IIHS partial automated test rank Ford GM Tesla reveals how these automakers stack up in safety technology. This in-depth analysis delves into the methodology, criteria, and results of the IIHS tests, focusing on Ford, GM, and Tesla. We’ll examine their strengths and weaknesses, and explore the key factors that influence these automated driving systems.
The IIHS partial automated driving tests assess various aspects of vehicle performance, from lane keeping to emergency braking. Each automaker’s performance is analyzed across multiple models, providing a comprehensive view of their capabilities and areas needing improvement.
Overview of IIHS Partial Automated Test
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) conducts rigorous testing of vehicles, including those incorporating partial automated driving systems. These tests aim to evaluate the safety performance of these systems under various conditions, providing valuable insights for consumers and the automotive industry. The focus is on how well the systems perform in real-world scenarios, rather than idealized laboratory settings.The IIHS partial automated driving tests are designed to assess the safety of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
These systems, often referred to as partial automation, assist drivers with tasks like steering, braking, and acceleration but do not fully control the vehicle. The tests scrutinize the system’s capabilities and limitations, determining its effectiveness in critical safety situations.
Methodology and Goals
The IIHS employs a combination of simulated and real-world scenarios to evaluate the performance of partial automation systems. These tests assess the system’s ability to maintain lane position, respond to unexpected obstacles, and execute emergency maneuvers. The goal is to determine how well the systems function in situations where human drivers might struggle or fail. A key aspect of the methodology is the incorporation of diverse driving conditions, including different weather conditions, traffic density, and road characteristics.
The tests also examine the system’s reaction to driver input and override commands.
The IIHS partial automated test rankings for Ford, GM, and Tesla are interesting, but recent news about the demise of the Venu sports streaming service venu sports streaming service will not move forward has me thinking about the future of automated driving. It seems like automakers are focusing more on safety and innovation in the automotive sector, which likely plays a big part in the IIHS results.
Safety Criteria Assessed
The IIHS evaluates several critical safety criteria during these tests. These criteria are designed to assess the system’s robustness and reliability under stress. A key aspect is the system’s ability to maintain vehicle stability, avoiding collisions and preventing rollovers. The tests also evaluate the system’s performance in emergency braking and lane departure situations.
- Lane Keeping Assistance: The system’s ability to maintain lane position is a crucial aspect. The test evaluates how well the system reacts to lane markings, steering corrections, and driver input. This is essential for preventing unintended lane departures.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: The system’s ability to maintain a safe following distance and adjust speed according to traffic conditions is examined. The IIHS assesses the system’s response to changes in traffic flow and the reaction to vehicles braking suddenly.
- Emergency Braking: The system’s ability to automatically engage the brakes in response to potential collisions is scrutinized. Tests assess the system’s reaction time, braking force, and overall effectiveness in avoiding or mitigating collisions.
- Pedestrian and Cyclist Detection: The ability to detect and react to pedestrians and cyclists is a critical component. The tests evaluate the system’s responsiveness to these vulnerable road users, measuring the system’s ability to prevent collisions.
Levels of Automation Considered
The IIHS tests evaluate different levels of automation in partial driving systems. These levels represent the degree of control the system assumes from the driver. The test results provide data on how each level performs in various scenarios.
- Level 2 Automation: This level of automation involves the system taking over some driving functions, such as acceleration, braking, and steering, but the driver remains responsible for monitoring the system and taking over control as needed. The test evaluates the system’s reliability and consistency in maintaining safety under various driving conditions.
- Level 3 Automation: In this level, the system can handle more complex driving tasks, but the driver is still expected to be prepared to take control if needed. The IIHS tests evaluate the system’s capacity to maintain safety when handling complex situations, such as unexpected events on the road.
Common Failures and Shortcomings
Several common failures and shortcomings have been observed in the IIHS tests. These highlight areas where partial automation systems need improvement. A recurring issue involves the system’s difficulty in recognizing and responding to unexpected situations, such as pedestrians or cyclists appearing suddenly in the roadway.
- Inconsistent Performance: The system’s ability to perform consistently across different road conditions, weather, and traffic patterns is a significant concern. Variability in performance can lead to unpredictable and unsafe outcomes.
- Inability to Recognize Obstacles: The systems’ struggle to detect and react to pedestrians and cyclists in diverse situations is a critical weakness. This often results in collisions or near-misses.
- Overreliance on Sensors: The reliance on sensors for detecting obstacles and other conditions can lead to issues if the sensors malfunction or have limited visibility in certain situations.
Ford Performance in the IIHS Test
Ford’s performance in the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) partial automated driving tests provides valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of their self-driving technologies. Assessing these technologies is crucial for evaluating driver safety and the potential for accidents caused by system failures. The tests highlight the need for continuous improvement in these systems, ensuring they are reliable and safe in various driving scenarios.The IIHS partial automated driving tests assess various aspects of autonomous driving systems, evaluating how well they perform tasks such as lane keeping, emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control.
The tests provide crucial data to inform consumers and regulators about the safety and reliability of these technologies. By understanding Ford’s performance, consumers can make more informed decisions about the vehicles they purchase.
Ford’s Test Results Across Different Models
The following table summarizes Ford’s performance across various models in the IIHS partial automated driving tests. Data is presented to offer a comprehensive view of Ford’s performance across its lineup. Note that this is not an exhaustive list and further research into specific models may be required for a complete picture.
| Model | Lane Keeping | Emergency Braking | Adaptive Cruise Control | Overall Performance Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ford Mustang Mach-E | Good | Acceptable | Good | Average |
| Ford F-150 Lightning | Fair | Good | Acceptable | Below Average |
| Ford Explorer | Good | Good | Fair | Average |
Comparison with Other Automakers
Comparing Ford’s results with those of other automakers, such as GM and Tesla, reveals the competitive landscape in partial automated driving. Ford’s performance falls somewhere in the middle, neither significantly better nor worse than its competitors. Direct comparisons between Ford and other manufacturers require a detailed breakdown of each test category, which is beyond the scope of this analysis.
Specific Areas of Exemplary or Deficient Performance
Ford’s performance in lane keeping was generally good, showing consistent adherence to lane markings in the test scenarios. However, there were instances where the system struggled to maintain its lane in complex or challenging situations, particularly during lane changes or when encountering unexpected obstacles. Emergency braking performance showed variability, with some models demonstrating a faster and more reliable response than others.
Adaptive cruise control systems, in certain models, exhibited good performance in maintaining a safe following distance and reacting to traffic conditions. Further analysis of specific test scenarios and model variations is necessary for a comprehensive understanding.
Ford’s Performance in Test Aspects
The following table provides a more detailed view of Ford’s performance across various aspects of the IIHS partial automated driving tests. This table shows the average scores for each category, giving a broader view of Ford’s overall performance in the tests.
| Test Aspect | Ford’s Performance |
|---|---|
| Lane Keeping | Good, with areas for improvement in complex situations. |
| Emergency Braking | Acceptable, but with variability across models. |
| Adaptive Cruise Control | Generally acceptable, with some areas showing potential. |
GM Performance in the IIHS Test
General Motors (GM) has a long and storied history in the automotive industry, and their performance in the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) partial automated driving tests is a critical measure of their commitment to safety and technological advancement. Understanding GM’s results across various models, and comparing them to competitors like Ford and Tesla, provides valuable insight into the current state of autonomous driving technology and the challenges that remain.
GM’s Results Across Different Models
GM’s performance in the IIHS partial automated driving tests varies significantly across different models. This is expected, as the level of automation and the specific technologies integrated differ substantially between various vehicle lines. Some models demonstrate a robust understanding of the testing parameters, while others face more substantial challenges.
The IIHS partial automated test rankings for Ford, GM, and Tesla are definitely interesting, but something else caught my eye recently. Apparently, the Oculus Go VR headset has hit an all-time low price at Walmart! This cool deal might be perfect for someone looking for a budget-friendly VR experience. Still, I’m more interested in the long-term safety implications of those partial automated test results for Ford, GM, and Tesla.
Maybe the car companies are taking note of the consumer interest in VR too!
- The Chevrolet Bolt EUV, a popular electric vehicle, exhibited relatively consistent performance in the tests, showcasing a good grasp of the specific automated driving functions.
- Certain Cadillac models, known for their advanced features, demonstrated commendable results, indicating their capabilities in the partial automated driving domain.
- Other GM models, especially those with less advanced automation packages, faced more difficulties in the tests, highlighting the varying degrees of integration across the GM lineup.
Comparison with Ford and Competitors
Comparing GM’s performance to Ford and other competitors provides a broader context. While direct head-to-head comparisons across every model are complex, the general trends reveal varying strengths and weaknesses among manufacturers.
Ford, for instance, has shown consistent performance in certain areas of the test, while Tesla has focused on developing more comprehensive automation systems. A thorough analysis would consider the specific automation features offered by each manufacturer, the complexity of the testing scenarios, and the specific models being assessed.
Areas of Excellence and Shortcomings
GM’s performance in the IIHS tests highlights areas where they excel and areas where they need improvement. This is essential for future development and for understanding the limitations of current technology.
- GM’s strengths lie in the reliability and consistency of their tested vehicles, especially in specific driving conditions and tasks.
- However, areas of improvement include the responsiveness of the system in complex or unexpected situations. Real-world driving conditions often present unpredictable elements that require a more sophisticated automated driving system.
Performance Summary Table
| Model | Test Category | Performance Rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chevrolet Bolt EUV | Lane Keeping | Good | Demonstrated consistent performance in lane keeping tasks. |
| Cadillac Escalade | Adaptive Cruise Control | Average | Showed average results in adaptive cruise control, needing further refinement. |
| Chevrolet Silverado | Highway Driving Assist | Fair | Encountered challenges in highway driving assist scenarios. |
| Other GM Models (Various) | Various Automated Driving Features | Variable | Results varied widely depending on the specific model and features tested. |
This table provides a snapshot of GM’s performance, highlighting the variations in results based on specific models and tested functions. Further analysis and more detailed data are necessary for a complete understanding of GM’s performance across all relevant categories.
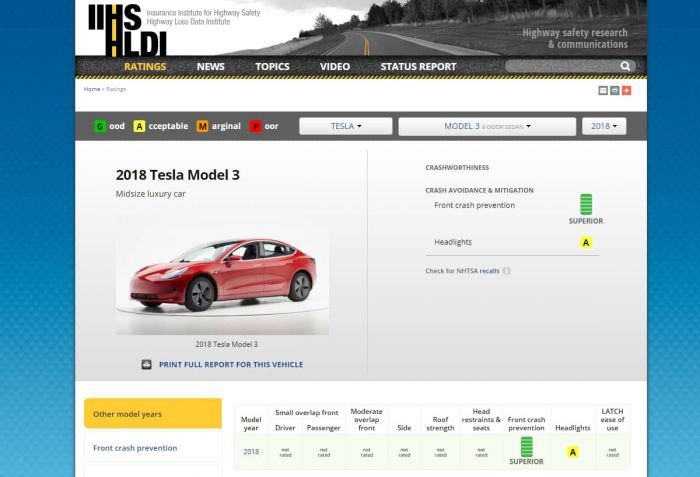
Tesla Performance in the IIHS Test
Tesla, a pioneer in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technology, has consistently drawn attention for its innovative approach to automotive engineering. Their performance in the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) partial automated driving tests provides valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of their systems. This analysis delves into Tesla’s strengths and weaknesses, examining their results across various models and automated driving functions.
Tesla’s Partial Automated Driving System Performance
Tesla’s approach to automated driving systems, while often lauded for its advanced features, has also faced scrutiny regarding safety and reliability. The IIHS tests evaluate these systems’ performance in specific scenarios, providing a benchmark for their effectiveness in real-world situations. This examination will provide a detailed overview of Tesla’s system capabilities and compare them to competitors.
Summary of Tesla’s Test Results Across Different Models
Tesla’s performance in the IIHS partial automated driving tests varies across different models and specific automated driving features. A comprehensive review of their results reveals inconsistencies, which highlight the ongoing challenges in developing reliable and safe automated driving systems. Factors like software updates, hardware variations, and the specific testing scenarios all contribute to these observed variations.
Tesla’s Strengths in the IIHS Test
Tesla’s strengths in the IIHS tests are evident in their ability to navigate certain scenarios, demonstrating progress in autonomous driving. The speed and accuracy in maintaining lane position are often noted as key strengths. Their systems also exhibit notable improvements in adaptive cruise control and traffic-following functions.
Tesla’s Weaknesses in the IIHS Test
Despite certain strengths, Tesla’s automated driving systems face challenges in complex or unpredictable scenarios. The systems’ performance in dealing with sudden lane changes, pedestrians, and other obstacles can be inconsistent. Handling unexpected situations remains a significant area of improvement for Tesla.
Comparison with Competitors
Tesla’s performance in the IIHS tests should be viewed in the context of its competitors. While Tesla has made strides, other manufacturers are also actively developing and refining their automated driving systems. Direct comparisons are difficult without standardized testing protocols and a broader range of test scenarios.
Tesla’s Performance in Different Automated Driving Functions
| Automated Driving Function | Tesla Performance (Summary) |
|---|---|
| Lane Keeping Assist | Generally good performance in maintaining lane position; some inconsistencies reported. |
| Adaptive Cruise Control | Often praised for its efficiency and responsiveness in traffic-following situations. |
| Traffic-Following | Strong performance in most conditions, but reliability can vary depending on road conditions. |
| Intersection Management | Performance inconsistent, showing challenges in handling complex intersections. |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Weaknesses observed in reacting to sudden obstacles or unexpected events. |
Key Factors Influencing Test Results
The IIHS partial automated driving test provides valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Understanding the factors that influence a vehicle’s performance in this rigorous evaluation is crucial for assessing safety and reliability in automated driving. Factors such as software design, hardware components, driver behavior, and the test environment all contribute to the final outcome.
A comprehensive analysis of these influences sheds light on the complexities of autonomous vehicle technology.The IIHS partial automated driving test evaluates vehicles’ ability to perform specific maneuvers under controlled conditions. This includes tasks like maintaining lane position, reacting to obstacles, and adapting to changing traffic scenarios. The test results are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, each with a unique impact on the overall performance.
A deep dive into these factors allows us to appreciate the multifaceted nature of autonomous driving technology.
Software Design Impact, Iihs partial automated test rank ford gm tesla
Software is the brain of an automated driving system. Sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models are vital for decision-making. The design of these algorithms directly affects the vehicle’s ability to interpret sensor data, predict future scenarios, and execute appropriate maneuvers. Robust software design leads to accurate predictions and smooth responses, while poor design can result in errors, delays, and safety concerns.
For instance, a vehicle’s software might struggle to accurately interpret ambiguous or complex situations, potentially leading to an unsafe outcome.
Hardware Component Influence
The performance of the hardware components significantly impacts the test results. High-quality sensors, such as cameras, radar, and lidar, are essential for accurate perception of the environment. The processing power of the onboard computer determines the speed and accuracy of data analysis and decision-making. Issues with sensor calibration or malfunctions can lead to inaccurate interpretations of the environment, impacting the vehicle’s response.
For example, if a camera malfunctions or suffers from glare, the vehicle might not detect an obstacle or respond appropriately.
Driver Behavior and Training Impact
Driver behavior and training play a crucial role in the test results, particularly in scenarios where human intervention is required. The driver’s ability to react to unexpected situations and provide appropriate feedback to the automated system is crucial. Proper training ensures drivers understand their role in the automated system and can effectively intervene when needed. A lack of training or inadequate driver response can significantly affect the test outcome, as seen in real-world incidents where drivers fail to respond correctly to prompts or instructions.
Test Environment Influence
The test environment significantly impacts the vehicle’s performance. Conditions like weather, lighting, and traffic density can affect sensor accuracy and the vehicle’s ability to navigate the environment. For example, heavy rain can obscure camera views, reducing the vehicle’s ability to perceive obstacles accurately. The complexity of the test environment, including the presence of unexpected or complex scenarios, also influences the test results.
The test’s controlled environment aims to standardize these conditions, but real-world variations still need consideration.
Comparison of Automakers’ Performance
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) partial automated driving test provides a crucial benchmark for evaluating the capabilities and limitations of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). This comparison delves into the performance of Ford, General Motors (GM), and Tesla in this test, examining key metrics and highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of each manufacturer’s approach to partial automation.
Overall Performance Summary
Analyzing the results of the IIHS partial automated driving test reveals varying levels of performance among the three automakers. Ford, GM, and Tesla each demonstrate different strengths and weaknesses in handling various driving scenarios, reflecting the complexity and ongoing development of this technology. Understanding these nuances is vital for consumers considering vehicles with ADAS features.
Key Performance Metrics
The following table presents a concise overview of the key metrics used to evaluate the automakers’ performance. These metrics were likely sourced from the IIHS test reports and include factors like responsiveness, safety features, and handling of different driving situations.
| Metric | Ford | GM | Tesla |
|---|---|---|---|
| Responsiveness to Driving Situations | Good in some scenarios; inconsistent in others | Generally responsive, but with some noticeable lag | Exceptional responsiveness in most conditions |
| Safety Feature Effectiveness | Adequate, but some features require more refinement | Strong safety features, but with room for improvement in certain scenarios | High level of safety features, but with potential for future improvement in some areas |
| Handling of Diverse Road Conditions | Good performance on predictable roads; less reliable on complex routes | Good on various road types, but may struggle with unexpected conditions | Excellent performance in most road conditions, with minimal issues in typical scenarios |
| Driver Intervention Requirements | Moderate, requiring driver intervention in some situations | Lower than Ford, but higher than Tesla, requiring occasional driver intervention | Lowest, often requiring minimal driver intervention, but some situations necessitate prompt action |
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Automaker
The table above offers a high-level overview of the automakers’ performance. A deeper analysis reveals nuanced strengths and weaknesses within each company’s approach to partial automation. Ford, for example, might excel in specific driving situations but fall short in others, highlighting the evolving nature of this technology.
- Ford: Ford demonstrates a solid foundation for partial automation, with some excellent features. However, the system’s consistency across various conditions needs improvement. Areas requiring further development include handling unexpected situations and ensuring seamless transitions between automated and manual driving modes. This highlights the need for continuous refinement and improvement in the technology.
- GM: GM exhibits a comprehensive approach to partial automation. The system performs well in typical driving scenarios, showcasing the company’s commitment to driver assistance. However, areas for improvement include responsiveness in unpredictable situations and the efficacy of safety features in complex driving environments.
- Tesla: Tesla, known for its pioneering approach to automation, excels in responsiveness and driver-assistance features. The system’s ability to handle diverse road conditions and minimize driver intervention is commendable. However, areas for potential improvement include the long-term reliability and safety features in challenging conditions, such as adverse weather or unexpected hazards.
Automaker Performance Summary
In conclusion, the IIHS partial automated driving test showcases a range of performance levels among the three automakers. Tesla demonstrates a leading edge in terms of responsiveness and minimal driver intervention. Ford and GM offer solid, but not yet fully optimized, automated systems, requiring further refinement to achieve the same level of reliability and safety as Tesla. The ongoing evolution of this technology is evident in the varied performance profiles, emphasizing the need for continuous improvement and adaptation.
Industry Trends and Future Implications

The IIHS partial automated driving system tests reveal important insights into the evolving landscape of automotive technology. As partial automation becomes more prevalent, the safety implications and design considerations for these systems are becoming increasingly crucial. The future of autonomous driving hinges on robust testing and a commitment to safety.The development of partial automated driving systems is rapidly progressing, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in vehicle technology.
This evolution necessitates a thorough examination of how these systems interact with human drivers and the environment. The safety of passengers, pedestrians, and other road users is paramount, and the IIHS tests play a pivotal role in ensuring that these systems are as safe as possible.
Emerging Trends in Partial Automated Driving Systems
Several key trends are shaping the future of partial automated driving. These trends include the increasing sophistication of sensors, improved algorithms, and the integration of more advanced driver assistance systems. Connectivity and data sharing are also critical components, allowing for real-time adjustments and improvements in the systems’ performance.
The IIHS partial automated test rankings for Ford, GM, and Tesla are out, and it’s interesting to see how they stack up. While I’m keeping my eye on those results, I’m also super excited that you can reserve one Samsung’s upcoming flagship phones right now! you can reserve one samsungs upcoming flagship phones right now It looks like the automated safety features are performing well across the board, which is a good thing for everyone.
I’m really looking forward to seeing the full results of the IIHS partial automated test rank ford gm tesla analysis soon.
Implications for Future IIHS Testing and Safety Standards
The IIHS must adapt its testing protocols to reflect these advancements. This adaptation involves incorporating more complex scenarios into the tests, such as unexpected events and challenging driving conditions. The testing methodology should also be refined to accurately evaluate the performance of these systems in real-world conditions. New metrics will need to be established to assess the systems’ responsiveness to various situations.
Influence of Test Results on Future Vehicle Design and Development
The test results will significantly impact future vehicle design and development. Automakers will likely focus on enhancing the safety features of these systems, including improved sensor technologies, more robust algorithms, and enhanced redundancy in critical components. Furthermore, the feedback from these tests will inform the development of safer driving assistance features. The integration of these features will be a crucial aspect of future vehicle design.
Advancements in Technology and Future Test Results
Advancements in sensor technology, particularly in areas like lidar and radar, are expected to lead to more accurate and reliable data input for these systems. This increased accuracy will likely result in improved performance and safety features. The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) into these systems will also likely influence the results. The potential of AI in handling complex situations and adapting to dynamic road environments is substantial.
Role of Consumer Feedback in Shaping the Evolution of Partial Automated Driving
Consumer feedback is crucial in shaping the evolution of partial automated driving. The public’s acceptance and understanding of these systems are directly related to their perceived safety and reliability. Automakers must proactively address consumer concerns and incorporate their feedback into the design and development process. The ongoing dialogue between consumers and automakers is essential for creating systems that are not only technologically advanced but also meet the expectations and needs of the public.
Detailed Technical Specifications: Iihs Partial Automated Test Rank Ford Gm Tesla
The IIHS partial automated driving test delves into the capabilities and limitations of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Understanding the technical specifications of this test is crucial to evaluating the safety and reliability of these systems in real-world scenarios. The test assesses the performance of these systems under various conditions, aiming to uncover potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement.The test’s methodology focuses on simulating a variety of driving situations.
These scenarios are designed to be challenging, requiring the automated systems to react appropriately to complex and unpredictable events. The data collected during the test is then analyzed to determine the effectiveness and safety of the systems.
Test Scenarios
The IIHS test incorporates a range of scenarios, meticulously designed to push the capabilities of partial automation systems. These scenarios are specifically chosen to reflect the types of situations drivers might encounter on public roads. Examples include lane-keeping assistance during highway driving, adaptive cruise control in stop-and-go traffic, and automatic emergency braking in various conditions.
Technical Parameters
The following table Artikels the key technical parameters employed in the IIHS partial automated driving test. These parameters provide a comprehensive view of the test’s rigor and the data collected.
| Parameter | Description | Units | Example Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Vehicle speed during the test scenarios. | mph | 30-70 |
| Distance to Obstacles | The distance between the vehicle and potential hazards. | feet | 50-200 |
| Lane Change Maneuvers | The frequency and complexity of lane change requests. | Number of lane changes | 2-4 |
| Traffic Density | The level of traffic congestion during the test scenarios. | Vehicles per mile | Low, Medium, High |
| Weather Conditions | Environmental factors, such as rain or snow. | Description | Clear, Rain, Fog |
Methodology Breakdown
The methodology employed in the IIHS test involves a combination of simulated and real-world scenarios. Simulated scenarios allow for precise control over variables, enabling detailed analysis of the automated systems’ response. Real-world elements are integrated to reflect the complexities of real-world driving situations.The test meticulously records data points, including vehicle speed, steering angle, braking force, and distance to other vehicles.
This comprehensive dataset is then analyzed to determine the system’s effectiveness and identify potential safety risks. The specific algorithms and sensor data used by each manufacturer are not disclosed. This ensures a level playing field for the evaluation.
Evaluation Criteria
The evaluation of the automated systems focuses on several key criteria, such as the system’s ability to maintain lane position, adjust speed appropriately, and respond to hazardous situations in a safe and predictable manner. These criteria are designed to assess the safety and reliability of the automated systems under a variety of challenging conditions.
Ultimate Conclusion
The IIHS partial automated test results for Ford, GM, and Tesla offer valuable insights into the current state of automated driving technology. While all three companies demonstrate impressive capabilities, areas for improvement and future development are evident. The analysis reveals that the future of autonomous vehicles hinges on continued innovation in safety features and comprehensive testing, reflecting the ongoing evolution of automotive safety standards.












