5G technology mobile network latency business is rapidly changing the landscape of mobile communication. This technology promises lightning-fast speeds, but latency, the delay in network communication, can significantly impact various industries. Understanding how 5G latency affects different businesses is crucial to maximizing its potential and mitigating its challenges.
This in-depth exploration delves into the intricacies of 5G latency, examining its impact on diverse sectors, from e-commerce to gaming. We’ll analyze the factors contributing to latency, explore mitigation strategies, and discuss the exciting opportunities and potential pitfalls of this revolutionary technology. Expect to gain valuable insights into how 5G is reshaping the future of business.
Introduction to 5G Technology
Fifth-generation (5G) mobile network technology represents a significant leap forward in wireless communication, offering unprecedented speed, capacity, and low latency compared to its predecessors. This transformative technology is poised to revolutionize numerous industries, from telecommunications to healthcare and manufacturing, by enabling new applications and services that were previously unimaginable.G builds upon the foundation of previous generations (2G, 3G, and 4G) while introducing innovative technologies and architectures.
Its key characteristics differentiate it significantly, enabling a wide range of applications demanding high bandwidth and low latency.
Key Characteristics of 5G
G’s enhanced capabilities stem from its unique architecture and advanced features. These characteristics are essential for understanding its advantages over previous generations. Key features include:
- Higher Data Rates: 5G boasts significantly higher data transmission rates than its predecessors, allowing for faster downloads, uploads, and streaming of large files. This is critical for applications requiring high bandwidth, such as high-definition video streaming and virtual reality experiences.
- Lower Latency: 5G’s lower latency, or delay in network communication, is a crucial factor enabling real-time applications like online gaming, remote surgery, and autonomous vehicles. Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another.
- Increased Capacity: 5G networks are designed to support a substantially larger number of connected devices compared to 4G networks. This is crucial for the Internet of Things (IoT) where millions of devices need to communicate simultaneously.
- Improved Reliability: 5G networks offer enhanced reliability and stability, ensuring consistent connectivity and minimizing disruptions in service.
Advantages of 5G over Previous Generations
G’s advantages stem from the combination of its innovative technologies and architectures. These advantages are transformative for a wide array of applications.
- Enhanced Speed: 5G’s significantly higher data rates enable users to experience faster downloads, uploads, and streaming compared to 4G, leading to improved user experience.
- Real-Time Applications: 5G’s low latency enables the seamless execution of real-time applications, such as online gaming, remote surgery, and autonomous vehicles. This allows for highly responsive and interactive experiences.
- Increased Connectivity: 5G’s increased capacity supports a massive number of connected devices, paving the way for the development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and its widespread adoption across various industries.
Understanding Latency in Network Communication
Latency in network communication refers to the delay experienced when transmitting data across a network. This delay can be attributed to various factors, including the distance between devices, the network’s infrastructure, and the processing power of the devices involved. Lower latency translates to a faster and more responsive user experience.
Latency is a critical factor for applications demanding real-time interactions, such as online gaming, video conferencing, and remote surgery.
Comparison of 5G, 4G, and 3G Latency
The table below illustrates the typical latency differences between 5G, 4G, and 3G networks. Lower latency values indicate a faster and more responsive network experience.
| Technology | Typical Latency (ms) |
|---|---|
| 5G | 1-10 ms |
| 4G | 10-30 ms |
| 3G | 30-100 ms |
Impact of 5G Latency on Mobile Business
G technology promises a revolution in mobile connectivity, but its success hinges on minimizing latency. This crucial factor directly impacts various business sectors, affecting everything from customer experience to operational efficiency. Understanding the nuanced relationship between 5G latency and business performance is essential for navigating the opportunities and challenges presented by this new era of mobile technology.The speed and reliability of 5G networks are not just technical specifications; they are fundamental to the success of numerous businesses.
Lower latency translates to faster response times, smoother interactions, and ultimately, a better customer experience. Conversely, high latency can lead to frustration, lost revenue, and a diminished brand reputation. Analyzing the impact of 5G latency on different business models is critical to maximizing the benefits and mitigating potential drawbacks.
Key Business Sectors Impacted by 5G Latency
The influence of 5G latency extends far beyond individual consumers. Numerous business sectors are profoundly affected by the speed and reliability of the network. From real-time applications to data-intensive processes, latency directly impacts operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Potential Positive and Negative Effects of 5G Latency
G latency can significantly influence businesses in both positive and negative ways. Low latency enables real-time data transmission, enabling seamless interactions and fostering greater efficiency. For instance, autonomous vehicles rely heavily on real-time data feeds to make split-second decisions, highlighting the critical role of low latency in enabling this technology. Conversely, high latency can result in delayed responses, impacting customer satisfaction and potentially leading to financial losses.
Imagine a live-streaming platform experiencing significant delays; this will directly affect viewer engagement and overall user satisfaction.
Impact on Customer Experience in Different Business Contexts
Customer experience is heavily influenced by latency. A video conferencing platform with high latency will likely lead to poor call quality and user dissatisfaction. In contrast, low latency in e-commerce platforms facilitates quick order processing and delivery tracking, enhancing customer satisfaction. Businesses need to understand how latency affects their specific customer interactions to optimize their services.
Latency Sensitivities Across Different Business Models
The sensitivity of various business models to 5G latency varies considerably. The table below Artikels different business models and their respective latency sensitivities, categorized as low, medium, or high. Understanding these sensitivities is critical for businesses to strategically adapt to the 5G environment.
| Business Model | Latency Sensitivity | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time video conferencing | High | Requires near-zero latency for smooth video and audio transmission. |
| E-commerce | Medium | Faster loading times and order processing improve customer satisfaction. |
| Online gaming | High | Latency affects responsiveness and gameplay experience. |
| Telemedicine | High | Real-time interactions between doctors and patients necessitate low latency. |
| Autonomous vehicles | Low | Critical for real-time data processing for navigation and safety. |
| Cloud computing | Medium | Faster data access improves user experience and application performance. |
Factors Affecting 5G Mobile Network Latency: 5g Technology Mobile Network Latency Business
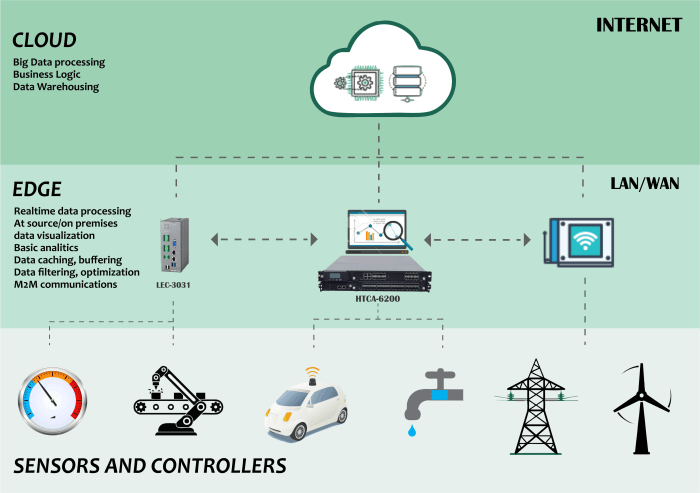
- G promises ultra-fast speeds and low latency, crucial for real-time applications like gaming, video conferencing, and autonomous vehicles. However, achieving this ideal performance is influenced by several factors that need careful consideration. Understanding these factors is vital for optimizing 5G networks and ensuring their effectiveness in various use cases.
- G network latency, the delay between sending and receiving data, is a complex phenomenon influenced by a multitude of interacting variables. Network infrastructure, user density, communication protocols, and even geographical location all contribute to the overall latency experienced by users. Analyzing these factors allows for a deeper understanding of 5G’s performance characteristics and the challenges in achieving optimal speed and responsiveness.
Network Infrastructure
The physical components of the 5G network, including base stations and core networks, significantly impact latency. Base stations, the points of contact between the network and users, need to be strategically positioned and efficiently managed to minimize signal travel time. The architecture of the core network, responsible for routing data and managing connections, also plays a critical role.
Problems in these areas, such as insufficient bandwidth or inefficient routing algorithms, will lead to increased latency.
Network Congestion and User Density
Network congestion, often a consequence of high user density, can substantially increase latency. Imagine a highway with heavy traffic – the more vehicles, the slower the overall flow. Similarly, a 5G network overloaded with concurrent user requests will experience delays in data transmission. Areas with dense populations, such as city centers, often exhibit higher latency due to increased network demand.
Efficient traffic management and resource allocation strategies are essential to mitigate these congestion-induced delays.
Communication Protocols and Standards
The protocols and standards governing data transmission in 5G networks directly affect latency. Different standards and protocols have varying overhead and efficiency levels. For instance, protocols with complex encryption or error correction mechanisms can introduce more delay compared to simpler ones. Selecting appropriate protocols and standards that balance security and performance is essential to minimize latency. Choosing the right protocol will influence the amount of data processing and transmission time, thus affecting the overall latency.
Geographical Location and Signal Strength
Geographical location and signal strength are crucial factors impacting latency. Signal strength can be weaker in areas with obstructions like tall buildings or dense foliage. The distance between the user device and the base station also affects the signal’s travel time. For example, a user located far from a base station will likely experience higher latency compared to one closer to a base station.
This highlights the importance of proper network planning, considering factors such as terrain and population density, to minimize latency in various geographic areas.
Correlation Between Factors and Latency
| Factor | Impact on Latency | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Network Infrastructure (Base Stations, Core Networks) | Poor infrastructure design leads to higher latency. | Insufficient capacity in base stations during peak hours. |
| Network Congestion | High user density and limited bandwidth increases latency. | High traffic in a stadium during a concert. |
| Communication Protocols | Complex protocols increase latency. | Using a protocol with extensive encryption processes. |
| Geographical Location | Distance from base stations and obstacles increase latency. | A user in a remote area with few base stations. |
| Signal Strength | Weaker signal strength leads to increased latency. | Signal fading due to interference from tall buildings. |
Strategies to Mitigate 5G Latency
Reducing latency is paramount for 5G’s success in various applications, from real-time gaming and video conferencing to autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. Optimizing 5G networks for minimal latency requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing network architecture, signal processing, and resource allocation strategies. This section delves into key strategies for mitigating 5G latency.Network optimization is crucial for efficient 5G operation.
5G technology’s impact on mobile network latency is a fascinating area, especially in business applications. Lower latency means faster data transfer, which is crucial for everything from real-time video conferencing to stock trading. Comparing the performance of older consoles like the PlayStation 4 Slim to the original PS4 playstation 4 slim vs ps4 might seem unrelated, but both highlight the importance of efficiency.
Ultimately, minimizing latency in 5G networks is essential for smooth and reliable operations across numerous sectors.
Latency is a significant factor in determining the overall performance of the network. By implementing effective optimization strategies, service providers can ensure a high-quality user experience.
Optimization Algorithms and Network Management Tools
Sophisticated algorithms are vital for dynamically adjusting network parameters, like resource allocation and routing protocols. These algorithms aim to optimize the flow of data across the network, reducing congestion and improving overall latency. Network management tools play a crucial role in monitoring network performance in real-time, identifying bottlenecks, and triggering automated adjustments to maintain optimal latency levels. Examples include AI-powered tools that predict potential congestion points and proactively adjust network configurations.
Edge Computing and Cloud-Based Solutions
Edge computing, which brings computing power closer to the user, significantly reduces latency. By processing data closer to the source, edge servers can handle tasks with minimal delay, improving responsiveness for applications that require low latency. Cloud-based solutions can also be leveraged to provide scalable resources for handling surges in network traffic, further mitigating latency issues. This approach reduces the distance data needs to travel, and enhances the overall responsiveness of the network.
Different Network Architectures
Various network architectures have varying degrees of latency impact. For instance, a distributed network architecture might offer greater resilience but potentially higher latency compared to a centralized architecture. Network architects must carefully consider the trade-offs between latency, reliability, and scalability when designing a 5G network. Choosing the right architecture is critical for maintaining a consistently low latency level.
5G technology’s impact on mobile network latency is a big deal for businesses, especially those relying on real-time data. Streamlining these networks is crucial for efficiency. However, issues like low-resolution video on YouTube can be a frustrating problem, and thankfully there’s a potential solution if you’re having trouble with this specific YouTube issue. Ultimately, optimizing 5G infrastructure and fixing user experience issues, like those on video streaming platforms, are both vital for a smooth and profitable business operation.
Advanced Signal Processing Techniques
Advanced signal processing techniques play a vital role in minimizing latency by optimizing the transmission and reception of signals. Techniques such as channel equalization and interference mitigation algorithms can significantly reduce signal distortion and interference, leading to improved data transmission rates and reduced latency. These techniques are crucial for optimizing the overall performance of the network and enabling reliable communication in high-density areas.
Impact of Different Latency Mitigation Strategies
| Mitigation Strategy | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Optimization Algorithms | Dynamically adjust network parameters to minimize congestion and optimize data flow. | High |
| Edge Computing | Bring computing power closer to the user, reducing data transmission distances. | High |
| Cloud-Based Solutions | Provide scalable resources for handling surges in network traffic, reducing latency. | Moderate to High |
| Advanced Signal Processing | Optimize signal transmission and reception, minimizing interference and distortion. | High |
| Network Architecture | Choose architectures that balance latency, reliability, and scalability. | Moderate to High |
Business Implications and Opportunities
G technology, with its significantly reduced latency, presents a plethora of opportunities for businesses across diverse sectors. The near-instantaneous communication speeds unlock new possibilities for real-time data processing, enhanced user experiences, and innovative service offerings. This opens doors for businesses to create more efficient operations, expand market reach, and introduce entirely new revenue streams. The potential for transforming existing business models and creating entirely new ones is substantial.Businesses can leverage the speed and reliability of 5G to enhance their existing processes and create entirely new services.
This transformative potential is particularly pronounced in industries that rely heavily on real-time data transmission, including healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
Potential Business Applications and Use Cases
The reduced latency of 5G empowers numerous business applications, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. These applications include, but aren’t limited to, remote surgery, real-time monitoring of industrial equipment, and autonomous vehicles. The ability to receive and process data almost instantly paves the way for more agile and responsive business operations.
- Remote Surgery and Telemedicine: 5G’s low latency enables high-definition video and data streams for remote surgery, allowing surgeons to operate on patients in remote locations. This capability expands access to specialized medical expertise, improving patient outcomes in underserved areas. This is already demonstrated in some pilot projects and is expected to become more prevalent.
- Real-time Monitoring and Control in Manufacturing: The near-instantaneous communication speeds allow real-time monitoring of industrial equipment, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. Data from sensors can be analyzed instantly, leading to proactive adjustments and optimized production processes. This can translate to significant cost savings and increased efficiency for manufacturers.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Logistics: 5G’s low latency is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of autonomous vehicles. Real-time data exchange between vehicles and infrastructure is essential for navigation, avoiding collisions, and optimizing traffic flow. This leads to improvements in transportation efficiency and safety.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences in Retail and Hospitality: 5G can create immersive customer experiences in retail and hospitality settings, allowing for real-time interactions with virtual assistants, personalized recommendations, and interactive displays. This technology fosters customer engagement and loyalty.
Role of 5G in Enabling New Business Models
G’s impact extends beyond simply improving existing processes; it fosters the creation of entirely new business models. Businesses can now explore opportunities in areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), smart cities, and augmented reality. The ability to connect and manage a large number of devices in real-time opens up possibilities for innovative solutions and services.
Potential Challenges and Limitations Associated with 5G Latency
Despite the immense potential, 5G latency isn’t without its challenges. Reliable and consistent 5G coverage is crucial for these applications. Infrastructure limitations, especially in rural areas, can hinder widespread adoption. Furthermore, security concerns associated with the transmission of sensitive data need careful consideration.
The 5G mobile network latency is a crucial factor in the business world, impacting everything from real-time data transmission to seamless online experiences. Improved platform stability, like that seen in the recent Android 15 beta 3 platform stability rollout, is essential for the smooth operation of 5G applications. A stable Android platform directly translates to lower latency in 5G mobile network applications, ultimately benefiting businesses relying on fast, reliable connections.
Android 15 beta 3 platform stability rollout shows that ongoing development is critical to the future of 5G technology’s business potential.
Examples of Successful Business Applications of 5G
Several businesses are already exploring and implementing 5G applications. Early adopters in industries like manufacturing and logistics are seeing improvements in efficiency and productivity. The deployment of 5G-enabled autonomous vehicles is gaining traction in certain pilot programs. These early successes demonstrate the potential of 5G to revolutionize various sectors.
Industries Benefiting from 5G’s Low Latency
| Industry | Potential Applications |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Remote surgery, telemedicine, real-time patient monitoring |
| Manufacturing | Real-time monitoring of equipment, predictive maintenance, automated production lines |
| Transportation | Autonomous vehicles, optimized traffic flow, real-time logistics tracking |
| Retail | Personalized shopping experiences, interactive displays, virtual assistants |
| Finance | Real-time trading, secure transactions, improved financial services |
Future Trends and Predictions

The 5G revolution is poised to reshape the mobile landscape, and latency reduction is a critical factor in its success. As 5G technology evolves, we can expect significant advancements in infrastructure and network architecture, leading to substantial improvements in real-time communication and data transfer speeds. This will drive new business models and applications, fundamentally altering how businesses operate and interact with customers.
Evolution of 5G Technology and Latency Impact
G technology is constantly evolving, with a focus on achieving lower latency. This includes advancements in radio access networks (RAN), core networks, and the overall network architecture. The development of new protocols and technologies like network slicing and edge computing is crucial in managing latency and enabling low-latency applications. 5G’s enhanced capabilities will significantly impact industries reliant on real-time data exchange, such as gaming, telemedicine, and autonomous vehicles.
Advancements in 5G Infrastructure and Network Architecture, 5g technology mobile network latency business
Several key advancements in 5G infrastructure are contributing to latency reduction. These include the deployment of more advanced base stations with enhanced signal processing capabilities, improved antenna design, and the utilization of mmWave frequencies. Additionally, the integration of cloud-native technologies and software-defined networking (SDN) is transforming network management, allowing for greater flexibility and dynamic resource allocation. These advancements are crucial for supporting the growing demands of high-bandwidth and low-latency applications.
Emerging Technologies for Lower 5G Latency
Emerging technologies hold significant promise for further reducing latency in 5G networks. Edge computing, by bringing computation closer to the user, minimizes the latency associated with data transmission to and from the central server. Network slicing, a technique for creating dedicated network segments for specific applications, enables customized latency and bandwidth requirements for different services. These emerging technologies will be vital in delivering the next generation of low-latency applications.
5G’s Role in Shaping Future Business Landscapes
G’s impact on business landscapes will be profound. Real-time data processing and analysis will become commonplace, leading to more responsive and efficient business operations. Low-latency applications will empower businesses to offer enhanced customer experiences, optimize workflows, and develop new revenue streams. Examples include remote surgery, real-time collaboration tools, and highly responsive cloud gaming services.
Research and Development Efforts in 5G Latency Reduction
Extensive research and development efforts are underway to address 5G latency challenges. Research institutions and technology companies are exploring innovative solutions, including new antenna designs, signal processing algorithms, and network optimization techniques. The pursuit of lower latency is driving significant investment in this field, ultimately leading to faster and more reliable 5G networks.
Summary Table of Future Trends and Predictions in 5G Technology
| Trend | Prediction | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased deployment of edge computing | Reduced latency for real-time applications | Enhanced user experience, improved business efficiency |
| Advancements in network slicing | Dedicated network segments for specific applications | Optimized latency and bandwidth for diverse services |
| Utilization of mmWave frequencies | Higher data rates and reduced latency | Support for demanding applications like AR/VR |
| Integration of SDN and cloud-native technologies | Improved network flexibility and dynamic resource allocation | Reduced latency and enhanced network scalability |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, 5G technology presents a fascinating interplay of opportunities and challenges in the mobile network latency business. While the potential for improved efficiency and customer experience is substantial, businesses must carefully consider the factors influencing latency and implement strategies to mitigate its negative impact. This examination highlights the importance of adapting to the evolving technological landscape and seizing the advantages of 5G while mitigating its potential risks.
The future of business hinges on understanding and effectively managing 5G latency.












