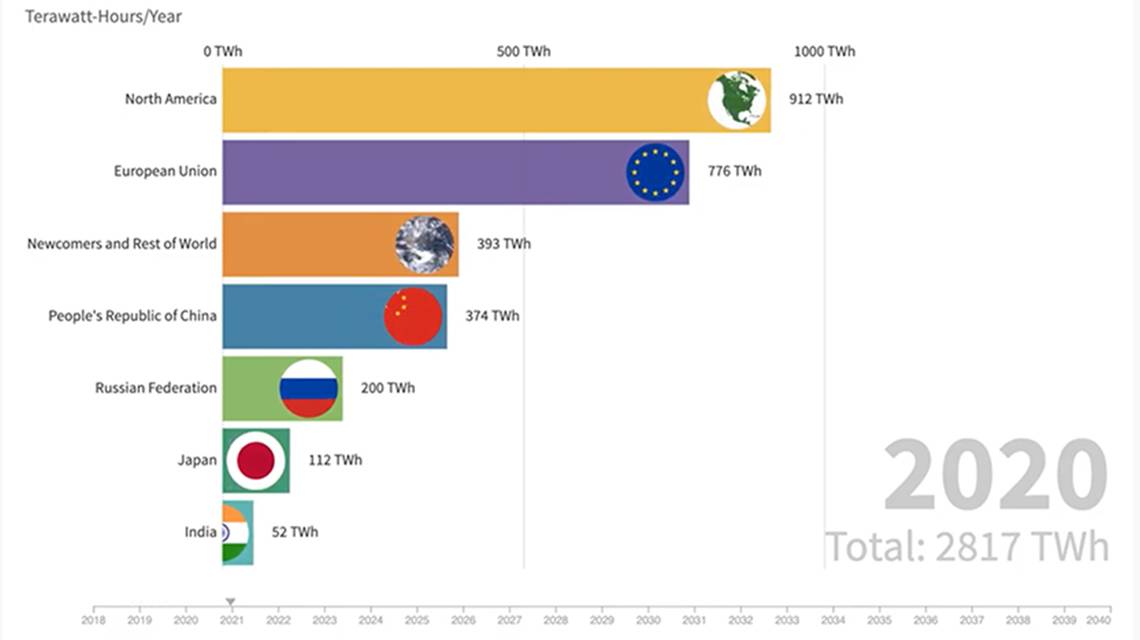
Countries are ramping up nuclear energy ambitions, a global trend with significant implications for energy security, the environment, and geopolitical landscapes. This surge in interest is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including economic incentives, environmental concerns, and a renewed focus on energy independence. We’ll explore the historical context, motivations, challenges, and potential future developments of this rapidly evolving energy sector.
The article delves into the reasons behind this global shift, examining the economic drivers, environmental considerations, and the role of technology in this renewed interest. From the specific case studies of countries like China, France, and India, to the potential future of small modular reactors and nuclear fusion, this piece provides a comprehensive overview of the current state and future prospects of nuclear energy.
Global Context of Nuclear Energy Ambitions
Nuclear energy, a controversial yet potent source of power, is experiencing a resurgence in global interest. Driven by a desire for energy independence, concerns about climate change, and technological advancements, many countries are actively pursuing or expanding their nuclear programs. This renewed focus requires a comprehensive understanding of the historical context, current global landscape, and the multifaceted factors behind this resurgence.The history of nuclear energy adoption reveals a complex trajectory.
Initially met with excitement for its potential, the industry faced setbacks due to accidents and public concerns. However, ongoing research and development have led to improvements in reactor designs and safety protocols, gradually restoring public trust and investor confidence.
Historical Overview of Nuclear Energy Adoption
Nuclear energy’s initial adoption was largely driven by the need for alternative energy sources and national prestige during the mid-20th century. Countries like the United States, the Soviet Union, and the United Kingdom spearheaded the early development of nuclear power plants, driven by geopolitical factors and a desire for technological advancement. Subsequently, many other countries, including France, Japan, and others, entered the field, driven by a mix of energy security and economic considerations.
This initial wave of adoption, however, was punctuated by accidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima, which led to a period of hesitation and reevaluation of nuclear energy’s role.
Current Global Landscape of Nuclear Power Plants
Globally, there are hundreds of operational nuclear power plants, contributing significantly to the electricity grids of various nations. The operational status of these plants varies, with some experiencing periods of maintenance or undergoing upgrades. Analyzing the current operational status of these plants provides insights into the stability and reliability of the global nuclear power sector. The distribution of these plants across continents and regions reflects the historical patterns of adoption and the evolving priorities of different countries.
Key Drivers Behind the Recent Surge in Nuclear Energy Ambitions
The recent surge in nuclear energy ambitions is rooted in a combination of factors. Rising energy prices, concerns about climate change, and the need for reliable and sustainable energy sources are pushing governments and corporations towards nuclear power. The increasing global demand for electricity and the need to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions further amplify the appeal of nuclear energy.
Different Approaches to Nuclear Energy Development
Countries are adopting diverse approaches to nuclear energy development, reflecting their unique contexts and priorities. Some prioritize the development of advanced reactor technologies, aiming for greater safety and efficiency. Others are focused on expanding their existing nuclear infrastructure, leveraging their existing expertise and infrastructure. The differing approaches underscore the varied factors that influence a country’s choice of nuclear energy development strategy.
Top 10 Countries with the Most Significant Nuclear Energy Programs, Countries are ramping up nuclear energy ambitions
| Country | Projected Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| United States | 3.5 |
| France | 2.8 |
| China | 5.2 |
| Russia | 4.0 |
| Japan | 2.2 |
| South Korea | 3.8 |
| India | 4.5 |
| Canada | 2.0 |
| United Kingdom | 2.5 |
| Germany | 1.0 |
Note: Projected growth rates are estimates based on current plans and market forecasts. These figures reflect the ambition and pace of nuclear power expansion in each nation.
Current Nuclear Power Capacity by Region
| Region | Nuclear Power Capacity (GW) |
|---|---|
| North America | 350 |
| Europe | 380 |
| Asia | 320 |
| South America | 15 |
| Africa | 5 |
These figures represent the total nuclear power capacity of each region, showcasing the geographical distribution of nuclear power plants worldwide. The figures underscore the concentration of nuclear power in specific regions, reflecting the historical patterns of adoption and the evolving priorities of different countries.
Motivations and Incentives for Increased Nuclear Energy
The global landscape of energy production is undergoing a significant shift, with many countries accelerating their pursuit of nuclear energy. This renewed interest is driven by a complex interplay of economic, environmental, and geopolitical factors. Understanding these motivations is crucial for navigating the future of energy.Nuclear energy’s resurgence stems from a multifaceted approach, considering its potential to address pressing global challenges.
The economic advantages, environmental considerations, and geopolitical implications are intricately linked, each playing a vital role in shaping national energy strategies.
Economic Factors Influencing Nuclear Energy Ambitions
Nuclear power plants, while requiring substantial upfront investment, offer long-term economic benefits. Stable and predictable electricity generation costs are attractive to industries and consumers alike. The substantial economies of scale associated with large-scale nuclear power projects can further reduce the unit cost of electricity, offering long-term cost competitiveness. Furthermore, the relatively low operational costs compared to other energy sources, particularly over the plant’s lifespan, contribute to the economic viability of nuclear energy.
Environmental Concerns and Energy Security Driving Ambitions
Environmental concerns are a powerful driver behind the renewed interest in nuclear energy. The low carbon emissions associated with nuclear power generation are increasingly recognized as crucial for mitigating climate change. This aligns with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition towards cleaner energy sources. Additionally, energy security is a major concern, and nuclear power offers a reliable and domestic source of energy, reducing dependence on volatile global energy markets.
This self-sufficiency is especially attractive to countries seeking to reduce their vulnerability to international energy price fluctuations.
Geopolitical Implications of Nuclear Energy Ramp-Up
The expansion of nuclear energy capabilities has geopolitical implications. The development of nuclear infrastructure can bolster a nation’s strategic independence and influence in the global energy arena. Furthermore, the possession of nuclear technology can impact international relations, potentially creating both opportunities and challenges. The need for robust safeguards and international cooperation to prevent the misuse of nuclear technology is paramount in this context.
Technological Advancements Contributing to Renewed Interest
Significant technological advancements are improving the safety and efficiency of nuclear power plants. Modern reactor designs, such as small modular reactors (SMRs), offer advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness and flexibility, making nuclear power more accessible to a wider range of countries. Improvements in waste management technologies and the development of innovative fuel cycles are also contributing factors. This technological progress is lowering the perceived risks and increasing the feasibility of nuclear power for a wider range of applications.
Government Policies and Subsidies Supporting Nuclear Energy
Governments worldwide are implementing policies to support the development of nuclear energy. Financial incentives, tax breaks, and research funding are crucial elements in stimulating investment and driving innovation in the nuclear sector. These initiatives demonstrate a government’s commitment to nuclear power as a viable energy source. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks and licensing procedures play a vital role in streamlining the development process.
International Cooperation in Facilitating Nuclear Energy Projects
International cooperation is essential for sharing expertise and knowledge in the nuclear field. Joint research and development initiatives can accelerate the pace of innovation and technological advancement. The establishment of international standards and safety protocols is crucial for ensuring responsible nuclear energy development. Cooperation agreements on nuclear materials and technology transfer can foster mutual benefit and reduce potential risks.
Incentives Offered by Governments to Support Nuclear Energy Projects
| Incentive Type | Description | Example ||—|—|—|| Financial Incentives | Direct subsidies, grants, and tax breaks for nuclear power projects. | A country offering a 20% tax credit for companies investing in SMR technology. || Regulatory Support | Streamlined licensing processes and favorable regulatory frameworks for nuclear energy development. | Expedited approval timelines for nuclear power plant construction.
|| Research Funding | Funding for research and development in nuclear technology and safety. | Grants to universities and research institutions for innovative reactor designs. || Infrastructure Support | Provision of infrastructure, land, and other resources for nuclear facilities. | Providing land for the construction of a new nuclear power plant. |
Countries are clearly ramping up their nuclear energy programs, a trend that’s creating both excitement and concern. Meanwhile, innovative tech like the rouyu flexipai foldable smartphone folding screen china is pushing the boundaries of mobile design. This technological leap forward, however, doesn’t diminish the ongoing debate surrounding the future of nuclear power. The drive for sustainable energy sources is definitely a significant factor.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Increased Nuclear Energy: Countries Are Ramping Up Nuclear Energy Ambitions
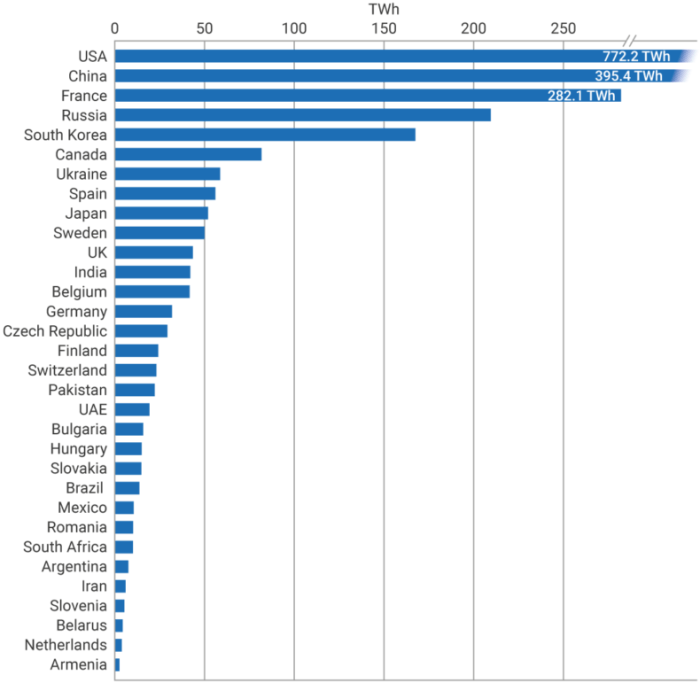
The allure of nuclear power, with its potential for vast energy production, is undeniable. However, the path to widespread adoption is fraught with significant challenges and risks, demanding careful consideration and robust mitigation strategies. These risks, ranging from safety concerns and proliferation threats to the complexities of waste management and financial burdens, must be addressed proactively to ensure responsible and sustainable development of nuclear energy.The increasing global interest in nuclear energy, driven by the need for cleaner energy alternatives, presents a compelling case for its expansion.
Yet, the inherent complexities and potential dangers associated with nuclear technology necessitate a thorough evaluation of its implications before widespread implementation. This evaluation must encompass the full spectrum of potential risks and challenges to ensure responsible and sustainable development.
Safety Concerns of Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power plants, while potentially powerful sources of energy, operate with hazardous materials and complex systems. Malfunctions or accidents, such as those at Chernobyl and Fukushima, highlight the catastrophic consequences of failures in safety protocols and engineering. The potential for human error, equipment malfunctions, or natural disasters poses a significant risk. Ensuring the robust design, maintenance, and operation of nuclear plants is crucial to prevent such incidents.
Safety regulations and stringent quality control measures are paramount to minimizing these risks.
With countries increasingly prioritizing nuclear energy, robust security measures are paramount. Modernizing security systems, like those offered by Prisma Access, is crucial to protecting sensitive data and infrastructure. This involves a multi-layered approach, incorporating advanced technology to counter threats. Ultimately, ensuring the safety and security of nuclear facilities is paramount as countries continue their push for nuclear energy.
To learn more about the top 3 reasons to modernize security with Prisma Access , check out this insightful guide.
Potential Risks of Nuclear Proliferation
The use of nuclear materials in energy production can inadvertently contribute to the potential for proliferation. The technology and materials used in nuclear power plants are often the same as those required for weapons development. Strict international regulations, robust safeguards, and robust non-proliferation agreements are vital to prevent the diversion of nuclear materials to illicit purposes. The risk of theft or sabotage of nuclear materials also necessitates strong security measures.
The historical context of nuclear proliferation, from the Manhattan Project to the Cold War, underscores the need for stringent international cooperation and control mechanisms.
Challenges in Managing Nuclear Waste Disposal
Nuclear waste disposal presents a significant long-term challenge. The radioactive nature of nuclear waste requires specialized containment and disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination and health risks. The need for secure, long-term storage solutions and the associated costs are substantial. Finding suitable geological formations for disposal and ensuring the safety of these facilities over centuries is crucial.
The long-term risks of potential leakage or contamination must be rigorously assessed and mitigated through innovative waste management technologies.
Financial Risks and Costs Associated with Nuclear Energy Projects
Nuclear power plants are extremely expensive to construct and operate. The high upfront capital costs, regulatory hurdles, and long construction times pose considerable financial risks for investors and governments. The potential for cost overruns and delays, coupled with the need for extensive safety measures, can make nuclear projects financially unsustainable. Economic viability needs to be carefully considered, alongside the long-term operational and maintenance costs.
Potential Impact on Local Communities and Environments
The construction and operation of nuclear power plants can have significant impacts on local communities and environments. Concerns about potential health effects from radiation, displacement of populations, and environmental damage need careful consideration. Environmental impact assessments and community engagement are essential to address these concerns and ensure that the benefits of nuclear energy outweigh the potential negative impacts.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks of Nuclear Energy
A comprehensive strategy for mitigating risks must incorporate multiple layers of safeguards. These include strict adherence to international safety standards, robust regulatory frameworks, enhanced security measures, and public education campaigns. The use of advanced reactor designs, improved waste management technologies, and enhanced financial models are also crucial aspects of risk mitigation.
Summary Table of Safety Protocols
| Country | Major Safety Protocols Implemented |
|---|---|
| United States | Strict adherence to NRC regulations, rigorous safety inspections, and advanced safety features in reactor designs. |
| France | Extensive safety regulations, robust emergency response plans, and a strong focus on continuous improvement of safety procedures. |
| Japan | Comprehensive safety protocols, including earthquake-resistant designs, and advanced emergency preparedness measures. |
| Russia | Regulations and procedures, albeit with varying levels of implementation and scrutiny in different periods. |
| South Korea | Emphasis on stringent safety regulations, rigorous inspections, and a commitment to maintaining high safety standards. |
Specific Case Studies of Countries with Increased Ambitions
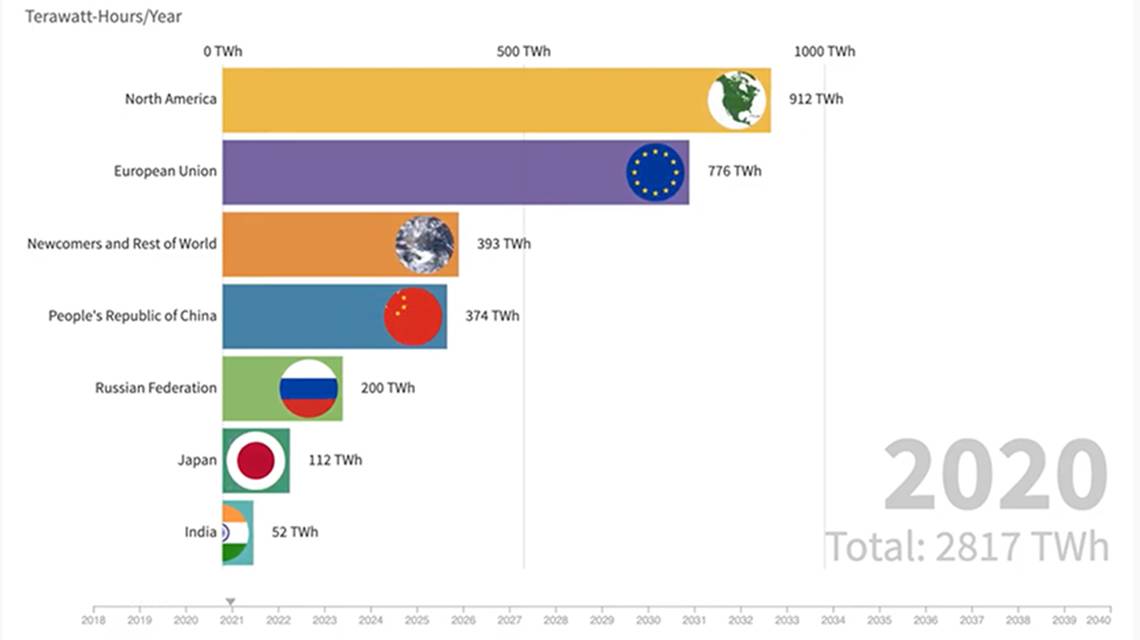
Nuclear energy, with its potential to provide a reliable and low-carbon power source, is attracting renewed interest globally. Several countries are aggressively pursuing nuclear power expansion, driven by diverse motivations. This section delves into the specific ambitions of China, France, and India, examining the factors propelling their nuclear programs, the unique challenges they face, and the potential benefits and drawbacks of their approaches.China, France, and India are each undertaking significant advancements in nuclear energy, motivated by a combination of energy security concerns, environmental ambitions, and economic considerations.
Their varied approaches highlight the complex interplay of political, economic, and technological forces shaping the future of nuclear power.
With countries increasingly focused on nuclear energy, it’s fascinating to see how this trend intersects with the tech world. A recent leak of the Fairphone 5 renders, available at fairphone 5 renders leak , highlights a potential shift towards sustainable tech solutions. While the future of energy is undeniably complex, perhaps this new phone design hints at a wider societal push for greener alternatives, mirroring the global interest in nuclear power.
Ultimately, the drive towards nuclear energy remains a significant factor in shaping the future.
China’s Nuclear Energy Ambitions
China is aiming to significantly expand its nuclear power capacity to meet its growing energy demands and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. The government has set ambitious targets for new reactor construction, recognizing the crucial role nuclear energy plays in achieving its environmental and economic goals. This includes a push for advanced reactor designs, potentially offering improved safety and efficiency.
France’s Nuclear Energy Ambitions
France, historically a leader in nuclear power, is seeking to maintain its position as a global nuclear energy powerhouse. This involves updating existing reactors, implementing advanced reactor designs, and pursuing new construction projects. France’s long-standing experience in nuclear technology gives it a unique advantage in this pursuit.
India’s Nuclear Energy Ambitions
India, facing significant energy demands, is actively developing its nuclear power sector. The country’s strategy involves diversifying its energy mix, and nuclear power plays a vital role in this diversification. India is also developing indigenous reactor designs and pursuing international collaborations to accelerate its nuclear program.
Role of Energy Independence in Driving Nuclear Ambitions
Energy independence is a crucial factor driving nuclear ambitions in several countries. A reliable and domestically produced energy source, such as nuclear power, can enhance a nation’s energy security, reducing its reliance on external suppliers and potential price volatility. The desire to mitigate risks associated with global energy markets is a key motivation for nations to invest in nuclear technology.
Technological Innovations Driving Advancements
Technological innovations are transforming the nuclear energy landscape. Advanced reactor designs, like Generation IV reactors, offer enhanced safety, efficiency, and fuel utilization. Improved waste management technologies and new fuel cycles promise to further reduce the environmental impact of nuclear power. These advancements are crucial to the long-term viability of nuclear energy.
Unique Challenges Faced by Each Country
Each country faces unique hurdles in its nuclear energy pursuit. China’s rapid expansion requires significant infrastructure development and the management of potential safety concerns. France faces challenges in maintaining public confidence in nuclear technology and updating its aging reactor fleet. India’s ambitious goals require significant investment in research and development, along with addressing regulatory hurdles.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The benefits of nuclear energy include low-carbon emissions, energy independence, and a potential role in mitigating climate change. However, concerns remain about nuclear waste disposal, safety risks, and the potential for proliferation. The specific approach of each country, including its technological choices and regulatory framework, will determine the balance between these benefits and drawbacks.
Comparison of Approaches
The differing political and economic structures of these countries influence their approaches to nuclear energy. China’s state-directed approach contrasts with France’s more market-oriented model and India’s mix of state and private sector involvement. Understanding these differences is essential to appreciating the nuances of each country’s strategy.
Projected Timeline for New Nuclear Power Plant Construction
| Country | Projected Timeline for New Plant Construction |
|---|---|
| China | 2025-2040 |
| France | 2025-2040 |
| India | 2025-2040 |
Note: These timelines are estimates and subject to change based on economic and political factors. Construction timelines often vary depending on the specific project and regulatory approvals.
Potential Future Developments in Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy, while facing ongoing debates and challenges, continues to hold a significant position in the global energy landscape. The future of nuclear power hinges on innovation, addressing safety concerns, and navigating public perception. This exploration delves into potential advancements, highlighting the role of small modular reactors, alternative reactor designs, international collaboration, and the tantalizing prospect of nuclear fusion.The path forward for nuclear energy is not predetermined.
Success will rely on a combination of technological advancements, proactive safety measures, and effective public engagement. This section examines the possible trajectory of nuclear energy development in the coming decades.
Growth Forecast of Nuclear Energy
The projected growth of nuclear energy over the next 10-20 years is contingent upon several factors. Significant investment in new reactor construction and the successful deployment of innovative reactor designs are crucial. The existing nuclear power plants’ lifespan and the decision to extend or replace them are major variables in the equation. The future of nuclear energy will be shaped by the political and regulatory landscape, and public acceptance of the technology.
Emerging markets and nations seeking to diversify their energy portfolios are likely to play a significant role in this growth.
Impact of Advancements in Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Small modular reactors (SMRs) offer the potential to revolutionize nuclear energy. Their smaller size and modular design make them more flexible and adaptable, allowing for easier construction and potentially lower capital costs compared to large-scale reactors. This adaptability could open up new opportunities for decentralized power generation, potentially serving remote communities or industrial clusters. The modularity of SMRs can also lead to quicker deployment and more efficient use of resources.
Potential Alternative Reactor Designs
Beyond SMRs, various alternative reactor designs are being explored. These designs often focus on enhanced safety features, improved efficiency, and reduced waste production. Some notable examples include Generation IV reactors, such as sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) and high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), which aim to enhance energy efficiency and reduce waste. The development and deployment of these innovative designs will be critical to the future of nuclear energy.
Importance of International Collaboration
Addressing the complex challenges and risks associated with nuclear energy necessitates international collaboration. Knowledge sharing, joint research, and the development of standardized safety protocols are essential. International collaborations can foster trust and ensure that the deployment of nuclear technology is carried out responsibly and safely across the globe.
Potential of Nuclear Fusion as a Future Energy Source
Nuclear fusion, the process that powers the sun, holds the promise of a virtually limitless clean energy source. Significant research and development efforts are underway, aiming to harness this power for practical applications. While significant hurdles remain, the potential for fusion to revolutionize energy production is immense. Success in this area would have a profound impact on the global energy landscape.
Societal Implications of Increased Reliance on Nuclear Energy
Increased reliance on nuclear energy will have various societal implications. These include job creation in the nuclear industry, potential concerns regarding nuclear waste disposal, and the need for public education and engagement to foster understanding and acceptance. Careful consideration of the social and environmental implications is essential for responsible development.
Comparison of Nuclear Reactor Types
| Reactor Type | Size | Cost | Safety | Waste | Deployment Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Reactor | Large | High | High | Significant | Slow |
| Small Modular Reactor (SMR) | Small | Lower | High | Significant | Faster |
| Sodium-Cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) | Variable | High | High | Lower | Slow |
| High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor (HTGR) | Variable | High | High | Lower | Slow |
This table provides a basic comparison of different nuclear reactor types. It highlights key differences in size, cost, safety features, waste production, and deployment speed. Further research and development are necessary to fully understand the nuances of each reactor type.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the global push towards nuclear energy presents a multifaceted challenge and opportunity. While economic incentives, energy security concerns, and technological advancements are driving this ambition, significant challenges remain, including safety protocols, waste disposal, and potential proliferation risks. The future of nuclear energy hinges on careful consideration of these challenges and the development of sustainable solutions, as nations navigate this complex energy transition.