periods.
Tariff Rate Trend Over a Specific Period
A line graph would effectively display the trend of tariff rates over a specific period. The x-axis would represent time, and the y-axis would represent the tariff rate. The line on the graph would visually represent the changes in tariff rates over time. This visualization would clearly highlight the fluctuating nature of the tariff rates during the period under review.
Such a graph would reveal patterns and trends in the tariff rates over the given timeframe, including any significant spikes or declines.
Final Review
In conclusion, the Trump China tariffs had far-reaching consequences, altering the global landscape of trade. DHL, as a key player in international shipping, experienced significant changes in operations and costs. Businesses faced substantial adjustments, and consumers bore the brunt of higher prices. This examination of the historical context, the impact on DHL, import duties, and global ramifications offers valuable insights into the complexities of international trade disputes and the need for alternative, more stable trade strategies.











