Apple iPhone iOS 16 android features google apps comparison sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of the ever-evolving mobile landscape. This in-depth comparison dives into the intricacies of iOS 16, scrutinizes Android’s robust ecosystem, and analyzes the performance and user experience of both platforms. We’ll dissect hardware specifications, delve into app ecosystems, and examine the seamless integration of Google apps with Android.
Get ready to uncover the strengths and weaknesses of each operating system and the impact on app development.
From the sleek design of the latest iPhones to the customizable nature of Android, we’ll navigate the world of mobile technology, comparing key features and performance metrics. This comparison also considers the evolving app development landscape, exploring the challenges and opportunities in building cross-platform applications. The discussion will encompass future trends and predictions for both iOS and Android, offering a comprehensive view of the mobile future.
iOS 16 Features Overview
iOS 16, Apple’s latest mobile operating system, introduces a range of enhancements across various aspects of the user experience. From refined user interfaces to enhanced privacy protections, this update aims to elevate both the ease of use and security for iPhone users. These improvements are designed to create a more seamless and intuitive experience, particularly for those who have grown accustomed to the Apple ecosystem.iOS 16 builds upon the strengths of previous iterations, incorporating feedback from users and industry trends to address common pain points.
This iterative approach reflects Apple’s commitment to continuous improvement and user satisfaction.
Key New Features
iOS 16 brings several noteworthy features that significantly impact how users interact with their iPhones. These new additions streamline workflows and introduce innovative functionalities.
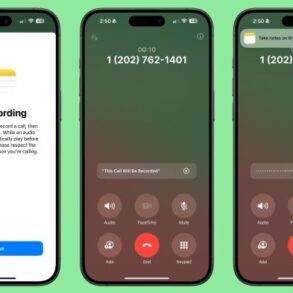
- Improved Lock Screen Customization: Users can now personalize their lock screens with widgets, photos, and more dynamic displays. This feature allows for a more visually engaging and personalized experience for users, reflecting their individual tastes and needs.
- Enhanced Messages App: The Messages app has been significantly enhanced, offering features like enhanced message editing, collaborative conversation threads, and the ability to unsend messages within a timeframe. These improvements aim to create a more efficient and controlled messaging experience for users.
- Redesigned iMessage Features: iMessage now offers more interactive and engaging features, such as animated stickers, shared photos and videos, and enhanced group communication capabilities. These additions aim to enhance the user experience by facilitating more interactive communication.
- Enhanced Live Activities: Users can now monitor real-time updates in various apps, such as ride-sharing or fitness activities, directly on the lock screen. These updates provide immediate access to important information and real-time status updates.
User Interface Improvements and Usability Enhancements
iOS 16 focuses on improving the overall user interface and usability, making it easier for users to navigate and interact with their iPhones.
- Redesigned Lock Screen: The lock screen now offers greater customization options, enabling users to personalize their displays with various widgets, photos, and other visual elements. This customization provides a more engaging and visually appealing user experience.
- Improved Widgets: Widgets have become more dynamic and informative, offering a more comprehensive overview of relevant information. This enhancement allows users to quickly access and interact with vital data, making the experience more convenient and efficient.
- Enhanced Accessibility Features: iOS 16 includes improved accessibility features, ensuring a more inclusive experience for users with diverse needs. These enhancements aim to cater to a wider range of users and make the platform more accessible to everyone.
Security and Privacy Enhancements
Security and privacy are paramount in iOS 16. The operating system incorporates significant enhancements in these areas to safeguard user data and protect their online activities.
- Enhanced Data Protection: iOS 16 employs enhanced data protection measures, offering users greater control over their data. This is a critical aspect of maintaining privacy in today’s digital world.
- Improved Privacy Controls: iOS 16 provides more granular privacy controls, allowing users to precisely manage the data they share with apps. This provides a stronger layer of protection against data misuse.
Comparison with Previous iOS Versions
| Feature | iOS 15 | iOS 16 |
|---|---|---|
| Lock Screen Customization | Basic widgets, limited personalization | Extensive customization, dynamic displays |
| Message Editing | Limited editing options | Enhanced editing, unsend option |
| Live Activities | Limited live activities | Real-time updates directly on lock screen |
| Accessibility Features | Basic accessibility features | Improved accessibility features for diverse needs |
Impact on App Development and Usage
iOS 16’s features directly impact app development and user experience.
Comparing Apple iPhone iOS 16 features with Android and Google apps is fascinating, but sometimes, it’s hard to ignore the bigger picture. Like the ongoing saga of Taylor Swift vs Apple, where neither side truly comes out on top, the battle of mobile operating systems often feels similar. Ultimately, the best choice depends on personal preferences and needs, and the sheer number of factors involved in this comparison, which can be further explored by reading this interesting take on the topic, Taylor Swift vs Apple nobody wins.
The Apple iPhone iOS 16 and Android ecosystems are both powerful and complex, offering various strengths and weaknesses.
- App Development: Developers need to adapt their apps to leverage the new features, such as the redesigned lock screen and improved widgets. This necessitates updates and enhancements to ensure compatibility with the latest iOS version.
- App Usage: Users benefit from more engaging and interactive app experiences due to iOS 16’s improvements in messaging, live activities, and customization. These enhancements make app usage more streamlined and enjoyable.
Android Features Comparison: Apple Iphone Ios 16 Android Features Google Apps Comparison
Android, a powerful and versatile mobile operating system, boasts a rich feature set that evolves with each new version. From customization options to performance enhancements, Android offers a dynamic platform for users. This comparison delves into the core features of different Android versions, highlighting key strengths and weaknesses, and examining the differences in user interface and experience between Android and iOS.Android’s strength lies in its open-source nature, allowing developers to create a vast array of applications and customizations.
Comparing Apple iPhone iOS 16 features with Android and Google apps is fascinating, but it’s also important to consider broader security concerns. For example, recent news about a Facebook security vulnerability impacting two-factor authentication via SMS notifications, as detailed in this article facebook two factor authentication sms notifications security bug , highlights the need for vigilance in the digital world.
Ultimately, these issues reinforce the importance of staying informed about security updates and features when choosing between different mobile operating systems and apps.
However, this also presents a challenge in maintaining a consistent user experience across various devices and manufacturers. This diversity, while offering freedom, can lead to fragmentation, potentially impacting software updates and overall stability. This exploration will analyze these aspects in greater detail.
Core Features of Different Android Versions
Different Android versions introduce new features and improvements, often focusing on enhanced security, improved performance, and user experience enhancements. Android 13, for example, introduced significant improvements in privacy controls, giving users more granular control over their data. Android 14 builds upon this foundation, with further enhancements to privacy, performance, and system efficiency. These iterative advancements reflect a continuous commitment to refining the user experience.
Android Ecosystem Strengths and Weaknesses
Android’s strength lies in its extensive ecosystem. The vast number of manufacturers and devices ensures broad market reach and diverse choices for consumers. The availability of countless apps in the Google Play Store further bolsters this strength. However, this breadth also presents a weakness in terms of maintaining a consistent user experience across different devices. Variances in hardware specifications and manufacturer implementations can result in inconsistencies in performance and features.
User Interface and User Experience Differences
Android and iOS offer distinct user interfaces and user experiences. Android’s approach is often characterized by customization, allowing users to personalize their device’s appearance and functionality. iOS, conversely, prioritizes a streamlined and consistent user interface, often perceived as more intuitive for first-time users. These differences reflect the distinct philosophies behind each platform.
Evolution of Android’s Customization Options
Android has always been lauded for its customization options. Users can personalize their home screens, widgets, and themes. Over time, these options have evolved from basic visual adjustments to more complex system-level modifications. For example, the ability to customize launchers and use third-party launchers is a testament to Android’s adaptability.
Recent Android Features and Their Impact on User Experience
Recent Android features have significantly improved user experience. Features like the enhanced privacy controls in Android 13 allow users to have greater control over their data. Similarly, improvements in performance and system efficiency contribute to a smoother and faster user experience, making daily tasks more seamless. The ability to seamlessly switch between multiple apps or switch between profiles, all with a single gesture, exemplifies the evolution of Android’s user experience.
Apple iPhone Hardware vs. Android Devices
The battle between Apple iPhones and Android devices extends beyond the software realm, deeply impacting user experience through hardware choices. Differences in processor speed, battery life, and camera technology contribute significantly to the distinct user journeys offered by each platform. Understanding these disparities provides insight into the rationale behind each manufacturer’s design philosophy and the ultimate impact on the end user.Recent years have witnessed a notable convergence in hardware specifications between Apple iPhones and leading Android phones.
However, core differences persist, leading to varied performance characteristics and user experiences. These differences stem from distinct design philosophies, which prioritize specific features and functionalities.
Hardware Specifications Comparison
A key differentiator lies in the diverse range of hardware specifications available across Android devices, in contrast to Apple’s more unified approach. This variability in Android hardware creates a broader spectrum of performance, battery life, and camera capabilities. Apple, on the other hand, prioritizes integration, striving for a cohesive experience across its ecosystem.
Performance and Battery Life
The performance of a device hinges on its processor, RAM, and storage capacity. While high-end Android devices often match or surpass Apple iPhones in raw processing power, the optimized nature of iOS can lead to a smoother user experience in some cases. Battery life is another crucial aspect, and the optimization strategies employed by each platform can significantly impact the overall user experience.
Factors such as screen size, processor efficiency, and background processes influence battery endurance. Apple’s focus on system integration often results in better battery management.
Camera Capabilities
Camera technology plays a vital role in modern smartphones. Both Apple and Android manufacturers invest heavily in this area. Apple iPhones often excel in image processing, known for their sophisticated algorithms. Android devices, especially high-end models, can offer comparable or even superior sensor capabilities. The choice of camera hardware, software optimizations, and user interface influence the user experience.
Screen Size and Resolution
The table below illustrates the varying screen sizes and resolutions offered by recent Apple iPhones and leading Android phones. This comparison demonstrates the diverse choices available to consumers, influenced by individual needs and preferences.
| Device | Screen Size (inches) | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| iPhone 14 Pro Max | 6.7 | 2778 x 1284 pixels |
| Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra | 6.8 | 3088 x 1440 pixels |
| Google Pixel 7 Pro | 6.7 | 3120 x 1440 pixels |
| OnePlus 11 Pro | 6.7 | 3216 x 1440 pixels |
Design Philosophies, Apple iphone ios 16 android features google apps comparison
Apple’s design philosophy emphasizes a seamless user experience through tight integration between hardware and software. This approach results in a streamlined interface and optimized performance. Android, conversely, embraces a wider range of hardware configurations, offering greater customization options. This approach, however, can sometimes lead to inconsistencies in performance across different devices.
Key Performance Differences Summary
Apple iPhones often offer a more consistent and streamlined user experience due to their integrated hardware and software design. Android devices, however, offer greater customization and potential for superior raw performance in specific areas. The choice between platforms ultimately depends on individual priorities and preferences. Furthermore, the cost of components and manufacturing play a significant role in the final pricing and affordability of the devices.
App Ecosystem Comparison (iOS vs. Android)
The app ecosystems of iOS and Android are fundamentally different, impacting user experiences and developer choices. This difference stems from the distinct operating systems, their philosophies, and the resulting approaches to app development and distribution. Understanding these differences is crucial for developers and users alike, allowing for informed decisions about which platform to prioritize.The sheer volume of apps available on each platform is impressive, but the quality, availability, and specific features of apps vary significantly.
The availability of specific niche apps can be influenced by factors like platform popularity, developer focus, and market demand.
App Availability and Popularity
The sheer breadth of available apps on both platforms is enormous. iOS, with its stricter approval process, often boasts higher-quality apps, but the sheer quantity of Android apps can be overwhelming. This difference in quantity can be attributed to the open-source nature of Android and its diverse hardware ecosystem.
Popular Apps and Unique Features
Numerous popular apps are available on both platforms, but their features and implementation may vary slightly due to the distinct nature of each OS. For example, productivity apps might leverage iOS’s intuitive design or Android’s customization options to offer unique features. Examples include productivity suites, social media apps, and gaming applications. The accessibility and ease of use vary based on the specific application and the user’s familiarity with the platform.
App Development Tools and Frameworks
The choice of development tools greatly influences the development process. A comparison of development tools highlights the differences between iOS and Android.
Comparing Apple iPhone iOS 16 features with Android and Google apps is always fascinating. While we’re diving deep into those tech battles, it’s interesting to note that LG mobile division chief Brian Kwon has also been making some moves in the home entertainment space. This shift, as seen in the latest news about LG mobile division chief Brian Kwon home entertainment , might just be a sign of things to come.
Ultimately, these trends all play into the broader landscape of mobile device and software development.
| Feature | iOS (Swift, Objective-C) | Android (Java, Kotlin) |
|---|---|---|
| Development Language | Swift, Objective-C | Java, Kotlin |
| Framework | SwiftUI, UIKit | Android SDK |
| Ease of Learning Curve | Swift is generally considered easier to learn than Objective-C. | Kotlin is gaining popularity and is considered more concise and readable than Java. |
| Community Support | Strong, dedicated community | Very large, diverse community |
The differences in tools and frameworks often result in different approaches to app design and functionality.
Ease of Use and Functionality
The ease of use and functionality of popular apps are often influenced by the underlying operating system. User interfaces and interactions vary, leading to differences in user experience. Users familiar with one platform may find the other less intuitive. The level of personalization and customization available on Android may appeal to some users.
App Store Policies and Approval Processes
iOS’s App Store has a more stringent approval process, aiming for higher quality and user safety. Android’s Google Play Store has a broader approach, with a focus on quantity and variety. Both platforms have their own set of guidelines for app submissions, including content restrictions and functionality requirements. These policies and approval processes affect the types of apps available on each platform.
Google Apps Integration
Google’s suite of apps, including Gmail, Google Drive, and Google Maps, forms a powerful ecosystem tightly integrated with Android devices. This seamless integration provides a cohesive user experience, enhancing productivity and convenience. While these apps are also available on iOS and other platforms, their native Android integration is undeniable, shaping the user experience in significant ways.The core philosophy behind Google’s app design is to enhance the Android experience.
By pre-installing and deeply integrating these apps, Google creates a consistent and familiar environment for users. This approach fosters user loyalty and encourages adoption of other Google services. This integration also extends beyond basic functionality, often leveraging Android’s unique capabilities for a more intuitive user experience.
Gmail
Gmail’s integration with Android is notable for its seamless synchronization across devices. Messages are readily available on any Android device where the account is logged in. This is a fundamental aspect of Google’s approach to email management, promoting a unified experience. Furthermore, Gmail’s powerful search functionality, combined with Android’s intuitive interface, enables quick and efficient message retrieval.
This integration allows users to stay connected and manage their emails effectively regardless of their location or device.
Google Drive
Google Drive is deeply integrated with Android’s file management system. Files are automatically synced across all devices, enabling users to access documents, spreadsheets, and presentations from any Android device. This feature is crucial for users who frequently work on documents across different devices. Furthermore, Google Drive leverages Android’s capabilities to provide a smooth and intuitive file-sharing experience.
The integration allows for quick and easy collaboration, making it a valuable tool for both personal and professional use.
Google Maps
Google Maps is a cornerstone of the Android experience, offering seamless navigation and location services. Its integration with Android’s location services and hardware ensures real-time updates and accurate navigation. The intuitive interface and extensive map data provide users with a reliable and convenient way to explore and navigate. Furthermore, Google Maps seamlessly integrates with other Android apps and services, enriching the overall user experience.
Key Features and Benefits of Google Apps
| Google App | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Gmail | Seamless synchronization across devices, powerful search, intuitive interface | Efficient email management, accessibility from any Android device, quick message retrieval |
| Google Drive | Automatic syncing across devices, intuitive file management, collaborative features | Easy access to files from any Android device, enhanced collaboration, versatile file management |
| Google Maps | Real-time navigation, accurate location services, extensive map data, integration with other apps | Reliable navigation, enhanced exploration, intuitive interface, improved user experience |
Cross-Platform Development

Developing apps that seamlessly work across different operating systems like iOS and Android presents a significant challenge, but also a wealth of opportunities. The increasing demand for mobile applications necessitates the ability to reach a broader audience, and cross-platform development strategies provide a viable path to achieve this goal. This approach enables developers to create applications that function flawlessly on various platforms, saving time and resources while maximizing their reach.
Challenges in Cross-Platform Development
The primary challenges in cross-platform development revolve around the inherent differences between iOS and Android. These differences encompass not only the underlying operating systems but also the distinct user interfaces and functionalities. Maintaining a consistent user experience across platforms while adhering to each platform’s specific design guidelines is a significant hurdle. Furthermore, ensuring optimal performance and responsiveness across various devices with varying hardware capabilities is crucial.
Handling platform-specific APIs and functionalities requires meticulous attention to detail, leading to increased development time and complexity.
Cross-Platform Development Approaches
Several approaches exist for developing applications compatible with multiple platforms. These methods offer varying levels of control and flexibility, impacting the development process and the final product’s quality.
React Native
React Native leverages JavaScript and React, a popular JavaScript library, to build mobile applications. This approach allows developers to reuse code across platforms, significantly reducing development time. The component-based architecture of React Native facilitates a streamlined development process. This method excels in scenarios where a significant portion of the application logic is similar across platforms. However, performance can sometimes lag behind native solutions, especially in complex or graphically intensive applications.
Flutter
Flutter, developed by Google, utilizes a unique approach that builds UI elements from scratch. Dart, a programming language developed by Google, is central to Flutter’s architecture. This framework provides a more native-like user experience. Its highly customizable UI elements and reactive programming model facilitate rapid development. Flutter offers a more comprehensive set of tools and libraries, leading to a potentially higher performance than React Native.
This approach also offers better control over the application’s UI. However, the learning curve associated with Dart and Flutter’s ecosystem can be steep for developers unfamiliar with it.
App Performance and User Experience
Maintaining a consistent user experience across platforms is critical for success. Factors such as responsiveness, visual consistency, and smooth animations significantly impact user satisfaction. The performance of a cross-platform application can be influenced by the underlying technology, the complexity of the application, and the specific hardware configuration of the target device. Thorough testing across various devices and operating system versions is crucial to ensure a positive user experience.
Comparative Analysis of Cross-Platform Tools
The choice of cross-platform development tool depends on various factors, including project scope, budget, and development team expertise.
| Feature | React Native | Flutter |
|---|---|---|
| Programming Language | JavaScript, React | Dart |
| UI Development | Component-based | Customizable UI elements |
| Performance | Potentially lower than native | Potentially higher than native |
| Learning Curve | Relatively low | Relatively high |
| Community Support | Large and active | Growing rapidly |
Factors such as project complexity, developer familiarity with the technology, and desired performance characteristics should be carefully evaluated when selecting a cross-platform development tool.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the apple iphone ios 16 android features google apps comparison reveals a dynamic rivalry between two dominant mobile platforms. iOS 16 shines with its refined user interface and strong focus on security, while Android boasts its extensive customization options and vast app ecosystem. The comparison highlights the nuances of each system, allowing users to make informed decisions based on their individual needs and preferences.
Ultimately, both platforms continue to shape the future of mobile technology, presenting a complex yet captivating landscape for developers and consumers alike.